Difference between AMOLED and IPS display technologies in efficiency.
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED vs IPS Background
Display technology has undergone significant advancements in recent years, with AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and IPS (In-Plane Switching) emerging as two prominent technologies in the market. These display technologies have revolutionized the way we interact with our devices, offering improved visual experiences across various applications.
AMOLED technology, first introduced in the early 2000s, utilizes organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. This self-emissive nature allows for individual pixel control, resulting in high contrast ratios and deep blacks. AMOLED displays have gained popularity in smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices due to their vibrant colors and energy efficiency in displaying dark content.
IPS technology, on the other hand, was developed in the mid-1990s as an improvement over traditional TFT LCD displays. It addresses the limited viewing angles and color shifts associated with earlier LCD technologies. IPS panels arrange liquid crystals in a parallel configuration, allowing for wider viewing angles and more accurate color reproduction. This technology has found widespread use in monitors, televisions, and various mobile devices.
Both AMOLED and IPS have evolved over time, with manufacturers continuously refining their respective technologies. AMOLED has seen improvements in pixel density, color accuracy, and longevity, while IPS has made strides in response times, contrast ratios, and power efficiency. The competition between these technologies has driven innovation in the display industry, benefiting consumers with better visual experiences across devices.
The efficiency of display technologies has become increasingly important in recent years, particularly in mobile devices where battery life is a critical factor. AMOLED's ability to selectively illuminate pixels has given it an advantage in power consumption, especially when displaying darker content. IPS displays, while traditionally less power-efficient, have made significant improvements in this area through advancements in backlighting technology and pixel design.
As the demand for high-quality displays continues to grow across various industries, including automotive, healthcare, and augmented reality, both AMOLED and IPS technologies are expected to play crucial roles. The ongoing development of these technologies focuses on addressing their respective limitations while capitalizing on their strengths to meet the evolving needs of consumers and industries alike.
Understanding the differences between AMOLED and IPS display technologies in terms of efficiency is crucial for device manufacturers, content creators, and end-users. This comparison not only influences device design and performance but also impacts user experience and energy consumption patterns in an increasingly connected world.
AMOLED technology, first introduced in the early 2000s, utilizes organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied. This self-emissive nature allows for individual pixel control, resulting in high contrast ratios and deep blacks. AMOLED displays have gained popularity in smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices due to their vibrant colors and energy efficiency in displaying dark content.
IPS technology, on the other hand, was developed in the mid-1990s as an improvement over traditional TFT LCD displays. It addresses the limited viewing angles and color shifts associated with earlier LCD technologies. IPS panels arrange liquid crystals in a parallel configuration, allowing for wider viewing angles and more accurate color reproduction. This technology has found widespread use in monitors, televisions, and various mobile devices.
Both AMOLED and IPS have evolved over time, with manufacturers continuously refining their respective technologies. AMOLED has seen improvements in pixel density, color accuracy, and longevity, while IPS has made strides in response times, contrast ratios, and power efficiency. The competition between these technologies has driven innovation in the display industry, benefiting consumers with better visual experiences across devices.
The efficiency of display technologies has become increasingly important in recent years, particularly in mobile devices where battery life is a critical factor. AMOLED's ability to selectively illuminate pixels has given it an advantage in power consumption, especially when displaying darker content. IPS displays, while traditionally less power-efficient, have made significant improvements in this area through advancements in backlighting technology and pixel design.
As the demand for high-quality displays continues to grow across various industries, including automotive, healthcare, and augmented reality, both AMOLED and IPS technologies are expected to play crucial roles. The ongoing development of these technologies focuses on addressing their respective limitations while capitalizing on their strengths to meet the evolving needs of consumers and industries alike.
Understanding the differences between AMOLED and IPS display technologies in terms of efficiency is crucial for device manufacturers, content creators, and end-users. This comparison not only influences device design and performance but also impacts user experience and energy consumption patterns in an increasingly connected world.
Display Market Analysis
The display market has witnessed significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for high-quality visual experiences across various devices. AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and IPS (In-Plane Switching) display technologies have emerged as two dominant players in this competitive landscape, each offering unique advantages in terms of efficiency and performance.
