The Role of Perchloric Acid in Green Chemistry Practices
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Perchloric Acid in Green Chemistry: Background and Objectives
Perchloric acid, a powerful oxidizing agent, has been a subject of interest in the field of green chemistry for its potential to contribute to more sustainable chemical processes. The evolution of green chemistry practices has led to a reevaluation of traditional reagents and methodologies, with a focus on reducing environmental impact and improving efficiency. In this context, perchloric acid's unique properties have garnered attention from researchers and industry professionals alike.
The historical use of perchloric acid in various industrial and laboratory applications has been well-documented, but its role in green chemistry is a more recent development. As the chemical industry shifts towards more environmentally friendly practices, the exploration of perchloric acid's capabilities in this domain has become increasingly relevant. The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively examine the potential of perchloric acid in advancing green chemistry initiatives.
One of the key areas of investigation is the use of perchloric acid as a catalyst in organic synthesis reactions. Its strong oxidizing properties make it a promising candidate for replacing more toxic or less efficient catalysts in certain chemical transformations. Additionally, researchers are exploring its potential in waste treatment processes, where its oxidizing power could be harnessed to break down persistent organic pollutants.
The development of safer handling and storage protocols for perchloric acid is another crucial aspect of its integration into green chemistry practices. While its reactivity presents challenges, advancements in containment and dilution techniques have made it possible to utilize perchloric acid more safely in laboratory and industrial settings. This progress aligns with the green chemistry principle of inherently safer chemistry for accident prevention.
Furthermore, the role of perchloric acid in analytical chemistry is being reevaluated through the lens of green chemistry. Its use in spectroscopic and electrochemical analyses is being optimized to reduce waste and improve energy efficiency. Researchers are also investigating novel applications of perchloric acid in the development of green materials and sustainable energy technologies.
As we delve deeper into the technical aspects of perchloric acid's role in green chemistry, it is essential to consider the broader implications for industrial processes and environmental protection. The potential for perchloric acid to contribute to cleaner production methods and more efficient resource utilization aligns with the overarching goals of sustainable development in the chemical industry.
The historical use of perchloric acid in various industrial and laboratory applications has been well-documented, but its role in green chemistry is a more recent development. As the chemical industry shifts towards more environmentally friendly practices, the exploration of perchloric acid's capabilities in this domain has become increasingly relevant. The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively examine the potential of perchloric acid in advancing green chemistry initiatives.
One of the key areas of investigation is the use of perchloric acid as a catalyst in organic synthesis reactions. Its strong oxidizing properties make it a promising candidate for replacing more toxic or less efficient catalysts in certain chemical transformations. Additionally, researchers are exploring its potential in waste treatment processes, where its oxidizing power could be harnessed to break down persistent organic pollutants.
The development of safer handling and storage protocols for perchloric acid is another crucial aspect of its integration into green chemistry practices. While its reactivity presents challenges, advancements in containment and dilution techniques have made it possible to utilize perchloric acid more safely in laboratory and industrial settings. This progress aligns with the green chemistry principle of inherently safer chemistry for accident prevention.
Furthermore, the role of perchloric acid in analytical chemistry is being reevaluated through the lens of green chemistry. Its use in spectroscopic and electrochemical analyses is being optimized to reduce waste and improve energy efficiency. Researchers are also investigating novel applications of perchloric acid in the development of green materials and sustainable energy technologies.
As we delve deeper into the technical aspects of perchloric acid's role in green chemistry, it is essential to consider the broader implications for industrial processes and environmental protection. The potential for perchloric acid to contribute to cleaner production methods and more efficient resource utilization aligns with the overarching goals of sustainable development in the chemical industry.
Market Analysis for Green Chemistry Solutions
The green chemistry market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations. The global green chemicals market size was valued at USD 11.9 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 16.5 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products across various industries.
Perchloric acid, despite its potential hazards, has found a niche in green chemistry practices due to its unique properties and applications. The market for perchloric acid in green chemistry is expected to grow steadily, albeit at a slower pace compared to other green chemistry solutions. This is primarily due to the challenges associated with its handling and disposal.
