AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) is a game-changing display technology known for its self-luminescence, flexibility, and high contrast ratios. Unlike traditional LCDs, AMOLED screens emit light directly from each pixel, enabling thinner, brighter, and more energy-efficient displays. As industries seek adaptable and power-conscious solutions for foldable phones, smartwatches, AR glasses, and transparent interfaces, AMOLED emerges as a key enabler.
This article unpacks the science behind AMOLED’s material composition and performance traits, highlights its applications across key sectors, evaluates its advantages and limitations, and outlines its future potential—leveraging PatSnap Eureka AI Agent for research-driven insights.
Material Composition & Key Properties
- Organic Semiconducting Materials:
AMOLED consists of organic semiconductors layered between electrodes on a thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane. - Emissive Layer Compounds:
- Small-molecule OLEDs
- Polymer-based OLEDs
- Backplane Technologies:
- LTPS (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon)
- LTPO (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Oxide)
- Encapsulation:
Protective layers are used to shield OLED materials from oxygen and moisture. - Key Properties:
- Self-emissive pixels enable ultra-high contrast ratios
- Extremely thin and lightweight design
- Rapid response times and adaptive refresh rates
- Flexible integration with curved and bendable substrates
- Wide color gamut with high color accuracy
Comparative Advantages & Limitations
Advantages of AMOLED
- High Contrast & True Blacks
Each pixel emits its own light and can be completely turned off, delivering infinite contrast ratios and deep blacks. - Vivid & Accurate Color Reproduction
Wide color gamut with excellent saturation and precision, ideal for HDR and color-critical applications. - Ultra-Thin & Lightweight Design
No need for a separate backlight enables sleek, lightweight panels suited for mobile and wearable devices. - Flexible & Foldable Capabilities
Organic layers and thin-film transistors allow integration into foldable, rollable, and curved form factors. - Energy Efficiency in Select Scenarios
Particularly efficient in dark-mode or content with large black areas, as black pixels consume no power. - Fast Refresh & Low Motion Blur
Near-instantaneous pixel response times support high frame rates and smooth motion rendering, outperforming LCDs in gaming and AR/VR contexts. - Transparency & Edge-to-Edge Design Potential
Can support semi-transparent screens, under-display sensors, and bezel-less designs.

Limitations of AMOLED
- Shorter Lifespan of Blue OLEDs
Blue organic compounds degrade faster than red and green, leading to color shift or brightness decay over time. - Image Retention & Burn-In Risks
Prolonged display of static content (e.g., UI elements) can cause permanent shadow images. - Higher Manufacturing Costs
Requires precise deposition, complex encapsulation, and tight material quality control, making it more expensive than LCD or MiniLED. - Environmental Vulnerability
Organic layers are highly sensitive to moisture and oxygen, requiring robust encapsulation to ensure long-term reliability. - Challenging Thermal Management
Self-emissive pixels generate heat locally, demanding careful thermal design to prevent uneven wear or device overheating.
AMOLED vs. LCD / MiniLED: A Comparative Snapshot
| Feature | AMOLED | LCD / MiniLED |
|---|---|---|
| Backlight Requirement | No (self-emissive) | Yes (edge/backlight unit) |
| Contrast Ratio | Infinite | ~1000:1 to 5000:1 |
| Flexibility | Foldable / curved possible | Rigid, limited flexibility |
| Power Efficiency | High (dark mode); variable overall | Constant backlight = higher baseline use |
| Production Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Lifespan & Burn-in | Risk of burn-in, shorter blue life | Longer with no burn-in |
| Color & Motion Quality | Superior | Good but limited by response time |
Application Domains
1. Wearable & Flexible Electronics
Wearable devices require ultra-lightweight, energy-efficient displays that can curve with the human body while providing clear, real-time feedback. AMOLED’s flexibility, low power consumption, and high-resolution performance make it ideal for this sector. Whether in fitness tracking, medical patches, or consumer smartwatches, AMOLED displays enhance both functionality and user comfort.