The global display market size was valued at over $100 billion in 2020, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. This expansion is fueled by the rising adoption of smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and other consumer electronics that rely heavily on advanced display technologies. AMOLED and IPS displays collectively account for a substantial portion of this market, with their applications spanning across mobile devices, televisions, monitors, and automotive displays.
AMOLED technology has gained significant traction in the high-end smartphone segment, with major manufacturers like Samsung and Apple incorporating it into their flagship devices. The AMOLED market share in smartphones has been steadily increasing, driven by the technology's superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency for displaying dark content. This trend is expected to continue as production costs decrease and manufacturing capabilities improve.
IPS displays, on the other hand, maintain a strong presence in the mid-range smartphone market and dominate the LCD TV and monitor segments. The technology's wide viewing angles, accurate color representation, and cost-effectiveness have contributed to its sustained popularity. IPS displays are particularly prevalent in larger screen applications, where their consistent performance across different viewing angles is highly valued.
In terms of efficiency, AMOLED displays generally consume less power when displaying darker content, making them particularly suitable for mobile devices where battery life is a critical factor. This characteristic has led to increased adoption in wearable devices and smartphones with always-on display features. However, IPS displays tend to be more energy-efficient when displaying brighter content, which can be advantageous in certain use cases and environments.
The automotive industry has emerged as a significant growth driver for both AMOLED and IPS technologies. As vehicles become more technologically advanced, the demand for high-quality, efficient displays for infotainment systems and digital dashboards has surged. Both technologies are competing in this space, with AMOLED gaining ground due to its flexibility and potential for curved or foldable displays, while IPS maintains its position with its reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Looking ahead, the display market is poised for further innovation and competition between AMOLED and IPS technologies. Manufacturers are investing heavily in research and development to enhance the efficiency, durability, and performance of both display types. As production processes improve and economies of scale are realized, the cost gap between AMOLED and IPS displays is expected to narrow, potentially reshaping market dynamics and consumer preferences in the coming years.
The global display market size was valued at over $100 billion in 2020, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. This expansion is fueled by the rising adoption of smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and other consumer electronics that rely heavily on advanced display technologies. AMOLED and IPS displays collectively account for a substantial portion of this market, with their applications spanning across mobile devices, televisions, monitors, and automotive displays.
AMOLED technology has gained significant traction in the high-end smartphone segment, with major manufacturers like Samsung and Apple incorporating it into their flagship devices. The AMOLED market share in smartphones has been steadily increasing, driven by the technology's superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency for displaying dark content. This trend is expected to continue as production costs decrease and manufacturing capabilities improve.
IPS displays, on the other hand, maintain a strong presence in the mid-range smartphone market and dominate the LCD TV and monitor segments. The technology's wide viewing angles, accurate color representation, and cost-effectiveness have contributed to its sustained popularity. IPS displays are particularly prevalent in larger screen applications, where their consistent performance across different viewing angles is highly valued.
In terms of efficiency, AMOLED displays generally consume less power when displaying darker content, making them particularly suitable for mobile devices where battery life is a critical factor. This characteristic has led to increased adoption in wearable devices and smartphones with always-on display features. However, IPS displays tend to be more energy-efficient when displaying brighter content, which can be advantageous in certain use cases and environments.
The automotive industry has emerged as a significant growth driver for both AMOLED and IPS technologies. As vehicles become more technologically advanced, the demand for high-quality, efficient displays for infotainment systems and digital dashboards has surged. Both technologies are competing in this space, with AMOLED gaining ground due to its flexibility and potential for curved or foldable displays, while IPS maintains its position with its reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Looking ahead, the display market is poised for further innovation and competition between AMOLED and IPS technologies. Manufacturers are investing heavily in research and development to enhance the efficiency, durability, and performance of both display types. As production processes improve and economies of scale are realized, the cost gap between AMOLED and IPS displays is expected to narrow, potentially reshaping market dynamics and consumer preferences in the coming years.
Technical Challenges
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and IPS (In-Plane Switching) display technologies face distinct technical challenges in terms of efficiency. These challenges stem from their fundamental differences in structure and operation.
AMOLED displays encounter issues with power consumption, particularly when displaying bright or white content. Each pixel in an AMOLED screen emits its own light, consuming more power for brighter colors. This can lead to increased battery drain, especially on devices with large screens or those frequently displaying bright content.
