What are the Regulations Governing Muriatic Acid Transport?
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muriatic Acid Regulations Overview
Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, is a highly corrosive substance widely used in various industries. Due to its hazardous nature, the transport of muriatic acid is subject to strict regulations to ensure safety and environmental protection. These regulations are primarily governed by national and international bodies responsible for the transportation of dangerous goods.
In the United States, the Department of Transportation (DOT) oversees the regulations for transporting muriatic acid. The DOT classifies muriatic acid as a Class 8 corrosive material, which requires specific packaging, labeling, and handling procedures. The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 49 provides detailed guidelines for the transportation of hazardous materials, including muriatic acid.
Internationally, the transport of muriatic acid is regulated by the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, which serves as a model for national and regional regulations. These recommendations are implemented through various modal regulations, such as the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code for sea transport and the International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations for air transport.
Key aspects of muriatic acid transport regulations include proper packaging requirements, which typically involve using corrosion-resistant containers with appropriate closures and venting mechanisms. Labeling and placarding of containers and vehicles are mandatory, with specific symbols and hazard information clearly displayed. Documentation requirements, including shipping papers and safety data sheets, must be meticulously followed to ensure compliance and facilitate emergency response.
Training and certification of personnel involved in the handling and transport of muriatic acid are crucial components of the regulatory framework. Drivers, packers, and other workers must receive specialized training on the properties of muriatic acid, emergency procedures, and proper handling techniques. Regular inspections and audits are conducted to ensure compliance with these regulations.
Storage and segregation requirements during transport are also strictly regulated. Muriatic acid must be kept separate from incompatible materials that could react dangerously if mixed. Temperature control and ventilation are important considerations, especially during long-distance transport or in extreme weather conditions.
Emergency response planning is a critical aspect of muriatic acid transport regulations. Carriers and shippers must have detailed procedures in place for handling spills, leaks, or accidents involving muriatic acid. This includes providing appropriate personal protective equipment, containment materials, and communication protocols for notifying authorities and coordinating response efforts.
Environmental protection measures are integral to muriatic acid transport regulations. Strict guidelines are in place to prevent releases into the environment, with requirements for spill containment, neutralization procedures, and proper disposal of contaminated materials. These measures aim to minimize the potential ecological impact of muriatic acid during transportation.
In the United States, the Department of Transportation (DOT) oversees the regulations for transporting muriatic acid. The DOT classifies muriatic acid as a Class 8 corrosive material, which requires specific packaging, labeling, and handling procedures. The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 49 provides detailed guidelines for the transportation of hazardous materials, including muriatic acid.
Internationally, the transport of muriatic acid is regulated by the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, which serves as a model for national and regional regulations. These recommendations are implemented through various modal regulations, such as the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code for sea transport and the International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations for air transport.
Key aspects of muriatic acid transport regulations include proper packaging requirements, which typically involve using corrosion-resistant containers with appropriate closures and venting mechanisms. Labeling and placarding of containers and vehicles are mandatory, with specific symbols and hazard information clearly displayed. Documentation requirements, including shipping papers and safety data sheets, must be meticulously followed to ensure compliance and facilitate emergency response.
Training and certification of personnel involved in the handling and transport of muriatic acid are crucial components of the regulatory framework. Drivers, packers, and other workers must receive specialized training on the properties of muriatic acid, emergency procedures, and proper handling techniques. Regular inspections and audits are conducted to ensure compliance with these regulations.
Storage and segregation requirements during transport are also strictly regulated. Muriatic acid must be kept separate from incompatible materials that could react dangerously if mixed. Temperature control and ventilation are important considerations, especially during long-distance transport or in extreme weather conditions.
Emergency response planning is a critical aspect of muriatic acid transport regulations. Carriers and shippers must have detailed procedures in place for handling spills, leaks, or accidents involving muriatic acid. This includes providing appropriate personal protective equipment, containment materials, and communication protocols for notifying authorities and coordinating response efforts.
Environmental protection measures are integral to muriatic acid transport regulations. Strict guidelines are in place to prevent releases into the environment, with requirements for spill containment, neutralization procedures, and proper disposal of contaminated materials. These measures aim to minimize the potential ecological impact of muriatic acid during transportation.