In the context of green chemistry, perchloric acid is utilized in various applications, including as a catalyst in organic synthesis, an oxidizing agent in analytical chemistry, and a component in specialized cleaning solutions. The electronics industry, in particular, has shown increased interest in perchloric acid for its use in etching and cleaning processes, which aligns with the industry's push towards more environmentally friendly manufacturing practices.
The pharmaceutical sector is another key market for perchloric acid in green chemistry applications. As the industry moves towards more sustainable drug development and manufacturing processes, perchloric acid's role in certain synthetic routes and analytical methods has gained attention. However, the adoption rate is tempered by safety concerns and the need for specialized handling equipment.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for green chemistry solutions, including those involving perchloric acid. These regions have well-established regulatory frameworks promoting sustainable practices and substantial investments in research and development. Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market for green chemistry solutions, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing environmental awareness in countries like China and India.
The market for perchloric acid in green chemistry faces several challenges, including safety concerns, regulatory hurdles, and competition from alternative green chemistry solutions. However, ongoing research into safer handling methods and novel applications in sustainable chemistry processes could potentially expand its market share in the coming years.
Key players in the green chemistry market are increasingly focusing on developing safer and more efficient processes involving perchloric acid. This includes research into recyclable catalyst systems, improved containment methods, and novel synthetic routes that minimize the use of hazardous substances while maximizing yield and efficiency.
Perchloric acid, despite its potential hazards, has found a niche in green chemistry practices due to its unique properties and applications. The market for perchloric acid in green chemistry is expected to grow steadily, albeit at a slower pace compared to other green chemistry solutions. This is primarily due to the challenges associated with its handling and disposal.
In the context of green chemistry, perchloric acid is utilized in various applications, including as a catalyst in organic synthesis, an oxidizing agent in analytical chemistry, and a component in specialized cleaning solutions. The electronics industry, in particular, has shown increased interest in perchloric acid for its use in etching and cleaning processes, which aligns with the industry's push towards more environmentally friendly manufacturing practices.
The pharmaceutical sector is another key market for perchloric acid in green chemistry applications. As the industry moves towards more sustainable drug development and manufacturing processes, perchloric acid's role in certain synthetic routes and analytical methods has gained attention. However, the adoption rate is tempered by safety concerns and the need for specialized handling equipment.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for green chemistry solutions, including those involving perchloric acid. These regions have well-established regulatory frameworks promoting sustainable practices and substantial investments in research and development. Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market for green chemistry solutions, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing environmental awareness in countries like China and India.
The market for perchloric acid in green chemistry faces several challenges, including safety concerns, regulatory hurdles, and competition from alternative green chemistry solutions. However, ongoing research into safer handling methods and novel applications in sustainable chemistry processes could potentially expand its market share in the coming years.
Key players in the green chemistry market are increasingly focusing on developing safer and more efficient processes involving perchloric acid. This includes research into recyclable catalyst systems, improved containment methods, and novel synthetic routes that minimize the use of hazardous substances while maximizing yield and efficiency.
Current Challenges in Perchloric Acid Usage
Despite the potential benefits of perchloric acid in green chemistry practices, several significant challenges persist in its usage. One of the primary concerns is the inherent safety risks associated with handling and storing perchloric acid. Its strong oxidizing properties make it highly reactive and potentially explosive when in contact with organic compounds or reducing agents. This necessitates stringent safety protocols and specialized equipment, which can be costly and challenging to implement, especially for smaller laboratories or industrial facilities.
Another major challenge is the environmental impact of perchloric acid production and disposal. The manufacturing process of perchloric acid often involves energy-intensive methods and the use of other hazardous chemicals, which can contribute to a significant carbon footprint. Additionally, the disposal of perchloric acid waste requires careful management to prevent contamination of soil and water resources, as perchlorate ions can persist in the environment and pose risks to human health and ecosystems.
The regulatory landscape surrounding perchloric acid usage presents further complications. Due to its potential use in explosive manufacturing, perchloric acid is subject to strict regulations and monitoring in many countries. These regulations can create barriers to research and industrial applications, requiring extensive documentation, permits, and compliance measures that may deter some organizations from utilizing this chemical.
Scalability issues also pose a significant challenge in the widespread adoption of perchloric acid in green chemistry practices. While perchloric acid may demonstrate promising results in laboratory-scale experiments, translating these benefits to industrial-scale processes can be problematic. The corrosive nature of perchloric acid necessitates specialized equipment and materials, which can be prohibitively expensive when scaled up to industrial levels.