Another significant challenge for AMOLED is the potential for burn-in or image retention. Static elements on the screen can cause uneven wear on the organic compounds, resulting in permanent ghosting effects. This issue is particularly problematic for devices with constant on-screen elements, such as smartphones or televisions.
IPS displays, on the other hand, face efficiency challenges related to their backlighting system. The constant illumination required by the LCD panel results in higher power consumption, especially when displaying darker content. This inefficiency is due to the need to block light for dark areas of the screen, rather than simply turning off pixels as in AMOLED displays.
Color accuracy and contrast ratio present ongoing challenges for both technologies. AMOLED displays often struggle with color shift at different viewing angles, while IPS displays may have difficulty achieving the deep blacks and high contrast ratios of AMOLED screens.
Manufacturing complexity and yield rates pose significant challenges for both technologies. AMOLED displays require precise deposition of organic materials, which can be difficult to scale efficiently. IPS displays, while more established, still face challenges in achieving uniform backlighting and minimizing light leakage.
Longevity and degradation are areas of concern, particularly for AMOLED technology. The organic compounds used in AMOLED displays can degrade over time, leading to reduced brightness and color accuracy. IPS displays generally have longer lifespans but may suffer from backlight degradation over extended periods.
Both technologies also face challenges in achieving higher refresh rates and response times while maintaining energy efficiency. This is particularly important for applications such as gaming and virtual reality, where smooth motion and low latency are crucial.
In summary, while both AMOLED and IPS display technologies have made significant advancements, they continue to face unique technical challenges in achieving optimal efficiency. Overcoming these hurdles remains a key focus for researchers and manufacturers in the display industry.
AMOLED displays encounter issues with power consumption, particularly when displaying bright or white content. Each pixel in an AMOLED screen emits its own light, consuming more power for brighter colors. This can lead to increased battery drain, especially on devices with large screens or those frequently displaying bright content.
Another significant challenge for AMOLED is the potential for burn-in or image retention. Static elements on the screen can cause uneven wear on the organic compounds, resulting in permanent ghosting effects. This issue is particularly problematic for devices with constant on-screen elements, such as smartphones or televisions.
IPS displays, on the other hand, face efficiency challenges related to their backlighting system. The constant illumination required by the LCD panel results in higher power consumption, especially when displaying darker content. This inefficiency is due to the need to block light for dark areas of the screen, rather than simply turning off pixels as in AMOLED displays.
Color accuracy and contrast ratio present ongoing challenges for both technologies. AMOLED displays often struggle with color shift at different viewing angles, while IPS displays may have difficulty achieving the deep blacks and high contrast ratios of AMOLED screens.
Manufacturing complexity and yield rates pose significant challenges for both technologies. AMOLED displays require precise deposition of organic materials, which can be difficult to scale efficiently. IPS displays, while more established, still face challenges in achieving uniform backlighting and minimizing light leakage.
Longevity and degradation are areas of concern, particularly for AMOLED technology. The organic compounds used in AMOLED displays can degrade over time, leading to reduced brightness and color accuracy. IPS displays generally have longer lifespans but may suffer from backlight degradation over extended periods.
Both technologies also face challenges in achieving higher refresh rates and response times while maintaining energy efficiency. This is particularly important for applications such as gaming and virtual reality, where smooth motion and low latency are crucial.
In summary, while both AMOLED and IPS display technologies have made significant advancements, they continue to face unique technical challenges in achieving optimal efficiency. Overcoming these hurdles remains a key focus for researchers and manufacturers in the display industry.
Current Efficiency Solutions
01 Power efficiency comparison between AMOLED and IPS
AMOLED displays generally offer better power efficiency compared to IPS displays, especially when displaying dark content. This is because AMOLED pixels emit their own light and can be turned off completely for black pixels, while IPS displays require constant backlighting. However, IPS displays may be more power-efficient when displaying bright content.- Power efficiency comparison between AMOLED and IPS: AMOLED displays generally offer better power efficiency compared to IPS displays, especially when displaying dark content. This is because AMOLED pixels emit their own light and can be turned off completely for black pixels, while IPS displays require constant backlighting. The power consumption difference is particularly noticeable in mobile devices and can significantly impact battery life.
