New panel configurations for maximizing AMOLED efficiency.
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Efficiency Evolution
The evolution of AMOLED efficiency has been a critical focus in display technology development over the past decade. Initially, AMOLED displays faced challenges in power consumption and brightness compared to traditional LCD technology. However, continuous advancements have led to significant improvements in efficiency and overall performance.
In the early stages of AMOLED development, the primary focus was on enhancing the organic materials used in the emissive layers. Researchers worked on developing more stable and efficient organic compounds, which resulted in improved luminous efficacy and longer lifespans for AMOLED panels. This phase saw the introduction of phosphorescent materials, which offered higher internal quantum efficiency compared to fluorescent counterparts.
As the technology matured, attention shifted towards optimizing the device architecture. The introduction of tandem OLED structures, where multiple emissive units are stacked vertically, allowed for higher current efficiency and extended device lifetime. This approach effectively doubled the light output for a given current, significantly improving overall panel efficiency.
Another crucial advancement in AMOLED efficiency came with the development of more sophisticated thin-film transistor (TFT) backplanes. The transition from amorphous silicon (a-Si) to low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) and oxide TFTs enabled higher electron mobility and better current uniformity across the display. This improvement in backplane technology directly contributed to enhanced power efficiency and image quality.
The integration of advanced optical designs has also played a vital role in AMOLED efficiency evolution. Microcavity structures and light outcoupling technologies have been implemented to reduce internal light reflection and improve light extraction from the OLED stack. These optical enhancements have led to substantial gains in external quantum efficiency, allowing AMOLED displays to produce brighter images with lower power consumption.
Recent years have seen a focus on color management and subpixel arrangements to further optimize AMOLED efficiency. The development of RGBW (Red, Green, Blue, White) pixel structures and the implementation of advanced color filters have enabled displays to achieve higher peak brightness while maintaining power efficiency. Additionally, the use of AI-driven algorithms for content-adaptive brightness and color adjustment has contributed to real-time optimization of display performance and energy consumption.
Looking ahead, the AMOLED efficiency evolution is expected to continue with the exploration of new materials such as TADF (Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence) emitters and the potential integration of quantum dot technology. These advancements promise to push the boundaries of AMOLED efficiency even further, paving the way for next-generation displays with unprecedented performance and energy efficiency.
In the early stages of AMOLED development, the primary focus was on enhancing the organic materials used in the emissive layers. Researchers worked on developing more stable and efficient organic compounds, which resulted in improved luminous efficacy and longer lifespans for AMOLED panels. This phase saw the introduction of phosphorescent materials, which offered higher internal quantum efficiency compared to fluorescent counterparts.
As the technology matured, attention shifted towards optimizing the device architecture. The introduction of tandem OLED structures, where multiple emissive units are stacked vertically, allowed for higher current efficiency and extended device lifetime. This approach effectively doubled the light output for a given current, significantly improving overall panel efficiency.
Another crucial advancement in AMOLED efficiency came with the development of more sophisticated thin-film transistor (TFT) backplanes. The transition from amorphous silicon (a-Si) to low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) and oxide TFTs enabled higher electron mobility and better current uniformity across the display. This improvement in backplane technology directly contributed to enhanced power efficiency and image quality.
The integration of advanced optical designs has also played a vital role in AMOLED efficiency evolution. Microcavity structures and light outcoupling technologies have been implemented to reduce internal light reflection and improve light extraction from the OLED stack. These optical enhancements have led to substantial gains in external quantum efficiency, allowing AMOLED displays to produce brighter images with lower power consumption.
Recent years have seen a focus on color management and subpixel arrangements to further optimize AMOLED efficiency. The development of RGBW (Red, Green, Blue, White) pixel structures and the implementation of advanced color filters have enabled displays to achieve higher peak brightness while maintaining power efficiency. Additionally, the use of AI-driven algorithms for content-adaptive brightness and color adjustment has contributed to real-time optimization of display performance and energy consumption.
Looking ahead, the AMOLED efficiency evolution is expected to continue with the exploration of new materials such as TADF (Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence) emitters and the potential integration of quantum dot technology. These advancements promise to push the boundaries of AMOLED efficiency even further, paving the way for next-generation displays with unprecedented performance and energy efficiency.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for new panel configurations to maximize AMOLED efficiency is driven by several key factors in the display industry. As consumer electronics continue to evolve, there is an increasing emphasis on energy efficiency, longer battery life, and improved display quality. AMOLED technology has gained significant traction in recent years due to its superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and potential for energy savings compared to traditional LCD displays.