Furthermore, the limited availability and high cost of high-purity perchloric acid can hinder its broader application in green chemistry. The production of perchloric acid with the required purity for certain applications can be technically challenging and resource-intensive, leading to supply chain issues and increased costs for end-users.
Lastly, there is a notable knowledge gap in understanding the long-term effects of perchloric acid usage in various chemical processes. While its potential in green chemistry is recognized, comprehensive studies on its life cycle analysis, long-term environmental impact, and potential alternatives are still lacking. This uncertainty can make it difficult for researchers and industry professionals to fully embrace perchloric acid as a sustainable option in their green chemistry initiatives.
Another major challenge is the environmental impact of perchloric acid production and disposal. The manufacturing process of perchloric acid often involves energy-intensive methods and the use of other hazardous chemicals, which can contribute to a significant carbon footprint. Additionally, the disposal of perchloric acid waste requires careful management to prevent contamination of soil and water resources, as perchlorate ions can persist in the environment and pose risks to human health and ecosystems.
The regulatory landscape surrounding perchloric acid usage presents further complications. Due to its potential use in explosive manufacturing, perchloric acid is subject to strict regulations and monitoring in many countries. These regulations can create barriers to research and industrial applications, requiring extensive documentation, permits, and compliance measures that may deter some organizations from utilizing this chemical.
Scalability issues also pose a significant challenge in the widespread adoption of perchloric acid in green chemistry practices. While perchloric acid may demonstrate promising results in laboratory-scale experiments, translating these benefits to industrial-scale processes can be problematic. The corrosive nature of perchloric acid necessitates specialized equipment and materials, which can be prohibitively expensive when scaled up to industrial levels.
Furthermore, the limited availability and high cost of high-purity perchloric acid can hinder its broader application in green chemistry. The production of perchloric acid with the required purity for certain applications can be technically challenging and resource-intensive, leading to supply chain issues and increased costs for end-users.
Lastly, there is a notable knowledge gap in understanding the long-term effects of perchloric acid usage in various chemical processes. While its potential in green chemistry is recognized, comprehensive studies on its life cycle analysis, long-term environmental impact, and potential alternatives are still lacking. This uncertainty can make it difficult for researchers and industry professionals to fully embrace perchloric acid as a sustainable option in their green chemistry initiatives.
Existing Green Alternatives to Perchloric Acid
01 Synthesis and production of perchloric acid
Methods for synthesizing and producing perchloric acid, including various chemical reactions and industrial processes. This may involve the use of specific catalysts, reactants, and equipment to ensure efficient and safe production of perchloric acid.- Synthesis and production of perchloric acid: Methods for synthesizing and producing perchloric acid, including various chemical reactions and industrial processes. This may involve the oxidation of chlorine compounds or the electrolysis of chlorate solutions under specific conditions to obtain high-purity perchloric acid.
- Applications in analytical chemistry: Use of perchloric acid in analytical chemistry, particularly for sample digestion, extraction, and as a reagent in various chemical analyses. Its strong oxidizing properties make it valuable for breaking down complex organic compounds and dissolving metal samples.
- Safety measures and handling precautions: Specialized equipment, storage methods, and handling procedures for safely working with perchloric acid due to its highly corrosive and potentially explosive nature. This includes the use of fume hoods, protective gear, and proper disposal techniques to minimize risks associated with its use.
- Use in battery technologies: Applications of perchloric acid in battery technologies, particularly in the development of high-performance lithium-ion batteries and other advanced energy storage systems. It may be used as an electrolyte component or in the preparation of electrode materials.
- Purification and concentration techniques: Methods for purifying and concentrating perchloric acid to obtain high-grade products suitable for various industrial and laboratory applications. This may involve distillation, membrane separation, or other advanced separation techniques to remove impurities and achieve desired concentrations.
