How AMOLED supports seamless display design in architecture?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED in Architecture
AMOLED technology has revolutionized the way we perceive and interact with displays, and its application in architecture is opening up new possibilities for seamless integration of digital interfaces into built environments. The evolution of AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays has been marked by significant milestones, from the first commercial AMOLED display in 2007 to the current flexible and transparent AMOLED panels.
In the context of architecture, AMOLED technology is poised to transform the way we design and experience spaces. The primary goal is to create seamless, interactive, and visually stunning surfaces that blur the line between the physical and digital realms. This technology aims to enable architects and designers to incorporate dynamic, high-resolution displays into building facades, interior walls, and even windows without compromising the structural integrity or aesthetic appeal of the architecture.
The technical objectives for AMOLED in architecture include developing ultra-thin, flexible displays that can conform to various architectural surfaces, enhancing durability to withstand environmental factors, and improving energy efficiency to make large-scale implementations sustainable. Additionally, there is a push towards creating transparent AMOLED displays that can function as both windows and information displays, further integrating technology into the built environment.
As AMOLED technology continues to advance, we are witnessing a trend towards higher pixel densities, improved color accuracy, and increased brightness levels. These improvements are crucial for architectural applications where displays may need to be visible in varying lighting conditions, from bright sunlight to dim interiors. The development of modular AMOLED systems is another key trend, allowing for scalable and customizable display solutions that can adapt to different architectural requirements.
The convergence of AMOLED technology with other emerging technologies, such as touch sensitivity, gesture recognition, and Internet of Things (IoT) integration, is setting the stage for truly interactive and responsive architectural elements. This synergy is driving the evolution of smart buildings and cities, where the very fabric of our constructed environment becomes a medium for information exchange and user interaction.
In the context of architecture, AMOLED technology is poised to transform the way we design and experience spaces. The primary goal is to create seamless, interactive, and visually stunning surfaces that blur the line between the physical and digital realms. This technology aims to enable architects and designers to incorporate dynamic, high-resolution displays into building facades, interior walls, and even windows without compromising the structural integrity or aesthetic appeal of the architecture.
The technical objectives for AMOLED in architecture include developing ultra-thin, flexible displays that can conform to various architectural surfaces, enhancing durability to withstand environmental factors, and improving energy efficiency to make large-scale implementations sustainable. Additionally, there is a push towards creating transparent AMOLED displays that can function as both windows and information displays, further integrating technology into the built environment.
As AMOLED technology continues to advance, we are witnessing a trend towards higher pixel densities, improved color accuracy, and increased brightness levels. These improvements are crucial for architectural applications where displays may need to be visible in varying lighting conditions, from bright sunlight to dim interiors. The development of modular AMOLED systems is another key trend, allowing for scalable and customizable display solutions that can adapt to different architectural requirements.
The convergence of AMOLED technology with other emerging technologies, such as touch sensitivity, gesture recognition, and Internet of Things (IoT) integration, is setting the stage for truly interactive and responsive architectural elements. This synergy is driving the evolution of smart buildings and cities, where the very fabric of our constructed environment becomes a medium for information exchange and user interaction.
Market Demand Analysis
The integration of AMOLED technology in architectural design has sparked a growing market demand for seamless display solutions. This innovative approach to incorporating digital displays into building facades and interiors has captured the attention of architects, designers, and property developers worldwide. The market for AMOLED-based architectural displays is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the increasing desire for interactive and visually striking urban environments.
One of the primary factors fueling this demand is the unique ability of AMOLED displays to create curved and flexible surfaces. This characteristic allows for seamless integration with various architectural elements, enabling designers to transform traditionally static structures into dynamic, interactive spaces. The versatility of AMOLED technology has opened up new possibilities for creating immersive experiences in public spaces, retail environments, and corporate settings.
The hospitality and entertainment sectors have shown particular interest in AMOLED-based seamless displays. Hotels, casinos, and theme parks are increasingly adopting this technology to create captivating environments that enhance visitor experiences. The ability to display high-quality, dynamic content on curved surfaces aligns perfectly with the industry's focus on creating memorable, Instagram-worthy spaces.
