How circular AMOLED displays innovate wearable designs?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Circular AMOLED Evolution
Circular AMOLED displays have undergone significant evolution since their inception, revolutionizing the design and functionality of wearable devices. The journey began with the introduction of small, round OLED displays in early smartwatches, which offered limited resolution and color depth. These initial iterations faced challenges in terms of power efficiency and brightness, limiting their practical applications in wearable technology.
As manufacturing processes improved, circular AMOLED displays saw rapid advancements in pixel density and color reproduction. This progression enabled the creation of more vibrant and detailed watch faces, enhancing the overall user experience. The introduction of flexible AMOLED technology marked a crucial milestone, allowing for thinner and more durable displays that could better conform to the curvature of the wrist.
A key development in circular AMOLED evolution was the integration of touch functionality directly into the display. This innovation eliminated the need for separate touch layers, resulting in slimmer device profiles and improved touch responsiveness. Manufacturers also focused on reducing the bezel size, maximizing the screen-to-body ratio and creating a more immersive visual experience for users.
Power efficiency became a critical focus area as wearables demanded longer battery life. Advancements in AMOLED technology, such as the implementation of low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) backplanes and the development of more efficient organic materials, significantly reduced power consumption while maintaining display quality.
The evolution of circular AMOLED displays also saw improvements in outdoor visibility. Enhanced brightness levels and anti-reflective coatings were introduced to combat sunlight glare, ensuring that wearable devices remained functional in various lighting conditions. This development was particularly crucial for fitness-focused wearables used during outdoor activities.
More recent innovations have centered around the integration of additional sensors beneath the display surface. This includes under-display cameras, heart rate monitors, and even fingerprint sensors, allowing for cleaner device designs and expanded functionality without compromising the circular aesthetic.
The latest advancements in circular AMOLED technology have focused on increasing refresh rates, with some displays now capable of 120Hz or higher. This improvement has resulted in smoother animations and more responsive user interfaces, further enhancing the premium feel of high-end wearable devices.
As circular AMOLED displays continue to evolve, we can expect to see further improvements in energy efficiency, durability, and integration with other technologies. These advancements will undoubtedly shape the future of wearable design, enabling more sophisticated and versatile devices that seamlessly blend form and function.
As manufacturing processes improved, circular AMOLED displays saw rapid advancements in pixel density and color reproduction. This progression enabled the creation of more vibrant and detailed watch faces, enhancing the overall user experience. The introduction of flexible AMOLED technology marked a crucial milestone, allowing for thinner and more durable displays that could better conform to the curvature of the wrist.
A key development in circular AMOLED evolution was the integration of touch functionality directly into the display. This innovation eliminated the need for separate touch layers, resulting in slimmer device profiles and improved touch responsiveness. Manufacturers also focused on reducing the bezel size, maximizing the screen-to-body ratio and creating a more immersive visual experience for users.
Power efficiency became a critical focus area as wearables demanded longer battery life. Advancements in AMOLED technology, such as the implementation of low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) backplanes and the development of more efficient organic materials, significantly reduced power consumption while maintaining display quality.
The evolution of circular AMOLED displays also saw improvements in outdoor visibility. Enhanced brightness levels and anti-reflective coatings were introduced to combat sunlight glare, ensuring that wearable devices remained functional in various lighting conditions. This development was particularly crucial for fitness-focused wearables used during outdoor activities.
More recent innovations have centered around the integration of additional sensors beneath the display surface. This includes under-display cameras, heart rate monitors, and even fingerprint sensors, allowing for cleaner device designs and expanded functionality without compromising the circular aesthetic.
The latest advancements in circular AMOLED technology have focused on increasing refresh rates, with some displays now capable of 120Hz or higher. This improvement has resulted in smoother animations and more responsive user interfaces, further enhancing the premium feel of high-end wearable devices.
As circular AMOLED displays continue to evolve, we can expect to see further improvements in energy efficiency, durability, and integration with other technologies. These advancements will undoubtedly shape the future of wearable design, enabling more sophisticated and versatile devices that seamlessly blend form and function.
Wearable Market Demand
The wearable technology market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for smart devices that seamlessly integrate into daily life. Circular AMOLED displays have emerged as a key innovation in this sector, particularly for smartwatches and fitness trackers. The global wearable market is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with smartwatches and fitness trackers accounting for a large portion of this growth.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards more aesthetically pleasing and functional wearable devices. Circular AMOLED displays address this demand by offering a more traditional watch-like appearance while providing the advanced features of smart devices. This design approach has proven popular among consumers who seek a balance between classic style and modern technology.
