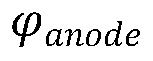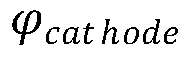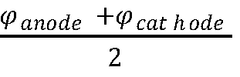AMOLED's role in advancing e-paper technology.
JUL 17, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED in E-Paper Tech
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has emerged as a potential game-changer in the advancement of e-paper technology. Traditionally, e-paper displays have relied on electrophoretic or electrowetting technologies, which offer excellent readability in various lighting conditions but suffer from slow refresh rates and limited color capabilities.
AMOLED displays, known for their vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and fast response times, are now being explored as a means to overcome these limitations in e-paper devices. The integration of AMOLED technology into e-paper displays promises to combine the best of both worlds: the energy efficiency and readability of e-paper with the color richness and responsiveness of AMOLED screens.
One of the key advantages of AMOLED in e-paper applications is its ability to produce true blacks by simply turning off individual pixels. This characteristic not only enhances contrast but also contributes to power efficiency, as black areas consume no energy. Furthermore, AMOLED's self-emissive nature eliminates the need for a backlight, potentially reducing the overall thickness and weight of e-paper devices.
The flexibility of AMOLED panels is another crucial factor in their potential for e-paper technology. Flexible AMOLED displays can be bent, rolled, or folded, opening up new form factors for e-readers and digital paper devices. This flexibility could lead to more durable and versatile e-paper products, capable of mimicking the feel and portability of traditional paper more closely than ever before.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing AMOLED's potential in e-paper technology. Power consumption, while improved, is still higher than traditional e-paper displays, especially when displaying dynamic content. Additionally, the cost of AMOLED panels remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption in e-paper devices, which typically target more budget-conscious markets.
Research and development efforts are focusing on addressing these challenges. Innovations in low-power AMOLED designs and more efficient driving schemes are being explored to reduce energy consumption. Simultaneously, advancements in manufacturing processes aim to bring down production costs, making AMOLED-based e-paper solutions more economically viable.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, its role in advancing e-paper technology is expected to grow. The potential for high-quality color displays with paper-like readability and flexibility could revolutionize not only e-readers but also digital signage, smart labels, and other applications where traditional e-paper has been limited. The convergence of AMOLED and e-paper technologies represents a promising direction for the future of digital reading and information display.
AMOLED displays, known for their vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and fast response times, are now being explored as a means to overcome these limitations in e-paper devices. The integration of AMOLED technology into e-paper displays promises to combine the best of both worlds: the energy efficiency and readability of e-paper with the color richness and responsiveness of AMOLED screens.
One of the key advantages of AMOLED in e-paper applications is its ability to produce true blacks by simply turning off individual pixels. This characteristic not only enhances contrast but also contributes to power efficiency, as black areas consume no energy. Furthermore, AMOLED's self-emissive nature eliminates the need for a backlight, potentially reducing the overall thickness and weight of e-paper devices.
The flexibility of AMOLED panels is another crucial factor in their potential for e-paper technology. Flexible AMOLED displays can be bent, rolled, or folded, opening up new form factors for e-readers and digital paper devices. This flexibility could lead to more durable and versatile e-paper products, capable of mimicking the feel and portability of traditional paper more closely than ever before.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing AMOLED's potential in e-paper technology. Power consumption, while improved, is still higher than traditional e-paper displays, especially when displaying dynamic content. Additionally, the cost of AMOLED panels remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption in e-paper devices, which typically target more budget-conscious markets.
Research and development efforts are focusing on addressing these challenges. Innovations in low-power AMOLED designs and more efficient driving schemes are being explored to reduce energy consumption. Simultaneously, advancements in manufacturing processes aim to bring down production costs, making AMOLED-based e-paper solutions more economically viable.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, its role in advancing e-paper technology is expected to grow. The potential for high-quality color displays with paper-like readability and flexibility could revolutionize not only e-readers but also digital signage, smart labels, and other applications where traditional e-paper has been limited. The convergence of AMOLED and e-paper technologies represents a promising direction for the future of digital reading and information display.