Market Analysis for Acid Transport
The market for muriatic acid transport is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand from various industries such as chemical manufacturing, metal processing, and water treatment. The global market size for hydrochloric acid, of which muriatic acid is a form, is projected to reach significant volumes in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the expanding industrial applications and the rising need for water treatment solutions worldwide.
Key factors influencing the market include stringent environmental regulations, safety concerns, and the need for efficient transportation methods. The transportation of muriatic acid requires specialized equipment and handling procedures due to its corrosive nature. This has led to the development of advanced containment systems and transport vehicles designed specifically for hazardous chemicals.
The market is segmented based on end-use industries, with the chemical sector being the largest consumer. Other significant sectors include steel pickling, oil well acidizing, and food processing. Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market due to rapid industrialization in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets and stringent regulatory frameworks.
The competitive landscape of the muriatic acid transport market is characterized by the presence of both large multinational corporations and regional players. Major chemical companies often have their own transportation divisions or partnerships with specialized logistics providers. The market also sees the participation of third-party logistics companies that have expertise in handling hazardous materials.
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in shaping the market. Innovations in corrosion-resistant materials, smart sensors for real-time monitoring, and improved safety systems are enhancing the efficiency and safety of muriatic acid transport. These advancements are not only improving operational efficiency but also helping companies comply with increasingly strict regulations.
The market faces challenges such as the high cost of specialized transport equipment and the complexity of regulatory compliance across different regions. However, these challenges also present opportunities for companies that can provide innovative solutions and comprehensive services in the acid transport sector.
Looking ahead, the market for muriatic acid transport is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as increasing industrial activities in emerging economies, growing emphasis on water treatment, and ongoing technological advancements will drive this growth. Additionally, the focus on sustainable practices and circular economy principles may lead to new opportunities in the recycling and reuse of muriatic acid, potentially impacting transport patterns and market dynamics.
Key factors influencing the market include stringent environmental regulations, safety concerns, and the need for efficient transportation methods. The transportation of muriatic acid requires specialized equipment and handling procedures due to its corrosive nature. This has led to the development of advanced containment systems and transport vehicles designed specifically for hazardous chemicals.
The market is segmented based on end-use industries, with the chemical sector being the largest consumer. Other significant sectors include steel pickling, oil well acidizing, and food processing. Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market due to rapid industrialization in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets and stringent regulatory frameworks.
The competitive landscape of the muriatic acid transport market is characterized by the presence of both large multinational corporations and regional players. Major chemical companies often have their own transportation divisions or partnerships with specialized logistics providers. The market also sees the participation of third-party logistics companies that have expertise in handling hazardous materials.
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in shaping the market. Innovations in corrosion-resistant materials, smart sensors for real-time monitoring, and improved safety systems are enhancing the efficiency and safety of muriatic acid transport. These advancements are not only improving operational efficiency but also helping companies comply with increasingly strict regulations.
The market faces challenges such as the high cost of specialized transport equipment and the complexity of regulatory compliance across different regions. However, these challenges also present opportunities for companies that can provide innovative solutions and comprehensive services in the acid transport sector.
Looking ahead, the market for muriatic acid transport is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as increasing industrial activities in emerging economies, growing emphasis on water treatment, and ongoing technological advancements will drive this growth. Additionally, the focus on sustainable practices and circular economy principles may lead to new opportunities in the recycling and reuse of muriatic acid, potentially impacting transport patterns and market dynamics.
Current Challenges in Acid Transportation
The transportation of muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, presents several significant challenges due to its corrosive and hazardous nature. One of the primary concerns is the risk of leaks or spills during transit, which can pose severe threats to human health, the environment, and infrastructure. The highly corrosive properties of muriatic acid require specialized containment and handling procedures to prevent accidents and ensure safe transport.
Regulatory compliance remains a complex challenge for acid transporters. Different countries and regions have varying regulations governing the transportation of hazardous materials, including muriatic acid. Navigating these diverse regulatory landscapes requires extensive knowledge and careful planning to ensure compliance across jurisdictions. This complexity is further compounded by frequent updates to regulations, necessitating constant vigilance and adaptation from transportation companies.
The selection of appropriate transportation containers and equipment poses another significant challenge. Containers must be resistant to corrosion and capable of withstanding the acid's aggressive nature. Regular inspection and maintenance of these containers are crucial to prevent degradation and potential failures during transport. Additionally, the loading and unloading processes require specialized equipment and trained personnel to minimize the risk of accidents and exposure.