- Color reproduction and contrast ratio: AMOLED displays typically provide better color reproduction and higher contrast ratios compared to IPS displays. This is due to the ability of AMOLED pixels to produce true blacks by turning off completely, resulting in infinite contrast ratios. IPS displays, while offering good color accuracy, struggle to achieve the same level of contrast and deep blacks as AMOLED technology.
- Pixel structure and subpixel arrangement: The efficiency of both AMOLED and IPS displays is influenced by their pixel structure and subpixel arrangement. AMOLED displays often use a PenTile matrix, which can affect perceived resolution and color accuracy. IPS displays typically use an RGB stripe arrangement, which can provide better sharpness for text and fine details. The choice of subpixel layout impacts power consumption and overall display quality.
- Refresh rate and response time: AMOLED displays generally offer faster refresh rates and shorter response times compared to IPS displays. This results in smoother motion and reduced motion blur, which is particularly beneficial for gaming and high-frame-rate content. The faster pixel response of AMOLED technology contributes to its overall efficiency in displaying dynamic content.
- Manufacturing processes and cost efficiency: The manufacturing processes for AMOLED and IPS displays differ significantly, impacting their cost efficiency and scalability. AMOLED displays are generally more expensive to produce due to complex manufacturing processes and lower yields. IPS displays benefit from more mature manufacturing techniques, making them more cost-effective for mass production. These factors influence the adoption of each technology in different market segments and device categories.
02 Pixel structure and light emission in AMOLED displays
AMOLED displays use organic light-emitting diodes for each pixel, allowing for individual pixel control and true blacks. The pixel structure typically includes multiple sub-pixels (red, green, and blue) and may incorporate additional elements for improved efficiency, such as micro-cavities or color filters.Expand Specific Solutions03 IPS display technology and backlight efficiency
IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays use a backlight and liquid crystal alignment to produce images. Efforts to improve efficiency in IPS displays focus on enhancing backlight technology, optimizing liquid crystal alignment, and implementing advanced light management techniques such as local dimming.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hybrid and advanced display technologies
Researchers are exploring hybrid and advanced display technologies that combine elements of AMOLED and IPS or introduce new concepts to improve efficiency. These may include quantum dot-enhanced displays, micro-LED displays, or novel pixel architectures that aim to maximize energy efficiency while maintaining image quality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Display driver and power management techniques
Efficiency in both AMOLED and IPS displays can be improved through advanced display driver ICs and power management techniques. These may include adaptive refresh rates, dynamic voltage scaling, and intelligent content-aware power management algorithms that optimize power consumption based on displayed content and ambient conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Display Manufacturers
The competition in AMOLED and IPS display technologies is characterized by a mature market with significant growth potential. The industry is in a phase of continuous innovation, with major players like Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE Technology Group leading the charge. The global market size for these technologies is substantial, driven by increasing demand in smartphones, televisions, and other consumer electronics. Technologically, AMOLED is gaining ground due to its superior color reproduction and energy efficiency, while IPS remains competitive in terms of cost and wide-angle viewing. Companies like Sharp, Innolux, and AUO are also making significant contributions to the advancement of these display technologies, focusing on improving efficiency and performance.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has been advancing both AMOLED and IPS technologies. In AMOLED, they've developed flexible OLED displays with reduced power consumption through optimized pixel circuits and driving methods[7]. Their IPS displays feature Advanced Super Dimension Switch (ADS) technology, which improves viewing angles and contrast ratios compared to traditional IPS[8]. BOE has also introduced oxide semiconductor backplanes for both AMOLED and IPS displays, enhancing electron mobility and reducing power consumption[9].
Strengths: Strong presence in both AMOLED and IPS markets, with innovative technologies in both fields. Weaknesses: Still catching up to market leaders in AMOLED production yield and quality.
LG Display Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Display has made significant strides in both AMOLED and IPS technologies. For AMOLED, they've developed WRGB OLED technology, which adds a white sub-pixel to the traditional RGB structure, improving brightness and energy efficiency[4]. In the IPS realm, LG has introduced Nano IPS technology, which uses nano-particles to absorb excess light wavelengths, enhancing color purity and viewing angles[5]. Their Advanced In-Cell Touch (AIT) technology for IPS displays integrates touch sensors directly into the LCD panel, reducing thickness and improving optical performance[6].