E-Paper Market Trends
The e-paper market has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for energy-efficient, eye-friendly display solutions. The global e-paper market size was valued at approximately $1.6 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $5.8 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 24.1% during the forecast period.
One of the key factors contributing to this growth is the expanding application of e-paper technology across various industries. While e-readers remain a primary use case, e-paper displays are increasingly being adopted in retail for electronic shelf labels, in transportation for digital signage, and in smart home devices for energy-efficient information displays. This diversification of applications is opening up new market opportunities and driving innovation in the sector.
The education sector has emerged as a particularly promising market for e-paper technology. With the rise of digital learning and the need for eye-friendly displays for extended reading, e-paper devices are gaining traction in schools and universities. This trend has been further accelerated by the global shift towards remote and hybrid learning models in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In terms of regional market trends, Asia Pacific is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the e-paper market. This can be attributed to the increasing adoption of e-readers, growing investments in digital infrastructure, and the presence of major display manufacturers in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, driven by technological advancements and the increasing focus on sustainable and energy-efficient display solutions.
The competitive landscape of the e-paper market is characterized by ongoing innovation and strategic partnerships. Key players are focusing on developing advanced e-paper technologies with improved color capabilities, faster refresh rates, and enhanced durability. Collaborations between e-paper manufacturers and device makers are becoming more common, aiming to create integrated solutions that cater to specific industry needs.
Environmental sustainability is emerging as a crucial factor shaping market trends. E-paper's low power consumption and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional displays are aligning well with the growing global emphasis on green technologies. This is likely to drive further adoption across various sectors, particularly in smart city initiatives and IoT applications.
One of the key factors contributing to this growth is the expanding application of e-paper technology across various industries. While e-readers remain a primary use case, e-paper displays are increasingly being adopted in retail for electronic shelf labels, in transportation for digital signage, and in smart home devices for energy-efficient information displays. This diversification of applications is opening up new market opportunities and driving innovation in the sector.
The education sector has emerged as a particularly promising market for e-paper technology. With the rise of digital learning and the need for eye-friendly displays for extended reading, e-paper devices are gaining traction in schools and universities. This trend has been further accelerated by the global shift towards remote and hybrid learning models in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In terms of regional market trends, Asia Pacific is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the e-paper market. This can be attributed to the increasing adoption of e-readers, growing investments in digital infrastructure, and the presence of major display manufacturers in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, driven by technological advancements and the increasing focus on sustainable and energy-efficient display solutions.
The competitive landscape of the e-paper market is characterized by ongoing innovation and strategic partnerships. Key players are focusing on developing advanced e-paper technologies with improved color capabilities, faster refresh rates, and enhanced durability. Collaborations between e-paper manufacturers and device makers are becoming more common, aiming to create integrated solutions that cater to specific industry needs.
Environmental sustainability is emerging as a crucial factor shaping market trends. E-paper's low power consumption and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional displays are aligning well with the growing global emphasis on green technologies. This is likely to drive further adoption across various sectors, particularly in smart city initiatives and IoT applications.
AMOLED vs E-Ink Tech
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and E-Ink technologies represent two distinct approaches to display technology, each with its own strengths and limitations. While E-Ink has long been the dominant technology in e-paper devices, AMOLED's advancements are beginning to challenge this status quo.
E-Ink technology, known for its paper-like appearance and low power consumption, has been the preferred choice for e-readers. It offers excellent readability in various lighting conditions, particularly in bright sunlight, and causes minimal eye strain during extended reading sessions. However, E-Ink displays typically suffer from slow refresh rates, limited color capabilities, and poor performance in low-light environments.
AMOLED, on the other hand, excels in areas where E-Ink falters. It provides vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and fast refresh rates, making it ideal for multimedia content and interactive applications. AMOLED displays are also thinner and more flexible, opening up new possibilities for device design. The technology's ability to selectively illuminate pixels results in true blacks and potentially lower power consumption for certain types of content.
