The Role of V12 Engines in Historical Transportation Design
AUG 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V12 Engine Evolution
The V12 engine has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed for luxury automobiles and aircraft, the V12 configuration quickly became synonymous with power, smoothness, and prestige. The early V12 engines were characterized by their large displacement and relatively low rpm, focusing on torque production rather than high-end horsepower.
In the 1920s and 1930s, V12 engines found their way into high-end automobiles, with manufacturers like Packard, Cadillac, and Lincoln leading the charge in the United States. These engines were known for their smooth operation and impressive low-end torque, making them ideal for large luxury vehicles. Concurrently, European manufacturers such as Rolls-Royce and Hispano-Suiza were developing their own V12 designs, often incorporating more advanced technologies like overhead camshafts and aluminum construction.
The post-World War II era saw a shift in V12 engine development. As aircraft design moved towards jet propulsion, automotive applications became the primary focus for V12 engines. Ferrari, in particular, became closely associated with V12 engines, using them in their road and racing cars from the 1940s onwards. The Italian manufacturer's V12 designs evolved from relatively simple pushrod engines to sophisticated quad-cam units, setting new standards for performance and engineering excellence.
The 1960s and 1970s marked a period of significant advancement in V12 technology. Fuel injection systems began to replace carburetors, improving efficiency and power output. Jaguar's introduction of the XJ12 in 1972 brought V12 power to a wider audience, showcasing the engine's potential in a more accessible luxury sedan. Meanwhile, in motorsports, V12 engines were pushing the boundaries of performance, with Formula One cars of the era utilizing high-revving V12 powerplants.
As environmental concerns and fuel efficiency became more prominent in the late 20th century, V12 engines faced new challenges. Manufacturers responded by incorporating advanced technologies such as variable valve timing, direct injection, and lightweight materials. These innovations allowed V12 engines to maintain their performance credentials while improving fuel economy and emissions.
In recent years, the role of V12 engines has evolved further. While they continue to power some of the world's most exclusive supercars and luxury vehicles, the advent of hybrid and electric powertrains has led to new interpretations of the V12 concept. Some manufacturers have combined V12 engines with electric motors to create hybrid powertrains that offer both high performance and improved efficiency.
In the 1920s and 1930s, V12 engines found their way into high-end automobiles, with manufacturers like Packard, Cadillac, and Lincoln leading the charge in the United States. These engines were known for their smooth operation and impressive low-end torque, making them ideal for large luxury vehicles. Concurrently, European manufacturers such as Rolls-Royce and Hispano-Suiza were developing their own V12 designs, often incorporating more advanced technologies like overhead camshafts and aluminum construction.
The post-World War II era saw a shift in V12 engine development. As aircraft design moved towards jet propulsion, automotive applications became the primary focus for V12 engines. Ferrari, in particular, became closely associated with V12 engines, using them in their road and racing cars from the 1940s onwards. The Italian manufacturer's V12 designs evolved from relatively simple pushrod engines to sophisticated quad-cam units, setting new standards for performance and engineering excellence.
The 1960s and 1970s marked a period of significant advancement in V12 technology. Fuel injection systems began to replace carburetors, improving efficiency and power output. Jaguar's introduction of the XJ12 in 1972 brought V12 power to a wider audience, showcasing the engine's potential in a more accessible luxury sedan. Meanwhile, in motorsports, V12 engines were pushing the boundaries of performance, with Formula One cars of the era utilizing high-revving V12 powerplants.
As environmental concerns and fuel efficiency became more prominent in the late 20th century, V12 engines faced new challenges. Manufacturers responded by incorporating advanced technologies such as variable valve timing, direct injection, and lightweight materials. These innovations allowed V12 engines to maintain their performance credentials while improving fuel economy and emissions.
In recent years, the role of V12 engines has evolved further. While they continue to power some of the world's most exclusive supercars and luxury vehicles, the advent of hybrid and electric powertrains has led to new interpretations of the V12 concept. Some manufacturers have combined V12 engines with electric motors to create hybrid powertrains that offer both high performance and improved efficiency.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for V12 engines in historical transportation design has been driven by a combination of performance requirements, luxury positioning, and technological advancements. In the early 20th century, as automotive technology progressed, there was a growing need for more powerful and refined engines, particularly in high-end vehicles and racing applications. The V12 configuration emerged as a solution that could deliver smooth operation, high power output, and prestige.