The smartphone market, being the largest consumer of AMOLED panels, is a primary driver of demand for more efficient configurations. With the global smartphone market expected to reach over 1.5 billion units annually in the coming years, manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to differentiate their products and improve user experience. Enhanced AMOLED efficiency translates to longer battery life, which is a crucial selling point for consumers.
Beyond smartphones, the demand for efficient AMOLED panels is expanding into other product categories. The wearable technology market, including smartwatches and fitness trackers, is experiencing rapid growth and requires displays that are both energy-efficient and visually appealing. Similarly, the automotive industry is increasingly adopting AMOLED displays for infotainment systems and digital dashboards, where energy efficiency is critical for electric vehicles.
The television market is another significant area driving demand for improved AMOLED efficiency. As consumers seek larger screens with higher resolutions, the energy consumption of these devices becomes a growing concern. More efficient AMOLED configurations can help mitigate this issue, making large-format OLED TVs more attractive and environmentally friendly.
In the commercial and industrial sectors, there is a rising demand for efficient AMOLED displays in applications such as digital signage, professional monitors, and medical imaging devices. These markets value the combination of high image quality and low power consumption that advanced AMOLED configurations can offer.
The global push for sustainability and energy conservation is also influencing market demand. Governments and regulatory bodies are implementing stricter energy efficiency standards for electronic devices, creating additional pressure on manufacturers to adopt more efficient display technologies.
From a market size perspective, the global AMOLED display market is projected to grow significantly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of AMOLED technology across various industries and the continuous improvement in panel efficiency. The demand for new, more efficient panel configurations is expected to be a key driver of innovation and competition among display manufacturers.
The smartphone market, being the largest consumer of AMOLED panels, is a primary driver of demand for more efficient configurations. With the global smartphone market expected to reach over 1.5 billion units annually in the coming years, manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to differentiate their products and improve user experience. Enhanced AMOLED efficiency translates to longer battery life, which is a crucial selling point for consumers.
Beyond smartphones, the demand for efficient AMOLED panels is expanding into other product categories. The wearable technology market, including smartwatches and fitness trackers, is experiencing rapid growth and requires displays that are both energy-efficient and visually appealing. Similarly, the automotive industry is increasingly adopting AMOLED displays for infotainment systems and digital dashboards, where energy efficiency is critical for electric vehicles.
The television market is another significant area driving demand for improved AMOLED efficiency. As consumers seek larger screens with higher resolutions, the energy consumption of these devices becomes a growing concern. More efficient AMOLED configurations can help mitigate this issue, making large-format OLED TVs more attractive and environmentally friendly.
In the commercial and industrial sectors, there is a rising demand for efficient AMOLED displays in applications such as digital signage, professional monitors, and medical imaging devices. These markets value the combination of high image quality and low power consumption that advanced AMOLED configurations can offer.
The global push for sustainability and energy conservation is also influencing market demand. Governments and regulatory bodies are implementing stricter energy efficiency standards for electronic devices, creating additional pressure on manufacturers to adopt more efficient display technologies.
From a market size perspective, the global AMOLED display market is projected to grow significantly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of AMOLED technology across various industries and the continuous improvement in panel efficiency. The demand for new, more efficient panel configurations is expected to be a key driver of innovation and competition among display manufacturers.
Current AMOLED Challenges
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has revolutionized display panels, offering superior image quality, energy efficiency, and form factor flexibility. However, as the demand for higher performance and more sustainable devices grows, AMOLED faces several significant challenges that need to be addressed to maximize its efficiency and maintain its competitive edge in the display market.
One of the primary challenges is the issue of differential aging among the organic materials used in AMOLED displays. Red, green, and blue subpixels degrade at different rates over time, leading to color shifts and potential burn-in effects. This non-uniform aging process not only affects the display's longevity but also impacts the overall efficiency of the panel, as compensating for these effects often requires increased power consumption.
Power efficiency remains a critical concern, particularly for mobile devices where battery life is paramount. While AMOLED displays are generally more energy-efficient than their LCD counterparts, there is still significant room for improvement. The challenge lies in reducing power consumption without compromising on brightness, color accuracy, or resolution. This is especially crucial as display resolutions continue to increase, demanding more power from each pixel.