Recent advancements in AMOLED technology are addressing some of its historical weaknesses, particularly in the realm of power efficiency. New pixel architectures and materials are reducing power consumption, bringing AMOLED closer to E-Ink in terms of battery life for static content display. Additionally, improvements in outdoor visibility and the development of low-temperature polycrystalline oxide (LTPO) backplanes are enhancing AMOLED's performance in bright light conditions.
The integration of AMOLED technology into e-paper devices could potentially revolutionize the e-reader market. By combining the benefits of both technologies, future devices could offer the readability of E-Ink with the versatility and visual appeal of AMOLED. This hybrid approach could lead to e-readers with color displays, faster page turns, and the ability to seamlessly switch between power-saving e-paper mode and high-performance video mode.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing AMOLED's potential in e-paper applications. Cost remains a significant factor, as AMOLED displays are generally more expensive to produce than E-Ink screens. Additionally, further improvements in power efficiency and outdoor readability are necessary to match E-Ink's performance in these critical areas for e-reader users.
As research and development continue, the gap between AMOLED and E-Ink technologies is likely to narrow. The future of e-paper technology may lie in a convergence of these display types, leveraging the strengths of each to create more versatile and capable reading devices.
E-Ink technology, known for its paper-like appearance and low power consumption, has been the preferred choice for e-readers. It offers excellent readability in various lighting conditions, particularly in bright sunlight, and causes minimal eye strain during extended reading sessions. However, E-Ink displays typically suffer from slow refresh rates, limited color capabilities, and poor performance in low-light environments.
AMOLED, on the other hand, excels in areas where E-Ink falters. It provides vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and fast refresh rates, making it ideal for multimedia content and interactive applications. AMOLED displays are also thinner and more flexible, opening up new possibilities for device design. The technology's ability to selectively illuminate pixels results in true blacks and potentially lower power consumption for certain types of content.
Recent advancements in AMOLED technology are addressing some of its historical weaknesses, particularly in the realm of power efficiency. New pixel architectures and materials are reducing power consumption, bringing AMOLED closer to E-Ink in terms of battery life for static content display. Additionally, improvements in outdoor visibility and the development of low-temperature polycrystalline oxide (LTPO) backplanes are enhancing AMOLED's performance in bright light conditions.
The integration of AMOLED technology into e-paper devices could potentially revolutionize the e-reader market. By combining the benefits of both technologies, future devices could offer the readability of E-Ink with the versatility and visual appeal of AMOLED. This hybrid approach could lead to e-readers with color displays, faster page turns, and the ability to seamlessly switch between power-saving e-paper mode and high-performance video mode.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing AMOLED's potential in e-paper applications. Cost remains a significant factor, as AMOLED displays are generally more expensive to produce than E-Ink screens. Additionally, further improvements in power efficiency and outdoor readability are necessary to match E-Ink's performance in these critical areas for e-reader users.
As research and development continue, the gap between AMOLED and E-Ink technologies is likely to narrow. The future of e-paper technology may lie in a convergence of these display types, leveraging the strengths of each to create more versatile and capable reading devices.
AMOLED-E-Paper Solutions
01 AMOLED display technology for e-paper applications
AMOLED technology is being adapted for e-paper applications, combining the benefits of OLED displays with the low power consumption of e-paper. This approach offers improved color reproduction, contrast, and refresh rates compared to traditional e-paper displays while maintaining energy efficiency.- AMOLED display technology for e-paper applications: AMOLED technology is being adapted for e-paper applications, combining the benefits of OLED displays with the low power consumption of e-paper. This approach offers improved color reproduction, contrast, and refresh rates compared to traditional e-paper displays while maintaining energy efficiency.
- Pixel circuit design for AMOLED e-paper displays: Specialized pixel circuits are developed for AMOLED e-paper displays to optimize power consumption and image retention. These circuits may include compensation mechanisms for voltage variations and aging effects, ensuring consistent performance over time.