The health and fitness segment of the wearable market has seen particularly strong growth, with consumers increasingly interested in devices that can monitor various health metrics. Circular AMOLED displays enhance the user experience in this area by providing a more intuitive and visually appealing interface for displaying health data. This has led to increased adoption of wearables for health monitoring, especially among older demographics and those with chronic health conditions.
In the corporate and enterprise sectors, there is a growing demand for wearable devices that can improve productivity and streamline communication. Circular AMOLED displays on smartwatches offer a discreet and efficient way to receive notifications and manage tasks, making them increasingly popular in professional settings. This trend is expected to continue as more businesses recognize the potential of wearable technology to enhance workplace efficiency.
The sports and fitness industry has also embraced wearable technology, with athletes and fitness enthusiasts seeking devices that can provide real-time performance data. Circular AMOLED displays offer improved visibility and durability for outdoor use, making them ideal for sports-oriented wearables. This has led to increased demand from both professional athletes and amateur sports enthusiasts.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem expands, there is a growing market for wearable devices that can integrate seamlessly with smart home systems and other connected devices. Circular AMOLED displays provide an attractive interface for controlling smart home features and accessing IoT functionalities, driving demand for more advanced and interconnected wearable devices.
The fashion and luxury goods sectors have also shown interest in wearable technology, with several high-end brands incorporating smart features into their products. Circular AMOLED displays allow for more elegant and customizable designs, appealing to fashion-conscious consumers who want both style and functionality in their wearable devices. This trend is expected to drive growth in the premium segment of the wearable market.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards more aesthetically pleasing and functional wearable devices. Circular AMOLED displays address this demand by offering a more traditional watch-like appearance while providing the advanced features of smart devices. This design approach has proven popular among consumers who seek a balance between classic style and modern technology.
The health and fitness segment of the wearable market has seen particularly strong growth, with consumers increasingly interested in devices that can monitor various health metrics. Circular AMOLED displays enhance the user experience in this area by providing a more intuitive and visually appealing interface for displaying health data. This has led to increased adoption of wearables for health monitoring, especially among older demographics and those with chronic health conditions.
In the corporate and enterprise sectors, there is a growing demand for wearable devices that can improve productivity and streamline communication. Circular AMOLED displays on smartwatches offer a discreet and efficient way to receive notifications and manage tasks, making them increasingly popular in professional settings. This trend is expected to continue as more businesses recognize the potential of wearable technology to enhance workplace efficiency.
The sports and fitness industry has also embraced wearable technology, with athletes and fitness enthusiasts seeking devices that can provide real-time performance data. Circular AMOLED displays offer improved visibility and durability for outdoor use, making them ideal for sports-oriented wearables. This has led to increased demand from both professional athletes and amateur sports enthusiasts.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem expands, there is a growing market for wearable devices that can integrate seamlessly with smart home systems and other connected devices. Circular AMOLED displays provide an attractive interface for controlling smart home features and accessing IoT functionalities, driving demand for more advanced and interconnected wearable devices.
The fashion and luxury goods sectors have also shown interest in wearable technology, with several high-end brands incorporating smart features into their products. Circular AMOLED displays allow for more elegant and customizable designs, appealing to fashion-conscious consumers who want both style and functionality in their wearable devices. This trend is expected to drive growth in the premium segment of the wearable market.
Technical Challenges
The development of circular AMOLED displays for wearable devices presents several significant technical challenges that manufacturers and researchers must overcome. One of the primary obstacles is the adaptation of traditional rectangular display manufacturing processes to accommodate circular geometries. This requires innovative approaches to pixel arrangement and circuit design to maximize the active display area while maintaining image quality and color accuracy.
Another major challenge lies in the power consumption of circular AMOLED displays. Wearable devices have limited battery capacity, necessitating highly efficient display technologies. Engineers must optimize the power management systems and develop new driving schemes that can reduce energy consumption without compromising display performance. This is particularly crucial for always-on display features that are common in smartwatches and fitness trackers.
The curvature of circular displays introduces complexities in touch sensitivity and accuracy. Implementing reliable touch functionality on a curved surface requires advanced sensing technologies and sophisticated algorithms to interpret user inputs correctly. Additionally, the integration of other sensors, such as ambient light sensors or fingerprint scanners, becomes more challenging due to the limited space and unconventional form factor.
Durability and longevity are also critical concerns for circular AMOLED displays in wearable designs. These devices are subjected to frequent physical interactions and environmental stresses, necessitating robust protection against impacts, scratches, and moisture. Developing thin yet durable cover glasses and protective coatings that conform to the circular shape without compromising display quality or touch sensitivity is a significant technical hurdle.
Manufacturing yield and cost-effectiveness present ongoing challenges for circular AMOLED production. The unique shape requires specialized equipment and processes, potentially leading to higher defect rates and increased production costs compared to traditional rectangular displays. Improving manufacturing techniques and scaling production to achieve economies of scale are essential for the widespread adoption of circular AMOLED displays in wearable devices.