Another major hurdle is the blue OLED material's relatively short lifespan compared to red and green OLEDs. Blue OLEDs typically degrade faster, which not only affects color balance but also overall panel efficiency. Developing more stable and efficient blue OLED materials is a key focus area for researchers and manufacturers alike.
Manufacturing challenges also persist, particularly in achieving high yields for large-size AMOLED panels. The complexity of the AMOLED structure, combined with the need for precise deposition of organic materials, makes large-scale production difficult and costly. This challenge is especially pronounced as the industry moves towards larger displays for televisions and monitors.
Heat management is another significant issue facing AMOLED technology. As displays become brighter and more power-dense, managing the heat generated becomes increasingly important. Excessive heat can accelerate the degradation of organic materials, reducing the display's lifespan and efficiency. Developing effective heat dissipation methods without adding bulk to the slim profile of AMOLED panels is a complex engineering challenge.
Lastly, the environmental impact of AMOLED production and disposal is a growing concern. The use of rare materials and the difficulty in recycling OLED panels pose sustainability challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the long-term viability of the technology.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches to panel design, material science, and manufacturing processes. The industry is actively exploring new panel configurations, advanced materials, and novel fabrication techniques to overcome these hurdles and push the boundaries of AMOLED efficiency.
One of the primary challenges is the issue of differential aging among the organic materials used in AMOLED displays. Red, green, and blue subpixels degrade at different rates over time, leading to color shifts and potential burn-in effects. This non-uniform aging process not only affects the display's longevity but also impacts the overall efficiency of the panel, as compensating for these effects often requires increased power consumption.
Power efficiency remains a critical concern, particularly for mobile devices where battery life is paramount. While AMOLED displays are generally more energy-efficient than their LCD counterparts, there is still significant room for improvement. The challenge lies in reducing power consumption without compromising on brightness, color accuracy, or resolution. This is especially crucial as display resolutions continue to increase, demanding more power from each pixel.
Another major hurdle is the blue OLED material's relatively short lifespan compared to red and green OLEDs. Blue OLEDs typically degrade faster, which not only affects color balance but also overall panel efficiency. Developing more stable and efficient blue OLED materials is a key focus area for researchers and manufacturers alike.
Manufacturing challenges also persist, particularly in achieving high yields for large-size AMOLED panels. The complexity of the AMOLED structure, combined with the need for precise deposition of organic materials, makes large-scale production difficult and costly. This challenge is especially pronounced as the industry moves towards larger displays for televisions and monitors.
Heat management is another significant issue facing AMOLED technology. As displays become brighter and more power-dense, managing the heat generated becomes increasingly important. Excessive heat can accelerate the degradation of organic materials, reducing the display's lifespan and efficiency. Developing effective heat dissipation methods without adding bulk to the slim profile of AMOLED panels is a complex engineering challenge.
Lastly, the environmental impact of AMOLED production and disposal is a growing concern. The use of rare materials and the difficulty in recycling OLED panels pose sustainability challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the long-term viability of the technology.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches to panel design, material science, and manufacturing processes. The industry is actively exploring new panel configurations, advanced materials, and novel fabrication techniques to overcome these hurdles and push the boundaries of AMOLED efficiency.
Existing Efficiency Solutions
01 Pixel circuit design for improved efficiency
Advanced pixel circuit designs are implemented to enhance the efficiency of AMOLED panels. These designs focus on optimizing the driving method of OLED pixels, reducing power consumption, and improving overall display performance. Techniques such as compensation circuits and voltage programming are utilized to achieve better uniformity and longevity of the display.- Pixel circuit design for improved efficiency: Advanced pixel circuit designs are implemented to enhance the efficiency of AMOLED panels. These designs focus on optimizing the driving method of OLED pixels, reducing power consumption, and improving overall display performance. Techniques such as compensation circuits and voltage programming are utilized to achieve better uniformity and longevity of the display.
- Organic material optimization: The efficiency of AMOLED panels is improved through the development and use of advanced organic materials. These materials are designed to enhance light emission efficiency, color purity, and lifetime of the OLED elements. Research focuses on creating new organic compounds and optimizing their molecular structures to achieve better performance in AMOLED displays.