- Integration of touch functionality in AMOLED e-paper displays: Touch sensing capabilities are being incorporated into AMOLED e-paper displays, enabling interactive features while maintaining the benefits of low power consumption. This integration may involve in-cell or on-cell touch technologies to minimize additional layers and preserve display quality.
- Color management and image processing for AMOLED e-paper: Advanced color management and image processing techniques are being developed to optimize the visual performance of AMOLED e-paper displays. These methods may include adaptive color gamut mapping, contrast enhancement, and power-efficient rendering algorithms to improve image quality while minimizing energy consumption.
- Flexible and foldable AMOLED e-paper displays: Research is being conducted on flexible and foldable AMOLED e-paper displays, combining the benefits of e-paper technology with the versatility of flexible OLED substrates. This approach enables new form factors and applications for e-paper devices, such as rollable or foldable e-readers and digital signage.
02 Pixel circuit design for AMOLED e-paper displays
Specialized pixel circuits are developed for AMOLED e-paper displays to optimize power consumption and image retention. These circuits may include compensation mechanisms for voltage variations and aging effects, ensuring consistent performance over time.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of touch functionality in AMOLED e-paper displays
Touch sensing capabilities are being incorporated into AMOLED e-paper displays, enabling interactive features while maintaining the benefits of low power consumption. This integration may involve in-cell or on-cell touch technologies to minimize additional layers and preserve display quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Color management and image processing for AMOLED e-paper
Advanced color management and image processing techniques are being developed to optimize the visual performance of AMOLED e-paper displays. These methods aim to enhance color accuracy, reduce power consumption, and improve readability in various lighting conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Flexible and foldable AMOLED e-paper displays
Research is being conducted on flexible and foldable AMOLED e-paper displays, combining the benefits of e-paper technology with the versatility of flexible OLED screens. This development aims to create more durable and adaptable e-paper devices for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key AMOLED Manufacturers
The AMOLED technology's role in advancing e-paper displays is at an early stage of development, with a growing market potential. The industry is transitioning from traditional e-paper to more advanced display technologies. Major players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology Group, and TCL China Star Optoelectronics are investing in AMOLED research for e-paper applications. While the technology is not yet fully mature for e-paper, these companies are leveraging their expertise in AMOLED displays to explore innovative solutions. The market size is expected to expand as AMOLED e-paper technology progresses, offering improved color reproduction, contrast, and energy efficiency compared to conventional e-paper displays.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has been working on integrating AMOLED technology into flexible e-paper displays. Their approach focuses on creating ultra-thin, bendable displays that combine the energy efficiency of e-paper with the color capabilities of AMOLED. BOE's flexible AMOLED e-paper uses a plastic substrate instead of glass, allowing for lighter and more durable devices[4]. They have developed a proprietary pixel structure that enables rapid switching between reflective and emissive modes, reducing power consumption by up to 70% compared to traditional AMOLED displays when in e-paper mode[5]. BOE has also introduced touch functionality to their AMOLED e-paper, enhancing interactivity while maintaining the low power benefits of e-ink technology[6].
Strengths: Ultra-thin and flexible design; significant power savings in e-paper mode; enhanced durability. Weaknesses: Higher production costs; potential color accuracy issues in reflective mode.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has been at the forefront of AMOLED technology development, which is now being applied to advance e-paper displays. Their approach involves integrating AMOLED's self-emitting pixels with e-paper's reflective properties. This hybrid technology allows for a display that can switch between emissive and reflective modes[1]. In emissive mode, it functions like a traditional AMOLED display with vibrant colors and high contrast. In reflective mode, it mimics e-paper, consuming minimal power and offering excellent readability in bright light[2]. Samsung has also developed a color-converting layer that enables full-color e-paper displays using AMOLED technology, potentially revolutionizing the e-reader market[3].
Strengths: High contrast and color vibrancy in emissive mode; low power consumption in reflective mode; potential for full-color e-paper displays. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional e-paper; complexity in manufacturing dual-mode displays.