Emergency response preparedness is a critical aspect of acid transportation that presents ongoing challenges. Transport companies must develop and maintain comprehensive emergency response plans, including procedures for containment, neutralization, and cleanup in case of spills or leaks. Ensuring that all personnel involved in the transportation chain are adequately trained in these procedures and equipped to handle emergencies is a continuous challenge.
The environmental impact of muriatic acid transportation is an increasing concern. Stringent regulations aim to minimize the potential for environmental contamination, requiring transporters to implement robust safeguards and monitoring systems. This includes not only preventing spills but also managing emissions and ensuring proper disposal of any waste generated during the transportation process.
Lastly, the cost implications of meeting these various challenges are significant. Investing in specialized equipment, training programs, safety measures, and compliance efforts can be substantial, impacting the economic viability of acid transportation operations. Balancing these costs with the need for safety and regulatory compliance remains an ongoing challenge for companies in this sector.
Regulatory compliance remains a complex challenge for acid transporters. Different countries and regions have varying regulations governing the transportation of hazardous materials, including muriatic acid. Navigating these diverse regulatory landscapes requires extensive knowledge and careful planning to ensure compliance across jurisdictions. This complexity is further compounded by frequent updates to regulations, necessitating constant vigilance and adaptation from transportation companies.
The selection of appropriate transportation containers and equipment poses another significant challenge. Containers must be resistant to corrosion and capable of withstanding the acid's aggressive nature. Regular inspection and maintenance of these containers are crucial to prevent degradation and potential failures during transport. Additionally, the loading and unloading processes require specialized equipment and trained personnel to minimize the risk of accidents and exposure.
Emergency response preparedness is a critical aspect of acid transportation that presents ongoing challenges. Transport companies must develop and maintain comprehensive emergency response plans, including procedures for containment, neutralization, and cleanup in case of spills or leaks. Ensuring that all personnel involved in the transportation chain are adequately trained in these procedures and equipped to handle emergencies is a continuous challenge.
The environmental impact of muriatic acid transportation is an increasing concern. Stringent regulations aim to minimize the potential for environmental contamination, requiring transporters to implement robust safeguards and monitoring systems. This includes not only preventing spills but also managing emissions and ensuring proper disposal of any waste generated during the transportation process.
Lastly, the cost implications of meeting these various challenges are significant. Investing in specialized equipment, training programs, safety measures, and compliance efforts can be substantial, impacting the economic viability of acid transportation operations. Balancing these costs with the need for safety and regulatory compliance remains an ongoing challenge for companies in this sector.
Existing Compliance Solutions
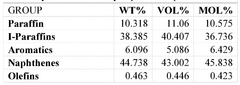
01 Industrial applications of muriatic acid
Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, has various industrial applications. It is used in metal cleaning and pickling processes, particularly in the steel industry. The acid is also employed in the production of chemicals, water treatment, and as a pH regulator in various industrial processes.- Industrial applications of muriatic acid: Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, has various industrial applications. It is used in metal cleaning and pickling processes, particularly in the steel industry. The acid is also employed in the production of chemicals, water treatment, and as a pH regulator in various industrial processes.
- Cleaning and etching applications: Muriatic acid is widely used for cleaning and etching purposes. It is effective in removing rust, scale, and other deposits from metal surfaces. In the construction industry, it is used for cleaning masonry and concrete surfaces. The acid is also utilized in pool maintenance to adjust pH levels and remove stains.
- Production and handling of muriatic acid: The production of muriatic acid involves various processes, including the reaction of hydrogen and chlorine gases. Specialized equipment and safety measures are required for its production, storage, and handling due to its corrosive nature. Innovations in production methods focus on improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Due to its corrosive nature, the use of muriatic acid requires strict safety protocols and environmental considerations. This includes proper storage, handling, and disposal methods to prevent accidents and environmental contamination. Innovations in this area focus on developing safer formulations and improved containment systems.
- Alternative applications and formulations: Research is ongoing to develop alternative applications and formulations of muriatic acid. This includes its use in specialized chemical processes, as a catalyst in certain reactions, and in the development of new materials. Some innovations focus on creating less hazardous alternatives or modifying the acid for specific industrial applications.
