The Role of Muriatic Acid in Food Processing
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muriatic Acid in Food: Background and Objectives
Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, has played a significant role in food processing for decades. This strong mineral acid, with its unique chemical properties, has become an indispensable component in various food industry applications. The evolution of muriatic acid usage in food processing can be traced back to the early 20th century when industrial-scale food production began to take shape.
Initially, muriatic acid found its primary use in the cleaning and sanitization of food processing equipment. Its ability to effectively remove mineral deposits and kill harmful microorganisms made it a valuable tool in maintaining hygiene standards. As food science advanced, researchers discovered additional applications for muriatic acid, expanding its role beyond mere sanitation.
One of the key developments was the utilization of muriatic acid in pH adjustment for food products. This application became crucial in preserving food quality, enhancing flavor profiles, and extending shelf life. The acid's ability to control acidity levels in various food items, from beverages to canned goods, revolutionized food preservation techniques.
In recent years, the focus of muriatic acid usage in food processing has shifted towards more specialized applications. These include its use in the production of modified food starches, hydrolysis of proteins, and extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials. The acid's versatility has made it an essential component in the development of novel food products and ingredients.
The technological objectives for muriatic acid in food processing are multifaceted. Researchers and industry professionals are continually striving to optimize its use while addressing safety concerns and environmental impacts. Key goals include developing more efficient and sustainable production methods for food-grade muriatic acid, improving its application techniques to minimize residual acid in final products, and exploring new potential uses in emerging food technologies.
Another significant objective is to enhance the precision of pH control in food processing. This involves developing advanced monitoring systems and automated dosing mechanisms to ensure optimal acid concentration and distribution throughout the production process. Such advancements aim to improve product consistency, reduce waste, and increase overall efficiency in food manufacturing.
As the food industry continues to evolve, the role of muriatic acid is expected to expand further. Emerging trends such as clean label products and functional foods present new challenges and opportunities for muriatic acid applications. Researchers are exploring ways to utilize this versatile acid in creating natural preservatives and functional ingredients that meet consumer demands for healthier, more transparent food options.
Initially, muriatic acid found its primary use in the cleaning and sanitization of food processing equipment. Its ability to effectively remove mineral deposits and kill harmful microorganisms made it a valuable tool in maintaining hygiene standards. As food science advanced, researchers discovered additional applications for muriatic acid, expanding its role beyond mere sanitation.
One of the key developments was the utilization of muriatic acid in pH adjustment for food products. This application became crucial in preserving food quality, enhancing flavor profiles, and extending shelf life. The acid's ability to control acidity levels in various food items, from beverages to canned goods, revolutionized food preservation techniques.
In recent years, the focus of muriatic acid usage in food processing has shifted towards more specialized applications. These include its use in the production of modified food starches, hydrolysis of proteins, and extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials. The acid's versatility has made it an essential component in the development of novel food products and ingredients.
The technological objectives for muriatic acid in food processing are multifaceted. Researchers and industry professionals are continually striving to optimize its use while addressing safety concerns and environmental impacts. Key goals include developing more efficient and sustainable production methods for food-grade muriatic acid, improving its application techniques to minimize residual acid in final products, and exploring new potential uses in emerging food technologies.
Another significant objective is to enhance the precision of pH control in food processing. This involves developing advanced monitoring systems and automated dosing mechanisms to ensure optimal acid concentration and distribution throughout the production process. Such advancements aim to improve product consistency, reduce waste, and increase overall efficiency in food manufacturing.
As the food industry continues to evolve, the role of muriatic acid is expected to expand further. Emerging trends such as clean label products and functional foods present new challenges and opportunities for muriatic acid applications. Researchers are exploring ways to utilize this versatile acid in creating natural preservatives and functional ingredients that meet consumer demands for healthier, more transparent food options.
Market Analysis: Food Processing Acid Demand
The global food processing acid market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by the increasing demand for processed and convenience foods. Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, plays a crucial role in this market segment. The demand for food processing acids, including muriatic acid, is primarily fueled by the expanding food and beverage industry, particularly in developing economies.
