Tartaric Acid vs Glycolic Acid: Cosmetic Formulations
AUG 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Acid Exfoliants Evolution and Formulation Goals
Acid exfoliants have undergone significant evolution in the cosmetic industry since their introduction in the 1970s. Initially, glycolic acid, derived from sugar cane, emerged as one of the first alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) to gain widespread acceptance in professional skincare treatments. The 1990s witnessed a surge in consumer products featuring glycolic acid, marking a pivotal shift from purely professional applications to mass-market availability. Concurrently, tartaric acid, extracted from grapes and other fruits, has followed a different evolutionary trajectory, initially receiving less attention but gradually gaining recognition for its unique properties.
The technological advancement in acid exfoliation has been characterized by progressive refinement in formulation techniques. Early formulations often presented challenges related to pH stability, skin irritation, and limited penetration capabilities. Over time, innovations in buffering systems, delivery mechanisms, and molecular modifications have significantly enhanced the efficacy and safety profiles of both acids. The development of controlled-release systems and encapsulation technologies represents a notable milestone, allowing for sustained activity while minimizing potential adverse reactions.
Current formulation goals for acid exfoliants center around achieving optimal balance between efficacy and tolerability. For glycolic acid, which has a smaller molecular structure (76.05 g/mol), the primary objective involves maximizing penetration while controlling irritation potential. Tartaric acid, with its larger molecular size (150.09 g/mol) and different chemical properties, presents distinct formulation challenges and opportunities, particularly in terms of exfoliation rate and sensory characteristics.
The industry has increasingly focused on synergistic formulations that combine multiple acids at lower concentrations to achieve enhanced results with reduced irritation. This approach has gained momentum as research demonstrates that strategic combinations can target multiple skin concerns simultaneously while maintaining favorable safety profiles. Additionally, there is growing interest in developing formulations that complement the skin's natural microbiome and barrier function rather than disrupting these systems.
Sustainability considerations have also emerged as a significant factor in acid exfoliant evolution. Manufacturers are exploring greener extraction methods, sustainable sourcing practices, and biodegradable formulation components. For tartaric acid, which can be sourced from wine industry byproducts, this represents a potential advantage in alignment with circular economy principles.
Looking forward, the technological trajectory points toward increasingly sophisticated delivery systems, including smart formulations that respond to skin conditions in real-time, adjusting activity levels based on environmental factors and skin needs. The integration of acid exfoliants with complementary technologies such as peptides, growth factors, and barrier-supporting ingredients represents the frontier of formulation goals, aiming to deliver comprehensive skin benefits beyond traditional exfoliation.
The technological advancement in acid exfoliation has been characterized by progressive refinement in formulation techniques. Early formulations often presented challenges related to pH stability, skin irritation, and limited penetration capabilities. Over time, innovations in buffering systems, delivery mechanisms, and molecular modifications have significantly enhanced the efficacy and safety profiles of both acids. The development of controlled-release systems and encapsulation technologies represents a notable milestone, allowing for sustained activity while minimizing potential adverse reactions.
Current formulation goals for acid exfoliants center around achieving optimal balance between efficacy and tolerability. For glycolic acid, which has a smaller molecular structure (76.05 g/mol), the primary objective involves maximizing penetration while controlling irritation potential. Tartaric acid, with its larger molecular size (150.09 g/mol) and different chemical properties, presents distinct formulation challenges and opportunities, particularly in terms of exfoliation rate and sensory characteristics.
The industry has increasingly focused on synergistic formulations that combine multiple acids at lower concentrations to achieve enhanced results with reduced irritation. This approach has gained momentum as research demonstrates that strategic combinations can target multiple skin concerns simultaneously while maintaining favorable safety profiles. Additionally, there is growing interest in developing formulations that complement the skin's natural microbiome and barrier function rather than disrupting these systems.
Sustainability considerations have also emerged as a significant factor in acid exfoliant evolution. Manufacturers are exploring greener extraction methods, sustainable sourcing practices, and biodegradable formulation components. For tartaric acid, which can be sourced from wine industry byproducts, this represents a potential advantage in alignment with circular economy principles.