Research Frontlines:
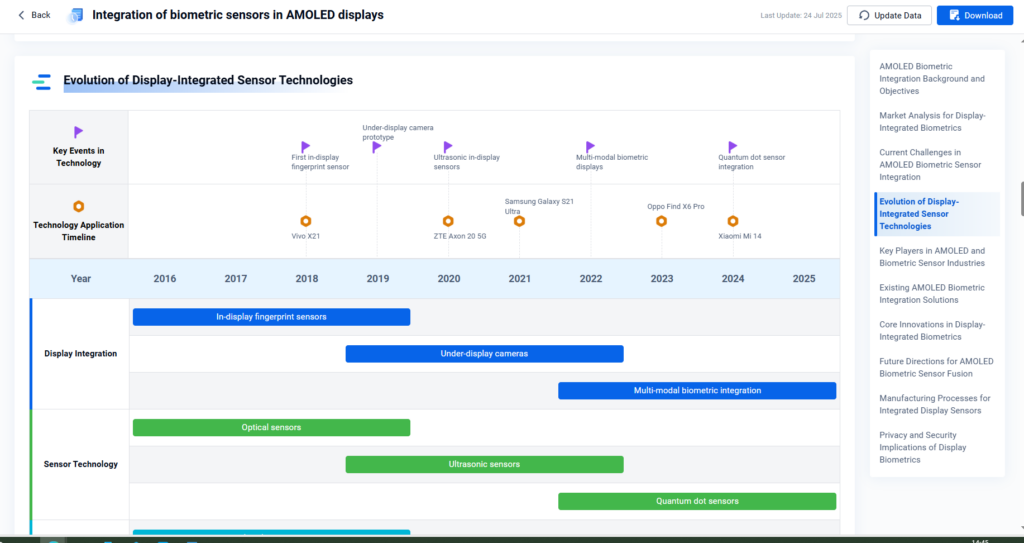
Ongoing innovations target energy-saving circular displays, integration with biosensors, and skin-mimicking electronic films.
Related Reports:
- How AMOLED addresses power consumption in smartwatches
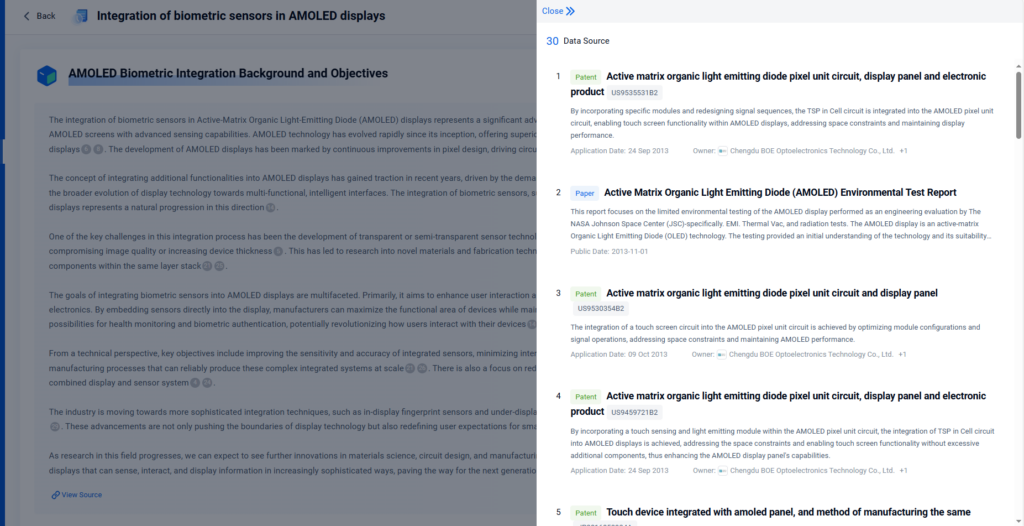
- Integration of biometric sensors in AMOLED displays
- How circular AMOLED displays innovate wearable designs
- Evaluating mechanical stresses on flexible AMOLED innovations
2. Automotive & Transportation Interfaces
In the automotive space, the shift toward digital cockpits and HUDs requires displays that are vibrant, durable, and flexible. AMOLED panels meet these needs through seamless dashboard integration, curved surfaces, and adaptability to lighting extremes. Transparent AMOLED is also opening doors to next-gen windshield displays.