In the luxury car segment, manufacturers recognized the appeal of V12 engines to discerning customers who sought the pinnacle of automotive engineering. Brands like Packard, Cadillac, and Lincoln introduced V12-powered models in the 1930s, catering to a niche market of wealthy enthusiasts. This trend continued in the post-war era, with European manufacturers such as Ferrari, Lamborghini, and Rolls-Royce adopting V12 engines to differentiate their premium offerings.
The aviation industry also played a significant role in driving demand for V12 engines. During World War II, high-performance aircraft required powerful and reliable powerplants, leading to the development of advanced V12 designs. This technology later found its way into civilian aviation and influenced automotive applications.
In the realm of motorsports, V12 engines became synonymous with ultimate performance. Formula One racing, in particular, saw extensive use of V12 power units from the 1960s through the 1990s. This racing pedigree further enhanced the desirability of V12 engines in road-going sports cars and supercars.
The market for V12 engines has historically been characterized by low volume but high value. While mass-market vehicles rarely featured V12 powerplants due to cost and complexity, the engines commanded premium prices in specialized applications. This exclusivity contributed to their status as a hallmark of engineering excellence and luxury.
However, the demand for V12 engines has fluctuated with changing economic conditions and environmental concerns. During periods of economic prosperity, there has been increased interest in high-performance and luxury vehicles, boosting V12 engine production. Conversely, economic downturns and stricter emissions regulations have periodically dampened demand.
In recent decades, the market for V12 engines has evolved. While they continue to be featured in ultra-luxury and high-performance vehicles, advancements in turbocharging and electrification technologies have provided alternatives that can deliver comparable power with improved efficiency. This has led to a gradual shift in market demand, with V12 engines increasingly becoming niche products valued for their heritage and emotional appeal rather than purely for their performance capabilities.
In the luxury car segment, manufacturers recognized the appeal of V12 engines to discerning customers who sought the pinnacle of automotive engineering. Brands like Packard, Cadillac, and Lincoln introduced V12-powered models in the 1930s, catering to a niche market of wealthy enthusiasts. This trend continued in the post-war era, with European manufacturers such as Ferrari, Lamborghini, and Rolls-Royce adopting V12 engines to differentiate their premium offerings.
The aviation industry also played a significant role in driving demand for V12 engines. During World War II, high-performance aircraft required powerful and reliable powerplants, leading to the development of advanced V12 designs. This technology later found its way into civilian aviation and influenced automotive applications.
In the realm of motorsports, V12 engines became synonymous with ultimate performance. Formula One racing, in particular, saw extensive use of V12 power units from the 1960s through the 1990s. This racing pedigree further enhanced the desirability of V12 engines in road-going sports cars and supercars.
The market for V12 engines has historically been characterized by low volume but high value. While mass-market vehicles rarely featured V12 powerplants due to cost and complexity, the engines commanded premium prices in specialized applications. This exclusivity contributed to their status as a hallmark of engineering excellence and luxury.
However, the demand for V12 engines has fluctuated with changing economic conditions and environmental concerns. During periods of economic prosperity, there has been increased interest in high-performance and luxury vehicles, boosting V12 engine production. Conversely, economic downturns and stricter emissions regulations have periodically dampened demand.
In recent decades, the market for V12 engines has evolved. While they continue to be featured in ultra-luxury and high-performance vehicles, advancements in turbocharging and electrification technologies have provided alternatives that can deliver comparable power with improved efficiency. This has led to a gradual shift in market demand, with V12 engines increasingly becoming niche products valued for their heritage and emotional appeal rather than purely for their performance capabilities.
Technical Challenges
The development of V12 engines in historical transportation design faced numerous technical challenges that required innovative solutions. One of the primary obstacles was the complexity of the engine design itself. With twelve cylinders arranged in a V-configuration, engineers had to overcome issues related to balance, vibration, and harmonics. The intricate nature of the V12 layout demanded precise engineering to ensure smooth operation and longevity.
Weight distribution posed another significant challenge. V12 engines were inherently heavy, which could negatively impact vehicle handling and performance. Engineers had to develop creative ways to integrate these large powerplants into vehicle chassis without compromising overall balance and drivability. This often required extensive redesigns of vehicle frames and suspension systems to accommodate the engine's size and weight.
Fuel efficiency was a persistent concern throughout the development of V12 engines. The large displacement and high cylinder count naturally led to increased fuel consumption. Engineers faced the challenge of optimizing combustion processes and reducing internal friction to improve efficiency without sacrificing the power output that made V12 engines desirable.
