How AMOLED revolutionizes mobile device aesthetics?
JUL 17, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Evolution and Objectives
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has revolutionized the aesthetics of mobile devices since its introduction in the early 2000s. This innovative display technology has undergone significant evolution, transforming the visual experience of smartphones, tablets, and wearables.
The journey of AMOLED began with the development of OLED technology in the 1980s. However, it wasn't until the early 2000s that AMOLED displays started appearing in commercial mobile devices. The primary objective of AMOLED technology was to overcome the limitations of traditional LCD displays, offering superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency.
As AMOLED technology progressed, manufacturers focused on enhancing pixel density, color accuracy, and power consumption. The introduction of Super AMOLED displays by Samsung in 2010 marked a significant milestone, integrating the touch sensors directly into the display and eliminating the air gap between the screen and the touch layer.
The evolution of AMOLED has been driven by the demand for thinner, lighter, and more visually appealing mobile devices. Flexible AMOLED displays emerged as a game-changer, enabling the creation of curved and foldable smartphones. This innovation opened up new possibilities for device form factors and user interactions.
One of the key objectives in AMOLED development has been to improve color accuracy and brightness. HDR (High Dynamic Range) AMOLED displays have become increasingly common, offering a wider color gamut and better contrast ratios. This enhancement has significantly improved the viewing experience for multimedia content on mobile devices.
Energy efficiency has been another crucial focus area for AMOLED technology. The ability of AMOLED displays to turn off individual pixels when displaying black has led to the development of dark mode interfaces, which not only save battery life but also contribute to a sleeker aesthetic.
The ongoing evolution of AMOLED technology aims to address challenges such as burn-in issues, outdoor visibility, and production costs. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring new materials and manufacturing techniques to overcome these limitations and further improve display quality.
Looking ahead, the objectives for AMOLED technology include achieving higher refresh rates for smoother animations, developing more durable flexible displays, and integrating additional functionalities like under-display cameras and sensors. These advancements will continue to push the boundaries of mobile device aesthetics and functionality.
The journey of AMOLED began with the development of OLED technology in the 1980s. However, it wasn't until the early 2000s that AMOLED displays started appearing in commercial mobile devices. The primary objective of AMOLED technology was to overcome the limitations of traditional LCD displays, offering superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency.
As AMOLED technology progressed, manufacturers focused on enhancing pixel density, color accuracy, and power consumption. The introduction of Super AMOLED displays by Samsung in 2010 marked a significant milestone, integrating the touch sensors directly into the display and eliminating the air gap between the screen and the touch layer.
The evolution of AMOLED has been driven by the demand for thinner, lighter, and more visually appealing mobile devices. Flexible AMOLED displays emerged as a game-changer, enabling the creation of curved and foldable smartphones. This innovation opened up new possibilities for device form factors and user interactions.
One of the key objectives in AMOLED development has been to improve color accuracy and brightness. HDR (High Dynamic Range) AMOLED displays have become increasingly common, offering a wider color gamut and better contrast ratios. This enhancement has significantly improved the viewing experience for multimedia content on mobile devices.
Energy efficiency has been another crucial focus area for AMOLED technology. The ability of AMOLED displays to turn off individual pixels when displaying black has led to the development of dark mode interfaces, which not only save battery life but also contribute to a sleeker aesthetic.
The ongoing evolution of AMOLED technology aims to address challenges such as burn-in issues, outdoor visibility, and production costs. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring new materials and manufacturing techniques to overcome these limitations and further improve display quality.
Looking ahead, the objectives for AMOLED technology include achieving higher refresh rates for smoother animations, developing more durable flexible displays, and integrating additional functionalities like under-display cameras and sensors. These advancements will continue to push the boundaries of mobile device aesthetics and functionality.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for AMOLED technology in mobile devices has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by consumer preferences for sleeker, more visually appealing smartphones and tablets. This surge in demand is primarily attributed to AMOLED's ability to deliver vibrant colors, deep blacks, and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD displays.
Consumer surveys consistently indicate a strong preference for devices with AMOLED screens, with users citing enhanced visual experiences and longer battery life as key factors in their purchasing decisions. This trend has led to a substantial increase in AMOLED adoption across various price segments of the mobile device market, from premium flagship models to mid-range offerings.
The global AMOLED market for smartphones is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with market research firms forecasting robust growth over the next five years. This expansion is fueled by increasing consumer awareness of display quality and the growing importance of visual aesthetics in mobile device design.
Major smartphone manufacturers have responded to this market demand by incorporating AMOLED displays into their product lineups. This shift has created a ripple effect throughout the supply chain, with display manufacturers ramping up production capacity to meet the growing demand for AMOLED panels.