Looking forward, the technological trajectory points toward increasingly sophisticated delivery systems, including smart formulations that respond to skin conditions in real-time, adjusting activity levels based on environmental factors and skin needs. The integration of acid exfoliants with complementary technologies such as peptides, growth factors, and barrier-supporting ingredients represents the frontier of formulation goals, aiming to deliver comprehensive skin benefits beyond traditional exfoliation.
Market Analysis of AHA-based Skincare Products
The global AHA-based skincare market has experienced substantial growth over the past decade, with a market value reaching $10.3 billion in 2022. This segment is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.7% through 2028, driven primarily by increasing consumer awareness about skin health and the efficacy of alpha hydroxy acids in addressing various skin concerns.
Glycolic acid dominates the AHA market, accounting for approximately 45% of all AHA-based formulations due to its smaller molecular size and superior penetration capabilities. Tartaric acid, while less prevalent at about 7% market share, has been gaining traction particularly in premium and natural skincare lines where its plant-derived credentials appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Regional analysis reveals North America as the largest market for AHA products, followed closely by Asia-Pacific where K-beauty and J-beauty trends have significantly boosted adoption. European markets show stronger preference for tartaric acid formulations compared to other regions, aligning with the continent's stricter regulations on chemical ingredients and greater consumer demand for natural derivatives.
Consumer demographic data indicates that women aged 25-45 represent the primary purchasers of AHA products, though male consumer segment is growing at 12.3% annually—significantly faster than the overall market. This shift reflects broader trends in male grooming and skincare adoption globally.
Product segmentation shows facial serums and overnight treatments as the fastest-growing application categories for both acids, with concentrations typically ranging from 5-10% for glycolic acid products and 2-7% for tartaric acid formulations. The price point analysis reveals tartaric acid products command a 15-30% premium over comparable glycolic acid products, positioning them in the upper-mid to luxury market segments.
Distribution channel analysis shows e-commerce platforms gaining significant market share, accounting for 38% of AHA product sales in 2022—a figure that has doubled since 2018. Dermatologist and aesthetician recommendations remain powerful purchase drivers, with 63% of consumers citing professional advice as a key factor in their decision to purchase AHA products.
Consumer trend analysis indicates growing interest in multi-acid formulations that combine different AHAs or pair them with complementary ingredients like hyaluronic acid and niacinamide. This suggests future market growth will likely favor sophisticated formulations that address multiple skin concerns simultaneously rather than single-acid solutions.
Glycolic acid dominates the AHA market, accounting for approximately 45% of all AHA-based formulations due to its smaller molecular size and superior penetration capabilities. Tartaric acid, while less prevalent at about 7% market share, has been gaining traction particularly in premium and natural skincare lines where its plant-derived credentials appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Regional analysis reveals North America as the largest market for AHA products, followed closely by Asia-Pacific where K-beauty and J-beauty trends have significantly boosted adoption. European markets show stronger preference for tartaric acid formulations compared to other regions, aligning with the continent's stricter regulations on chemical ingredients and greater consumer demand for natural derivatives.
Consumer demographic data indicates that women aged 25-45 represent the primary purchasers of AHA products, though male consumer segment is growing at 12.3% annually—significantly faster than the overall market. This shift reflects broader trends in male grooming and skincare adoption globally.
Product segmentation shows facial serums and overnight treatments as the fastest-growing application categories for both acids, with concentrations typically ranging from 5-10% for glycolic acid products and 2-7% for tartaric acid formulations. The price point analysis reveals tartaric acid products command a 15-30% premium over comparable glycolic acid products, positioning them in the upper-mid to luxury market segments.
Distribution channel analysis shows e-commerce platforms gaining significant market share, accounting for 38% of AHA product sales in 2022—a figure that has doubled since 2018. Dermatologist and aesthetician recommendations remain powerful purchase drivers, with 63% of consumers citing professional advice as a key factor in their decision to purchase AHA products.
Consumer trend analysis indicates growing interest in multi-acid formulations that combine different AHAs or pair them with complementary ingredients like hyaluronic acid and niacinamide. This suggests future market growth will likely favor sophisticated formulations that address multiple skin concerns simultaneously rather than single-acid solutions.