AMOLED E-Paper Patents
Amoled double-side display
PatentActiveUS20200219957A1
Innovation
- An AMOLED double-sided display design featuring a substrate with alternating top-emitting and bottom-emitting OLED units, where the anode of top-emitting units is thicker and reflective, and the cathode of bottom-emitting units is thicker and light-transmissive, allowing for single IC control and eliminating mirrored images.
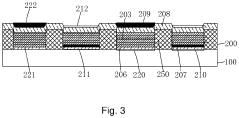
Organic light-emitting diode structure and fabrication method thereof, related display panel, and related display device
PatentWO2017070892A1
Innovation
- Addressing the low efficiency and short service time of blue light-emitting organic materials in AMOLED displays.
- Utilizing AMOLED technology to enhance e-paper display performance, potentially combining the advantages of both technologies.
- Developing fabrication methods specific to OLED structures for e-paper applications.
Energy Efficiency Impact
The integration of AMOLED technology into e-paper displays has significant implications for energy efficiency in the realm of electronic reading devices. AMOLED screens, known for their low power consumption when displaying dark content, offer a unique advantage in e-paper applications where text is typically presented on a light background.
When compared to traditional e-paper technologies like E Ink, AMOLED displays can potentially reduce power consumption during active reading sessions. This is particularly evident when users opt for dark mode settings, where the majority of pixels remain unlit. The self-emissive nature of AMOLED pixels means that power is only consumed by the illuminated areas, resulting in substantial energy savings.
However, it's important to note that the energy efficiency of AMOLED in e-paper applications is context-dependent. For scenarios involving prolonged static image display, such as leaving an e-book page open for extended periods, traditional e-paper technologies may still hold an advantage due to their bistable nature, which requires no power to maintain an image once it's set.
The potential for AMOLED to enhance e-paper energy efficiency extends beyond mere power consumption. The technology's ability to selectively activate pixels allows for innovative power management strategies. For instance, partial screen updates and localized refresh rates can be implemented more effectively, further optimizing energy usage during reading sessions.
Moreover, the color capabilities of AMOLED displays open up new possibilities for energy-efficient content presentation in e-paper devices. By utilizing darker color schemes and optimizing contrast ratios, developers can create reading experiences that are both visually appealing and power-efficient. This flexibility in color manipulation is particularly beneficial for educational materials, magazines, and interactive e-books.
As battery technology continues to evolve, the synergy between high-capacity, long-lasting batteries and AMOLED's energy-efficient display characteristics could lead to e-paper devices with unprecedented battery life. This combination has the potential to address one of the primary concerns of e-reader users: the need for frequent charging.
In conclusion, while the energy efficiency impact of AMOLED on e-paper technology is promising, it requires careful consideration of use cases and reading habits. The technology's potential to revolutionize e-paper energy efficiency is significant, but its full realization depends on thoughtful implementation and continued advancements in both display and power management technologies.
When compared to traditional e-paper technologies like E Ink, AMOLED displays can potentially reduce power consumption during active reading sessions. This is particularly evident when users opt for dark mode settings, where the majority of pixels remain unlit. The self-emissive nature of AMOLED pixels means that power is only consumed by the illuminated areas, resulting in substantial energy savings.
However, it's important to note that the energy efficiency of AMOLED in e-paper applications is context-dependent. For scenarios involving prolonged static image display, such as leaving an e-book page open for extended periods, traditional e-paper technologies may still hold an advantage due to their bistable nature, which requires no power to maintain an image once it's set.
The potential for AMOLED to enhance e-paper energy efficiency extends beyond mere power consumption. The technology's ability to selectively activate pixels allows for innovative power management strategies. For instance, partial screen updates and localized refresh rates can be implemented more effectively, further optimizing energy usage during reading sessions.
Moreover, the color capabilities of AMOLED displays open up new possibilities for energy-efficient content presentation in e-paper devices. By utilizing darker color schemes and optimizing contrast ratios, developers can create reading experiences that are both visually appealing and power-efficient. This flexibility in color manipulation is particularly beneficial for educational materials, magazines, and interactive e-books.