02 Cleaning and etching applications
Muriatic acid is widely used in cleaning and etching applications. It is effective in removing rust, scale, and other deposits from metal surfaces. In the construction industry, it is used for cleaning masonry and concrete surfaces. The acid is also utilized in pool maintenance to adjust pH levels and remove stains.Expand Specific Solutions03 Production and handling of muriatic acid
The production and handling of muriatic acid involve specific processes and safety measures. This includes methods for manufacturing high-purity hydrochloric acid, storage and transportation techniques, and the development of corrosion-resistant materials for handling the acid. Safety protocols and equipment for handling muriatic acid are also crucial in industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and waste management
Muriatic acid plays a role in environmental and waste management processes. It is used in the treatment of industrial wastewater and in the neutralization of alkaline waste. The acid is also employed in air pollution control systems and in the remediation of contaminated soils. Proper disposal and recycling methods for muriatic acid are important for environmental protection.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovations in muriatic acid formulations
Recent innovations have led to the development of improved muriatic acid formulations. These include the creation of low-fuming and inhibited muriatic acid products, which reduce corrosive effects and improve safety. New formulations also focus on enhancing the acid's effectiveness in specific applications, such as scale removal in industrial equipment or as a component in specialty chemical products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Stakeholders in Acid Transport Industry
The regulations governing muriatic acid transport are part of a complex competitive landscape influenced by industry maturity, market size, and technological advancements. The chemical transportation sector is well-established, with stringent safety protocols and environmental regulations shaping the market. Companies like Dow Global Technologies LLC, Marathon Petroleum Co. LP, and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. play significant roles in this space, leveraging their extensive experience and technological capabilities. The market size for hazardous material transport, including muriatic acid, is substantial and growing, driven by industrial demand. Technological advancements in containment, monitoring, and safety systems are continually evolving, with firms like Hitachi Ltd. and SAP SE contributing to innovations in logistics and supply chain management for dangerous goods.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies LLC has developed advanced containment and transportation systems for muriatic acid. Their technology includes corrosion-resistant linings for tank trucks and rail cars, as well as specialized valves and fittings designed to prevent leaks during transport. They have implemented a real-time monitoring system that tracks temperature, pressure, and pH levels of the acid during transit, ensuring compliance with regulations[1]. Dow's approach also incorporates safety features such as double-walled containers and spill containment systems to mitigate risks associated with accidents or equipment failure[2].
Strengths: Comprehensive safety features, real-time monitoring capabilities, and expertise in chemical handling. Weaknesses: Potentially higher costs associated with advanced technology implementation.
Marathon Petroleum Co. LP
Technical Solution: Marathon Petroleum Co. LP has implemented a multi-faceted approach to muriatic acid transport regulations. They utilize specialized corrosion-resistant tanker trucks and rail cars equipped with safety relief valves and rupture discs to prevent over-pressurization[3]. Their transport vehicles are fitted with GPS tracking systems and telemetry devices that provide real-time data on location, temperature, and pressure. Marathon has also developed a proprietary training program for drivers and handlers, focusing on emergency response procedures and proper handling techniques[4]. Additionally, they have implemented a rigorous maintenance and inspection schedule for all transport equipment to ensure compliance with DOT regulations.
Strengths: Comprehensive safety measures, advanced tracking systems, and well-trained personnel. Weaknesses: Potential for higher operational costs due to extensive safety measures.