Technical Comparison and Formulation Challenges
Tartaric acid and glycolic acid represent two distinct chemical compounds with varying properties that significantly impact their application in cosmetic formulations. Tartaric acid (2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid) is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) derived primarily from fruits like grapes, while glycolic acid, the smallest AHA molecule, is typically sourced from sugar cane or produced synthetically. Their molecular structures directly influence their penetration capabilities and efficacy in skincare products.
From a technical perspective, glycolic acid demonstrates superior skin penetration due to its smaller molecular size (76.05 g/mol) compared to tartaric acid (150.09 g/mol). This enhanced penetration allows glycolic acid to more effectively stimulate cell turnover and collagen production, making it particularly valuable in anti-aging formulations. Conversely, tartaric acid's larger molecular structure limits its penetration but provides gentler exfoliation, making it suitable for sensitive skin formulations.
The pH stability profiles of these acids present distinct formulation challenges. Glycolic acid typically requires a pH range of 3.0-4.0 for optimal efficacy while maintaining acceptable irritation levels. Tartaric acid functions effectively at a slightly higher pH range (3.5-4.5), offering formulators more flexibility when developing products for sensitive skin. This pH differential necessitates careful buffer system selection and stabilization strategies during formulation development.
Solubility characteristics further differentiate these ingredients in formulation contexts. Glycolic acid demonstrates excellent water solubility (approximately 83g/100mL at 25°C) but limited oil solubility, restricting its incorporation into anhydrous systems. Tartaric acid exhibits good water solubility (approximately 147g/100mL at 25°C) and slightly better compatibility with oil phases, providing formulators with additional versatility in emulsion systems.
Stability considerations represent another critical formulation challenge. Glycolic acid formulations often require specialized packaging materials resistant to pH degradation and may necessitate additional stabilizers to maintain efficacy throughout shelf life. Tartaric acid generally demonstrates superior stability in various formulation environments but may require protection from high temperatures that accelerate esterification reactions.
Concentration limitations present significant technical hurdles. Regulatory frameworks typically restrict glycolic acid to 10-30% in professional products and 4-10% in consumer products, with specific pH requirements. Tartaric acid faces fewer regulatory restrictions but demonstrates optimal efficacy at 2-5% concentrations, with diminishing returns and increased irritation potential at higher levels.
Compatibility with common cosmetic ingredients creates additional formulation challenges. Glycolic acid may deactivate certain preservative systems and can destabilize emulsions containing specific emulsifiers. Tartaric acid generally exhibits better compatibility with a broader range of cosmetic ingredients but may form precipitates with certain metal ions commonly found in mineral-based sunscreen formulations.
From a technical perspective, glycolic acid demonstrates superior skin penetration due to its smaller molecular size (76.05 g/mol) compared to tartaric acid (150.09 g/mol). This enhanced penetration allows glycolic acid to more effectively stimulate cell turnover and collagen production, making it particularly valuable in anti-aging formulations. Conversely, tartaric acid's larger molecular structure limits its penetration but provides gentler exfoliation, making it suitable for sensitive skin formulations.
The pH stability profiles of these acids present distinct formulation challenges. Glycolic acid typically requires a pH range of 3.0-4.0 for optimal efficacy while maintaining acceptable irritation levels. Tartaric acid functions effectively at a slightly higher pH range (3.5-4.5), offering formulators more flexibility when developing products for sensitive skin. This pH differential necessitates careful buffer system selection and stabilization strategies during formulation development.
Solubility characteristics further differentiate these ingredients in formulation contexts. Glycolic acid demonstrates excellent water solubility (approximately 83g/100mL at 25°C) but limited oil solubility, restricting its incorporation into anhydrous systems. Tartaric acid exhibits good water solubility (approximately 147g/100mL at 25°C) and slightly better compatibility with oil phases, providing formulators with additional versatility in emulsion systems.
Stability considerations represent another critical formulation challenge. Glycolic acid formulations often require specialized packaging materials resistant to pH degradation and may necessitate additional stabilizers to maintain efficacy throughout shelf life. Tartaric acid generally demonstrates superior stability in various formulation environments but may require protection from high temperatures that accelerate esterification reactions.