The automotive and wearable technology sectors are also contributing to the overall market growth for AMOLED displays. As these industries increasingly adopt AMOLED technology for their products, it further solidifies the technology's position in the broader consumer electronics market.
However, challenges remain in meeting the full extent of market demand. Production costs and yield rates continue to be areas of concern for manufacturers, potentially limiting the widespread adoption of AMOLED displays in lower-priced devices. Additionally, the ongoing development of alternative display technologies, such as microLED, may impact future market dynamics.
Despite these challenges, the overall industry trend points towards continued growth in AMOLED adoption. The technology's ability to enable innovative form factors, such as foldable and rollable displays, is expected to open up new market opportunities and drive further demand in the coming years.
As mobile device aesthetics become increasingly important in consumer decision-making, AMOLED technology is well-positioned to maintain its strong market presence. The ongoing refinement of AMOLED manufacturing processes and the potential for cost reductions are likely to further expand its market reach, solidifying its role in revolutionizing mobile device aesthetics across various price points and device categories.
Consumer surveys consistently indicate a strong preference for devices with AMOLED screens, with users citing enhanced visual experiences and longer battery life as key factors in their purchasing decisions. This trend has led to a substantial increase in AMOLED adoption across various price segments of the mobile device market, from premium flagship models to mid-range offerings.
The global AMOLED market for smartphones is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with market research firms forecasting robust growth over the next five years. This expansion is fueled by increasing consumer awareness of display quality and the growing importance of visual aesthetics in mobile device design.
Major smartphone manufacturers have responded to this market demand by incorporating AMOLED displays into their product lineups. This shift has created a ripple effect throughout the supply chain, with display manufacturers ramping up production capacity to meet the growing demand for AMOLED panels.
The automotive and wearable technology sectors are also contributing to the overall market growth for AMOLED displays. As these industries increasingly adopt AMOLED technology for their products, it further solidifies the technology's position in the broader consumer electronics market.
However, challenges remain in meeting the full extent of market demand. Production costs and yield rates continue to be areas of concern for manufacturers, potentially limiting the widespread adoption of AMOLED displays in lower-priced devices. Additionally, the ongoing development of alternative display technologies, such as microLED, may impact future market dynamics.
Despite these challenges, the overall industry trend points towards continued growth in AMOLED adoption. The technology's ability to enable innovative form factors, such as foldable and rollable displays, is expected to open up new market opportunities and drive further demand in the coming years.
As mobile device aesthetics become increasingly important in consumer decision-making, AMOLED technology is well-positioned to maintain its strong market presence. The ongoing refinement of AMOLED manufacturing processes and the potential for cost reductions are likely to further expand its market reach, solidifying its role in revolutionizing mobile device aesthetics across various price points and device categories.
AMOLED Tech Challenges
Despite the remarkable advancements in AMOLED technology, several significant challenges persist in its development and implementation for mobile devices. One of the primary hurdles is the issue of burn-in, where static images displayed for extended periods can lead to permanent ghosting effects on the screen. This phenomenon occurs due to the organic compounds in OLED pixels degrading at different rates, resulting in uneven wear and reduced display quality over time.
Another critical challenge is the susceptibility of AMOLED displays to water damage. The organic materials used in these screens are highly sensitive to moisture, which can cause rapid deterioration of the display if exposed. This vulnerability necessitates advanced sealing techniques and protective measures, adding complexity and cost to the manufacturing process.
Color accuracy and consistency across different viewing angles remain ongoing concerns for AMOLED technology. While improvements have been made, ensuring uniform color reproduction and maintaining vibrant hues at various angles continues to be a technical hurdle. This challenge is particularly crucial for mobile devices, where users frequently view screens from different positions.
Power consumption, especially when displaying bright or white content, is another area of concern. Although AMOLED displays are generally more energy-efficient than traditional LCD screens, they can consume significantly more power when displaying lighter colors. This characteristic poses challenges for battery life management in mobile devices and requires sophisticated power optimization techniques.
Manufacturing scalability and yield rates present additional obstacles. The production of AMOLED displays involves complex processes and requires stringent quality control measures. Achieving high yield rates while maintaining cost-effectiveness remains a challenge, particularly for larger screen sizes and higher resolutions.
Lastly, the limited lifespan of blue OLED materials compared to red and green counterparts is a persistent issue. Blue OLEDs tend to degrade faster, leading to color shifts and reduced overall display longevity. Addressing this imbalance in material durability is crucial for ensuring long-term display quality and device aesthetics.
These technical challenges collectively impact the widespread adoption and further advancement of AMOLED technology in mobile devices. Overcoming these hurdles requires continuous research and development efforts, innovative materials science, and engineering solutions to fully realize the aesthetic and functional potential of AMOLED displays in the mobile device ecosystem.