In the commercial real estate market, there is a growing trend towards smart buildings that incorporate advanced display technologies. AMOLED-based seamless displays are being used to create interactive lobbies, information hubs, and wayfinding systems. This not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of buildings but also improves functionality and user experience, potentially increasing property values and attracting high-profile tenants.
The retail sector is another significant driver of market demand for AMOLED-based seamless displays in architecture. Retailers are increasingly looking for innovative ways to engage customers and create immersive shopping experiences. The ability to integrate large, flexible displays into store designs allows for dynamic product showcases and interactive marketing campaigns, blurring the lines between physical and digital retail environments.
As cities worldwide focus on creating smart urban spaces, there is a rising demand for AMOLED technology in public infrastructure projects. From transportation hubs to civic centers, architects and urban planners are exploring ways to incorporate seamless displays into the fabric of city life. This trend is expected to accelerate as municipalities invest in digital infrastructure to improve communication, wayfinding, and public engagement.
The market for AMOLED-based seamless displays in architecture is also being driven by advancements in energy efficiency and durability. As the technology continues to improve, concerns about power consumption and longevity are being addressed, making it a more viable option for long-term architectural applications. This has led to increased interest from sustainability-focused projects looking to balance technological innovation with environmental responsibility.
One of the primary factors fueling this demand is the unique ability of AMOLED displays to create curved and flexible surfaces. This characteristic allows for seamless integration with various architectural elements, enabling designers to transform traditionally static structures into dynamic, interactive spaces. The versatility of AMOLED technology has opened up new possibilities for creating immersive experiences in public spaces, retail environments, and corporate settings.
The hospitality and entertainment sectors have shown particular interest in AMOLED-based seamless displays. Hotels, casinos, and theme parks are increasingly adopting this technology to create captivating environments that enhance visitor experiences. The ability to display high-quality, dynamic content on curved surfaces aligns perfectly with the industry's focus on creating memorable, Instagram-worthy spaces.
In the commercial real estate market, there is a growing trend towards smart buildings that incorporate advanced display technologies. AMOLED-based seamless displays are being used to create interactive lobbies, information hubs, and wayfinding systems. This not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of buildings but also improves functionality and user experience, potentially increasing property values and attracting high-profile tenants.
The retail sector is another significant driver of market demand for AMOLED-based seamless displays in architecture. Retailers are increasingly looking for innovative ways to engage customers and create immersive shopping experiences. The ability to integrate large, flexible displays into store designs allows for dynamic product showcases and interactive marketing campaigns, blurring the lines between physical and digital retail environments.
As cities worldwide focus on creating smart urban spaces, there is a rising demand for AMOLED technology in public infrastructure projects. From transportation hubs to civic centers, architects and urban planners are exploring ways to incorporate seamless displays into the fabric of city life. This trend is expected to accelerate as municipalities invest in digital infrastructure to improve communication, wayfinding, and public engagement.
The market for AMOLED-based seamless displays in architecture is also being driven by advancements in energy efficiency and durability. As the technology continues to improve, concerns about power consumption and longevity are being addressed, making it a more viable option for long-term architectural applications. This has led to increased interest from sustainability-focused projects looking to balance technological innovation with environmental responsibility.
Technical Challenges
The integration of AMOLED technology into seamless display designs for architectural applications presents several significant technical challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the need for flexible and bendable displays that can conform to various architectural surfaces and shapes. While AMOLED displays offer inherent flexibility, achieving the level of malleability required for seamless integration with curved or irregular building structures remains a complex engineering task.
Durability and longevity pose another critical challenge. Architectural displays are expected to withstand diverse environmental conditions, including exposure to sunlight, temperature fluctuations, and moisture. AMOLED displays are sensitive to these factors, and developing robust encapsulation techniques to protect the organic materials from degradation is crucial for ensuring long-term performance and reliability in architectural settings.
Power consumption and heat management are additional concerns when implementing large-scale AMOLED displays in buildings. As the display size increases, so does the power requirement and heat generation. Developing efficient power management systems and effective heat dissipation methods is essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent overheating, which can lead to reduced lifespan and potential safety hazards.