Cooling systems presented another hurdle for V12 engine designers. The increased heat generation from twelve cylinders required more advanced cooling solutions. Engineers had to develop larger radiators, more efficient water pumps, and improved coolant flow paths to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating.
Manufacturing complexity was a significant technical challenge in V12 engine production. The intricate design required precise machining and assembly processes, which were often costly and time-consuming. Engineers had to develop specialized tooling and manufacturing techniques to ensure consistent quality and reliability in production.
Emissions control became an increasingly important challenge as environmental regulations tightened. V12 engines, with their high fuel consumption and large exhaust output, required sophisticated emission control systems. Engineers had to integrate catalytic converters, exhaust gas recirculation systems, and advanced fuel injection technologies to meet evolving emissions standards.
Durability and reliability were ongoing concerns in V12 engine development. The increased number of moving parts and complex systems meant more potential points of failure. Engineers had to focus on materials science and lubrication technology to ensure that these engines could withstand the rigors of high-performance operation over extended periods.
As automotive technology progressed, the integration of electronic systems presented new challenges for V12 engine designers. Developing engine management systems capable of optimizing the performance of twelve cylinders required advanced sensors, processors, and software. Engineers had to balance the pursuit of power with the need for precise control and efficiency.
Weight distribution posed another significant challenge. V12 engines were inherently heavy, which could negatively impact vehicle handling and performance. Engineers had to develop creative ways to integrate these large powerplants into vehicle chassis without compromising overall balance and drivability. This often required extensive redesigns of vehicle frames and suspension systems to accommodate the engine's size and weight.
Fuel efficiency was a persistent concern throughout the development of V12 engines. The large displacement and high cylinder count naturally led to increased fuel consumption. Engineers faced the challenge of optimizing combustion processes and reducing internal friction to improve efficiency without sacrificing the power output that made V12 engines desirable.
Cooling systems presented another hurdle for V12 engine designers. The increased heat generation from twelve cylinders required more advanced cooling solutions. Engineers had to develop larger radiators, more efficient water pumps, and improved coolant flow paths to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating.
Manufacturing complexity was a significant technical challenge in V12 engine production. The intricate design required precise machining and assembly processes, which were often costly and time-consuming. Engineers had to develop specialized tooling and manufacturing techniques to ensure consistent quality and reliability in production.
Emissions control became an increasingly important challenge as environmental regulations tightened. V12 engines, with their high fuel consumption and large exhaust output, required sophisticated emission control systems. Engineers had to integrate catalytic converters, exhaust gas recirculation systems, and advanced fuel injection technologies to meet evolving emissions standards.
Durability and reliability were ongoing concerns in V12 engine development. The increased number of moving parts and complex systems meant more potential points of failure. Engineers had to focus on materials science and lubrication technology to ensure that these engines could withstand the rigors of high-performance operation over extended periods.
As automotive technology progressed, the integration of electronic systems presented new challenges for V12 engine designers. Developing engine management systems capable of optimizing the performance of twelve cylinders required advanced sensors, processors, and software. Engineers had to balance the pursuit of power with the need for precise control and efficiency.
Current V12 Solutions
01 V12 Engine Design and Configuration
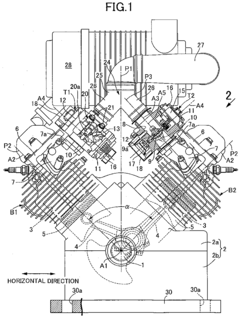
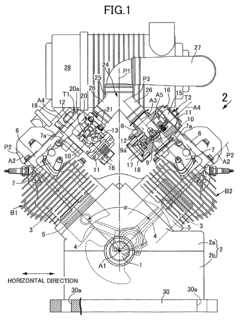
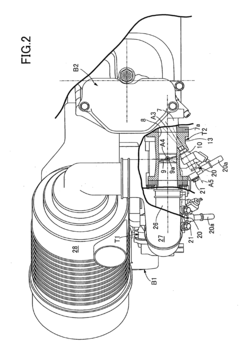
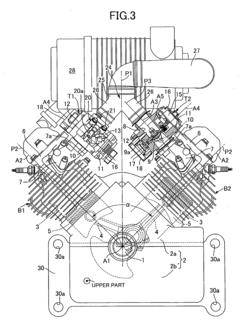
V12 engines are characterized by their unique configuration of twelve cylinders arranged in two banks of six, forming a V shape. This design offers a balance of power, smoothness, and compact packaging, making it popular in high-performance and luxury vehicles. The V12 layout allows for excellent power output and torque characteristics while maintaining a relatively compact overall size.- V12 Engine Design and Configuration: V12 engines are typically designed with two banks of six cylinders arranged in a V-shape. This configuration allows for a compact engine design while providing high power output and smooth operation. The V12 layout is often used in high-performance and luxury vehicles due to its balance of power and refinement.