Another critical challenge is the susceptibility of AMOLED displays to water damage. The organic materials used in these screens are highly sensitive to moisture, which can cause rapid deterioration of the display if exposed. This vulnerability necessitates advanced sealing techniques and protective measures, adding complexity and cost to the manufacturing process.
Color accuracy and consistency across different viewing angles remain ongoing concerns for AMOLED technology. While improvements have been made, ensuring uniform color reproduction and maintaining vibrant hues at various angles continues to be a technical hurdle. This challenge is particularly crucial for mobile devices, where users frequently view screens from different positions.
Power consumption, especially when displaying bright or white content, is another area of concern. Although AMOLED displays are generally more energy-efficient than traditional LCD screens, they can consume significantly more power when displaying lighter colors. This characteristic poses challenges for battery life management in mobile devices and requires sophisticated power optimization techniques.
Manufacturing scalability and yield rates present additional obstacles. The production of AMOLED displays involves complex processes and requires stringent quality control measures. Achieving high yield rates while maintaining cost-effectiveness remains a challenge, particularly for larger screen sizes and higher resolutions.
Lastly, the limited lifespan of blue OLED materials compared to red and green counterparts is a persistent issue. Blue OLEDs tend to degrade faster, leading to color shifts and reduced overall display longevity. Addressing this imbalance in material durability is crucial for ensuring long-term display quality and device aesthetics.