Critical Safety Protocols and Standards
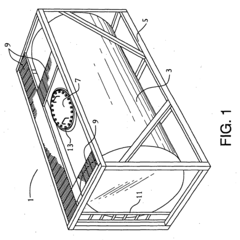
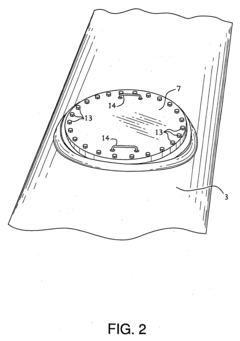
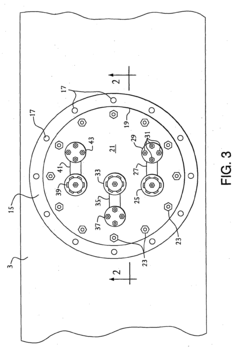
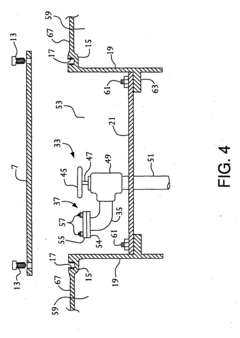
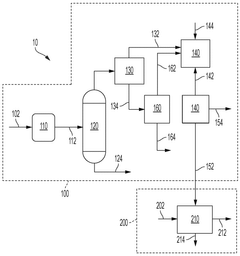
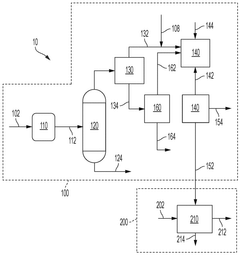
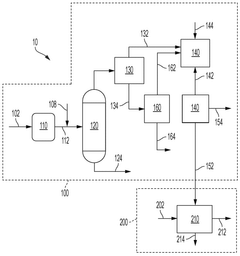
Tank comprising a valve-box
PatentInactiveEP1522786A2
Innovation
- A modular transportation and storage system featuring a cylindrical tank with a valve box and purge valve, sealed to isolate the product from the atmosphere, and a rigid framework for standard shipping methods, along with temperature and pressure monitoring to ensure product integrity and purity.
Methods for producing liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHC)
PatentWO2025128506A1
Innovation
- The production of Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers (LOHCs) through hydrogenation and dehydrogenation cycles, where hydrocarbon streams are processed in a series of reactors and separation units to generate LOHCs, which can store hydrogen in a high-density liquid form.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The transportation of muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, poses significant environmental risks that require careful assessment and mitigation strategies. The potential impacts on air, water, and soil quality must be thoroughly evaluated to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and minimize ecological damage.
Atmospheric emissions during transport are a primary concern. Muriatic acid vapors can contribute to air pollution and pose respiratory hazards to both humans and wildlife. Proper containment and ventilation systems are essential to prevent the release of acid fumes into the environment. Additionally, the potential for acid rain formation due to atmospheric reactions with released vapors must be considered in long-term environmental impact assessments.
Water contamination risks are particularly critical when transporting muriatic acid. Accidental spills or leaks can have severe consequences for aquatic ecosystems, potentially altering pH levels and causing widespread damage to flora and fauna. Groundwater contamination is another significant risk, as muriatic acid can percolate through soil layers and affect underground water sources. Comprehensive spill prevention and response plans are crucial to mitigate these risks and protect water resources.
Soil contamination is another environmental concern associated with muriatic acid transport. Acid spills can lead to soil acidification, impacting soil fertility and microbial communities. This, in turn, can affect plant growth and ecosystem stability in affected areas. Long-term monitoring of soil quality in transport corridors and storage facilities is necessary to detect and address any persistent contamination issues.
The potential for habitat destruction and biodiversity loss must also be considered in environmental impact assessments. Muriatic acid spills can create inhospitable conditions for local flora and fauna, potentially leading to long-term ecological imbalances. Sensitive ecosystems along transport routes require special attention and protection measures to preserve biodiversity and maintain ecological integrity.
Climate change considerations are increasingly relevant in environmental impact assessments for chemical transport. The energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with muriatic acid transportation, including vehicle emissions and potential refrigeration requirements, should be evaluated. Strategies to minimize carbon footprint and promote sustainable transport practices should be integrated into overall environmental management plans.
To effectively address these environmental concerns, a comprehensive life cycle assessment approach is recommended. This involves evaluating the environmental impacts of muriatic acid from production through transportation to final use or disposal. Such an approach enables the identification of critical points for environmental protection and the development of targeted mitigation strategies throughout the supply chain.
Atmospheric emissions during transport are a primary concern. Muriatic acid vapors can contribute to air pollution and pose respiratory hazards to both humans and wildlife. Proper containment and ventilation systems are essential to prevent the release of acid fumes into the environment. Additionally, the potential for acid rain formation due to atmospheric reactions with released vapors must be considered in long-term environmental impact assessments.
Water contamination risks are particularly critical when transporting muriatic acid. Accidental spills or leaks can have severe consequences for aquatic ecosystems, potentially altering pH levels and causing widespread damage to flora and fauna. Groundwater contamination is another significant risk, as muriatic acid can percolate through soil layers and affect underground water sources. Comprehensive spill prevention and response plans are crucial to mitigate these risks and protect water resources.