Strengths: Expertise in both AMOLED and IPS, allowing for diverse product offerings. Weaknesses: WRGB OLED may have lower color volume compared to RGB OLED.
Core Display Innovations
Amoled double-side display
PatentActiveUS20200219957A1
Innovation
- An AMOLED double-sided display design featuring a substrate with alternating top-emitting and bottom-emitting OLED units, where the anode of top-emitting units is thicker and reflective, and the cathode of bottom-emitting units is thicker and light-transmissive, allowing for single IC control and eliminating mirrored images.
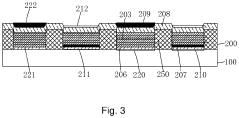
Yield enchancement pixel structure for active matrix organic light-emitting diode displays
PatentInactiveUS6731064B2
Innovation
- Passivating the entire active array surface with an insulating layer, such as PECVD deposited SiOx or SiNx, that is patterned and etched to completely cover the lower electrode sidewalls with a shallow taper, preventing electrical shorts and enhancing chemical robustness and optical efficiency.
Power Consumption Analysis
Power consumption is a critical factor in comparing the efficiency of AMOLED and IPS display technologies. AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays generally consume less power than IPS (In-Plane Switching) LCD displays, particularly when displaying darker content.
AMOLED displays have a significant advantage in power efficiency due to their emissive nature. Each pixel in an AMOLED display emits its own light, allowing for selective pixel illumination. When displaying black or dark colors, AMOLED pixels can be turned off completely, resulting in minimal power consumption for those areas. This characteristic makes AMOLED displays particularly energy-efficient when displaying content with dark themes or black backgrounds.
In contrast, IPS LCD displays require a constant backlight to illuminate the entire screen, regardless of the content being displayed. This backlight consumes a consistent amount of power, even when showing dark or black images. As a result, IPS displays tend to consume more power overall, especially when displaying darker content.
However, the power consumption dynamics change when displaying brighter content. AMOLED displays consume more power as the brightness of the displayed content increases, since each pixel needs to emit more light. In scenarios where the screen is predominantly white or very bright, AMOLED displays may consume more power than IPS displays.
IPS displays maintain a relatively constant power consumption across different content types due to the consistent backlight. This can make them more power-efficient when displaying predominantly bright or white content. The power consumption of IPS displays is primarily influenced by the backlight intensity rather than the specific colors being displayed.
It's worth noting that advancements in both technologies have led to improvements in power efficiency. Newer AMOLED displays incorporate more efficient organic materials and pixel structures, reducing power consumption even at higher brightness levels. Similarly, IPS displays have seen enhancements in backlight technology and pixel design, leading to improved overall efficiency.
The choice between AMOLED and IPS in terms of power efficiency often depends on the specific use case and typical content displayed. For devices that frequently show darker content or utilize dark themes, AMOLED displays generally offer superior power efficiency. However, for applications with predominantly bright interfaces, the difference in power consumption between the two technologies may be less pronounced.
AMOLED displays have a significant advantage in power efficiency due to their emissive nature. Each pixel in an AMOLED display emits its own light, allowing for selective pixel illumination. When displaying black or dark colors, AMOLED pixels can be turned off completely, resulting in minimal power consumption for those areas. This characteristic makes AMOLED displays particularly energy-efficient when displaying content with dark themes or black backgrounds.
In contrast, IPS LCD displays require a constant backlight to illuminate the entire screen, regardless of the content being displayed. This backlight consumes a consistent amount of power, even when showing dark or black images. As a result, IPS displays tend to consume more power overall, especially when displaying darker content.
However, the power consumption dynamics change when displaying brighter content. AMOLED displays consume more power as the brightness of the displayed content increases, since each pixel needs to emit more light. In scenarios where the screen is predominantly white or very bright, AMOLED displays may consume more power than IPS displays.
IPS displays maintain a relatively constant power consumption across different content types due to the consistent backlight. This can make them more power-efficient when displaying predominantly bright or white content. The power consumption of IPS displays is primarily influenced by the backlight intensity rather than the specific colors being displayed.
