Future outlook on miniaturizing AMOLED components.
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Miniaturization Background and Objectives
Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode (AMOLED) technology has revolutionized the display industry since its inception in the late 1990s. The journey of AMOLED displays has been marked by continuous advancements in performance, efficiency, and form factor. As we look towards the future, the miniaturization of AMOLED components emerges as a critical focus area, promising to unlock new possibilities in display technology and device design.
The evolution of AMOLED technology has been driven by the increasing demand for high-quality, energy-efficient displays in a wide range of applications, from smartphones and tablets to wearable devices and automotive displays. The ability to produce vibrant colors, deep blacks, and high contrast ratios has made AMOLED displays a preferred choice for many manufacturers and consumers alike.
Miniaturization of AMOLED components is not merely about reducing size; it encompasses a holistic approach to optimizing the entire display system. This includes shrinking pixel sizes, thinning substrate materials, integrating driver circuits, and developing more efficient organic materials. The overarching goal is to create displays that are not only smaller and lighter but also more power-efficient and capable of higher resolutions.
The push for miniaturization is fueled by several factors. First, there is an ever-present consumer demand for sleeker, more compact devices with larger screen-to-body ratios. Second, emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) require ultra-high-resolution displays in very small form factors. Third, the automotive industry is increasingly adopting curved and flexible AMOLED displays for both instrument clusters and infotainment systems, necessitating more compact and adaptable display solutions.
As we delve into the future outlook of AMOLED miniaturization, it's crucial to understand the current technological limitations and the potential breakthroughs that could overcome them. Key areas of focus include developing new organic materials with improved efficiency and longevity, advancing thin-film transistor (TFT) technologies to enable higher pixel densities, and innovating in manufacturing processes to reduce costs and increase yields at smaller scales.
The miniaturization of AMOLED components also opens up new possibilities for flexible and foldable displays. By reducing the thickness of the display stack and developing more robust materials, manufacturers can create displays that can be bent, folded, or rolled without compromising performance or durability. This could lead to entirely new device form factors and use cases, further expanding the potential applications of AMOLED technology.
In conclusion, the future outlook for miniaturizing AMOLED components is both exciting and challenging. It promises to push the boundaries of what's possible in display technology, enabling new device designs and enhancing user experiences across multiple industries. As we explore the technical details and market implications in the following sections, it becomes clear that AMOLED miniaturization is not just a trend, but a fundamental driver of innovation in the display industry.
The evolution of AMOLED technology has been driven by the increasing demand for high-quality, energy-efficient displays in a wide range of applications, from smartphones and tablets to wearable devices and automotive displays. The ability to produce vibrant colors, deep blacks, and high contrast ratios has made AMOLED displays a preferred choice for many manufacturers and consumers alike.
Miniaturization of AMOLED components is not merely about reducing size; it encompasses a holistic approach to optimizing the entire display system. This includes shrinking pixel sizes, thinning substrate materials, integrating driver circuits, and developing more efficient organic materials. The overarching goal is to create displays that are not only smaller and lighter but also more power-efficient and capable of higher resolutions.
The push for miniaturization is fueled by several factors. First, there is an ever-present consumer demand for sleeker, more compact devices with larger screen-to-body ratios. Second, emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) require ultra-high-resolution displays in very small form factors. Third, the automotive industry is increasingly adopting curved and flexible AMOLED displays for both instrument clusters and infotainment systems, necessitating more compact and adaptable display solutions.
As we delve into the future outlook of AMOLED miniaturization, it's crucial to understand the current technological limitations and the potential breakthroughs that could overcome them. Key areas of focus include developing new organic materials with improved efficiency and longevity, advancing thin-film transistor (TFT) technologies to enable higher pixel densities, and innovating in manufacturing processes to reduce costs and increase yields at smaller scales.
The miniaturization of AMOLED components also opens up new possibilities for flexible and foldable displays. By reducing the thickness of the display stack and developing more robust materials, manufacturers can create displays that can be bent, folded, or rolled without compromising performance or durability. This could lead to entirely new device form factors and use cases, further expanding the potential applications of AMOLED technology.