Color accuracy and uniformity across large display areas present another technical hurdle. Ensuring consistent color reproduction and brightness across expansive architectural surfaces requires advanced calibration techniques and sophisticated control systems. This challenge is further compounded by the potential for uneven aging of OLED pixels, which can result in visible inconsistencies over time.
Scalability and manufacturing processes also pose significant challenges. Producing AMOLED displays at the scale required for architectural applications demands innovative fabrication techniques and specialized equipment. Current manufacturing methods may need to be adapted or entirely reimagined to accommodate the production of seamless, large-format displays while maintaining cost-effectiveness and yield rates.
Integration with building management systems and content delivery platforms presents an additional layer of complexity. Developing interfaces and protocols that allow seamless communication between the AMOLED displays and existing building infrastructure is crucial for creating responsive and interactive architectural elements. This integration must also consider data security and privacy concerns, particularly in public spaces.
Lastly, the challenge of modular design and maintenance cannot be overlooked. Creating a system that allows for easy replacement of individual display components without compromising the overall seamless aesthetic is essential for practical implementation in architecture. This requires innovative approaches to modular design, connectivity, and installation techniques that balance aesthetics with serviceability.
Durability and longevity pose another critical challenge. Architectural displays are expected to withstand diverse environmental conditions, including exposure to sunlight, temperature fluctuations, and moisture. AMOLED displays are sensitive to these factors, and developing robust encapsulation techniques to protect the organic materials from degradation is crucial for ensuring long-term performance and reliability in architectural settings.
Power consumption and heat management are additional concerns when implementing large-scale AMOLED displays in buildings. As the display size increases, so does the power requirement and heat generation. Developing efficient power management systems and effective heat dissipation methods is essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent overheating, which can lead to reduced lifespan and potential safety hazards.
Color accuracy and uniformity across large display areas present another technical hurdle. Ensuring consistent color reproduction and brightness across expansive architectural surfaces requires advanced calibration techniques and sophisticated control systems. This challenge is further compounded by the potential for uneven aging of OLED pixels, which can result in visible inconsistencies over time.
Scalability and manufacturing processes also pose significant challenges. Producing AMOLED displays at the scale required for architectural applications demands innovative fabrication techniques and specialized equipment. Current manufacturing methods may need to be adapted or entirely reimagined to accommodate the production of seamless, large-format displays while maintaining cost-effectiveness and yield rates.
Integration with building management systems and content delivery platforms presents an additional layer of complexity. Developing interfaces and protocols that allow seamless communication between the AMOLED displays and existing building infrastructure is crucial for creating responsive and interactive architectural elements. This integration must also consider data security and privacy concerns, particularly in public spaces.
Lastly, the challenge of modular design and maintenance cannot be overlooked. Creating a system that allows for easy replacement of individual display components without compromising the overall seamless aesthetic is essential for practical implementation in architecture. This requires innovative approaches to modular design, connectivity, and installation techniques that balance aesthetics with serviceability.
Current AMOLED Solutions
01 Display panel structure for seamless AMOLED displays
Innovative panel structures are designed to achieve seamless AMOLED displays. These structures may include specialized pixel arrangements, substrate configurations, and encapsulation techniques to minimize bezels and create a seamless appearance. The designs focus on reducing the non-display areas and optimizing the active display region to create a more immersive viewing experience.- Display panel structure for seamless AMOLED displays: Innovative panel structures are developed to achieve seamless AMOLED displays. These structures may include specialized pixel arrangements, substrate designs, and encapsulation techniques to minimize bezels and create a seamless appearance. The designs focus on reducing the non-display areas and optimizing the active display regions to create a more immersive viewing experience.
- Driving methods for seamless AMOLED displays: Advanced driving methods are implemented to control seamless AMOLED displays effectively. These methods may include specialized timing controllers, data processing algorithms, and compensation techniques to ensure uniform brightness and color across the entire display area, particularly at the edges and corners where seamless integration is critical.
- Flexible AMOLED technology for seamless displays: Flexible AMOLED technology is utilized to create seamless displays that can conform to various shapes and curves. This involves developing flexible substrates, bendable display elements, and stretchable electrodes to enable the creation of displays that can wrap around edges or form continuous surfaces without visible seams.