These technical challenges collectively impact the widespread adoption and further advancement of AMOLED technology in mobile devices. Overcoming these hurdles requires continuous research and development efforts, innovative materials science, and engineering solutions to fully realize the aesthetic and functional potential of AMOLED displays in the mobile device ecosystem.
Current AMOLED Solutions
01 AMOLED display design and optimization
This category focuses on the design and optimization of AMOLED displays to enhance their aesthetic appeal. It includes techniques for improving display quality, color accuracy, and overall visual performance. These advancements contribute to creating more visually pleasing and efficient AMOLED screens for various devices.- AMOLED display design and optimization: This category focuses on the design and optimization of AMOLED displays to enhance their aesthetic appeal. It includes techniques for improving display quality, color accuracy, and overall visual performance. The designs aim to create more visually pleasing and efficient AMOLED screens for various applications.
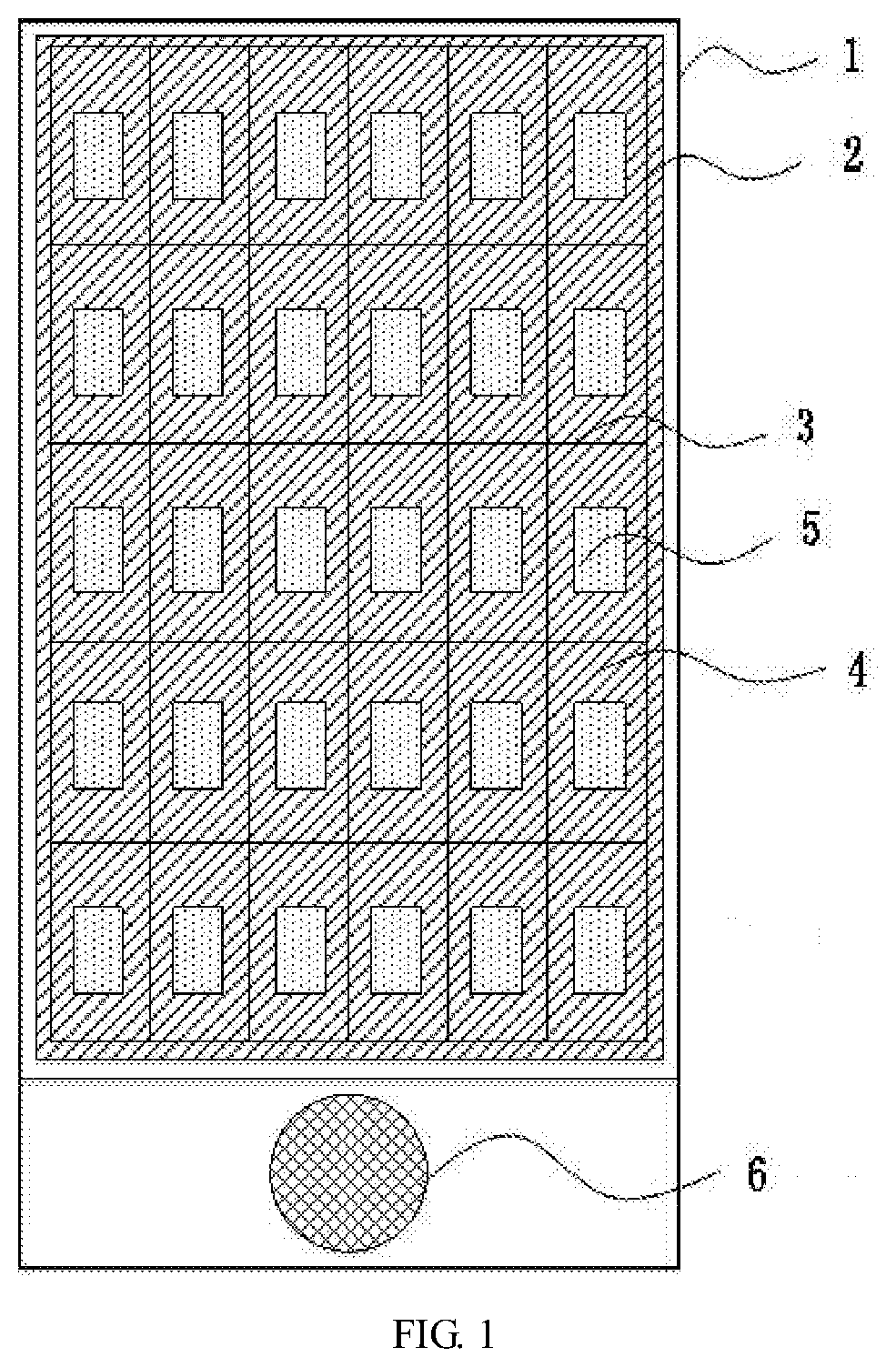
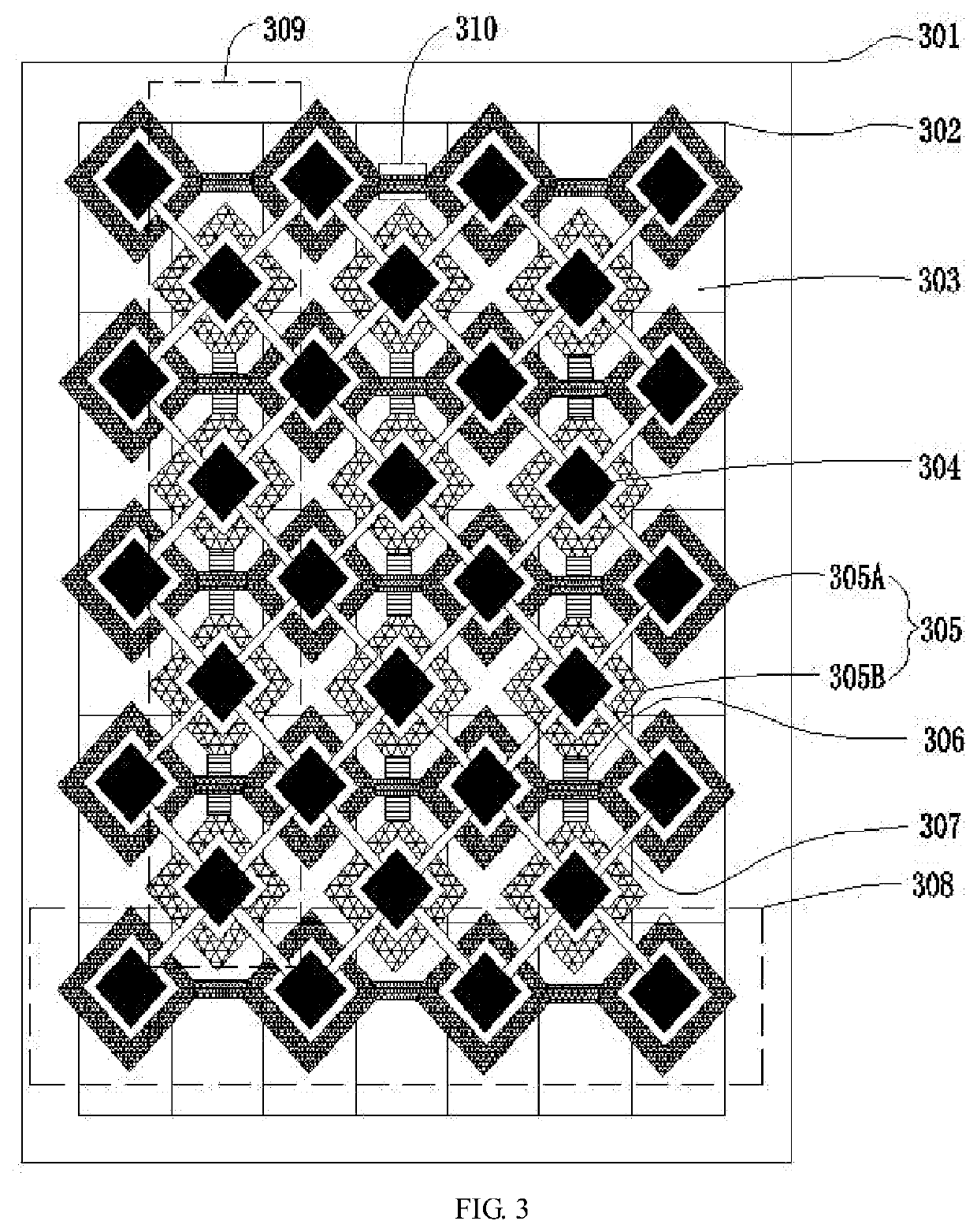
- AMOLED pixel structure and arrangement: This point covers innovations in AMOLED pixel structure and arrangement to improve display aesthetics. It includes advancements in sub-pixel layouts, pixel density optimization, and novel pixel configurations that enhance visual quality and reduce power consumption while maintaining aesthetic appeal.