In recent years, the market for food processing acids has shown a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5-6%. This growth is attributed to the rising consumption of processed foods, changing dietary habits, and the need for extended shelf life of food products. Muriatic acid, specifically, finds applications in various food processing activities, including pH adjustment, flavor enhancement, and as a cleaning agent in food processing equipment.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a significant market for food processing acids, with countries like China and India leading the demand. This is largely due to the rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and changing food preferences in these countries. North America and Europe also maintain a substantial market share, driven by the well-established food processing industry and stringent food safety regulations.
Within the food processing acid market, muriatic acid holds a notable position due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. It is widely used in the production of various food products, including beverages, dairy, and confectionery. The demand for muriatic acid in food processing is expected to grow further as manufacturers seek efficient and economical solutions for food preservation and quality enhancement.
However, the market for food processing acids, including muriatic acid, faces challenges related to stringent regulations on food additives and growing consumer preference for natural and organic products. This has led to increased research and development efforts to find alternative natural acids or to develop safer and more environmentally friendly production methods for existing acids.
The beverage industry represents a significant portion of the demand for food processing acids. Muriatic acid is used in the production of various beverages, including soft drinks and fruit juices, for pH adjustment and flavor enhancement. The growing popularity of flavored and functional beverages is expected to further drive the demand for food processing acids in this sector.
In conclusion, the market analysis indicates a positive outlook for food processing acids, with muriatic acid playing a significant role. The increasing demand for processed foods, coupled with technological advancements in food processing techniques, is expected to sustain the growth of this market in the coming years. However, manufacturers will need to address regulatory challenges and evolving consumer preferences to maintain their market position and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
In recent years, the market for food processing acids has shown a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5-6%. This growth is attributed to the rising consumption of processed foods, changing dietary habits, and the need for extended shelf life of food products. Muriatic acid, specifically, finds applications in various food processing activities, including pH adjustment, flavor enhancement, and as a cleaning agent in food processing equipment.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a significant market for food processing acids, with countries like China and India leading the demand. This is largely due to the rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and changing food preferences in these countries. North America and Europe also maintain a substantial market share, driven by the well-established food processing industry and stringent food safety regulations.
Within the food processing acid market, muriatic acid holds a notable position due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. It is widely used in the production of various food products, including beverages, dairy, and confectionery. The demand for muriatic acid in food processing is expected to grow further as manufacturers seek efficient and economical solutions for food preservation and quality enhancement.
However, the market for food processing acids, including muriatic acid, faces challenges related to stringent regulations on food additives and growing consumer preference for natural and organic products. This has led to increased research and development efforts to find alternative natural acids or to develop safer and more environmentally friendly production methods for existing acids.
The beverage industry represents a significant portion of the demand for food processing acids. Muriatic acid is used in the production of various beverages, including soft drinks and fruit juices, for pH adjustment and flavor enhancement. The growing popularity of flavored and functional beverages is expected to further drive the demand for food processing acids in this sector.
In conclusion, the market analysis indicates a positive outlook for food processing acids, with muriatic acid playing a significant role. The increasing demand for processed foods, coupled with technological advancements in food processing techniques, is expected to sustain the growth of this market in the coming years. However, manufacturers will need to address regulatory challenges and evolving consumer preferences to maintain their market position and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Current Applications and Challenges
Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, plays a significant role in various food processing applications. Its primary use is in the pH adjustment of food products, which is crucial for controlling microbial growth, enhancing flavor, and improving texture. In the beverage industry, muriatic acid is employed to adjust the acidity of soft drinks and fruit juices, ensuring optimal taste and preservation.
In meat processing, muriatic acid is utilized for carcass washing and as a processing aid in the production of gelatin. It effectively removes surface contaminants and helps in the extraction of collagen from animal tissues. The dairy industry also benefits from muriatic acid, particularly in the production of cheese, where it aids in curd formation and whey separation.