In conclusion, the future outlook for miniaturizing AMOLED components is both exciting and challenging. It promises to push the boundaries of what's possible in display technology, enabling new device designs and enhancing user experiences across multiple industries. As we explore the technical details and market implications in the following sections, it becomes clear that AMOLED miniaturization is not just a trend, but a fundamental driver of innovation in the display industry.
Market Demand for Compact Display Technologies
The demand for compact display technologies, particularly in the realm of AMOLED components, has been steadily increasing across various sectors. This surge is primarily driven by the growing consumer preference for sleeker, more portable electronic devices with enhanced visual capabilities. The smartphone industry, being at the forefront of this trend, continues to push for thinner and lighter devices without compromising on display quality or functionality.
In the wearable technology market, the need for miniaturized AMOLED components is even more pronounced. Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and augmented reality glasses require displays that are not only compact but also energy-efficient and capable of delivering high-quality visuals. This demand is fueling research and development efforts to create AMOLED components that can fit into increasingly smaller form factors while maintaining or improving performance.
The automotive industry is another significant driver of demand for compact display technologies. As vehicles become more technologically advanced, there is a growing need for sleek, integrated displays for infotainment systems, digital dashboards, and heads-up displays. AMOLED technology, with its potential for flexibility and thinness, is particularly attractive for these applications.
Market analysts project substantial growth in the compact display technology sector over the next five years. This growth is expected to be particularly strong in emerging markets, where the adoption of smartphones and other personal electronic devices is rapidly increasing. Additionally, the development of foldable and rollable displays is creating new opportunities for AMOLED technology, further driving demand for miniaturized components.
The medical and healthcare sectors are also showing increased interest in compact AMOLED displays. Portable diagnostic devices, wearable health monitors, and minimally invasive surgical equipment all benefit from smaller, high-quality displays. This trend is likely to continue as healthcare becomes more personalized and technology-driven.
However, the market demand for compact display technologies also faces challenges. The cost of production for miniaturized AMOLED components remains high, which can limit adoption in price-sensitive markets. Additionally, there are technical hurdles to overcome, such as maintaining display brightness and longevity while reducing size. Despite these challenges, the overall market trajectory remains positive, with ongoing research and development efforts aimed at addressing these issues and meeting the growing demand for smaller, more efficient display technologies.
In the wearable technology market, the need for miniaturized AMOLED components is even more pronounced. Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and augmented reality glasses require displays that are not only compact but also energy-efficient and capable of delivering high-quality visuals. This demand is fueling research and development efforts to create AMOLED components that can fit into increasingly smaller form factors while maintaining or improving performance.
The automotive industry is another significant driver of demand for compact display technologies. As vehicles become more technologically advanced, there is a growing need for sleek, integrated displays for infotainment systems, digital dashboards, and heads-up displays. AMOLED technology, with its potential for flexibility and thinness, is particularly attractive for these applications.
Market analysts project substantial growth in the compact display technology sector over the next five years. This growth is expected to be particularly strong in emerging markets, where the adoption of smartphones and other personal electronic devices is rapidly increasing. Additionally, the development of foldable and rollable displays is creating new opportunities for AMOLED technology, further driving demand for miniaturized components.
The medical and healthcare sectors are also showing increased interest in compact AMOLED displays. Portable diagnostic devices, wearable health monitors, and minimally invasive surgical equipment all benefit from smaller, high-quality displays. This trend is likely to continue as healthcare becomes more personalized and technology-driven.
However, the market demand for compact display technologies also faces challenges. The cost of production for miniaturized AMOLED components remains high, which can limit adoption in price-sensitive markets. Additionally, there are technical hurdles to overcome, such as maintaining display brightness and longevity while reducing size. Despite these challenges, the overall market trajectory remains positive, with ongoing research and development efforts aimed at addressing these issues and meeting the growing demand for smaller, more efficient display technologies.
Current Challenges in AMOLED Component Miniaturization
The miniaturization of AMOLED components presents several significant challenges that researchers and manufacturers are currently grappling with. One of the primary obstacles is the reduction of pixel size while maintaining or improving display quality. As pixels become smaller, it becomes increasingly difficult to maintain sufficient brightness and color accuracy, which are crucial for high-quality displays.