- Color management and enhancement in AMOLED displays: This category encompasses techniques for color management and enhancement in AMOLED displays. It includes methods for improving color accuracy, expanding color gamut, and implementing advanced color processing algorithms to enhance the overall visual aesthetics of AMOLED screens.
- AMOLED display integration and form factor: This point focuses on the integration of AMOLED displays into various devices and the development of new form factors. It includes innovations in flexible and foldable AMOLED displays, as well as techniques for seamlessly incorporating AMOLED screens into different product designs to enhance overall aesthetics.
- User interface and interaction design for AMOLED displays: This category covers the design of user interfaces and interaction methods specifically tailored for AMOLED displays. It includes innovations in touch sensitivity, gesture recognition, and adaptive UI elements that take advantage of AMOLED's unique characteristics to create more visually appealing and intuitive user experiences.
02 AMOLED pixel structure and arrangement
This point addresses the development of innovative pixel structures and arrangements for AMOLED displays. It involves optimizing pixel layouts, sub-pixel configurations, and pixel density to enhance image quality, resolution, and energy efficiency. These improvements contribute to the overall aesthetic appeal of AMOLED screens.Expand Specific Solutions03 AMOLED color management and enhancement
This category focuses on techniques for managing and enhancing color reproduction in AMOLED displays. It includes methods for color calibration, gamut expansion, and dynamic color adjustment to improve visual aesthetics and accuracy. These advancements result in more vibrant and lifelike images on AMOLED screens.Expand Specific Solutions04 AMOLED power efficiency and brightness control
This point addresses the development of power-efficient AMOLED displays with improved brightness control. It includes techniques for optimizing power consumption, implementing adaptive brightness, and enhancing display visibility in various lighting conditions. These advancements contribute to both the aesthetic appeal and practical usability of AMOLED screens.Expand Specific Solutions05 AMOLED user interface and interaction design
This category focuses on designing user interfaces and interaction methods specifically tailored for AMOLED displays. It includes techniques for creating visually appealing UI elements, implementing gesture controls, and optimizing touch sensitivity. These advancements enhance the overall user experience and aesthetic appeal of devices featuring AMOLED screens.Expand Specific Solutions
Key AMOLED Manufacturers
The AMOLED technology market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption in mobile devices due to its superior display quality and energy efficiency. The global AMOLED market size is projected to expand significantly, driven by rising demand for smartphones and wearables. Technologically, AMOLED is maturing rapidly, with key players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology, and TCL China Star Optoelectronics leading innovation. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to improve AMOLED performance, durability, and manufacturing processes. Emerging players like Everdisplay Optronics and Visionox are also contributing to market competitiveness, particularly in the Chinese market. The industry is seeing advancements in flexible and foldable AMOLED displays, indicating a trend towards more versatile and aesthetically pleasing mobile device designs.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has made significant strides in AMOLED technology, focusing on flexible displays to revolutionize mobile device aesthetics. Their 6th generation flexible AMOLED production line in Chongqing achieved mass production in 2017, with a designed capacity of 48,000 glass substrates per month[5]. BOE's AMOLED displays feature high color saturation, achieving over 100% NTSC color gamut, and ultra-high contrast ratios exceeding 1,000,000:1[6]. The company has developed various AMOLED solutions, including in-display fingerprint sensors and under-display cameras, enabling full-screen designs without notches or punch-holes[7]. BOE's flexible AMOLED technology allows for the creation of foldable and rollable devices, pushing the boundaries of mobile device form factors[8].