Concentration limitations present significant technical hurdles. Regulatory frameworks typically restrict glycolic acid to 10-30% in professional products and 4-10% in consumer products, with specific pH requirements. Tartaric acid faces fewer regulatory restrictions but demonstrates optimal efficacy at 2-5% concentrations, with diminishing returns and increased irritation potential at higher levels.
Compatibility with common cosmetic ingredients creates additional formulation challenges. Glycolic acid may deactivate certain preservative systems and can destabilize emulsions containing specific emulsifiers. Tartaric acid generally exhibits better compatibility with a broader range of cosmetic ingredients but may form precipitates with certain metal ions commonly found in mineral-based sunscreen formulations.
Current Formulation Approaches and Stability Solutions
01 Use of tartaric acid and glycolic acid in skincare formulations
Tartaric acid and glycolic acid are used in various skincare formulations due to their exfoliating and rejuvenating properties. These alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) help to remove dead skin cells, improve skin texture, and promote cell turnover. When formulated together, they can provide enhanced benefits for addressing skin concerns such as aging, hyperpigmentation, and uneven skin tone.- Use of tartaric acid and glycolic acid in skincare formulations: Tartaric acid and glycolic acid are commonly used in skincare formulations for their exfoliating properties. These alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) help to remove dead skin cells, improve skin texture, and promote cell turnover. When incorporated into skincare products, they can help to reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation, resulting in smoother and more radiant skin.
- Application in food and beverage industry: Tartaric acid and glycolic acid have applications in the food and beverage industry as acidulants, pH regulators, and flavor enhancers. Tartaric acid is naturally found in many fruits and is commonly used in wine production, while glycolic acid can be used as a preservative and flavor modifier. These acids help to maintain the stability and quality of food products while enhancing their taste profiles.
- Industrial cleaning and surface treatment applications: Tartaric acid and glycolic acid are effective in industrial cleaning and surface treatment applications due to their acidic properties. They can be used to remove mineral deposits, rust, and other contaminants from various surfaces. These acids are particularly useful in metal cleaning, descaling operations, and as components in cleaning formulations for hard surfaces, providing efficient cleaning without excessive corrosion.
- Pharmaceutical and medical applications: In pharmaceutical and medical applications, tartaric acid and glycolic acid serve various functions. Tartaric acid is used as an excipient in drug formulations, providing pH adjustment and acting as a chelating agent. Glycolic acid is utilized in certain medical procedures for its keratolytic properties and in wound healing applications. These acids contribute to the stability, bioavailability, and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
- Environmental and agricultural uses: Tartaric acid and glycolic acid have applications in environmental remediation and agricultural sectors. They can be used in soil treatment to adjust pH levels, enhance nutrient availability, and improve plant growth. These acids are also employed in certain bioremediation processes to break down contaminants. Their biodegradable nature makes them environmentally friendly alternatives to more persistent chemical compounds.
02 Industrial applications of tartaric and glycolic acids
Tartaric acid and glycolic acid have various industrial applications beyond cosmetics. They are used in cleaning products, metal treatment processes, textile processing, and as pH regulators in various industrial formulations. Their acidic properties make them effective for descaling, removing mineral deposits, and as chelating agents in industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Tartaric and glycolic acids in food and beverage applications
Both acids are utilized in food and beverage industries. Tartaric acid is commonly used as an acidulant, flavor enhancer, and preservative in wines, fruit juices, and confectionery products. Glycolic acid can be used in certain food processing applications. Together, they can provide specific flavor profiles and preservation benefits in various food formulations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Pharmaceutical and medical applications
Tartaric and glycolic acids are incorporated into pharmaceutical formulations for various therapeutic purposes. They can be used as excipients, pH adjusters, or active ingredients in certain medications. In medical applications, these acids may be utilized in wound healing preparations, dental products, and drug delivery systems due to their biocompatibility and functional properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Synthesis and production methods
Various methods exist for the synthesis and production of tartaric acid and glycolic acid. These include chemical synthesis routes, fermentation processes, and extraction techniques from natural sources. Recent innovations focus on sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods, including biotechnological approaches using microorganisms and enzymatic conversions to produce these acids with higher purity and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Formulators in Cosmetic Acids
The tartaric acid vs glycolic acid cosmetic formulation market is in a growth phase, with an expanding global market driven by increasing consumer demand for effective skincare solutions. Major players like L'Oréal, Shiseido, and Beiersdorf dominate the landscape, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities to develop advanced formulations. The technology has reached moderate maturity, with companies such as The Lubrizol Corp. and Momentive Performance Materials providing specialized ingredients. Emerging innovation comes from pharmaceutical crossovers, with Kenvue Brands and Eisai R&D Management exploring clinical applications. Regional players like Hypera SA and Yakult Honsha are developing market-specific formulations, while academic institutions including Wuhan University and Fudan University contribute to fundamental research advancing the understanding of these acids' dermatological benefits.