- Engine Control Systems for V12 Engines: Advanced control systems are crucial for optimizing the performance and efficiency of V12 engines. These systems may include electronic fuel injection, variable valve timing, and sophisticated engine management computers to regulate various parameters such as fuel mixture, ignition timing, and emissions control.
- Fuel Efficiency Improvements in V12 Engines: Despite their high power output, modern V12 engines incorporate various technologies to improve fuel efficiency. These may include direct fuel injection, cylinder deactivation, and advanced materials to reduce weight and friction, allowing for better fuel economy without sacrificing performance.
- Historical Development of V12 Engines: The development of V12 engines has a rich history dating back to the early 20th century. Early designs were often used in luxury automobiles and aircraft. Over time, V12 engines have evolved with advancements in materials, manufacturing techniques, and engineering principles to improve power, reliability, and efficiency.
- Applications of V12 Engines: V12 engines find applications in various fields beyond automotive use. They are employed in marine vessels, military vehicles, and even in some industrial applications where high power and torque are required. The versatility of V12 engines makes them suitable for a wide range of high-performance applications.
02 Performance Optimization in V12 Engines
Various techniques are employed to optimize the performance of V12 engines, including advanced fuel injection systems, variable valve timing, and turbocharging. These technologies help improve power output, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. Engine management systems play a crucial role in coordinating these features to achieve optimal performance across different operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Manufacturing and Assembly Processes for V12 Engines
The production of V12 engines involves specialized manufacturing and assembly processes due to their complexity. Advanced machining techniques, precision assembly methods, and quality control measures are essential to ensure the reliability and performance of these high-end engines. Innovations in manufacturing processes focus on improving efficiency, reducing costs, and maintaining high quality standards.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cooling and Lubrication Systems in V12 Engines
Effective cooling and lubrication are critical for the proper functioning and longevity of V12 engines. Advanced cooling systems, including precision-engineered water jackets and oil coolers, help manage the high heat output. Sophisticated lubrication systems ensure proper oil distribution to all moving parts, reducing wear and enhancing engine life. These systems are often designed to handle the high-performance demands of V12 engines.Expand Specific Solutions05 Historical Development and Evolution of V12 Engines
The V12 engine has a rich history dating back to the early 20th century. Its development has been marked by continuous improvements in materials, design, and technology. From early aviation applications to modern luxury cars, the V12 engine has evolved to meet changing performance, efficiency, and emissions requirements while maintaining its status as a symbol of automotive excellence.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers
The V12 engine market in historical transportation design is in a mature phase, characterized by limited but stable demand. The market size remains relatively small, catering to luxury and high-performance vehicles. Technologically, V12 engines have reached a high level of sophistication, with companies like Honda Motor Co., Ltd., Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd., and GM Global Technology Operations LLC leading innovation. These firms have refined V12 designs for optimal power, efficiency, and reliability. However, the industry faces challenges from emerging technologies and environmental regulations, prompting manufacturers to explore hybrid and electric alternatives while maintaining V12 offerings for niche markets.
Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honda, while not primarily known for V12 engines, has made significant contributions to engine technology that influence V12 design principles. Their approach to engine development focuses on efficiency, reliability, and performance. Honda's VTEC (Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control) technology, originally developed for smaller engines, has concepts applicable to V12 designs. In the context of V12 engines, Honda's expertise in high-revving engines and precise engineering could theoretically be applied to create a compact, efficient V12. While Honda hasn't produced a V12 for road cars, their experience in Formula 1 racing with V12 engines in the 1990s demonstrated their capability in high-performance engine design[7][8]. Honda's potential approach to V12 engines would likely emphasize lightweight construction, advanced materials, and innovative valve control systems.
Strengths: Potential for high-revving, efficient V12 designs leveraging Honda's engineering expertise. Weaknesses: Lack of recent experience in V12 production and limited market demand for such engines in Honda's typical vehicle segments.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM has a rich history in V12 engine development, particularly for luxury brands like Cadillac. Their V12 engines, such as the Cadillac V12 from the 1930s, were known for their smooth operation and high power output. GM's approach to V12 design focused on balancing performance with refinement, utilizing advanced materials and precision engineering techniques. In modern times, GM has shifted focus to more fuel-efficient options, but their historical V12 designs remain significant in automotive engineering history[1][3]. GM's V12 engines often featured innovative cooling systems and valve arrangements to maximize efficiency and power delivery.