Strengths: Large-scale production capacity, diverse AMOLED solutions, advancements in flexible display technology. Weaknesses: Still catching up to Samsung in terms of overall display quality and market share.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has been at the forefront of AMOLED technology, revolutionizing mobile device aesthetics with their Dynamic AMOLED displays. Their latest innovation, the Dynamic AMOLED 2X, offers a 120Hz refresh rate, HDR10+ certification, and a peak brightness of 1500 nits[1]. Samsung's AMOLED displays feature organic materials that emit their own light, eliminating the need for a backlight. This allows for thinner and more flexible displays, enabling the creation of foldable and rollable devices[2]. The technology also provides perfect blacks, infinite contrast ratios, and vibrant colors, covering 100% of the DCI-P3 color gamut[3]. Samsung's AMOLED displays incorporate advanced features like Always-On Display and Edge lighting, enhancing user interaction and device aesthetics[4].
Strengths: Industry-leading display quality, innovative form factors, power efficiency. Weaknesses: Higher production costs, potential for screen burn-in over extended periods.
AMOLED Display Innovations
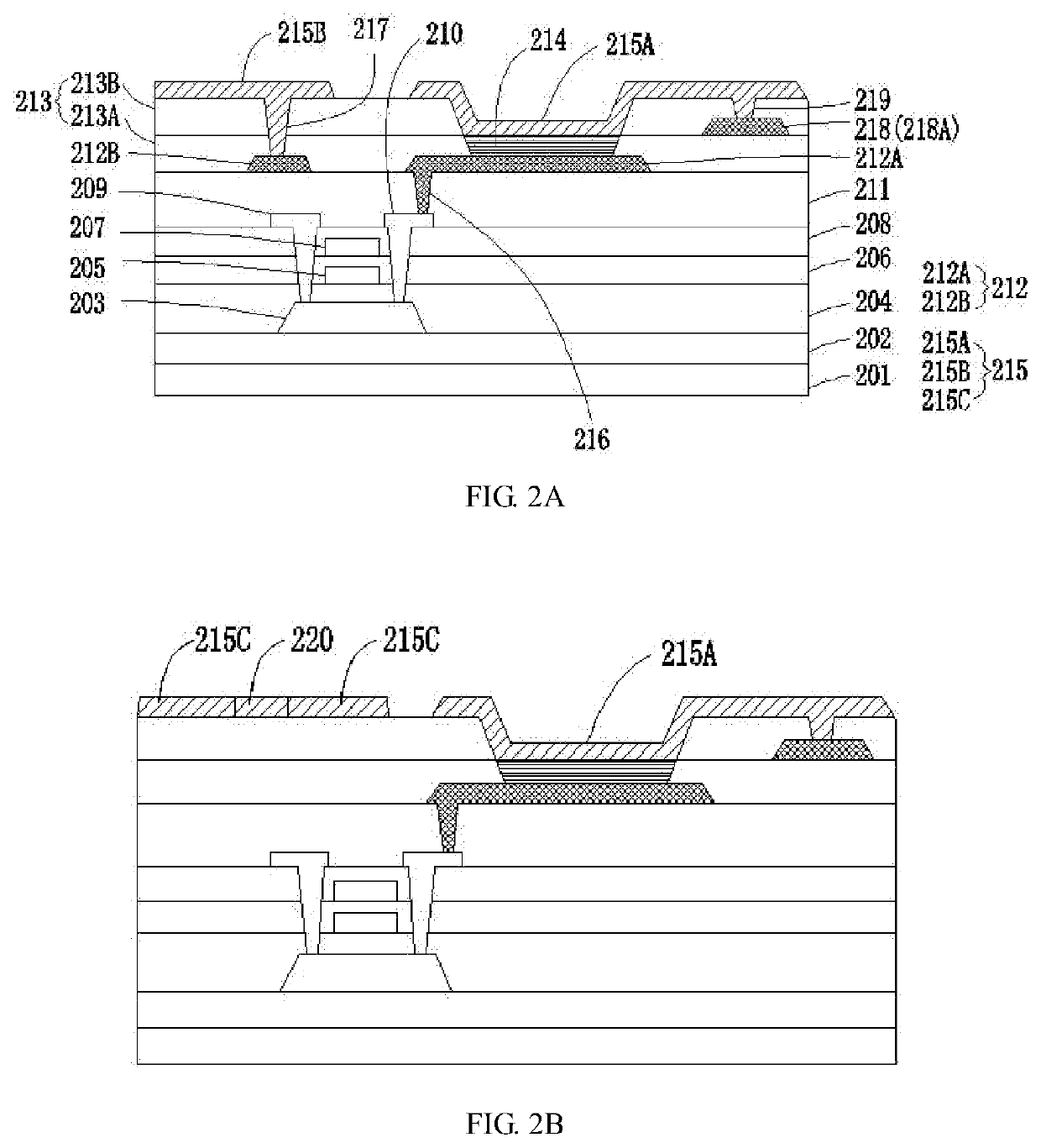
Active matrix organic light emitting diode display
PatentInactiveUS20090201235A1
Innovation
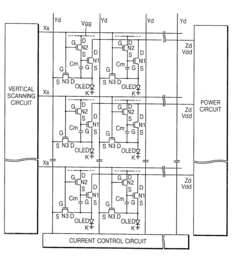
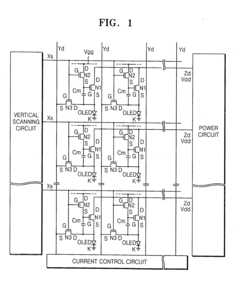
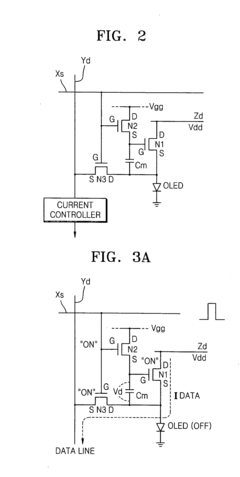
- An AMOLED display with a 3-transistor-1-capacitor structure using N-channel transistors, including a driving transistor, a switching transistor, and a programming transistor, along with a current controller, which determines the current flowing through the transistors to maintain uniform brightness by compensating for threshold voltage shifts, allowing for the use of amorphous silicon and simplifying the pixel structure.