Another important application is in sugar refining, where muriatic acid is used to invert sucrose into glucose and fructose, creating invert sugar syrup. This process enhances sweetness and prevents crystallization in various confectionery products. Additionally, muriatic acid serves as a cleaning and sanitizing agent in food processing facilities, effectively removing mineral deposits and killing harmful microorganisms.
Despite its widespread use, the application of muriatic acid in food processing faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is safety, as improper handling or excessive use can pose risks to workers and potentially compromise food quality. Strict regulations and safety protocols must be followed to mitigate these risks, including proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures.
Another challenge is the potential for corrosion of processing equipment. Muriatic acid's highly corrosive nature necessitates the use of specialized materials and protective coatings to prevent damage to machinery and storage tanks. This requirement can increase operational costs and maintenance requirements for food processing facilities.
The precise control of acid concentration and pH levels presents another technical challenge. Accurate dosing systems and monitoring equipment are essential to maintain the desired acidity without affecting the sensory properties or safety of the final product. This requires sophisticated process control systems and well-trained personnel.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to the use of muriatic acid in food processing. Proper waste management and neutralization of acid residues are crucial to comply with environmental regulations and minimize ecological impact. Some facilities are exploring alternative acids or processing methods to reduce their reliance on muriatic acid and improve their environmental footprint.
As the food industry continues to evolve, addressing these challenges while maximizing the benefits of muriatic acid remains a key focus for food processors and technology developers. Innovations in acid handling, dosing systems, and safety protocols are ongoing to enhance the efficiency and safety of muriatic acid applications in food processing.
In meat processing, muriatic acid is utilized for carcass washing and as a processing aid in the production of gelatin. It effectively removes surface contaminants and helps in the extraction of collagen from animal tissues. The dairy industry also benefits from muriatic acid, particularly in the production of cheese, where it aids in curd formation and whey separation.
Another important application is in sugar refining, where muriatic acid is used to invert sucrose into glucose and fructose, creating invert sugar syrup. This process enhances sweetness and prevents crystallization in various confectionery products. Additionally, muriatic acid serves as a cleaning and sanitizing agent in food processing facilities, effectively removing mineral deposits and killing harmful microorganisms.
Despite its widespread use, the application of muriatic acid in food processing faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is safety, as improper handling or excessive use can pose risks to workers and potentially compromise food quality. Strict regulations and safety protocols must be followed to mitigate these risks, including proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures.
Another challenge is the potential for corrosion of processing equipment. Muriatic acid's highly corrosive nature necessitates the use of specialized materials and protective coatings to prevent damage to machinery and storage tanks. This requirement can increase operational costs and maintenance requirements for food processing facilities.
The precise control of acid concentration and pH levels presents another technical challenge. Accurate dosing systems and monitoring equipment are essential to maintain the desired acidity without affecting the sensory properties or safety of the final product. This requires sophisticated process control systems and well-trained personnel.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to the use of muriatic acid in food processing. Proper waste management and neutralization of acid residues are crucial to comply with environmental regulations and minimize ecological impact. Some facilities are exploring alternative acids or processing methods to reduce their reliance on muriatic acid and improve their environmental footprint.
As the food industry continues to evolve, addressing these challenges while maximizing the benefits of muriatic acid remains a key focus for food processors and technology developers. Innovations in acid handling, dosing systems, and safety protocols are ongoing to enhance the efficiency and safety of muriatic acid applications in food processing.
Existing Muriatic Acid Processing Methods
01 Chemical properties and applications of muriatic acid
Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, is a strong mineral acid with various industrial and household applications. It is commonly used for cleaning, pH adjustment, and as a reagent in chemical processes. Its corrosive nature makes it effective for removing rust, scale, and other deposits.- Chemical properties and applications: Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, is a strong mineral acid with various industrial and commercial applications. It is commonly used in metal cleaning, pH adjustment, and as a reagent in chemical processes. Its corrosive nature and ability to dissolve certain metals make it useful in surface preparation and etching.