02 Applications of perchloric acid in chemical analysis
Utilization of perchloric acid in various analytical techniques and procedures. This includes its use as a strong oxidizing agent in sample preparation, digestion of organic compounds, and as a component in analytical reagents for detecting and quantifying specific substances.Expand Specific Solutions03 Safety measures and handling of perchloric acid
Protocols and equipment designed for the safe handling, storage, and disposal of perchloric acid. This includes specialized fume hoods, personal protective equipment, and containment systems to minimize risks associated with its corrosive and potentially explosive nature.Expand Specific Solutions04 Perchloric acid in battery technology
Applications of perchloric acid in the development and improvement of battery technologies. This may involve its use as an electrolyte component or in the preparation of electrode materials to enhance battery performance and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Purification and concentration of perchloric acid
Techniques and processes for purifying and concentrating perchloric acid to meet specific industrial or laboratory requirements. This may include distillation, membrane separation, or other advanced purification methods to achieve high-purity perchloric acid.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Green Chemistry Industry
The field of green chemistry utilizing perchloric acid is in a nascent stage, with growing market potential driven by increasing environmental concerns. The global market for green chemistry is expanding, estimated to reach $100 billion by 2025. However, the technology's maturity varies across applications. Leading companies like Ecolab USA, Inc. and DuPont de Nemours, Inc. are investing in research and development to advance perchloric acid-based green chemistry practices. Academic institutions such as Zhejiang University and the Naval Research Laboratory are contributing to fundamental research, while companies like Kemira Oyj and Nalco Co. are focusing on industrial applications. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established chemical companies and emerging startups vying for market share in this promising field.
Ecolab USA, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ecolab has developed a green chemistry application utilizing perchloric acid in industrial cleaning processes. Their technology employs perchloric acid as a key component in formulating high-performance, environmentally friendly cleaning solutions for various industries[7]. The company's approach involves using perchloric acid in low concentrations, combined with biodegradable surfactants and chelating agents, to create cleaning products that are both effective and eco-friendly. Ecolab's formulations have been shown to reduce water consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional cleaning methods[8]. Furthermore, they have implemented a closed-loop system for the collection and treatment of spent cleaning solutions, allowing for the recovery and reuse of perchloric acid, thus minimizing waste generation[9].
Strengths: Reduced water consumption, effective cleaning performance, and minimized waste generation. Weaknesses: Potential corrosion issues with certain materials and the need for careful handling of perchloric acid-containing products.
Naval Research Laboratory
Technical Solution: The Naval Research Laboratory has conducted extensive research on the use of perchloric acid in green energetics and propellant formulations. Their approach focuses on developing high-energy materials with reduced environmental impact[10]. By utilizing perchloric acid as an oxidizer in novel propellant compositions, they have achieved improved combustion efficiency and reduced toxic emissions. The laboratory has also explored the use of stabilized perchloric acid solutions in the synthesis of energetic materials, which has led to safer manufacturing processes and reduced waste generation[11]. Additionally, their research has resulted in the development of new analytical techniques for trace perchlorate detection in environmental samples, contributing to improved monitoring and remediation efforts[12].
Strengths: Enhanced energy density of materials, reduced toxic emissions, and improved safety in manufacturing processes. Weaknesses: Challenges in large-scale implementation and potential regulatory hurdles for military applications.
Innovations in Perchloric Acid Handling and Disposal
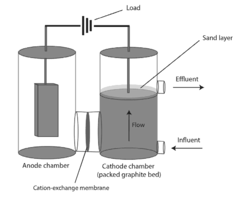
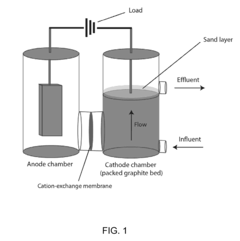
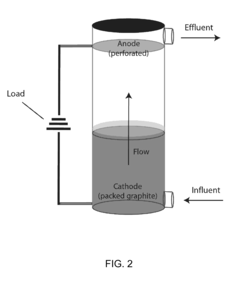
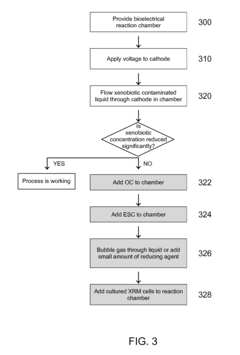
Bioelectrical treatment of xenobiotics
PatentInactiveUS20100108522A1
Innovation
- A bioelectrical reactor system that uses an electric current to provide electrons for microbial perchlorate reduction, eliminating the need for chemical electron donors and utilizing a cathode as an electron donor, thereby reducing biofouling and corrosion issues while maintaining long-term operation.