Research Frontlines:
Current development explores encapsulation for high-temp stability, visibility in glare conditions, and integration with automotive UX systems.
Related Reports:
- Transformational AMOLED applications in automotive interiors
- The future of transparent AMOLED in automotive displays
- AMOLED advancements in autonomous vehicle interfaces
- Enhancements in AMOLED for extreme low-temperature operations
- Real-world applications of transparent AMOLED displays
- How AMOLED supports seamless display design in architecture
- How AMOLED enhances environmental monitoring systems

3. Smart Devices & Advanced Displays
Smartphones, tablets, and AR/VR devices demand high refresh rates, color accuracy, and compact components. AMOLED empowers these applications with self-emissive pixels, minimal bezels, and HDR capabilities. It is also pivotal in immersive gaming and edge-to-edge UX design.
Research Frontlines:
Efforts center on integrating AI-controlled display tuning, tactile feedback, and holographic enhancements.
Related Reports:
- Innovations in variable refresh rate designs for AMOLED displays
- AMOLED’s impact on virtual reality headset displays
- AMOLED display integration in augmented reality glasses
- How AMOLED complements edge-to-edge display solutions
- Impact of AMOLED on next-gen mobile gaming experiences
- How AMOLED technology supports HDR in flexible displays
4. Transparent & Ambient Interfaces
Transparent AMOLED displays enable futuristic interactions in public infrastructure, smart homes, and digital signage. These displays maintain full transparency when inactive, and vivid imagery when powered, transforming glass surfaces into dynamic content hubs.
Research Frontlines:
Research focuses on improving transparency without sacrificing pixel performance, and integrating AMOLED into architectural or public-facing glass panels.
Related Reports:
- The role of AMOLED in next-gen transparent displays
- Real-world applications of transparent AMOLED displays
- How transparent AMOLED can benefit public safety communication
- Innovations in integrating AMOLED with holographic display systems
- Innovations in AMOLED protective film materials
- Implications of variable AMOLED transparency in privacy enhancements
5. Energy-Efficient & Sustainable Electronics
Reducing power usage and integrating renewable energy sources are critical across industries. AMOLED enables pixel-level power control and supports integration with photovoltaic systems. These advantages align well with green technology and off-grid use cases.
Research Frontlines:
Development includes solar-charged AMOLED panels, AI-driven refresh control, and recyclable or biodegradable AMOLED components.
Related Reports:
- How AMOLED improves energy efficiency in flexible screens
- Energy-efficient AMOLED applications in healthcare devices
- How renewable energy aligns with AMOLED production synergies
- Utilizing AI for efficient AMOLED power management
- How AMOLED encourages eco-friendly smartphone manufacturing
- Exploration of AMOLED’s role in sustainable smart architecture
Future Outlook & Research Frontiers
Over the next decade, AMOLED is poised to redefine how we see and interact with digital content. Key trends include:
● Self-powered AMOLED in off-grid applications
● Biodegradable, recyclable AMOLED components
● AMOLED with AI-driven dynamic tuning
● Hybrid AMOLED with micro-LED and quantum dots
● Transparent interfaces in consumer and public displays
● AMOLED for biomedical wearables and neural interfaces
● Holographic and multisensory AMOLED experiences
As research converges with sustainability and AI, AMOLED will transition from “display” to “interactive system.”

Conclusion & Strategic Takeaways
AMOLED is not just a display technology—it is a foundational platform enabling innovation across sectors. From smartwatches to vehicles and smart cities, its impact spans flexibility, energy efficiency, and interactivity. Its seamless integration into future-forward designs makes AMOLED a strategic material for product differentiation and long-term value creation.
Ready to Power Innovation with AMOLED?
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent helps R&D teams cut through the noise with:● Access to AMOLED-related patents and technical disclosures
● Comparative trend mapping of LTPO, quantum dot, and foldable substrates
● Competitive landscape analysis across consumer electronics, automotive, and healthcare
● AI-assisted forecasting of research momentum and emerging white spaces
👉 Book a Eureka demo and unlock the AMOLED advantage for your next R&D challenge.