- Thin-film transistor (TFT) technology: Advancements in thin-film transistor technology contribute to the increased efficiency of AMOLED panels. High-performance TFTs, such as low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) or oxide TFTs, are developed to improve electron mobility, reduce power consumption, and enhance the overall performance of the display. These improvements lead to better image quality and energy efficiency.
- Power management and driving schemes: Innovative power management techniques and driving schemes are implemented to optimize the energy efficiency of AMOLED panels. These include adaptive brightness control, dynamic refresh rate adjustment, and intelligent power distribution systems. Such approaches help reduce overall power consumption while maintaining high display quality.
- Light extraction and optical enhancements: Various optical enhancements and light extraction techniques are employed to improve the efficiency of AMOLED panels. These include the use of microlens arrays, nanostructures, and specialized optical films to increase light output and reduce internal reflections. Such improvements lead to higher brightness and better energy efficiency in AMOLED displays.
02 OLED material and structure optimization
Efficiency improvements in AMOLED panels are achieved through the optimization of OLED materials and structures. This includes developing new organic light-emitting materials, enhancing the layer structure of OLEDs, and improving electron and hole transport layers. These advancements result in higher luminous efficiency and extended lifespan of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions03 Power management and driving schemes
Innovative power management techniques and driving schemes are employed to increase the efficiency of AMOLED panels. These methods involve optimizing the power supply to individual pixels, implementing adaptive brightness control, and utilizing advanced timing controllers. Such approaches help reduce power consumption while maintaining image quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Thermal management for enhanced efficiency
Effective thermal management strategies are developed to improve the efficiency and longevity of AMOLED panels. These include innovative heat dissipation structures, temperature-sensitive driving methods, and the use of thermally conductive materials. By managing heat generation and dissipation, the overall performance and lifespan of AMOLED displays are enhanced.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of energy-saving features
AMOLED panels incorporate various energy-saving features to boost overall efficiency. These include selective pixel dimming, dynamic refresh rate adjustment, and intelligent power-saving modes. By implementing these features, AMOLED displays can significantly reduce power consumption without compromising visual quality, especially in mobile and wearable devices.Expand Specific Solutions
Key AMOLED Manufacturers
The competition landscape for new panel configurations to maximize AMOLED efficiency is characterized by intense rivalry among major players in a rapidly evolving market. The industry is in a growth phase, with increasing demand for high-efficiency displays driving innovation. Market size is expanding, fueled by applications in smartphones, wearables, and automotive sectors. Technologically, advancements are ongoing, with companies like Samsung Display, BOE Technology, and LG Display leading in R&D. Emerging players such as Visionox and Tianma are also making significant strides. The technology's maturity varies, with established firms having a competitive edge, while newer entrants focus on niche innovations to gain market share.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed innovative panel configurations for AMOLED efficiency maximization. Their approach includes the use of advanced pixel structures, such as RGBW (Red, Green, Blue, White) arrangements, which can increase light transmission by up to 30% compared to traditional RGB layouts[1]. BOE has also implemented micro-lens array (MLA) technology, which enhances light extraction efficiency by redirecting light that would otherwise be trapped within the OLED structure. This technology has shown to improve overall panel efficiency by 10-15%[3]. Additionally, BOE has introduced a novel cathode structure using silver nanowires, which reduces electrical resistance and improves current distribution across the panel, resulting in more uniform brightness and increased power efficiency[5].
Strengths: Advanced pixel structures and MLA technology significantly boost light efficiency. The silver nanowire cathode improves current distribution and uniformity. Weaknesses: Implementation costs may be higher, potentially affecting market competitiveness in the short term.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has pioneered several technologies to maximize AMOLED efficiency. Their latest innovation includes the implementation of quantum dot color conversion (QDCC) layers in AMOLED panels, which enhances color purity and increases overall efficiency by up to 20%[2]. Samsung has also developed an advanced thin-film encapsulation (TFE) process that reduces the number of layers in the OLED stack, thereby improving light transmission. This technique has shown to increase panel efficiency by 15-18%[4]. Furthermore, Samsung has introduced a new pixel circuit design that minimizes power consumption during low brightness conditions, which is particularly beneficial for Always-On Display features in mobile devices[6].
Strengths: QDCC technology provides superior color performance and efficiency. Advanced TFE process improves overall panel thinness and light transmission. Weaknesses: The complex manufacturing process for QDCC may lead to higher production costs initially.