Lastly, software optimization for circular displays poses a distinct challenge. User interfaces and applications designed for rectangular screens must be adapted or completely reimagined for circular formats. This requires new design paradigms and development tools to create intuitive and visually appealing experiences that take full advantage of the circular display's unique characteristics while maintaining usability and functionality.
Another major challenge lies in the power consumption of circular AMOLED displays. Wearable devices have limited battery capacity, necessitating highly efficient display technologies. Engineers must optimize the power management systems and develop new driving schemes that can reduce energy consumption without compromising display performance. This is particularly crucial for always-on display features that are common in smartwatches and fitness trackers.
The curvature of circular displays introduces complexities in touch sensitivity and accuracy. Implementing reliable touch functionality on a curved surface requires advanced sensing technologies and sophisticated algorithms to interpret user inputs correctly. Additionally, the integration of other sensors, such as ambient light sensors or fingerprint scanners, becomes more challenging due to the limited space and unconventional form factor.
Durability and longevity are also critical concerns for circular AMOLED displays in wearable designs. These devices are subjected to frequent physical interactions and environmental stresses, necessitating robust protection against impacts, scratches, and moisture. Developing thin yet durable cover glasses and protective coatings that conform to the circular shape without compromising display quality or touch sensitivity is a significant technical hurdle.