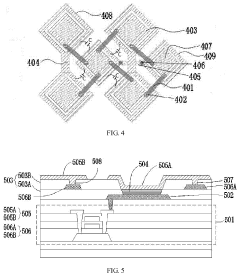
Active matrix organic light emitting diode (amoled) display panel
PatentInactiveUS20210343972A1
Innovation
- The integration of sensing electrodes into the AMOLED display panel allows for underscreen fingerprint identification, utilizing a patterned cathode layer with insulated first and second electrode rows and conductive bridges to form capacitors for fingerprint recognition, thereby embedding fingerprint identification within the screen and increasing the display area ratio.
AMOLED Energy Efficiency
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has significantly improved the energy efficiency of mobile devices, revolutionizing their aesthetics and functionality. This advancement has been crucial in addressing the ever-increasing demand for longer battery life in smartphones and other portable electronics.
One of the key factors contributing to AMOLED's energy efficiency is its ability to selectively illuminate individual pixels. Unlike traditional LCD displays that require constant backlighting across the entire screen, AMOLED panels can turn off pixels completely when displaying black, resulting in true blacks and significant power savings. This feature is particularly beneficial for devices with dark mode interfaces, as large portions of the screen can remain unlit, dramatically reducing power consumption.
The self-emissive nature of AMOLED displays eliminates the need for a separate backlight layer, further enhancing energy efficiency. This design not only reduces power consumption but also allows for thinner and lighter device profiles, contributing to the overall aesthetic appeal of mobile devices. The absence of a backlight also improves contrast ratios and color accuracy, resulting in more vibrant and lifelike images while consuming less power.
AMOLED technology has evolved to incorporate advanced power management techniques. Modern AMOLED displays utilize sophisticated algorithms that dynamically adjust pixel brightness based on content and ambient lighting conditions. This adaptive brightness control ensures optimal visibility while minimizing unnecessary power usage, further enhancing the energy efficiency of mobile devices.
The development of more efficient OLED materials has also played a crucial role in improving the energy efficiency of AMOLED displays. Researchers have made significant strides in creating organic compounds that emit light more efficiently, requiring less power to achieve the same level of brightness as earlier generations. This ongoing improvement in material science continues to push the boundaries of AMOLED efficiency.
Furthermore, the integration of AMOLED technology with system-on-chip (SoC) designs has led to more holistic power management solutions. Modern mobile processors are optimized to work in tandem with AMOLED displays, implementing features such as frame rate adjustment and selective refresh rates. These innovations allow devices to conserve energy by reducing display refresh rates during static content viewing or low-activity periods.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED technology has not only improved battery life but also enabled new form factors and design possibilities for mobile devices. The flexibility of AMOLED panels allows for the creation of curved and foldable displays, opening up new avenues for device aesthetics and functionality while maintaining power efficiency. This versatility has led to the development of innovative smartphone designs that were previously impractical with traditional display technologies.
One of the key factors contributing to AMOLED's energy efficiency is its ability to selectively illuminate individual pixels. Unlike traditional LCD displays that require constant backlighting across the entire screen, AMOLED panels can turn off pixels completely when displaying black, resulting in true blacks and significant power savings. This feature is particularly beneficial for devices with dark mode interfaces, as large portions of the screen can remain unlit, dramatically reducing power consumption.
The self-emissive nature of AMOLED displays eliminates the need for a separate backlight layer, further enhancing energy efficiency. This design not only reduces power consumption but also allows for thinner and lighter device profiles, contributing to the overall aesthetic appeal of mobile devices. The absence of a backlight also improves contrast ratios and color accuracy, resulting in more vibrant and lifelike images while consuming less power.