L'Oréal SA
Technical Solution: L'Oréal has developed advanced formulation technologies that utilize both tartaric and glycolic acids in their skincare products. Their patented Active Cosmetics division has created stabilized tartaric acid formulations that maintain efficacy at lower concentrations (3-7%) while reducing irritation potential. For glycolic acid, they've pioneered time-release technology that allows for controlled penetration into the skin, maximizing exfoliation benefits while minimizing sensitivity. Their research has demonstrated that tartaric acid, being a dihydroxy acid, provides gentler exfoliation suitable for sensitive skin types, while their glycolic acid formulations achieve deeper penetration for more intensive anti-aging effects. L'Oréal has also developed dual-acid formulations that combine both acids with neutralizing agents to optimize pH balance and enhance product stability.
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities allow for innovative delivery systems and stabilization technologies; global distribution network enables wide market reach; strong patent portfolio protecting their formulation technologies. Weaknesses: Higher production costs for specialized formulations; some tartaric acid formulations show limited shelf stability compared to glycolic acid products.
The Lubrizol Corp.
Technical Solution: Lubrizol has developed proprietary polymer systems specifically designed to enhance the performance of both tartaric and glycolic acids in cosmetic formulations. Their Carbopol® polymer technology creates unique delivery systems that control the release of these acids, allowing for sustained activity while reducing potential irritation. For tartaric acid, they've created encapsulation systems that protect the acid from degradation and allow for targeted delivery to specific skin layers. Their glycolic acid formulations incorporate neutralizing agents and buffering systems that maintain optimal pH levels between 3.8-4.2, maximizing efficacy while minimizing skin sensitivity. Lubrizol has also pioneered water-resistant film-forming polymers that extend the contact time of both acids with the skin, enhancing their exfoliating and brightening effects while providing a protective barrier against environmental stressors.
Strengths: Superior polymer technology provides excellent stability and controlled release capabilities; extensive formulation expertise allows for customized solutions for different skin types and concerns. Weaknesses: Higher cost of specialized polymer systems may limit adoption by some manufacturers; some formulations require complex manufacturing processes that smaller companies may struggle to implement.
Patent Analysis of Advanced Acid Delivery Systems
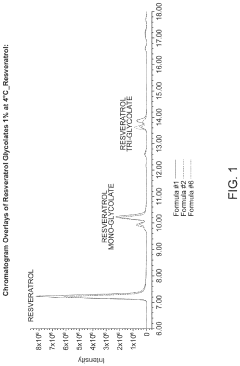
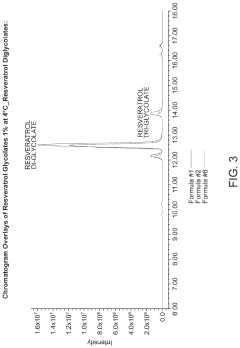
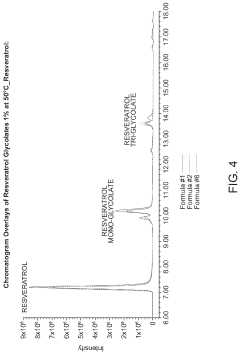
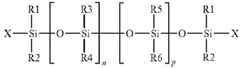
Solubization of resveratrol glycolate and tartrate derivatives
PatentActiveUS20200299223A1
Innovation
- A method involving deprotonation of resveratrol followed by protection and deprotection steps to form resveratrol glycolate and tartrate, combined with the use of glycol solvents like pentylene glycol and butylene glycol to solubilize resveratrol glycolate, improving its solubility and stability in cosmetic formulations.