- Touch integration in seamless AMOLED displays: Touch functionality is seamlessly integrated into AMOLED displays to create a unified touch-display solution. This may involve in-cell or on-cell touch technologies, specialized touch sensors, and advanced algorithms to ensure accurate touch detection across the entire seamless display surface, including curved or flexible areas.
- Optical enhancements for seamless AMOLED displays: Various optical enhancements are implemented to improve the visual quality of seamless AMOLED displays. These may include specialized color filters, light management films, and anti-reflection coatings to reduce glare, improve contrast, and ensure consistent color reproduction across the entire seamless display area, particularly at the edges and corners.
02 Flexible AMOLED display technology for seamless integration
Flexible AMOLED display technology is utilized to create seamless displays that can be curved or bent. This approach allows for the creation of displays with unique form factors, enabling seamless integration into various devices and surfaces. The flexibility of the display components contributes to reducing visible seams and enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal of the device.Expand Specific Solutions03 Driving and control methods for seamless AMOLED displays
Advanced driving and control methods are developed to manage seamless AMOLED displays effectively. These techniques may include specialized timing controllers, data processing algorithms, and power management systems. The methods aim to ensure uniform brightness, color accuracy, and smooth transitions across the entire display surface, contributing to the seamless visual experience.Expand Specific Solutions04 Optical solutions for minimizing seams in AMOLED displays
Various optical solutions are implemented to minimize visible seams in AMOLED displays. These may include specialized light-guiding structures, optical bonding techniques, and advanced materials that help to blend the edges of display panels. The optical approaches aim to create a visually continuous surface, even when multiple display panels are used together.Expand Specific Solutions05 Touch integration in seamless AMOLED displays
Innovative methods for integrating touch functionality into seamless AMOLED displays are developed. These solutions may involve in-cell or on-cell touch sensors, specialized electrode designs, and advanced signal processing techniques. The integration aims to maintain the seamless appearance of the display while providing accurate and responsive touch capabilities across the entire surface.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The AMOLED technology for seamless display design in architecture is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and evolving technological maturity. Major players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology, and LG Display are driving innovation in this field. The market is characterized by intense competition among established display manufacturers and emerging companies specializing in AMOLED technology. As the technology matures, we're seeing advancements in flexible displays, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced visual quality, making AMOLED increasingly suitable for architectural applications. The integration of AMOLED in architecture is expected to grow significantly as the technology becomes more cost-effective and adaptable to large-scale implementations.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed flexible AMOLED displays that support seamless architectural design. Their technology allows for curved and bendable screens that can be integrated into building structures. BOE's AMOLED panels offer high contrast ratios, wide color gamut, and fast response times[1]. They have implemented advanced pixel compensation algorithms to ensure uniform brightness and color across curved surfaces[2]. BOE's flexible AMOLED displays can achieve bending radii as small as 1mm, enabling them to conform to various architectural shapes[3]. The company has also developed transparent AMOLED technology, which can be used for smart windows and interactive building facades[4].
Strengths: Advanced flexible display technology, high-performance AMOLED panels, ability to create curved and transparent displays. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional displays, potential for image retention in static architectural applications.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has pioneered AMOLED technology for architectural applications. Their displays feature ultra-thin profiles and flexibility, allowing for seamless integration into building designs. Samsung's AMOLED panels offer exceptional color accuracy, with the ability to reproduce over 100% of the DCI-P3 color space[5]. They have developed advanced driver ICs that enable precise control of individual pixels, ensuring uniform brightness across large architectural displays[6]. Samsung's AMOLED technology also incorporates low-reflection films to enhance visibility in bright environments, making it suitable for outdoor architectural installations[7]. The company has demonstrated AMOLED displays with resolutions up to 4K for large-format architectural applications[8].
Strengths: Industry-leading AMOLED technology, high color accuracy, advanced driver ICs for large displays. Weaknesses: Premium pricing may limit widespread adoption in architectural projects, potential for burn-in with static content.
Core AMOLED Innovations
Organic light-emitting diode structure and fabrication method thereof, related display panel, and related display device
PatentWO2017070892A1
Innovation
- Addressing the low efficiency and short service time of blue light-emitting organic materials in AMOLED displays.
- Optimizing the OLED structure to enhance the performance of blue light-emitting components.