Manufacturing yield and cost-effectiveness present ongoing challenges for circular AMOLED production. The unique shape requires specialized equipment and processes, potentially leading to higher defect rates and increased production costs compared to traditional rectangular displays. Improving manufacturing techniques and scaling production to achieve economies of scale are essential for the widespread adoption of circular AMOLED displays in wearable devices.
Lastly, software optimization for circular displays poses a distinct challenge. User interfaces and applications designed for rectangular screens must be adapted or completely reimagined for circular formats. This requires new design paradigms and development tools to create intuitive and visually appealing experiences that take full advantage of the circular display's unique characteristics while maintaining usability and functionality.
Current Design Solutions
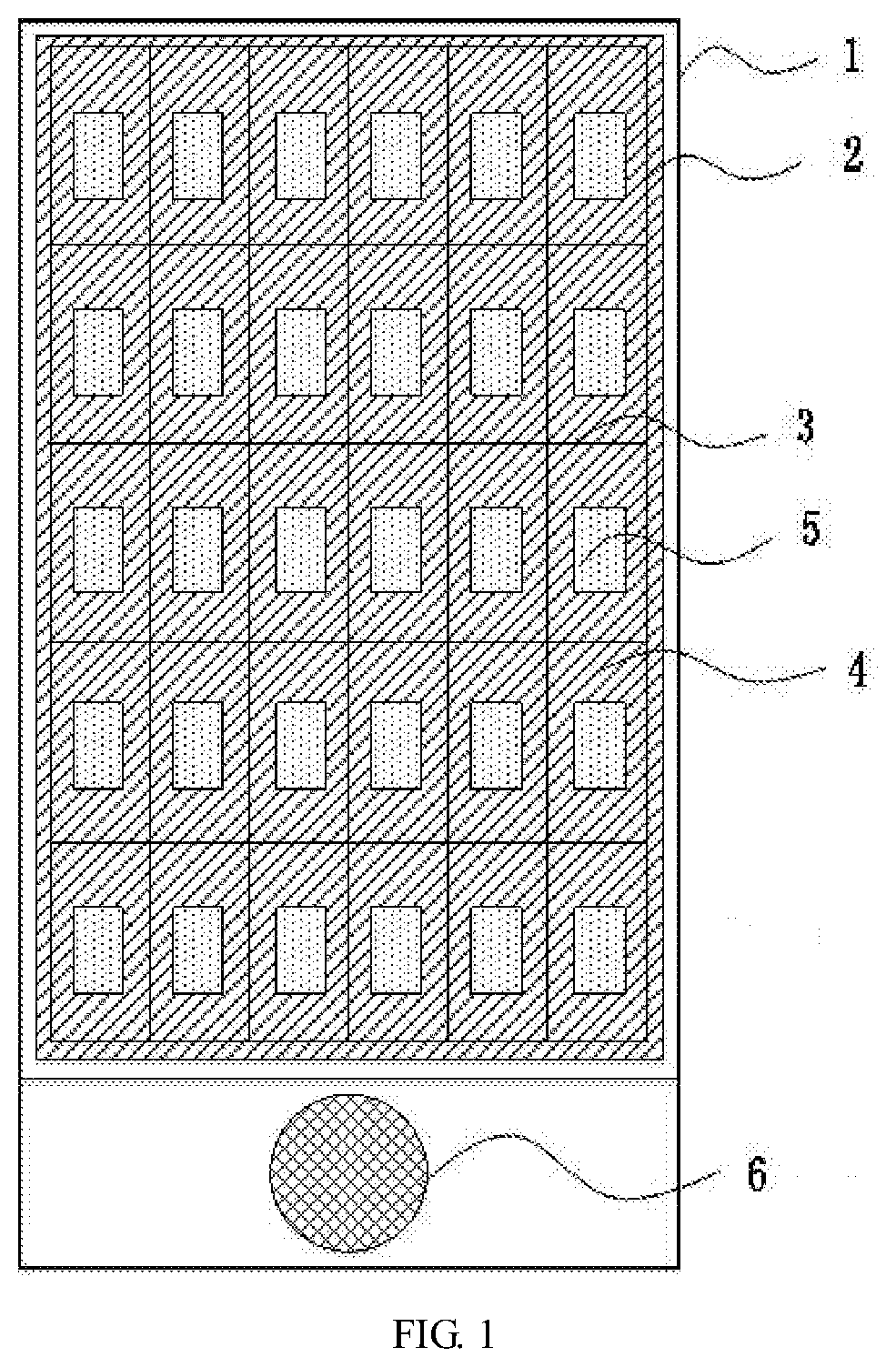
01 Pixel arrangement in circular AMOLED displays
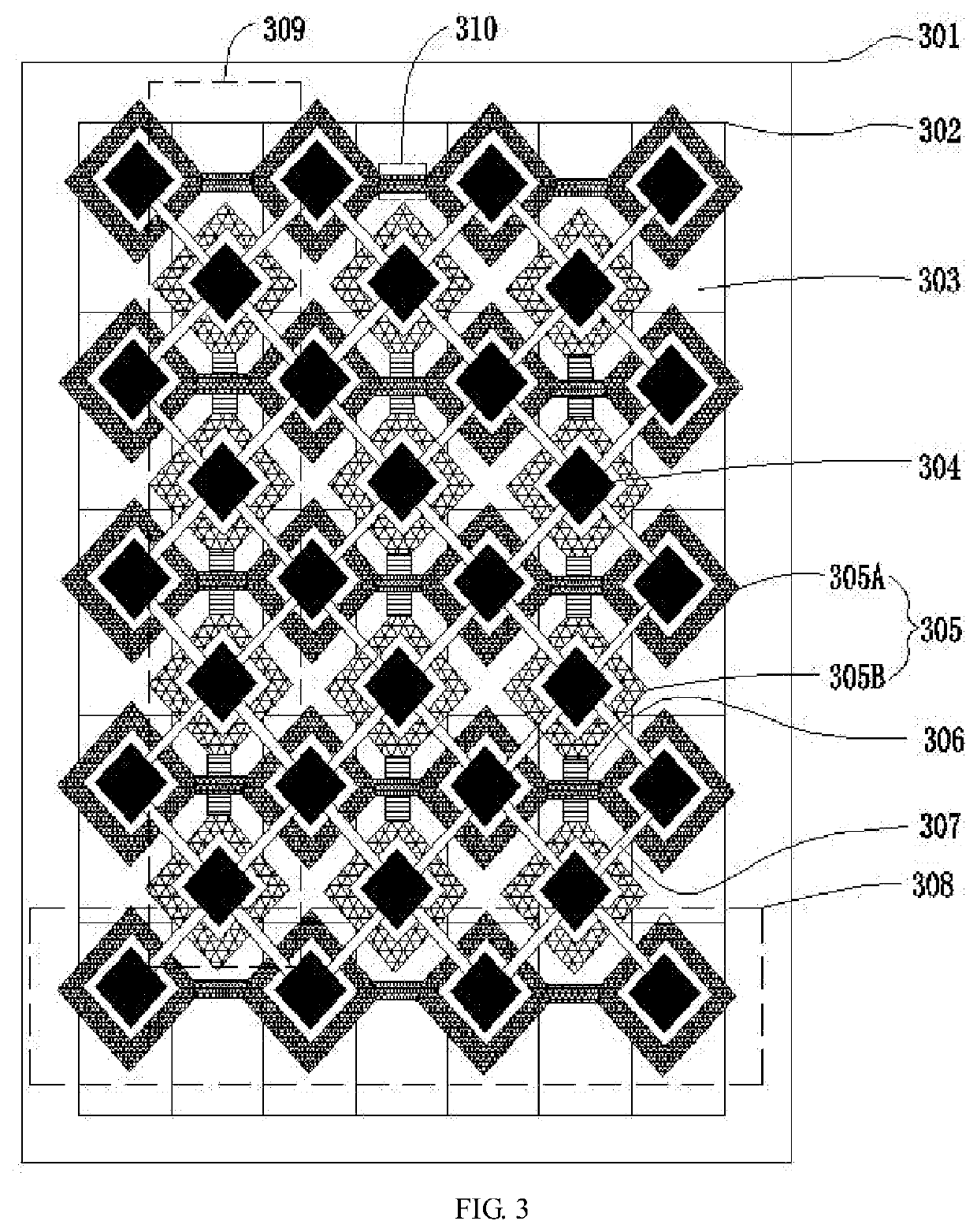
Circular AMOLED displays require specialized pixel arrangements to optimize the use of space and maintain image quality. This involves designing pixel layouts that efficiently fill the circular area, often using non-rectangular grids or radial patterns. Such arrangements help to maximize the active display area and minimize dead space at the edges of the circular screen.- Pixel arrangement in circular AMOLED displays: Circular AMOLED displays require specialized pixel arrangements to optimize the use of space and maintain image quality. This involves designing pixel layouts that efficiently fill the circular area, often using non-rectangular subpixel shapes or varying pixel densities across the display to accommodate the circular form factor.