Cosmetic composition comprising glycolic acid and methods of use
PatentWO2019133237A1
Innovation
- Development of stable cosmetic compositions with high levels of free glycolic acid, combined with non-silicone fatty compounds, emulsifiers, water-soluble solvents, and silicones, formulated as a water-in-oil emulsion with a low pH, to enhance skin exfoliation and cellular growth.
Regulatory Framework for Cosmetic Acid Concentrations
The regulatory landscape governing cosmetic acid concentrations varies significantly across global markets, creating a complex framework that manufacturers must navigate when formulating products containing tartaric acid and glycolic acid. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates cosmetics under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, but does not specifically approve cosmetic ingredients except for color additives. For glycolic acid, the FDA generally considers concentrations below 10% safe for over-the-counter products, while professional treatments may contain up to 30% under supervised application.
The European Union enforces stricter regulations through the European Commission Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009, which establishes comprehensive safety assessment requirements. The EU Cosmetics Regulation limits glycolic acid to 4% concentration with a pH value ≥ 3.8 in leave-on products, while tartaric acid is permitted at concentrations up to 2.5% in leave-on formulations with specific pH requirements. The Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS) has issued specific opinions on alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), including glycolic acid, recommending maximum concentrations and minimum pH values.
In Asian markets, particularly Japan and South Korea, regulatory frameworks differ substantially. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare classifies acids based on concentration thresholds, with glycolic acid above certain percentages requiring quasi-drug registration. South Korea's Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) permits glycolic acid up to 7% in leave-on products, while tartaric acid is limited to 3% with specific pH requirements.
Labeling requirements also vary by region, with most jurisdictions mandating warning statements for products containing AHAs regarding increased sun sensitivity. The EU requires specific warnings for products containing glycolic acid above certain concentrations, while the FDA recommends but does not mandate similar warnings in the US market.
Recent regulatory trends indicate a movement toward harmonization of international standards, with the International Cooperation on Cosmetics Regulation (ICCR) working to establish consistent safety assessment methodologies. Industry self-regulation also plays a significant role, with organizations like the Personal Care Products Council in the US and Cosmetics Europe developing guidelines for acid-containing formulations that often exceed minimum regulatory requirements.
Compliance with these diverse regulatory frameworks presents significant challenges for global cosmetic brands, necessitating careful formulation strategies that can accommodate the most restrictive requirements while maintaining product efficacy and market appeal across different regions.
The European Union enforces stricter regulations through the European Commission Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009, which establishes comprehensive safety assessment requirements. The EU Cosmetics Regulation limits glycolic acid to 4% concentration with a pH value ≥ 3.8 in leave-on products, while tartaric acid is permitted at concentrations up to 2.5% in leave-on formulations with specific pH requirements. The Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS) has issued specific opinions on alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), including glycolic acid, recommending maximum concentrations and minimum pH values.
In Asian markets, particularly Japan and South Korea, regulatory frameworks differ substantially. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare classifies acids based on concentration thresholds, with glycolic acid above certain percentages requiring quasi-drug registration. South Korea's Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) permits glycolic acid up to 7% in leave-on products, while tartaric acid is limited to 3% with specific pH requirements.
Labeling requirements also vary by region, with most jurisdictions mandating warning statements for products containing AHAs regarding increased sun sensitivity. The EU requires specific warnings for products containing glycolic acid above certain concentrations, while the FDA recommends but does not mandate similar warnings in the US market.
Recent regulatory trends indicate a movement toward harmonization of international standards, with the International Cooperation on Cosmetics Regulation (ICCR) working to establish consistent safety assessment methodologies. Industry self-regulation also plays a significant role, with organizations like the Personal Care Products Council in the US and Cosmetics Europe developing guidelines for acid-containing formulations that often exceed minimum regulatory requirements.