- Use in construction and building materials: Muriatic acid is utilized in the construction industry for cleaning masonry, concrete, and other building materials. It can remove efflorescence, stains, and mineral deposits from surfaces. The acid is also used in the production of certain construction materials and in the treatment of swimming pool water.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Handling and disposal of muriatic acid require careful attention to safety protocols and environmental regulations. Proper storage, transportation, and use of protective equipment are essential. Neutralization and treatment methods are employed to mitigate environmental impact when disposing of the acid or its byproducts.
- Industrial processes and manufacturing: Muriatic acid plays a crucial role in various industrial processes, including metal processing, oil well acidizing, and food production. It is used in the manufacture of chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and in the treatment of water and wastewater. The acid's ability to control pH and remove impurities makes it valuable in many manufacturing applications.
- Innovations in production and purification: Advancements in the production and purification of muriatic acid focus on improving efficiency, reducing impurities, and enhancing safety. Novel methods for synthesizing high-purity hydrochloric acid and recovering it from industrial waste streams have been developed. These innovations aim to meet the growing demand for high-quality acid while minimizing environmental impact.
02 Use in water treatment and purification
Muriatic acid plays a crucial role in water treatment and purification processes. It is used to adjust pH levels in swimming pools, industrial water systems, and municipal water supplies. The acid helps to control alkalinity and prevent the growth of harmful microorganisms.Expand Specific Solutions03 Industrial cleaning and surface preparation
Muriatic acid is widely used in industrial cleaning applications, particularly for removing rust, scale, and mineral deposits from metal surfaces. It is also employed in surface preparation processes for painting, coating, and other treatments, helping to improve adhesion and durability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Production and handling of muriatic acid
The production, storage, and handling of muriatic acid require specialized equipment and safety measures due to its corrosive nature. Various processes and apparatus have been developed to manufacture, transport, and dispense the acid safely and efficiently in industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
The use of muriatic acid presents environmental and safety challenges due to its corrosive properties and potential for harmful emissions. Efforts have been made to develop safer alternatives, improve handling procedures, and implement proper disposal methods to minimize risks to human health and the environment.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Food-Grade Acid Production
The market for muriatic acid in food processing is in a mature stage, with established players and well-defined applications. The global market size is estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars, driven by its use in various food processing applications. Technologically, the use of muriatic acid is well-established, with companies like Ecolab USA, Inc., DSM IP Assets BV, and Purac Biochem BV leading in innovation and application development. These firms, along with others such as Novozymes A/S and Ajinomoto Co., Inc., are continually refining processes and developing new applications to maintain their competitive edge in this stable but evolving market.
Ecolab USA, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ecolab has developed advanced cleaning and sanitizing solutions utilizing muriatic acid for food processing applications. Their technology involves precise formulations that optimize the acid's effectiveness while minimizing corrosion risks. The company's approach includes automated dosing systems that carefully control acid concentration and application, ensuring consistent results across large-scale food processing operations[1]. Ecolab's solutions also incorporate safety features such as low-foam additives and pH indicators to prevent overuse and protect workers[2]. Their research has shown that properly applied muriatic acid treatments can reduce microbial contamination by up to 99.9% on food contact surfaces[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive sanitization solutions, automated application systems, proven efficacy in pathogen reduction. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns, need for specialized handling and safety protocols.
Ajinomoto Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Ajinomoto has leveraged muriatic acid in innovative ways for amino acid production and flavor enhancement. The company uses controlled hydrolysis with muriatic acid to break down proteins into specific amino acids, which are then used in various food applications[7]. Their process involves precise temperature and pressure control to optimize yield and purity. Ajinomoto has also developed a patented method using muriatic acid for the extraction and purification of glutamic acid, a key component in their signature MSG product[8]. Furthermore, the company has explored the use of muriatic acid in the production of low-sodium salt alternatives, where it plays a role in mineral extraction and flavor balancing[9].