- Flexible substrate for curved AMOLED displays: Implementing flexible substrates in circular AMOLED displays allows for the creation of curved or bendable screens. These substrates enable the display to conform to circular shapes while maintaining functionality and durability. The design often incorporates materials and manufacturing techniques that support flexibility without compromising display performance.
- Bezel-less design for circular displays: Achieving a bezel-less design in circular AMOLED displays involves innovative approaches to integrate display drivers, touch sensors, and other components within the active display area or around the periphery. This design strategy maximizes the usable screen area and enhances the aesthetic appeal of circular devices.
- Power efficiency in circular AMOLED displays: Enhancing power efficiency in circular AMOLED displays is crucial for battery life in wearable devices. This involves optimizing pixel circuits, implementing advanced power management techniques, and utilizing energy-efficient materials. The design focuses on reducing power consumption while maintaining display quality in the circular form factor.
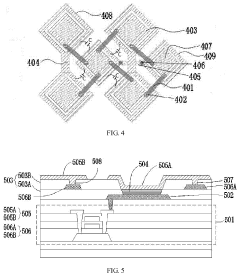
- Touch integration in circular AMOLED displays: Integrating touch functionality into circular AMOLED displays presents unique challenges due to the non-rectangular shape. Designs focus on optimizing touch sensor layouts, improving touch accuracy near the edges, and developing algorithms to interpret touch inputs accurately on the circular surface. This integration aims to provide seamless touch interaction while maintaining the display's visual quality.
02 Flexible substrate for circular displays
Implementing flexible substrates in circular AMOLED displays allows for better conformity to curved surfaces and improved durability. These substrates can be made from materials like polyimide or thin glass, enabling the display to maintain its circular shape while providing necessary flexibility for various applications, such as wearable devices.Expand Specific Solutions03 Bezel-less design for circular AMOLED displays
Achieving a bezel-less design in circular AMOLED displays involves innovative approaches to integrate display drivers, touch sensors, and other components within the active display area or around the periphery. This may include using transparent electrodes, embedding circuits under the display, or utilizing advanced packaging techniques to minimize the non-display area.Expand Specific Solutions04 Power efficiency in circular AMOLED displays
Improving power efficiency in circular AMOLED displays is crucial, especially for battery-powered devices. This can be achieved through optimized pixel designs, advanced driving schemes, and the use of low-power materials. Additionally, implementing selective pixel activation or variable refresh rates can further reduce power consumption in these displays.Expand Specific Solutions05 Touch integration in circular AMOLED displays
Integrating touch functionality into circular AMOLED displays presents unique challenges due to the non-rectangular shape. Solutions may include developing curved touch sensors, implementing in-cell or on-cell touch technology, and creating specialized algorithms for accurate touch detection and gesture recognition on the circular surface.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The circular AMOLED display market for wearables is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for smartwatches and fitness trackers. The market size is expanding rapidly, with major players like Samsung Display, BOE Technology, and LG Display competing for market share. Technologically, circular AMOLED displays are maturing, with companies like Samsung and BOE leading in innovation. These firms are developing more advanced, energy-efficient, and flexible displays to meet the evolving needs of wearable devices. The competition is intensifying as more manufacturers enter the market, pushing for further advancements in display quality, form factor, and power efficiency.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has made significant strides in circular AMOLED technology for wearables. They've developed flexible OLED displays with a resolution of up to 466x466 pixels and a pixel density of 326 PPI[2]. BOE's circular displays feature low power consumption, utilizing LTPO (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Oxide) backplane technology, which allows for variable refresh rates from 1Hz to 60Hz, significantly improving battery life in wearables[4]. The company has also focused on enhancing color gamut coverage, achieving over 100% DCI-P3 color space in their latest models. BOE's circular AMOLEDs incorporate in-display fingerprint sensors and support Always-On Display functionality[6].