Another major challenge lies in the development of more efficient and compact thin-film transistors (TFTs) that drive each pixel. Current backplane technologies, such as low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) and oxide TFTs, face limitations in scaling down while preserving electrical performance. This bottleneck affects the overall pixel density and power efficiency of AMOLED displays.
The integration of ever-smaller components also poses significant manufacturing hurdles. As dimensions shrink, the precision required in deposition, patterning, and encapsulation processes increases exponentially. This demands advancements in manufacturing equipment and techniques to achieve the necessary accuracy and yield rates for mass production.
Heat management is another critical issue in AMOLED miniaturization. As components are packed more tightly, heat dissipation becomes more challenging, potentially leading to reduced lifespan and performance degradation of the display. Innovative thermal management solutions are needed to address this problem effectively.
Furthermore, the miniaturization of AMOLED components is constrained by the limitations of current materials. Developing new materials that can maintain their properties and performance at smaller scales is crucial for advancing miniaturization efforts. This includes research into novel organic light-emitting materials, electrode materials, and encapsulation layers.
Power efficiency remains a persistent challenge in AMOLED miniaturization. As displays become more compact and pixel densities increase, maintaining low power consumption becomes more difficult. This is particularly crucial for mobile devices where battery life is a key consideration.
Lastly, the cost of manufacturing highly miniaturized AMOLED components is a significant barrier. The complexity of production processes and the need for advanced equipment and materials drive up costs, potentially limiting the widespread adoption of these technologies in consumer devices. Balancing miniaturization with cost-effectiveness is a key challenge that manufacturers must address to ensure market viability.
Another major challenge lies in the development of more efficient and compact thin-film transistors (TFTs) that drive each pixel. Current backplane technologies, such as low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) and oxide TFTs, face limitations in scaling down while preserving electrical performance. This bottleneck affects the overall pixel density and power efficiency of AMOLED displays.
The integration of ever-smaller components also poses significant manufacturing hurdles. As dimensions shrink, the precision required in deposition, patterning, and encapsulation processes increases exponentially. This demands advancements in manufacturing equipment and techniques to achieve the necessary accuracy and yield rates for mass production.
Heat management is another critical issue in AMOLED miniaturization. As components are packed more tightly, heat dissipation becomes more challenging, potentially leading to reduced lifespan and performance degradation of the display. Innovative thermal management solutions are needed to address this problem effectively.
Furthermore, the miniaturization of AMOLED components is constrained by the limitations of current materials. Developing new materials that can maintain their properties and performance at smaller scales is crucial for advancing miniaturization efforts. This includes research into novel organic light-emitting materials, electrode materials, and encapsulation layers.
Power efficiency remains a persistent challenge in AMOLED miniaturization. As displays become more compact and pixel densities increase, maintaining low power consumption becomes more difficult. This is particularly crucial for mobile devices where battery life is a key consideration.
Lastly, the cost of manufacturing highly miniaturized AMOLED components is a significant barrier. The complexity of production processes and the need for advanced equipment and materials drive up costs, potentially limiting the widespread adoption of these technologies in consumer devices. Balancing miniaturization with cost-effectiveness is a key challenge that manufacturers must address to ensure market viability.
Existing Approaches to AMOLED Miniaturization
01 AMOLED pixel structure and size optimization
AMOLED displays utilize various pixel structures and sizes to optimize performance. This includes designing compact pixel layouts, implementing sub-pixel arrangements, and adjusting pixel densities to enhance resolution and image quality while maintaining a small overall display size.- AMOLED pixel structure and size optimization: AMOLED displays utilize various pixel structures and sizes to optimize performance. This includes designing compact pixel layouts, implementing sub-pixel arrangements, and adjusting pixel densities to enhance image quality and energy efficiency. These optimizations contribute to improved display resolution and overall device compactness.
- Thin-film transistor (TFT) design for AMOLED: The design of thin-film transistors plays a crucial role in AMOLED display performance and size reduction. Advanced TFT structures, materials, and fabrication techniques are employed to minimize transistor dimensions while maintaining or improving electrical characteristics. This allows for higher pixel densities and more compact display modules.