Strengths: Smooth operation, high power output, and prestigious image. Weaknesses: High fuel consumption, complex maintenance, and limited practicality for mass-market vehicles.
Core V12 Innovations
General-purpose V-type engine
PatentInactiveEP2141345A1
Innovation
- The engine design features throttle bodies with butterfly-type throttle valves and fuel injection valves positioned such that their axes are orthogonal to the intake path and parallel to the engine banks, allowing condensation to drain and fuel to flow downward, preventing freezing and clogging, respectively, regardless of engine orientation. This design also allows for compatible and easily maintainable throttle bodies with fuel injection valves facing the same outer surface.
V-type internal combustion engine and vehicle with a transversely placed V-type internal combustion engine
PatentInactiveEP1148219A3
Innovation
- The engine design incorporates a staggered cylinder bank configuration with accessory drives positioned on the rear side, allowing for a greater number of cylinders and a compact assembly, while the induction system is optimized with a single plenum chamber over the right cylinder bank to maintain a low hood line.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of V12 engines in historical transportation design has been significant and multifaceted. These powerful engines, known for their smooth operation and high performance, have left a considerable ecological footprint throughout their use in various vehicles.
V12 engines, due to their large displacement and high cylinder count, typically consume substantial amounts of fuel. This increased fuel consumption has directly contributed to higher carbon dioxide emissions, a primary greenhouse gas responsible for climate change. The transportation sector, particularly vehicles equipped with V12 engines, has been a major contributor to global CO2 emissions over the past century.
Air pollution has been another critical environmental concern associated with V12 engines. These engines produce significant amounts of nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter, and other harmful pollutants. In urban areas, where luxury vehicles and high-performance cars often featuring V12 engines are more prevalent, this has led to decreased air quality and associated health risks for local populations.
The manufacturing process of V12 engines also carries environmental implications. The production of these complex powerplants requires more raw materials and energy compared to smaller engines, resulting in increased resource consumption and industrial emissions. Additionally, the specialized materials often used in high-performance V12 engines, such as rare metals for catalytic converters, can have environmental impacts related to mining and processing.
Noise pollution is another environmental factor to consider. While V12 engines are often praised for their smooth operation, they can still produce significant noise levels, especially in high-performance applications. This has led to concerns about noise pollution in both urban and natural environments, potentially affecting wildlife and human well-being.
The longevity and durability of V12 engines have had mixed environmental effects. On one hand, their robust construction has meant that many V12-powered vehicles have remained in service for extended periods, reducing the need for replacement and the associated environmental costs of manufacturing new vehicles. On the other hand, this longevity has also meant that older, less environmentally friendly V12 engines have remained in use longer than they might have otherwise.
As environmental awareness has grown, the automotive industry has been forced to address the ecological impact of V12 engines. This has led to technological advancements aimed at improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions, such as the development of more efficient fuel injection systems, improved engine management technologies, and the integration of hybrid systems in some V12-powered vehicles.
V12 engines, due to their large displacement and high cylinder count, typically consume substantial amounts of fuel. This increased fuel consumption has directly contributed to higher carbon dioxide emissions, a primary greenhouse gas responsible for climate change. The transportation sector, particularly vehicles equipped with V12 engines, has been a major contributor to global CO2 emissions over the past century.
Air pollution has been another critical environmental concern associated with V12 engines. These engines produce significant amounts of nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter, and other harmful pollutants. In urban areas, where luxury vehicles and high-performance cars often featuring V12 engines are more prevalent, this has led to decreased air quality and associated health risks for local populations.
The manufacturing process of V12 engines also carries environmental implications. The production of these complex powerplants requires more raw materials and energy compared to smaller engines, resulting in increased resource consumption and industrial emissions. Additionally, the specialized materials often used in high-performance V12 engines, such as rare metals for catalytic converters, can have environmental impacts related to mining and processing.
Noise pollution is another environmental factor to consider. While V12 engines are often praised for their smooth operation, they can still produce significant noise levels, especially in high-performance applications. This has led to concerns about noise pollution in both urban and natural environments, potentially affecting wildlife and human well-being.