Core AMOLED Innovations
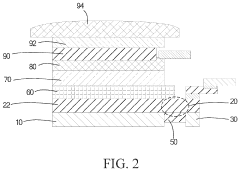
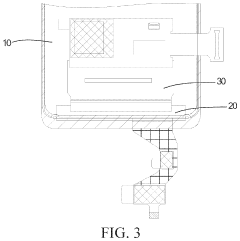
Active matrix organic light emitting diode panel
PatentInactiveUS20200185645A1
Innovation
- An AMOLED panel design featuring a hydrogel layer coated between two backing plates at the bent portion, which is then solidified with ultraviolet light, providing structural strength and toughness to the fillet formed when the panel is folded, thereby preventing deformation and breakage.
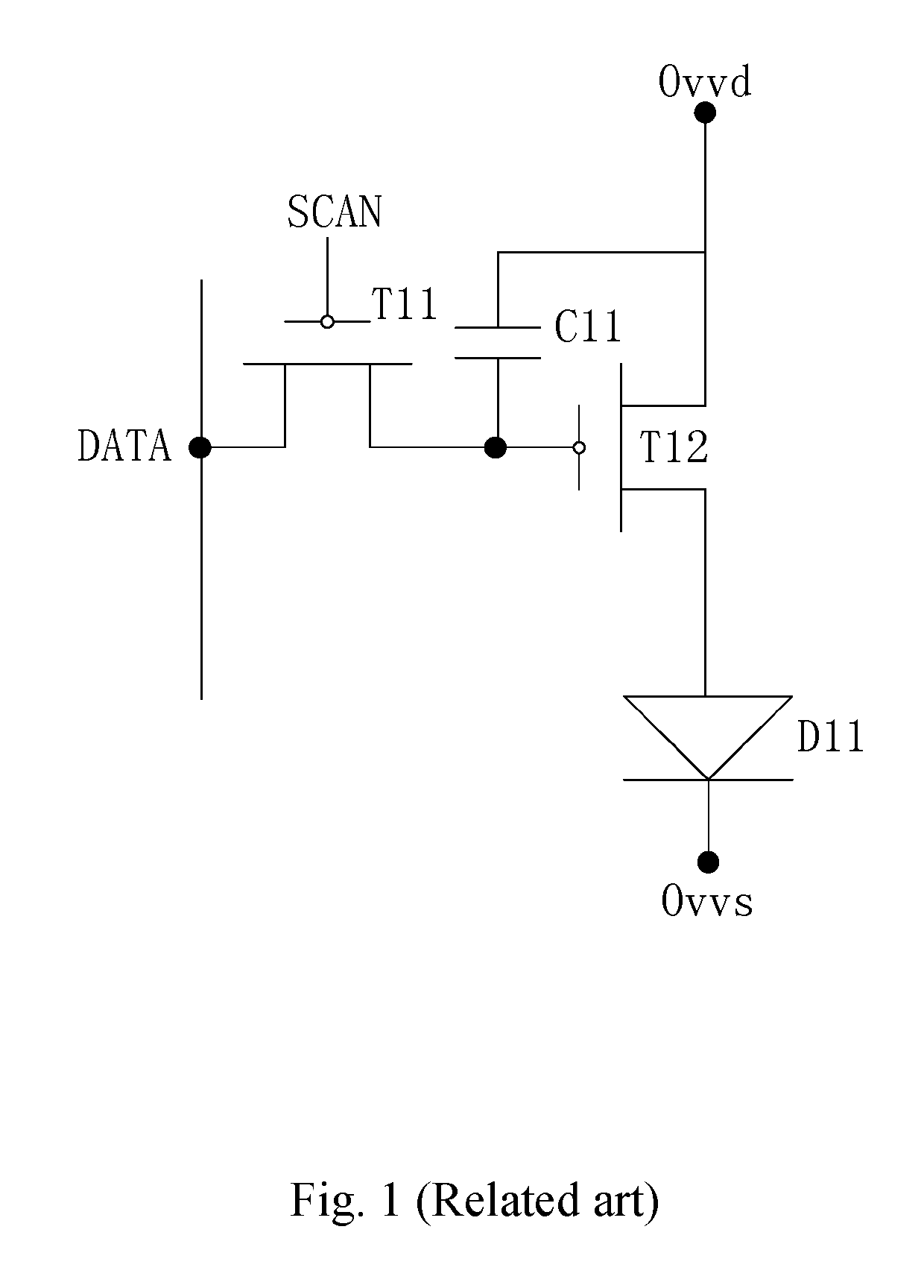