Perhydrolase providing improved specific activity
PatentWO2011119706A1
Innovation
- A library of variant enzymes with perhydrolytic activity is created by mutating the Thermotoga maritima acetyl xylan esterase, resulting in enzymes with increased specific activity for producing peroxycarboxylic acids, characterized by specific amino acid sequences such as SEQ ID NO: 10, which are used in combination with substrates and a source of peroxygen to produce peroxycarboxylic acids under suitable reaction conditions.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of perchloric acid in green chemistry practices reveals a complex interplay between its potential benefits and risks. Perchloric acid, a strong oxidizing agent, has found applications in various green chemistry processes due to its efficiency and selectivity. However, its use necessitates careful consideration of environmental consequences.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with perchloric acid is its potential for contamination of water sources. If not properly managed, perchlorate ions can persist in groundwater and surface water, posing risks to aquatic ecosystems and human health. Studies have shown that perchlorate can interfere with iodine uptake in the thyroid gland, potentially affecting hormonal balance in exposed organisms.
Despite these risks, the use of perchloric acid in green chemistry can lead to reduced overall environmental impact when compared to traditional chemical processes. Its high oxidizing power allows for more efficient reactions, often resulting in fewer byproducts and waste streams. This efficiency can translate to lower energy consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions associated with chemical manufacturing.
The environmental fate of perchloric acid and its derivatives is an important consideration. While perchlorate ions can be persistent in the environment, research has shown that certain microorganisms can biodegrade perchlorates under anaerobic conditions. This natural attenuation process offers potential for remediation strategies in contaminated sites.
In terms of air quality, the use of perchloric acid in green chemistry applications generally presents low risks of atmospheric pollution. Unlike some other strong acids, perchloric acid has a low vapor pressure, reducing the likelihood of significant air emissions during handling and use. However, proper ventilation and safety measures are still crucial to minimize any potential exposure.
The life cycle assessment of perchloric acid in green chemistry processes indicates that its environmental impact is heavily dependent on proper handling, storage, and disposal practices. When used in controlled laboratory or industrial settings with appropriate safety measures, the environmental risks can be significantly mitigated. However, accidental releases or improper disposal can lead to localized environmental contamination.
Efforts to develop greener alternatives to perchloric acid are ongoing, with researchers exploring less hazardous oxidizing agents that can match its efficiency. These alternatives aim to maintain the benefits of perchloric acid while further reducing environmental risks. As green chemistry practices continue to evolve, the role of perchloric acid may shift, potentially being replaced by safer options in certain applications while remaining valuable in others where its unique properties are essential.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with perchloric acid is its potential for contamination of water sources. If not properly managed, perchlorate ions can persist in groundwater and surface water, posing risks to aquatic ecosystems and human health. Studies have shown that perchlorate can interfere with iodine uptake in the thyroid gland, potentially affecting hormonal balance in exposed organisms.
Despite these risks, the use of perchloric acid in green chemistry can lead to reduced overall environmental impact when compared to traditional chemical processes. Its high oxidizing power allows for more efficient reactions, often resulting in fewer byproducts and waste streams. This efficiency can translate to lower energy consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions associated with chemical manufacturing.
The environmental fate of perchloric acid and its derivatives is an important consideration. While perchlorate ions can be persistent in the environment, research has shown that certain microorganisms can biodegrade perchlorates under anaerobic conditions. This natural attenuation process offers potential for remediation strategies in contaminated sites.
In terms of air quality, the use of perchloric acid in green chemistry applications generally presents low risks of atmospheric pollution. Unlike some other strong acids, perchloric acid has a low vapor pressure, reducing the likelihood of significant air emissions during handling and use. However, proper ventilation and safety measures are still crucial to minimize any potential exposure.
The life cycle assessment of perchloric acid in green chemistry processes indicates that its environmental impact is heavily dependent on proper handling, storage, and disposal practices. When used in controlled laboratory or industrial settings with appropriate safety measures, the environmental risks can be significantly mitigated. However, accidental releases or improper disposal can lead to localized environmental contamination.