- Developing fabrication methods to overcome limitations in blue OLED performance.
Active matrix organic light emitting diode display panel structure
PatentActiveUS10181505B2
Innovation
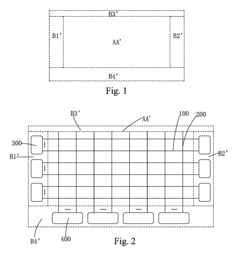
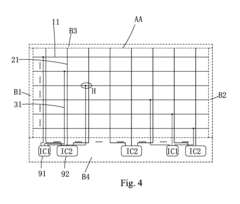
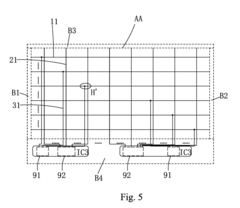
- The AMOLED display panel structure features ultra-narrow border frames by relocating row and column driving circuits to the lower border frame region, using vertically extending switching lines coupled to horizontally extending scan lines, and employing thin film packaging in the left, right, and upper border frames for packaging only, with a substrate and layers optimized for efficient signal transmission.
Architectural Integration
The integration of AMOLED technology into architectural design represents a significant advancement in creating seamless and visually striking building facades. AMOLED displays offer several advantages that make them particularly suitable for architectural applications, including their flexibility, thinness, and ability to produce vibrant colors with high contrast ratios.
One of the primary ways AMOLED supports seamless display design in architecture is through its ability to conform to curved surfaces. Unlike traditional rigid displays, AMOLED panels can be bent and shaped to follow the contours of a building's exterior. This flexibility allows architects to incorporate displays into unconventional building shapes without compromising the overall design aesthetic.
The thinness of AMOLED displays is another crucial factor in their architectural integration. With panels that can be less than a millimeter thick, AMOLED technology can be seamlessly embedded into building materials such as glass or composite panels. This integration creates a unified surface where the display becomes an integral part of the building's skin, rather than an add-on element.
AMOLED's superior color reproduction and contrast ratios contribute to its effectiveness in architectural applications. The technology's ability to produce deep blacks and vibrant colors ensures that displayed content remains visible and impactful even in bright outdoor environments. This characteristic is particularly valuable for buildings that aim to use their facades as dynamic communication platforms or artistic canvases.
Energy efficiency is another aspect where AMOLED technology excels in architectural integration. AMOLED displays consume power only for the pixels that are lit, which can result in significant energy savings for large-scale architectural implementations. This efficiency is crucial for sustainable building design and long-term operational costs.
The scalability of AMOLED technology allows for seamless integration across various building sizes and types. From small-scale installations on storefronts to massive displays covering entire skyscrapers, AMOLED can be adapted to suit diverse architectural needs. This versatility enables architects to create cohesive visual experiences that can transform the urban landscape.
Moreover, the durability and longevity of modern AMOLED displays make them suitable for long-term architectural applications. Advancements in materials and manufacturing processes have improved the resistance of AMOLED panels to environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and UV exposure, ensuring their viability in outdoor architectural settings.
One of the primary ways AMOLED supports seamless display design in architecture is through its ability to conform to curved surfaces. Unlike traditional rigid displays, AMOLED panels can be bent and shaped to follow the contours of a building's exterior. This flexibility allows architects to incorporate displays into unconventional building shapes without compromising the overall design aesthetic.
The thinness of AMOLED displays is another crucial factor in their architectural integration. With panels that can be less than a millimeter thick, AMOLED technology can be seamlessly embedded into building materials such as glass or composite panels. This integration creates a unified surface where the display becomes an integral part of the building's skin, rather than an add-on element.
AMOLED's superior color reproduction and contrast ratios contribute to its effectiveness in architectural applications. The technology's ability to produce deep blacks and vibrant colors ensures that displayed content remains visible and impactful even in bright outdoor environments. This characteristic is particularly valuable for buildings that aim to use their facades as dynamic communication platforms or artistic canvases.
Energy efficiency is another aspect where AMOLED technology excels in architectural integration. AMOLED displays consume power only for the pixels that are lit, which can result in significant energy savings for large-scale architectural implementations. This efficiency is crucial for sustainable building design and long-term operational costs.