The longevity and durability of V12 engines have had mixed environmental effects. On one hand, their robust construction has meant that many V12-powered vehicles have remained in service for extended periods, reducing the need for replacement and the associated environmental costs of manufacturing new vehicles. On the other hand, this longevity has also meant that older, less environmentally friendly V12 engines have remained in use longer than they might have otherwise.
As environmental awareness has grown, the automotive industry has been forced to address the ecological impact of V12 engines. This has led to technological advancements aimed at improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions, such as the development of more efficient fuel injection systems, improved engine management technologies, and the integration of hybrid systems in some V12-powered vehicles.
Luxury Vehicle Trends
The luxury vehicle market has witnessed significant shifts in recent years, with V12 engines playing a crucial role in shaping historical transportation design and influencing current trends. As consumer preferences evolve and environmental concerns gain prominence, luxury automakers are adapting their strategies to maintain relevance in a changing landscape.
Traditionally, V12 engines have been synonymous with prestige, power, and exclusivity in the luxury automotive sector. These powerplants, with their smooth operation and impressive performance, have long been the hallmark of high-end vehicles from manufacturers such as Rolls-Royce, Bentley, and Ferrari. The legacy of V12 engines in historical transportation design has set a benchmark for luxury and performance that continues to influence modern vehicle development.
However, the luxury vehicle market is experiencing a paradigm shift driven by several factors. Increasing environmental awareness and stringent emissions regulations are pushing manufacturers to explore alternative powertrains. As a result, many luxury brands are investing heavily in electrification technologies, with some committing to fully electric lineups in the near future.
Despite this trend towards electrification, there remains a segment of the market that values the heritage and emotional appeal of traditional combustion engines, particularly V12s. This has led to a dichotomy in luxury vehicle offerings, with brands striving to balance innovation with tradition.
Another notable trend is the growing emphasis on technology and connectivity in luxury vehicles. Advanced driver assistance systems, autonomous driving capabilities, and seamless integration with personal devices are becoming standard features in high-end automobiles. This shift reflects changing consumer expectations, where luxury is increasingly defined by technological sophistication as much as by traditional markers of opulence.
The concept of luxury itself is evolving, with a growing focus on sustainability and ethical consumption. This has led to the emergence of eco-luxury vehicles, which combine premium features with environmentally friendly technologies. Some manufacturers are exploring sustainable materials and production processes to appeal to environmentally conscious luxury consumers.
In response to changing urban landscapes and mobility patterns, luxury automakers are also diversifying their product portfolios. There is a growing trend towards luxury SUVs and crossovers, catering to consumers who desire both practicality and prestige. This shift has even led traditionally sports car-focused brands to enter the SUV market, reflecting the changing dynamics of luxury vehicle preferences.
Traditionally, V12 engines have been synonymous with prestige, power, and exclusivity in the luxury automotive sector. These powerplants, with their smooth operation and impressive performance, have long been the hallmark of high-end vehicles from manufacturers such as Rolls-Royce, Bentley, and Ferrari. The legacy of V12 engines in historical transportation design has set a benchmark for luxury and performance that continues to influence modern vehicle development.
However, the luxury vehicle market is experiencing a paradigm shift driven by several factors. Increasing environmental awareness and stringent emissions regulations are pushing manufacturers to explore alternative powertrains. As a result, many luxury brands are investing heavily in electrification technologies, with some committing to fully electric lineups in the near future.
Despite this trend towards electrification, there remains a segment of the market that values the heritage and emotional appeal of traditional combustion engines, particularly V12s. This has led to a dichotomy in luxury vehicle offerings, with brands striving to balance innovation with tradition.
Another notable trend is the growing emphasis on technology and connectivity in luxury vehicles. Advanced driver assistance systems, autonomous driving capabilities, and seamless integration with personal devices are becoming standard features in high-end automobiles. This shift reflects changing consumer expectations, where luxury is increasingly defined by technological sophistication as much as by traditional markers of opulence.
The concept of luxury itself is evolving, with a growing focus on sustainability and ethical consumption. This has led to the emergence of eco-luxury vehicles, which combine premium features with environmentally friendly technologies. Some manufacturers are exploring sustainable materials and production processes to appeal to environmentally conscious luxury consumers.
In response to changing urban landscapes and mobility patterns, luxury automakers are also diversifying their product portfolios. There is a growing trend towards luxury SUVs and crossovers, catering to consumers who desire both practicality and prestige. This shift has even led traditionally sports car-focused brands to enter the SUV market, reflecting the changing dynamics of luxury vehicle preferences.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!