Efforts to develop greener alternatives to perchloric acid are ongoing, with researchers exploring less hazardous oxidizing agents that can match its efficiency. These alternatives aim to maintain the benefits of perchloric acid while further reducing environmental risks. As green chemistry practices continue to evolve, the role of perchloric acid may shift, potentially being replaced by safer options in certain applications while remaining valuable in others where its unique properties are essential.
Safety Regulations and Compliance
The implementation of green chemistry practices involving perchloric acid necessitates strict adherence to safety regulations and compliance standards. Given the highly reactive and potentially hazardous nature of perchloric acid, regulatory bodies worldwide have established comprehensive guidelines to ensure its safe handling, storage, and use in laboratory and industrial settings.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set forth specific standards for perchloric acid use under the Hazardous Materials regulations. These guidelines mandate proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, and face shields. Additionally, OSHA requires the installation of specialized fume hoods equipped with wash-down systems to prevent the accumulation of explosive perchlorates.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the disposal of perchloric acid and its waste products under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). Proper neutralization and dilution procedures must be followed before disposal, and in many cases, perchloric acid waste must be treated as hazardous waste and disposed of accordingly.
Internationally, the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation classifies perchloric acid as a substance of very high concern (SVHC) due to its oxidizing properties. This classification imposes strict controls on its manufacture, import, and use within the EU, requiring extensive documentation and risk assessment procedures.
To ensure compliance with these regulations, organizations working with perchloric acid must implement robust safety management systems. This includes regular staff training on proper handling techniques, emergency response procedures, and the use of safety equipment. Detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs) must be developed and strictly followed for all processes involving perchloric acid.
Regular safety audits and inspections are crucial to maintaining compliance. These audits should assess the integrity of storage containers, the functionality of safety equipment, and the adherence to established protocols. Documentation of these audits, along with records of employee training and incident reports, is essential for regulatory compliance and potential inspections.
In the context of green chemistry, while perchloric acid can contribute to more efficient and selective chemical processes, its use must be carefully balanced against safety and environmental concerns. Researchers and industry professionals are encouraged to explore safer alternatives or develop methods to minimize the quantity of perchloric acid used in reactions, aligning with the principles of green chemistry while maintaining regulatory compliance.
As regulations continue to evolve, staying informed about updates and changes in safety standards is crucial. Organizations should maintain close relationships with regulatory bodies and industry associations to ensure ongoing compliance and to contribute to the development of best practices in the safe and sustainable use of perchloric acid in green chemistry applications.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set forth specific standards for perchloric acid use under the Hazardous Materials regulations. These guidelines mandate proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, and face shields. Additionally, OSHA requires the installation of specialized fume hoods equipped with wash-down systems to prevent the accumulation of explosive perchlorates.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the disposal of perchloric acid and its waste products under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). Proper neutralization and dilution procedures must be followed before disposal, and in many cases, perchloric acid waste must be treated as hazardous waste and disposed of accordingly.
Internationally, the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation classifies perchloric acid as a substance of very high concern (SVHC) due to its oxidizing properties. This classification imposes strict controls on its manufacture, import, and use within the EU, requiring extensive documentation and risk assessment procedures.
To ensure compliance with these regulations, organizations working with perchloric acid must implement robust safety management systems. This includes regular staff training on proper handling techniques, emergency response procedures, and the use of safety equipment. Detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs) must be developed and strictly followed for all processes involving perchloric acid.
Regular safety audits and inspections are crucial to maintaining compliance. These audits should assess the integrity of storage containers, the functionality of safety equipment, and the adherence to established protocols. Documentation of these audits, along with records of employee training and incident reports, is essential for regulatory compliance and potential inspections.
In the context of green chemistry, while perchloric acid can contribute to more efficient and selective chemical processes, its use must be carefully balanced against safety and environmental concerns. Researchers and industry professionals are encouraged to explore safer alternatives or develop methods to minimize the quantity of perchloric acid used in reactions, aligning with the principles of green chemistry while maintaining regulatory compliance.
As regulations continue to evolve, staying informed about updates and changes in safety standards is crucial. Organizations should maintain close relationships with regulatory bodies and industry associations to ensure ongoing compliance and to contribute to the development of best practices in the safe and sustainable use of perchloric acid in green chemistry applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!