- OLED material and stack optimization: The selection and optimization of OLED materials and layer stacks significantly impact the overall size and performance of AMOLED displays. This includes developing high-efficiency emissive materials, optimizing layer thicknesses, and implementing advanced deposition techniques to reduce the overall thickness of the OLED stack while maintaining or improving luminous efficiency.
- Flexible and foldable AMOLED technologies: Advancements in flexible and foldable AMOLED technologies enable new form factors and size configurations. This involves developing bendable substrates, flexible encapsulation methods, and stress-resistant pixel structures that maintain display performance while allowing for compact folded states and expanded unfolded states.
- Driver circuit integration and bezel reduction: Integrating driver circuits and reducing bezel size contribute to overall AMOLED component size reduction. This includes developing advanced gate and data drivers, implementing narrow bezel designs, and utilizing chip-on-glass or chip-on-plastic technologies to minimize the non-display areas of the module.
02 Thin-film transistor (TFT) design for AMOLED
The size and design of thin-film transistors play a crucial role in AMOLED displays. Innovations in TFT structures, materials, and fabrication techniques aim to reduce transistor size while improving performance, allowing for higher pixel densities and more compact display components.Expand Specific Solutions03 OLED material and stack optimization
Advancements in OLED materials and stack designs focus on reducing the overall thickness of the emissive layers while enhancing efficiency and longevity. This includes developing new organic compounds, optimizing layer thicknesses, and improving charge transport to achieve thinner and more efficient AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions04 Miniaturization of AMOLED driver circuits
Efforts to miniaturize AMOLED driver circuits aim to reduce the overall size of display components. This involves developing more efficient and compact integrated circuits, implementing advanced packaging techniques, and optimizing circuit layouts to minimize the footprint of driving electronics.Expand Specific Solutions05 Flexible and foldable AMOLED technologies
Innovations in flexible and foldable AMOLED technologies focus on creating displays that can be bent or folded while maintaining functionality. This includes developing thin and flexible substrates, implementing stretchable electrodes, and designing robust encapsulation methods to enable compact, foldable devices with AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in AMOLED Manufacturing Industry
The future outlook for miniaturizing AMOLED components is characterized by intense competition in a rapidly evolving market. The industry is in a growth phase, with increasing demand for smaller, more efficient displays across various applications. Market size is expanding, driven by adoption in smartphones, wearables, and emerging AR/VR technologies. Technologically, companies like Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE are at the forefront, investing heavily in R&D to overcome challenges in pixel density, power consumption, and manufacturing processes. Chinese firms like TCL CSOT and Everdisplay are also making significant strides, intensifying global competition. The race to achieve higher resolutions and lower power consumption in smaller form factors continues to drive innovation in this space.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE is actively pursuing AMOLED miniaturization through various technological innovations. They are developing advanced thin-film transistor (TFT) backplanes using low-temperature poly-silicon (LTPS) and oxide semiconductor materials to reduce component size and power consumption[4]. BOE has also made progress in flexible OLED displays, which contribute to overall device miniaturization. Their research includes the development of new organic materials and optimized pixel structures to enhance efficiency and lifespan while reducing size[5]. Recently, BOE has demonstrated a 0.99-inch AMOLED display with a resolution of 582 PPI, showcasing their capabilities in small, high-resolution displays[6].
Strengths: Large-scale production capacity, strong presence in the Chinese market, and diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Relatively newer to OLED technology compared to some competitors, potentially playing catch-up in some advanced areas.
LG Display Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Display is focusing on AMOLED miniaturization through several key technologies. They are developing advanced OLED materials and pixel structures to reduce component size while improving efficiency. LG has made significant progress in WOLED (White OLED) technology, which allows for simpler manufacturing processes and potentially smaller overall display structures[7]. They are also exploring the use of inkjet printing techniques for OLED production, which could lead to more precise deposition of materials and further miniaturization[8]. LG Display has recently showcased a 0.42-inch 1280x720 pixel OLED display with a pixel density of 3,000 PPI, demonstrating their capability in producing extremely high-resolution micro-displays[9].
Strengths: Leader in large OLED displays, strong patent portfolio, and expertise in WOLED technology. Weaknesses: Less focus on small OLED displays historically, which may impact their progress in certain miniaturization aspects.