Strengths: Expertise in amino acid production, efficient extraction processes, diverse applications in flavor enhancement. Weaknesses: Energy-intensive processes, potential for by-product generation requiring additional processing.
Innovations in Muriatic Acid Purification
Synthetic acid compositions and uses thereof
PatentInactiveCA2852729A1
Innovation
- A synthetic acid composition comprising urea and hydrogen chloride in a specific molar ratio, combined with phosphonic acid derivatives and metal iodides, which reduces corrosion and toxicity, is biodegradable, non-fuming, and compatible with equipment and the environment, offering a safer and more effective alternative for industrial applications.
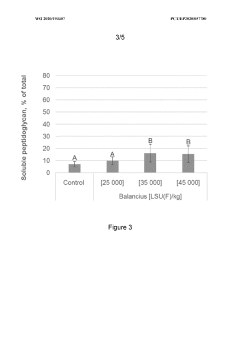
Use of muramic acid as a biomarker for gastrointestinal peptidoglycan hydrolysis
PatentWO2020193407A1
Innovation
- The use of muramic acid measurements in acid-hydrolyzed digesta samples to quantify peptidoglycan hydrolysis by muramidases, allowing for the determination of soluble peptidoglycan levels relative to total muramic acid, thereby assessing the degree of peptidoglycan hydrolysis in the gastrointestinal tract.
Regulatory Framework for Food Additives
The regulatory framework for food additives plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe and appropriate use of muriatic acid in food processing. Governments and international organizations have established comprehensive guidelines and regulations to govern the use of food additives, including muriatic acid, to protect consumer health and maintain food quality.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for regulating food additives. The FDA has classified muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices. This designation allows for its use in specific food processing applications, such as pH adjustment and as a processing aid.
The European Union (EU) has its own regulatory framework for food additives, governed by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EU has approved hydrochloric acid (E507) for use in food processing, subject to specific conditions and limitations. These regulations outline the permitted uses, maximum levels, and labeling requirements for muriatic acid in various food products.
Internationally, the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) provides scientific evaluations of food additives, including muriatic acid. JECFA's assessments inform the development of global standards and guidelines, which are often adopted or referenced by national regulatory bodies.
Many countries have implemented their own regulatory frameworks for food additives, often based on or aligned with international standards. These frameworks typically include provisions for the approval process, safety assessments, permitted uses, and maximum levels of muriatic acid in food processing.
Regulatory bodies also require manufacturers to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) when using muriatic acid in food processing. This ensures that the additive is used at the minimum levels necessary to achieve the desired technological effect, without compromising food safety or quality.
Labeling requirements are another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. In many jurisdictions, the use of muriatic acid as a food additive must be declared on product labels, either by its specific name or by its E-number (E507). This transparency allows consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase and consume.
As scientific knowledge and food processing technologies evolve, regulatory frameworks are periodically reviewed and updated. This ongoing process ensures that the use of muriatic acid and other food additives remains safe and appropriate in light of new research and changing consumer preferences.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for regulating food additives. The FDA has classified muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices. This designation allows for its use in specific food processing applications, such as pH adjustment and as a processing aid.
The European Union (EU) has its own regulatory framework for food additives, governed by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EU has approved hydrochloric acid (E507) for use in food processing, subject to specific conditions and limitations. These regulations outline the permitted uses, maximum levels, and labeling requirements for muriatic acid in various food products.
Internationally, the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) provides scientific evaluations of food additives, including muriatic acid. JECFA's assessments inform the development of global standards and guidelines, which are often adopted or referenced by national regulatory bodies.
Many countries have implemented their own regulatory frameworks for food additives, often based on or aligned with international standards. These frameworks typically include provisions for the approval process, safety assessments, permitted uses, and maximum levels of muriatic acid in food processing.
Regulatory bodies also require manufacturers to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) when using muriatic acid in food processing. This ensures that the additive is used at the minimum levels necessary to achieve the desired technological effect, without compromising food safety or quality.