Strengths: Advanced LTPO technology for power efficiency, high resolution, and color accuracy. Weaknesses: Less market presence in high-end wearables compared to competitors like Samsung.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has pioneered circular AMOLED displays for wearables, particularly in their Galaxy Watch series. Their technology utilizes a flexible OLED panel that can be curved to fit round watch faces. The display incorporates an integrated touch layer and is protected by Corning Gorilla Glass DX+. Samsung's circular AMOLED displays offer high resolution (up to 450x450 pixels), vibrant colors with 16M color depth, and excellent contrast ratios (typically 1:100,000)[1][3]. They've also developed Always-On Display technology, which allows for constant time and notification display while conserving battery life. Recent innovations include increasing the display's brightness to 2000 nits for better outdoor visibility[5].
Strengths: Industry-leading display quality, high brightness, and power efficiency. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional displays, potential for screen burn-in over extended use.
Innovative Display Tech
Array substrate, display device, and method for manufacturing array substrate
PatentActiveUS20170148862A1
Innovation
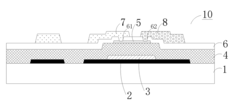
- An array substrate with a light-absorbing layer covering the gate, source, and drain metal layers of a bottom-gate thin film transistor unit, preventing ambient light irradiation while allowing useful light to pass through.
Active matrix organic light emitting diode (amoled) display panel
PatentInactiveUS20210343972A1
Innovation
- The integration of sensing electrodes into the AMOLED display panel allows for underscreen fingerprint identification, utilizing a patterned cathode layer with insulated first and second electrode rows and conductive bridges to form capacitors for fingerprint recognition, thereby embedding fingerprint identification within the screen and increasing the display area ratio.
Manufacturing Processes
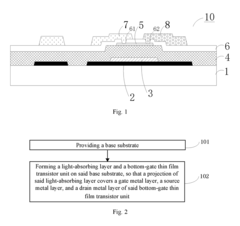
The manufacturing processes for circular AMOLED displays used in wearable designs involve several sophisticated steps and technologies. These processes are crucial for creating high-quality, durable, and efficient displays that can withstand the unique demands of wearable devices.
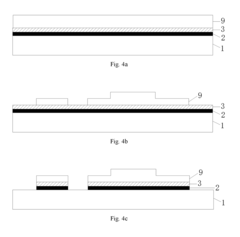
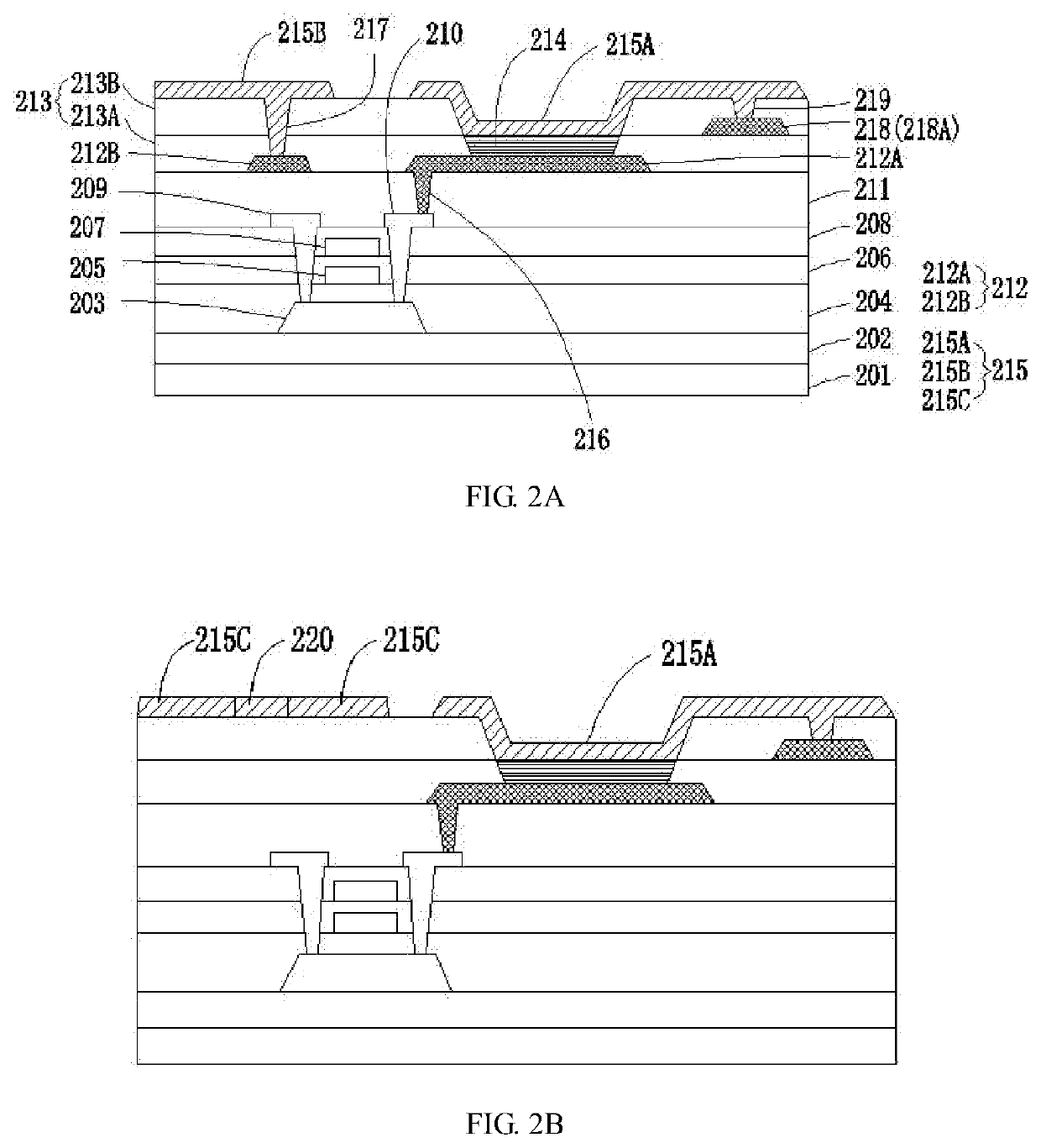
The production of circular AMOLED displays begins with the fabrication of the substrate, typically made from flexible plastic or ultra-thin glass. This substrate must be carefully prepared to ensure a smooth, defect-free surface that can support the subsequent layers of the display. The circular shape presents unique challenges, requiring specialized cutting and shaping techniques to achieve the desired form factor without compromising structural integrity.
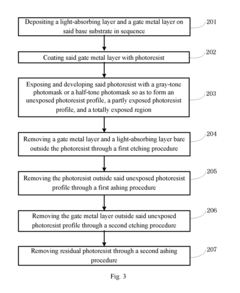
Next, the thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane is deposited onto the substrate. This layer is responsible for controlling individual pixels and is typically made using low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) or indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) technologies. The circular geometry necessitates innovative approaches to TFT layout and addressing schemes to maintain uniform performance across the entire display area.