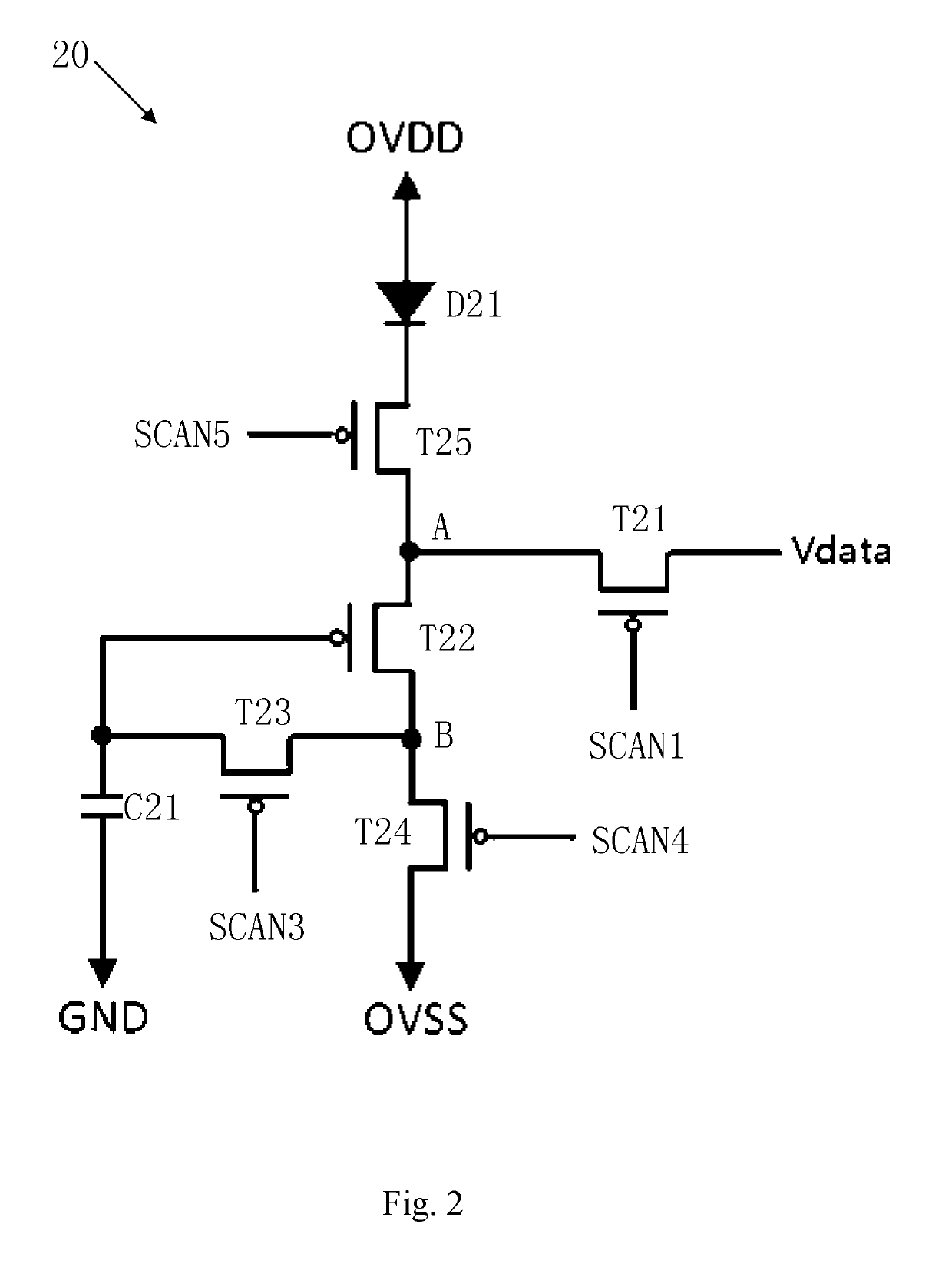
Driving circuit for AMOLED display panel and AMOLED display panel
PatentInactiveUS10304377B2
Innovation
- A driving circuit comprising five TFTs and a storage capacitor, operating in stages such as electric-potential-initialization, charge-storage, and illumination-display, where specific TFTs are turned on or off to charge the storage capacitor and control the luminance of the OLED, ensuring the voltage across the capacitor is independent of the TFT's threshold voltage.