Breakthrough Innovations in Nano-scale AMOLED Components
Array substrate, display device, and method for manufacturing array substrate
PatentActiveUS20170148862A1
Innovation
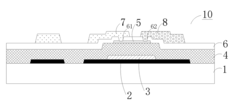
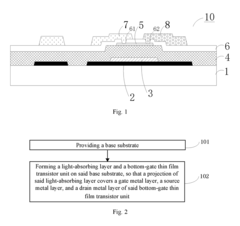
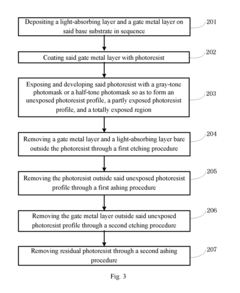
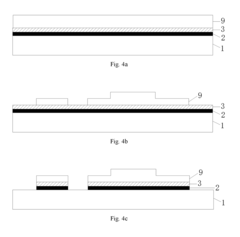
- An array substrate with a light-absorbing layer covering the gate, source, and drain metal layers of a bottom-gate thin film transistor unit, preventing ambient light irradiation while allowing useful light to pass through.
Active-matrix organic light emitting diode display
PatentInactiveUS20070268223A1
Innovation
- The indium tin oxide region is redesigned to be a rectangular shape with a surrounding silicon nitride isolation region, allowing for a more efficient layout by arranging the thin film transistors and capacitor regions in a hoof or L shape, maximizing the opening area and minimizing the isolation region.
Supply Chain Implications of AMOLED Miniaturization
The miniaturization of AMOLED components is poised to have significant implications for the supply chain of display manufacturers and their partners. As components become smaller, the precision requirements for manufacturing processes will increase dramatically. This shift will likely lead to a consolidation of suppliers capable of meeting these exacting standards, potentially reducing the number of players in the supply chain but increasing their technological sophistication.
Material suppliers will need to develop and provide increasingly specialized and high-performance materials to support the miniaturization trend. This may include advanced organic compounds for OLED emitters, ultra-thin encapsulation materials, and high-resolution photoresists for patterning. The demand for these materials will drive innovation in the chemical and materials science sectors, potentially creating new market leaders in niche areas of AMOLED technology.
Equipment manufacturers will face the challenge of developing tools capable of handling and processing these miniaturized components with unprecedented accuracy. This may lead to the emergence of new equipment vendors specializing in nano-scale fabrication and inspection technologies. Existing equipment suppliers will need to invest heavily in R&D to maintain their market position, potentially leading to increased equipment costs for display manufacturers.
The logistics of handling and transporting miniaturized components will also become more complex. Specialized packaging and transportation methods may need to be developed to protect these delicate parts from environmental factors and physical stress. This could lead to the emergence of new logistics providers specializing in the transport of high-value, miniaturized electronic components.
As the complexity of the manufacturing process increases, there may be a shift towards more vertically integrated supply chains. Display manufacturers may choose to bring certain critical processes in-house or form closer partnerships with key suppliers to ensure quality control and protect proprietary technologies. This could result in longer-term supply agreements and more strategic alliances within the industry.
The geographical distribution of the supply chain may also evolve. Regions with a strong foundation in precision manufacturing and advanced materials science may see increased investment and activity. This could potentially shift some aspects of the supply chain away from traditional manufacturing hubs, creating new centers of excellence for AMOLED miniaturization technologies.
Material suppliers will need to develop and provide increasingly specialized and high-performance materials to support the miniaturization trend. This may include advanced organic compounds for OLED emitters, ultra-thin encapsulation materials, and high-resolution photoresists for patterning. The demand for these materials will drive innovation in the chemical and materials science sectors, potentially creating new market leaders in niche areas of AMOLED technology.
Equipment manufacturers will face the challenge of developing tools capable of handling and processing these miniaturized components with unprecedented accuracy. This may lead to the emergence of new equipment vendors specializing in nano-scale fabrication and inspection technologies. Existing equipment suppliers will need to invest heavily in R&D to maintain their market position, potentially leading to increased equipment costs for display manufacturers.
The logistics of handling and transporting miniaturized components will also become more complex. Specialized packaging and transportation methods may need to be developed to protect these delicate parts from environmental factors and physical stress. This could lead to the emergence of new logistics providers specializing in the transport of high-value, miniaturized electronic components.