The OLED material deposition is a critical step in the manufacturing process. Organic layers are precisely deposited using techniques such as vacuum thermal evaporation or inkjet printing. For circular displays, custom-designed shadow masks or advanced printing technologies are employed to ensure accurate and uniform deposition of the organic materials in a circular pattern.
Encapsulation is particularly important for wearable AMOLED displays to protect the sensitive organic materials from moisture and oxygen. Advanced thin-film encapsulation techniques, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD), are used to create ultra-thin, flexible barrier layers that conform to the circular shape while providing excellent protection.
The integration of touch functionality is often achieved through the use of on-cell or in-cell touch technologies, which reduce the overall thickness of the display module. For circular displays, specialized touch sensor patterns and algorithms are developed to accurately detect touch inputs across the curved surface.
Finally, the display undergoes rigorous testing and quality control processes. These include visual inspections, electrical tests, and stress tests to ensure the circular AMOLED display meets the stringent requirements for wearable applications, including durability, color accuracy, and power efficiency.
Throughout the manufacturing process, advanced automation and precision control systems are employed to maintain consistency and yield, especially given the unique challenges posed by the circular form factor. Continuous innovation in manufacturing techniques and materials science is driving improvements in the production of circular AMOLED displays, enabling more sophisticated and capable wearable designs.
The production of circular AMOLED displays begins with the fabrication of the substrate, typically made from flexible plastic or ultra-thin glass. This substrate must be carefully prepared to ensure a smooth, defect-free surface that can support the subsequent layers of the display. The circular shape presents unique challenges, requiring specialized cutting and shaping techniques to achieve the desired form factor without compromising structural integrity.
Next, the thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane is deposited onto the substrate. This layer is responsible for controlling individual pixels and is typically made using low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) or indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) technologies. The circular geometry necessitates innovative approaches to TFT layout and addressing schemes to maintain uniform performance across the entire display area.
The OLED material deposition is a critical step in the manufacturing process. Organic layers are precisely deposited using techniques such as vacuum thermal evaporation or inkjet printing. For circular displays, custom-designed shadow masks or advanced printing technologies are employed to ensure accurate and uniform deposition of the organic materials in a circular pattern.