Material Advancements
Material advancements play a crucial role in maximizing AMOLED efficiency through new panel configurations. Recent developments in organic and inorganic materials have significantly improved the performance and longevity of AMOLED displays.
One of the key areas of focus has been the enhancement of emissive layer materials. Researchers have made substantial progress in developing new phosphorescent and thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) emitters. These materials offer higher internal quantum efficiency, leading to improved light output and reduced power consumption. For instance, novel iridium-based complexes have shown promising results in achieving near-100% internal quantum efficiency for red and green emissions.
The development of more stable and efficient blue emitters remains a significant challenge in AMOLED technology. However, recent breakthroughs in blue TADF materials have shown potential for overcoming this hurdle. These materials exhibit reduced efficiency roll-off at high current densities, addressing one of the primary limitations of traditional fluorescent blue emitters.
Advancements in hole and electron transport layers have also contributed to improved AMOLED efficiency. Novel organic compounds with optimized energy levels and charge mobility characteristics have been developed, facilitating more efficient charge injection and transport within the device structure. This results in lower driving voltages and reduced power consumption.
The introduction of advanced barrier and encapsulation materials has significantly enhanced the longevity and reliability of AMOLED displays. Thin-film encapsulation technologies utilizing hybrid organic-inorganic materials have demonstrated superior moisture and oxygen barrier properties, effectively protecting the sensitive organic layers from degradation.
Innovations in electrode materials have further contributed to AMOLED efficiency improvements. Transparent conductive oxides with enhanced conductivity and transparency, such as indium tin oxide (ITO) alternatives, have been developed. These materials offer lower sheet resistance and higher optical transmittance, leading to improved light extraction and reduced power consumption.
The integration of quantum dot (QD) materials into AMOLED structures has emerged as a promising approach for enhancing color gamut and efficiency. QD color conversion layers can be utilized to achieve wider color gamuts while maintaining high efficiency, particularly for blue light conversion.
In conclusion, material advancements across various components of AMOLED panels have collectively contributed to significant improvements in efficiency and performance. Ongoing research in this field continues to push the boundaries of AMOLED technology, paving the way for more energy-efficient and visually stunning displays in the future.
One of the key areas of focus has been the enhancement of emissive layer materials. Researchers have made substantial progress in developing new phosphorescent and thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) emitters. These materials offer higher internal quantum efficiency, leading to improved light output and reduced power consumption. For instance, novel iridium-based complexes have shown promising results in achieving near-100% internal quantum efficiency for red and green emissions.
The development of more stable and efficient blue emitters remains a significant challenge in AMOLED technology. However, recent breakthroughs in blue TADF materials have shown potential for overcoming this hurdle. These materials exhibit reduced efficiency roll-off at high current densities, addressing one of the primary limitations of traditional fluorescent blue emitters.
Advancements in hole and electron transport layers have also contributed to improved AMOLED efficiency. Novel organic compounds with optimized energy levels and charge mobility characteristics have been developed, facilitating more efficient charge injection and transport within the device structure. This results in lower driving voltages and reduced power consumption.
The introduction of advanced barrier and encapsulation materials has significantly enhanced the longevity and reliability of AMOLED displays. Thin-film encapsulation technologies utilizing hybrid organic-inorganic materials have demonstrated superior moisture and oxygen barrier properties, effectively protecting the sensitive organic layers from degradation.
Innovations in electrode materials have further contributed to AMOLED efficiency improvements. Transparent conductive oxides with enhanced conductivity and transparency, such as indium tin oxide (ITO) alternatives, have been developed. These materials offer lower sheet resistance and higher optical transmittance, leading to improved light extraction and reduced power consumption.
The integration of quantum dot (QD) materials into AMOLED structures has emerged as a promising approach for enhancing color gamut and efficiency. QD color conversion layers can be utilized to achieve wider color gamuts while maintaining high efficiency, particularly for blue light conversion.
In conclusion, material advancements across various components of AMOLED panels have collectively contributed to significant improvements in efficiency and performance. Ongoing research in this field continues to push the boundaries of AMOLED technology, paving the way for more energy-efficient and visually stunning displays in the future.