AMOLED technology has evolved to incorporate advanced power management techniques. Modern AMOLED displays utilize sophisticated algorithms that dynamically adjust pixel brightness based on content and ambient lighting conditions. This adaptive brightness control ensures optimal visibility while minimizing unnecessary power usage, further enhancing the energy efficiency of mobile devices.
The development of more efficient OLED materials has also played a crucial role in improving the energy efficiency of AMOLED displays. Researchers have made significant strides in creating organic compounds that emit light more efficiently, requiring less power to achieve the same level of brightness as earlier generations. This ongoing improvement in material science continues to push the boundaries of AMOLED efficiency.
Furthermore, the integration of AMOLED technology with system-on-chip (SoC) designs has led to more holistic power management solutions. Modern mobile processors are optimized to work in tandem with AMOLED displays, implementing features such as frame rate adjustment and selective refresh rates. These innovations allow devices to conserve energy by reducing display refresh rates during static content viewing or low-activity periods.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED technology has not only improved battery life but also enabled new form factors and design possibilities for mobile devices. The flexibility of AMOLED panels allows for the creation of curved and foldable displays, opening up new avenues for device aesthetics and functionality while maintaining power efficiency. This versatility has led to the development of innovative smartphone designs that were previously impractical with traditional display technologies.
AMOLED Supply Chain Analysis
The AMOLED supply chain plays a crucial role in the production and distribution of AMOLED displays, which have revolutionized mobile device aesthetics. This complex network involves multiple stages, from raw material sourcing to final product integration.
At the foundation of the AMOLED supply chain are the raw material suppliers. These companies provide essential components such as organic compounds, glass substrates, and conductive materials. Key players in this segment include Merck, UDC, and Corning, who have developed proprietary technologies to enhance AMOLED performance and durability.
The next stage involves panel manufacturers, who utilize these raw materials to produce AMOLED displays. Samsung Display dominates this sector, holding a significant market share. Other notable manufacturers include LG Display, BOE, and Visionox. These companies invest heavily in research and development to improve display quality, energy efficiency, and production yields.
Display driver IC manufacturers form another critical link in the chain. Companies like Samsung LSI, Synaptics, and Novatek develop the integrated circuits that control AMOLED displays, enabling features such as high refresh rates and HDR support.
Assembly and integration companies then incorporate these AMOLED panels into mobile devices. This stage involves close collaboration between display manufacturers and device makers to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance.
The AMOLED supply chain faces several challenges, including high production costs, yield management, and intellectual property concerns. However, ongoing technological advancements and increased competition are gradually addressing these issues, leading to wider adoption of AMOLED technology in mobile devices.
As demand for AMOLED displays continues to grow, the supply chain is evolving to meet market needs. New entrants, particularly from China, are expanding production capacity and challenging established players. This increased competition is driving innovation and cost reduction throughout the supply chain.
The geographical distribution of the AMOLED supply chain is primarily concentrated in East Asia, with South Korea, China, and Japan being major hubs. However, efforts to diversify production locations are underway, with companies exploring opportunities in other regions to mitigate geopolitical risks and reduce dependency on specific markets.
At the foundation of the AMOLED supply chain are the raw material suppliers. These companies provide essential components such as organic compounds, glass substrates, and conductive materials. Key players in this segment include Merck, UDC, and Corning, who have developed proprietary technologies to enhance AMOLED performance and durability.
The next stage involves panel manufacturers, who utilize these raw materials to produce AMOLED displays. Samsung Display dominates this sector, holding a significant market share. Other notable manufacturers include LG Display, BOE, and Visionox. These companies invest heavily in research and development to improve display quality, energy efficiency, and production yields.
Display driver IC manufacturers form another critical link in the chain. Companies like Samsung LSI, Synaptics, and Novatek develop the integrated circuits that control AMOLED displays, enabling features such as high refresh rates and HDR support.
Assembly and integration companies then incorporate these AMOLED panels into mobile devices. This stage involves close collaboration between display manufacturers and device makers to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance.
The AMOLED supply chain faces several challenges, including high production costs, yield management, and intellectual property concerns. However, ongoing technological advancements and increased competition are gradually addressing these issues, leading to wider adoption of AMOLED technology in mobile devices.
As demand for AMOLED displays continues to grow, the supply chain is evolving to meet market needs. New entrants, particularly from China, are expanding production capacity and challenging established players. This increased competition is driving innovation and cost reduction throughout the supply chain.
The geographical distribution of the AMOLED supply chain is primarily concentrated in East Asia, with South Korea, China, and Japan being major hubs. However, efforts to diversify production locations are underway, with companies exploring opportunities in other regions to mitigate geopolitical risks and reduce dependency on specific markets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!