As the complexity of the manufacturing process increases, there may be a shift towards more vertically integrated supply chains. Display manufacturers may choose to bring certain critical processes in-house or form closer partnerships with key suppliers to ensure quality control and protect proprietary technologies. This could result in longer-term supply agreements and more strategic alliances within the industry.
The geographical distribution of the supply chain may also evolve. Regions with a strong foundation in precision manufacturing and advanced materials science may see increased investment and activity. This could potentially shift some aspects of the supply chain away from traditional manufacturing hubs, creating new centers of excellence for AMOLED miniaturization technologies.
Environmental Impact of Miniaturized AMOLED Production
The miniaturization of AMOLED components has significant environmental implications, both positive and negative. As the production processes for smaller AMOLED components evolve, there is potential for reduced material consumption and energy usage. Smaller components require less raw material input, which can lead to a decrease in resource extraction and associated environmental impacts. Additionally, the reduced size of components may result in more efficient manufacturing processes, potentially lowering energy consumption during production.
However, the miniaturization process itself may introduce new environmental challenges. The production of smaller components often requires more precise and sophisticated manufacturing techniques, which could potentially increase energy consumption in certain stages of production. Moreover, the use of new materials or chemical processes to achieve miniaturization may introduce additional environmental risks if not properly managed.
The disposal and recycling of miniaturized AMOLED components also present environmental considerations. While smaller components may reduce overall electronic waste volume, they can be more challenging to recycle due to their intricate design and the mix of materials used. This could potentially lead to increased e-waste if proper recycling technologies and processes are not developed in parallel with miniaturization efforts.
From a lifecycle perspective, miniaturized AMOLED components may contribute to improved energy efficiency in end-use devices. Smaller components often consume less power during operation, which can extend battery life and reduce overall energy consumption of electronic devices. This indirect environmental benefit should be considered when assessing the overall environmental impact of AMOLED miniaturization.
The shift towards miniaturization may also influence supply chain dynamics and transportation-related emissions. Smaller components could potentially reduce shipping volumes and weights, leading to decreased transportation-related carbon emissions. However, this benefit may be offset if the production of miniaturized components becomes more geographically concentrated due to specialized manufacturing requirements.
As the industry moves towards increasingly miniaturized AMOLED components, it is crucial to adopt a holistic approach to environmental impact assessment. This should include considerations of raw material sourcing, production processes, energy consumption, waste management, and end-of-life recycling. Implementing eco-design principles and circular economy concepts in the development of miniaturized AMOLED technologies will be essential to maximize environmental benefits and mitigate potential negative impacts.
However, the miniaturization process itself may introduce new environmental challenges. The production of smaller components often requires more precise and sophisticated manufacturing techniques, which could potentially increase energy consumption in certain stages of production. Moreover, the use of new materials or chemical processes to achieve miniaturization may introduce additional environmental risks if not properly managed.
The disposal and recycling of miniaturized AMOLED components also present environmental considerations. While smaller components may reduce overall electronic waste volume, they can be more challenging to recycle due to their intricate design and the mix of materials used. This could potentially lead to increased e-waste if proper recycling technologies and processes are not developed in parallel with miniaturization efforts.
From a lifecycle perspective, miniaturized AMOLED components may contribute to improved energy efficiency in end-use devices. Smaller components often consume less power during operation, which can extend battery life and reduce overall energy consumption of electronic devices. This indirect environmental benefit should be considered when assessing the overall environmental impact of AMOLED miniaturization.
The shift towards miniaturization may also influence supply chain dynamics and transportation-related emissions. Smaller components could potentially reduce shipping volumes and weights, leading to decreased transportation-related carbon emissions. However, this benefit may be offset if the production of miniaturized components becomes more geographically concentrated due to specialized manufacturing requirements.
As the industry moves towards increasingly miniaturized AMOLED components, it is crucial to adopt a holistic approach to environmental impact assessment. This should include considerations of raw material sourcing, production processes, energy consumption, waste management, and end-of-life recycling. Implementing eco-design principles and circular economy concepts in the development of miniaturized AMOLED technologies will be essential to maximize environmental benefits and mitigate potential negative impacts.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!