Energy Consumption Impact
The energy consumption impact of new panel configurations for maximizing AMOLED efficiency is a critical consideration in the development of next-generation display technologies. AMOLED displays have gained significant popularity due to their superior image quality, flexibility, and potential for energy efficiency. However, their power consumption remains a key area for improvement, especially in mobile devices where battery life is paramount.
Recent advancements in panel configurations have shown promising results in reducing energy consumption while maintaining or even enhancing display performance. One of the most significant improvements comes from the implementation of more efficient pixel structures. Traditional RGB subpixel arrangements are being replaced by configurations that incorporate additional subpixels, such as RGBW (Red, Green, Blue, White) or RGBG (Red, Green, Blue, Green) layouts. These new configurations allow for more efficient light emission and better power distribution across the panel.
The introduction of variable refresh rate technologies has also contributed to substantial energy savings. By dynamically adjusting the refresh rate based on the content being displayed, AMOLED panels can significantly reduce power consumption during static or low-motion scenes. This adaptive approach ensures that energy is not wasted on unnecessary screen updates, leading to improved battery life without compromising user experience.
Another area of focus has been the optimization of the OLED materials themselves. Research into new organic compounds and emitter materials has yielded molecules with higher quantum efficiency, resulting in brighter displays that require less power to operate. This improvement in material efficiency translates directly to lower energy consumption across the entire panel.
The implementation of local dimming techniques in AMOLED displays has further enhanced energy efficiency. By selectively dimming or turning off individual pixels in darker areas of the screen, these panels can achieve deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios while simultaneously reducing power draw. This granular control over pixel illumination allows for more precise power management across the entire display surface.
Advancements in driver circuitry and power management systems have also played a crucial role in reducing overall energy consumption. More efficient voltage regulators and improved charge pump designs have minimized power losses in the display driving process. Additionally, the integration of sophisticated power management algorithms has enabled smarter control over display brightness and power states, further optimizing energy usage based on ambient lighting conditions and user preferences.
The cumulative effect of these innovations in panel configurations has led to significant reductions in AMOLED energy consumption, with some estimates suggesting power savings of up to 30% compared to previous generations. This improvement not only extends battery life in mobile devices but also opens up new possibilities for AMOLED technology in larger-format displays and automotive applications, where energy efficiency is increasingly important.
Recent advancements in panel configurations have shown promising results in reducing energy consumption while maintaining or even enhancing display performance. One of the most significant improvements comes from the implementation of more efficient pixel structures. Traditional RGB subpixel arrangements are being replaced by configurations that incorporate additional subpixels, such as RGBW (Red, Green, Blue, White) or RGBG (Red, Green, Blue, Green) layouts. These new configurations allow for more efficient light emission and better power distribution across the panel.
The introduction of variable refresh rate technologies has also contributed to substantial energy savings. By dynamically adjusting the refresh rate based on the content being displayed, AMOLED panels can significantly reduce power consumption during static or low-motion scenes. This adaptive approach ensures that energy is not wasted on unnecessary screen updates, leading to improved battery life without compromising user experience.
Another area of focus has been the optimization of the OLED materials themselves. Research into new organic compounds and emitter materials has yielded molecules with higher quantum efficiency, resulting in brighter displays that require less power to operate. This improvement in material efficiency translates directly to lower energy consumption across the entire panel.
The implementation of local dimming techniques in AMOLED displays has further enhanced energy efficiency. By selectively dimming or turning off individual pixels in darker areas of the screen, these panels can achieve deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios while simultaneously reducing power draw. This granular control over pixel illumination allows for more precise power management across the entire display surface.
Advancements in driver circuitry and power management systems have also played a crucial role in reducing overall energy consumption. More efficient voltage regulators and improved charge pump designs have minimized power losses in the display driving process. Additionally, the integration of sophisticated power management algorithms has enabled smarter control over display brightness and power states, further optimizing energy usage based on ambient lighting conditions and user preferences.
The cumulative effect of these innovations in panel configurations has led to significant reductions in AMOLED energy consumption, with some estimates suggesting power savings of up to 30% compared to previous generations. This improvement not only extends battery life in mobile devices but also opens up new possibilities for AMOLED technology in larger-format displays and automotive applications, where energy efficiency is increasingly important.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!