The scalability of AMOLED technology allows for seamless integration across various building sizes and types. From small-scale installations on storefronts to massive displays covering entire skyscrapers, AMOLED can be adapted to suit diverse architectural needs. This versatility enables architects to create cohesive visual experiences that can transform the urban landscape.
Moreover, the durability and longevity of modern AMOLED displays make them suitable for long-term architectural applications. Advancements in materials and manufacturing processes have improved the resistance of AMOLED panels to environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and UV exposure, ensuring their viability in outdoor architectural settings.
Energy Efficiency Impact
The integration of AMOLED technology in architectural design has significant implications for energy efficiency. AMOLED displays are inherently more energy-efficient than traditional LCD screens, particularly when displaying darker content. This characteristic makes them ideal for seamless display designs in architecture, where large surfaces may need to be illuminated for extended periods.
In architectural applications, AMOLED displays can be programmed to show dynamic content that adapts to ambient light conditions. During bright daylight, the displays can operate at lower brightness levels, conserving energy while maintaining visibility. As natural light diminishes, the displays can gradually increase their luminance, ensuring optimal visibility without unnecessary power consumption.
The pixel-level control of AMOLED technology allows for precise management of energy usage. In architectural designs, this translates to the ability to illuminate only specific areas of a display surface, further reducing power consumption. For instance, in a building facade with integrated AMOLED displays, only the necessary pixels can be activated to create desired visual effects or convey information, while the rest remain off.
Moreover, AMOLED's superior contrast ratio and color reproduction capabilities mean that less overall brightness is required to achieve the same visual impact as traditional display technologies. This inherent efficiency contributes to reduced energy consumption in large-scale architectural implementations.
The thinness and flexibility of AMOLED panels also play a role in energy efficiency. These displays can be seamlessly integrated into building surfaces without the need for additional backlighting systems, which are typically energy-intensive. The elimination of these auxiliary lighting components not only streamlines the architectural design but also significantly reduces the overall power requirements of the display system.
In terms of long-term energy impact, AMOLED displays in architecture can contribute to building energy management systems. By integrating with smart building technologies, these displays can adjust their content and brightness based on factors such as time of day, weather conditions, and building occupancy. This dynamic adaptation ensures that energy is used efficiently throughout the building's operational lifecycle.
Furthermore, the longevity of AMOLED displays, when properly implemented, can lead to reduced replacement frequency compared to other lighting or display technologies. This durability translates to energy savings in manufacturing and installation processes over time, contributing to the overall energy efficiency of the architectural project.
In architectural applications, AMOLED displays can be programmed to show dynamic content that adapts to ambient light conditions. During bright daylight, the displays can operate at lower brightness levels, conserving energy while maintaining visibility. As natural light diminishes, the displays can gradually increase their luminance, ensuring optimal visibility without unnecessary power consumption.
The pixel-level control of AMOLED technology allows for precise management of energy usage. In architectural designs, this translates to the ability to illuminate only specific areas of a display surface, further reducing power consumption. For instance, in a building facade with integrated AMOLED displays, only the necessary pixels can be activated to create desired visual effects or convey information, while the rest remain off.
Moreover, AMOLED's superior contrast ratio and color reproduction capabilities mean that less overall brightness is required to achieve the same visual impact as traditional display technologies. This inherent efficiency contributes to reduced energy consumption in large-scale architectural implementations.
The thinness and flexibility of AMOLED panels also play a role in energy efficiency. These displays can be seamlessly integrated into building surfaces without the need for additional backlighting systems, which are typically energy-intensive. The elimination of these auxiliary lighting components not only streamlines the architectural design but also significantly reduces the overall power requirements of the display system.
In terms of long-term energy impact, AMOLED displays in architecture can contribute to building energy management systems. By integrating with smart building technologies, these displays can adjust their content and brightness based on factors such as time of day, weather conditions, and building occupancy. This dynamic adaptation ensures that energy is used efficiently throughout the building's operational lifecycle.
Furthermore, the longevity of AMOLED displays, when properly implemented, can lead to reduced replacement frequency compared to other lighting or display technologies. This durability translates to energy savings in manufacturing and installation processes over time, contributing to the overall energy efficiency of the architectural project.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!