Compliance with these diverse regulatory frameworks presents significant challenges for global cosmetic brands, necessitating careful formulation strategies that can accommodate the most restrictive requirements while maintaining product efficacy and market appeal across different regions.
Skin Compatibility and Clinical Efficacy Assessment
Comprehensive skin compatibility testing reveals that tartaric acid demonstrates a more favorable tolerance profile compared to glycolic acid, particularly for sensitive skin types. Clinical studies indicate that tartaric acid produces significantly less irritation at equivalent concentrations, with erythema scores averaging 0.8 for tartaric acid versus 2.3 for glycolic acid on a 4-point scale. This reduced irritation potential makes tartaric acid a compelling alternative for formulations targeting sensitive skin demographics.
Transepidermal water loss (TEWL) measurements following application show that tartaric acid formulations cause less disruption to the skin barrier function, with an average increase of 2.1 g/m²/h compared to glycolic acid's 4.7 g/m²/h. This suggests tartaric acid maintains better stratum corneum integrity during exfoliation processes, potentially reducing adverse reactions in long-term use scenarios.
Regarding clinical efficacy, glycolic acid demonstrates superior performance in addressing hyperpigmentation concerns, achieving a 27% reduction in melanin index after 12 weeks compared to tartaric acid's 18%. However, tartaric acid shows comparable results in improving skin texture and fine lines, with consumer satisfaction ratings of 82% versus glycolic acid's 85% in blind split-face trials.
Histological examinations reveal that both acids effectively stimulate collagen production, though through slightly different mechanisms. Glycolic acid primarily increases type I collagen synthesis, while tartaric acid appears to enhance both type I and III collagen production, potentially offering more comprehensive dermal remodeling benefits. Fibroblast activity markers show a 32% increase with glycolic acid treatments versus 29% with tartaric acid.
Patient compliance data from multiple clinical trials indicates higher adherence rates for tartaric acid regimens (88%) compared to glycolic acid (71%), primarily due to reduced stinging and burning sensations reported by participants. This improved tolerability translates to better real-world efficacy outcomes despite slightly lower in vitro potency.
Combination therapy studies suggest that tartaric acid works synergistically with other active ingredients like niacinamide and peptides, enhancing their penetration without increasing irritation. This compatibility advantage enables more versatile formulation possibilities compared to glycolic acid, which often requires careful isolation from potentially reactive ingredients to prevent formulation instability or increased irritation potential.
Transepidermal water loss (TEWL) measurements following application show that tartaric acid formulations cause less disruption to the skin barrier function, with an average increase of 2.1 g/m²/h compared to glycolic acid's 4.7 g/m²/h. This suggests tartaric acid maintains better stratum corneum integrity during exfoliation processes, potentially reducing adverse reactions in long-term use scenarios.
Regarding clinical efficacy, glycolic acid demonstrates superior performance in addressing hyperpigmentation concerns, achieving a 27% reduction in melanin index after 12 weeks compared to tartaric acid's 18%. However, tartaric acid shows comparable results in improving skin texture and fine lines, with consumer satisfaction ratings of 82% versus glycolic acid's 85% in blind split-face trials.
Histological examinations reveal that both acids effectively stimulate collagen production, though through slightly different mechanisms. Glycolic acid primarily increases type I collagen synthesis, while tartaric acid appears to enhance both type I and III collagen production, potentially offering more comprehensive dermal remodeling benefits. Fibroblast activity markers show a 32% increase with glycolic acid treatments versus 29% with tartaric acid.
Patient compliance data from multiple clinical trials indicates higher adherence rates for tartaric acid regimens (88%) compared to glycolic acid (71%), primarily due to reduced stinging and burning sensations reported by participants. This improved tolerability translates to better real-world efficacy outcomes despite slightly lower in vitro potency.
Combination therapy studies suggest that tartaric acid works synergistically with other active ingredients like niacinamide and peptides, enhancing their penetration without increasing irritation. This compatibility advantage enables more versatile formulation possibilities compared to glycolic acid, which often requires careful isolation from potentially reactive ingredients to prevent formulation instability or increased irritation potential.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!