Soil contamination is another environmental concern associated with muriatic acid transport. Acid spills can lead to soil acidification, impacting soil fertility and microbial communities. This, in turn, can affect plant growth and ecosystem stability in affected areas. Long-term monitoring of soil quality in transport corridors and storage facilities is necessary to detect and address any persistent contamination issues.
The potential for habitat destruction and biodiversity loss must also be considered in environmental impact assessments. Muriatic acid spills can create inhospitable conditions for local flora and fauna, potentially leading to long-term ecological imbalances. Sensitive ecosystems along transport routes require special attention and protection measures to preserve biodiversity and maintain ecological integrity.
Climate change considerations are increasingly relevant in environmental impact assessments for chemical transport. The energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with muriatic acid transportation, including vehicle emissions and potential refrigeration requirements, should be evaluated. Strategies to minimize carbon footprint and promote sustainable transport practices should be integrated into overall environmental management plans.
To effectively address these environmental concerns, a comprehensive life cycle assessment approach is recommended. This involves evaluating the environmental impacts of muriatic acid from production through transportation to final use or disposal. Such an approach enables the identification of critical points for environmental protection and the development of targeted mitigation strategies throughout the supply chain.
International Regulatory Harmonization
International regulatory harmonization efforts for muriatic acid transport have gained significant momentum in recent years. The global nature of chemical trade necessitates a unified approach to ensure safety, environmental protection, and efficient cross-border movement. Key international bodies, such as the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) and the International Maritime Organization (IMO), have been instrumental in developing standardized regulations.
The UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods serve as a cornerstone for harmonization efforts. These recommendations provide a framework for the classification, packaging, labeling, and documentation of hazardous materials, including muriatic acid. Many countries have adopted these recommendations into their national regulations, facilitating smoother international transport.
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) has also played a crucial role in aligning international standards. By providing a common system for hazard classification and communication, GHS has significantly improved the consistency of safety information across different jurisdictions.
In the maritime sector, the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code, developed by the IMO, provides comprehensive guidelines for the safe transport of dangerous goods by sea. This code is widely adopted and helps ensure consistent handling of muriatic acid during ocean transport.
For air transport, the International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations harmonize the requirements for shipping hazardous materials by air. These regulations are based on the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Technical Instructions and are universally applied by airlines worldwide.
Despite these harmonization efforts, challenges remain. Differences in implementation timelines, interpretation of regulations, and enforcement practices can still create discrepancies between countries. Additionally, some nations maintain stricter requirements beyond the international standards, which can complicate compliance for global shippers.
To address these challenges, ongoing collaboration between regulatory bodies, industry stakeholders, and governments is essential. Regular review and updating of international agreements, coupled with capacity-building initiatives in developing countries, can further enhance regulatory harmonization. The ultimate goal is to create a seamless, globally consistent regulatory framework that ensures the safe and efficient transport of muriatic acid across international borders.
The UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods serve as a cornerstone for harmonization efforts. These recommendations provide a framework for the classification, packaging, labeling, and documentation of hazardous materials, including muriatic acid. Many countries have adopted these recommendations into their national regulations, facilitating smoother international transport.
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) has also played a crucial role in aligning international standards. By providing a common system for hazard classification and communication, GHS has significantly improved the consistency of safety information across different jurisdictions.
In the maritime sector, the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code, developed by the IMO, provides comprehensive guidelines for the safe transport of dangerous goods by sea. This code is widely adopted and helps ensure consistent handling of muriatic acid during ocean transport.
For air transport, the International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations harmonize the requirements for shipping hazardous materials by air. These regulations are based on the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Technical Instructions and are universally applied by airlines worldwide.
Despite these harmonization efforts, challenges remain. Differences in implementation timelines, interpretation of regulations, and enforcement practices can still create discrepancies between countries. Additionally, some nations maintain stricter requirements beyond the international standards, which can complicate compliance for global shippers.
To address these challenges, ongoing collaboration between regulatory bodies, industry stakeholders, and governments is essential. Regular review and updating of international agreements, coupled with capacity-building initiatives in developing countries, can further enhance regulatory harmonization. The ultimate goal is to create a seamless, globally consistent regulatory framework that ensures the safe and efficient transport of muriatic acid across international borders.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!