Labeling requirements are another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. In many jurisdictions, the use of muriatic acid as a food additive must be declared on product labels, either by its specific name or by its E-number (E507). This transparency allows consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase and consume.
As scientific knowledge and food processing technologies evolve, regulatory frameworks are periodically reviewed and updated. This ongoing process ensures that the use of muriatic acid and other food additives remains safe and appropriate in light of new research and changing consumer preferences.
Environmental Impact of Muriatic Acid Use
The use of muriatic acid in food processing raises significant environmental concerns due to its potential impacts on ecosystems and human health. When improperly handled or disposed of, muriatic acid can lead to soil and water contamination, affecting both aquatic and terrestrial environments. The acidic nature of this chemical can alter the pH balance of water bodies, potentially harming fish and other aquatic organisms.
In industrial food processing facilities, the release of muriatic acid into wastewater systems without proper treatment can cause corrosion of pipes and damage to sewage treatment infrastructure. This not only poses risks to the environment but also increases maintenance costs for water treatment facilities. Furthermore, the production and transportation of muriatic acid contribute to carbon emissions, adding to the overall environmental footprint of food processing operations.
The volatility of muriatic acid also presents air quality concerns. When exposed to air, it can release harmful fumes that may contribute to local air pollution and pose health risks to workers and nearby communities. Proper ventilation and handling procedures are crucial to mitigate these risks, but they do not entirely eliminate the potential for environmental impact.
Efforts to reduce the environmental impact of muriatic acid in food processing include the development of closed-loop systems that minimize waste and emissions. Some facilities have implemented advanced treatment technologies to neutralize acid waste before discharge. Additionally, there is a growing trend towards using alternative, less hazardous substances where possible, such as organic acids or enzymatic solutions for certain food processing applications.
Regulatory bodies have established guidelines for the safe use and disposal of muriatic acid in industrial settings, including food processing. These regulations aim to protect both the environment and human health by setting limits on emissions and mandating proper handling and disposal practices. Compliance with these regulations is essential for food processing companies to minimize their environmental impact and maintain sustainable operations.
As the food industry continues to evolve, there is an increasing focus on sustainable practices and environmental stewardship. This has led to research into more environmentally friendly alternatives to muriatic acid and improved methods for its use and disposal. The development of green chemistry solutions and circular economy principles in food processing may further reduce the reliance on harsh chemicals like muriatic acid, ultimately lessening the environmental burden of food production processes.
In industrial food processing facilities, the release of muriatic acid into wastewater systems without proper treatment can cause corrosion of pipes and damage to sewage treatment infrastructure. This not only poses risks to the environment but also increases maintenance costs for water treatment facilities. Furthermore, the production and transportation of muriatic acid contribute to carbon emissions, adding to the overall environmental footprint of food processing operations.
The volatility of muriatic acid also presents air quality concerns. When exposed to air, it can release harmful fumes that may contribute to local air pollution and pose health risks to workers and nearby communities. Proper ventilation and handling procedures are crucial to mitigate these risks, but they do not entirely eliminate the potential for environmental impact.
Efforts to reduce the environmental impact of muriatic acid in food processing include the development of closed-loop systems that minimize waste and emissions. Some facilities have implemented advanced treatment technologies to neutralize acid waste before discharge. Additionally, there is a growing trend towards using alternative, less hazardous substances where possible, such as organic acids or enzymatic solutions for certain food processing applications.
Regulatory bodies have established guidelines for the safe use and disposal of muriatic acid in industrial settings, including food processing. These regulations aim to protect both the environment and human health by setting limits on emissions and mandating proper handling and disposal practices. Compliance with these regulations is essential for food processing companies to minimize their environmental impact and maintain sustainable operations.
As the food industry continues to evolve, there is an increasing focus on sustainable practices and environmental stewardship. This has led to research into more environmentally friendly alternatives to muriatic acid and improved methods for its use and disposal. The development of green chemistry solutions and circular economy principles in food processing may further reduce the reliance on harsh chemicals like muriatic acid, ultimately lessening the environmental burden of food production processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!