Encapsulation is particularly important for wearable AMOLED displays to protect the sensitive organic materials from moisture and oxygen. Advanced thin-film encapsulation techniques, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD), are used to create ultra-thin, flexible barrier layers that conform to the circular shape while providing excellent protection.
The integration of touch functionality is often achieved through the use of on-cell or in-cell touch technologies, which reduce the overall thickness of the display module. For circular displays, specialized touch sensor patterns and algorithms are developed to accurately detect touch inputs across the curved surface.
Finally, the display undergoes rigorous testing and quality control processes. These include visual inspections, electrical tests, and stress tests to ensure the circular AMOLED display meets the stringent requirements for wearable applications, including durability, color accuracy, and power efficiency.
Throughout the manufacturing process, advanced automation and precision control systems are employed to maintain consistency and yield, especially given the unique challenges posed by the circular form factor. Continuous innovation in manufacturing techniques and materials science is driving improvements in the production of circular AMOLED displays, enabling more sophisticated and capable wearable designs.
Energy Efficiency Impact
The adoption of circular AMOLED displays in wearable devices has significantly impacted energy efficiency, revolutionizing the design and functionality of these products. Circular displays offer unique advantages in power consumption compared to traditional rectangular screens, primarily due to their optimized shape and reduced pixel count.
One of the key factors contributing to improved energy efficiency is the reduction in active display area. Circular displays eliminate corner pixels that are often underutilized in rectangular screens, resulting in fewer pixels to power and manage. This reduction in pixel count directly translates to lower power consumption, as each pixel requires energy to illuminate and maintain its state.
Furthermore, the circular form factor allows for more efficient use of OLED technology. OLED displays are known for their ability to selectively illuminate pixels, and the circular shape capitalizes on this feature by concentrating the most frequently used information in the center of the display. This concentration of active pixels in a smaller area leads to reduced power draw compared to larger rectangular displays with similar functionality.
The curvature of circular displays also contributes to energy savings. The rounded edges of these displays can help distribute light more evenly across the surface, potentially reducing the need for higher brightness levels to achieve the same visibility as flat displays. This can result in lower power consumption while maintaining optimal readability in various lighting conditions.
Circular AMOLED displays have also driven innovations in power management systems for wearable devices. Manufacturers have developed specialized algorithms and hardware solutions to optimize power usage based on the unique characteristics of circular displays. These advancements include adaptive brightness controls, selective pixel activation, and more efficient refresh rates tailored to the circular form factor.
The energy efficiency gains from circular displays have a cascading effect on overall wearable device design. With reduced power consumption, manufacturers can opt for smaller batteries without compromising device longevity. This, in turn, allows for sleeker, more compact wearable designs that are both aesthetically pleasing and functionally superior.
Moreover, the energy savings achieved through circular displays enable the integration of additional features and sensors without significantly impacting battery life. This has led to the development of more sophisticated wearable devices that can perform a wider range of functions while maintaining extended usage times between charges.
One of the key factors contributing to improved energy efficiency is the reduction in active display area. Circular displays eliminate corner pixels that are often underutilized in rectangular screens, resulting in fewer pixels to power and manage. This reduction in pixel count directly translates to lower power consumption, as each pixel requires energy to illuminate and maintain its state.
Furthermore, the circular form factor allows for more efficient use of OLED technology. OLED displays are known for their ability to selectively illuminate pixels, and the circular shape capitalizes on this feature by concentrating the most frequently used information in the center of the display. This concentration of active pixels in a smaller area leads to reduced power draw compared to larger rectangular displays with similar functionality.
The curvature of circular displays also contributes to energy savings. The rounded edges of these displays can help distribute light more evenly across the surface, potentially reducing the need for higher brightness levels to achieve the same visibility as flat displays. This can result in lower power consumption while maintaining optimal readability in various lighting conditions.
Circular AMOLED displays have also driven innovations in power management systems for wearable devices. Manufacturers have developed specialized algorithms and hardware solutions to optimize power usage based on the unique characteristics of circular displays. These advancements include adaptive brightness controls, selective pixel activation, and more efficient refresh rates tailored to the circular form factor.
The energy efficiency gains from circular displays have a cascading effect on overall wearable device design. With reduced power consumption, manufacturers can opt for smaller batteries without compromising device longevity. This, in turn, allows for sleeker, more compact wearable designs that are both aesthetically pleasing and functionally superior.
Moreover, the energy savings achieved through circular displays enable the integration of additional features and sensors without significantly impacting battery life. This has led to the development of more sophisticated wearable devices that can perform a wider range of functions while maintaining extended usage times between charges.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!