It's worth noting that advancements in both technologies have led to improvements in power efficiency. Newer AMOLED displays incorporate more efficient organic materials and pixel structures, reducing power consumption even at higher brightness levels. Similarly, IPS displays have seen enhancements in backlight technology and pixel design, leading to improved overall efficiency.
The choice between AMOLED and IPS in terms of power efficiency often depends on the specific use case and typical content displayed. For devices that frequently show darker content or utilize dark themes, AMOLED displays generally offer superior power efficiency. However, for applications with predominantly bright interfaces, the difference in power consumption between the two technologies may be less pronounced.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of display technologies is a crucial consideration in the ongoing debate between AMOLED and IPS displays. AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and IPS (In-Plane Switching) technologies differ significantly in their energy consumption patterns and manufacturing processes, which directly influence their ecological footprint.
AMOLED displays are known for their energy efficiency, particularly when displaying darker content. This is due to their ability to turn off individual pixels completely, resulting in true blacks and reduced power consumption. In contrast, IPS displays require constant backlighting, even for dark scenes, leading to higher energy consumption across all types of content. This difference in power efficiency translates to longer battery life in devices using AMOLED displays, potentially reducing the frequency of charging cycles and, by extension, the overall energy demand over the device's lifetime.
However, the manufacturing process of AMOLED displays is more complex and resource-intensive compared to IPS. The production of organic materials used in AMOLED panels requires specialized facilities and involves more steps, potentially leading to higher energy consumption and waste generation during manufacturing. IPS displays, being based on more established LCD technology, benefit from optimized production processes that may have a lower environmental impact in terms of manufacturing emissions and resource utilization.
The lifespan of the display technology also plays a crucial role in its environmental impact. AMOLED displays are susceptible to burn-in and color degradation over time, which may lead to earlier replacement of devices. IPS displays, on the other hand, tend to have longer lifespans with more consistent performance, potentially reducing electronic waste generation.
Recycling and disposal considerations further differentiate the environmental profiles of these technologies. AMOLED displays contain organic compounds that may require specialized recycling processes, while IPS displays are composed of more common materials that fit into established recycling streams. The presence of rare earth elements in both technologies poses challenges for sustainable resource management and necessitates the development of efficient recycling methods.
As the display industry evolves, both AMOLED and IPS technologies are undergoing continuous improvements aimed at enhancing their environmental performance. Manufacturers are investing in research to develop more eco-friendly production methods, increase energy efficiency, and improve the recyclability of display components. The ultimate environmental impact of these technologies will depend on ongoing innovations in materials science, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life management strategies.
AMOLED displays are known for their energy efficiency, particularly when displaying darker content. This is due to their ability to turn off individual pixels completely, resulting in true blacks and reduced power consumption. In contrast, IPS displays require constant backlighting, even for dark scenes, leading to higher energy consumption across all types of content. This difference in power efficiency translates to longer battery life in devices using AMOLED displays, potentially reducing the frequency of charging cycles and, by extension, the overall energy demand over the device's lifetime.
However, the manufacturing process of AMOLED displays is more complex and resource-intensive compared to IPS. The production of organic materials used in AMOLED panels requires specialized facilities and involves more steps, potentially leading to higher energy consumption and waste generation during manufacturing. IPS displays, being based on more established LCD technology, benefit from optimized production processes that may have a lower environmental impact in terms of manufacturing emissions and resource utilization.
The lifespan of the display technology also plays a crucial role in its environmental impact. AMOLED displays are susceptible to burn-in and color degradation over time, which may lead to earlier replacement of devices. IPS displays, on the other hand, tend to have longer lifespans with more consistent performance, potentially reducing electronic waste generation.
Recycling and disposal considerations further differentiate the environmental profiles of these technologies. AMOLED displays contain organic compounds that may require specialized recycling processes, while IPS displays are composed of more common materials that fit into established recycling streams. The presence of rare earth elements in both technologies poses challenges for sustainable resource management and necessitates the development of efficient recycling methods.
As the display industry evolves, both AMOLED and IPS technologies are undergoing continuous improvements aimed at enhancing their environmental performance. Manufacturers are investing in research to develop more eco-friendly production methods, increase energy efficiency, and improve the recyclability of display components. The ultimate environmental impact of these technologies will depend on ongoing innovations in materials science, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life management strategies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!