As battery technology continues to evolve, the synergy between high-capacity, long-lasting batteries and AMOLED's energy-efficient display characteristics could lead to e-paper devices with unprecedented battery life. This combination has the potential to address one of the primary concerns of e-reader users: the need for frequent charging.
In conclusion, while the energy efficiency impact of AMOLED on e-paper technology is promising, it requires careful consideration of use cases and reading habits. The technology's potential to revolutionize e-paper energy efficiency is significant, but its full realization depends on thoughtful implementation and continued advancements in both display and power management technologies.
Supply Chain Analysis
The supply chain for AMOLED technology in e-paper applications involves a complex network of manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors. Key components in this chain include substrate materials, organic light-emitting materials, thin-film transistors, and encapsulation technologies.
Major AMOLED panel manufacturers like Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE play crucial roles in the supply chain. These companies have invested heavily in research and development to improve AMOLED technology for various applications, including e-paper displays. Their advancements in flexible and foldable AMOLED panels have opened new possibilities for e-paper devices.
The production of organic light-emitting materials is a critical aspect of the AMOLED supply chain. Companies such as Universal Display Corporation and Idemitsu Kosan are leading suppliers of these materials, continuously developing new compounds to enhance display performance and efficiency.
Thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane technology is another essential component. Manufacturers like Japan Display Inc. and Sharp Corporation have made significant progress in low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) TFT technology, which is crucial for high-resolution AMOLED displays in e-paper applications.
The integration of AMOLED technology into e-paper devices requires specialized manufacturing processes. Companies like E Ink Holdings, which traditionally focus on electrophoretic displays, are exploring partnerships with AMOLED manufacturers to develop hybrid solutions that combine the benefits of both technologies.
Supply chain challenges for AMOLED in e-paper technology include the high cost of materials and manufacturing processes, yield issues in large-scale production, and the need for specialized equipment. These factors have limited the widespread adoption of AMOLED in e-paper devices, particularly in cost-sensitive markets.
However, ongoing innovations in manufacturing techniques and materials science are gradually addressing these challenges. For instance, advancements in solution-processed OLED materials and printing technologies are paving the way for more cost-effective production methods, potentially making AMOLED more viable for e-paper applications.
The global nature of the AMOLED supply chain also presents both opportunities and challenges. While it allows for specialization and economies of scale, it also makes the industry vulnerable to geopolitical tensions and supply disruptions, as seen in recent years with semiconductor shortages.
Major AMOLED panel manufacturers like Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE play crucial roles in the supply chain. These companies have invested heavily in research and development to improve AMOLED technology for various applications, including e-paper displays. Their advancements in flexible and foldable AMOLED panels have opened new possibilities for e-paper devices.
The production of organic light-emitting materials is a critical aspect of the AMOLED supply chain. Companies such as Universal Display Corporation and Idemitsu Kosan are leading suppliers of these materials, continuously developing new compounds to enhance display performance and efficiency.
Thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane technology is another essential component. Manufacturers like Japan Display Inc. and Sharp Corporation have made significant progress in low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) TFT technology, which is crucial for high-resolution AMOLED displays in e-paper applications.
The integration of AMOLED technology into e-paper devices requires specialized manufacturing processes. Companies like E Ink Holdings, which traditionally focus on electrophoretic displays, are exploring partnerships with AMOLED manufacturers to develop hybrid solutions that combine the benefits of both technologies.
Supply chain challenges for AMOLED in e-paper technology include the high cost of materials and manufacturing processes, yield issues in large-scale production, and the need for specialized equipment. These factors have limited the widespread adoption of AMOLED in e-paper devices, particularly in cost-sensitive markets.
However, ongoing innovations in manufacturing techniques and materials science are gradually addressing these challenges. For instance, advancements in solution-processed OLED materials and printing technologies are paving the way for more cost-effective production methods, potentially making AMOLED more viable for e-paper applications.
The global nature of the AMOLED supply chain also presents both opportunities and challenges. While it allows for specialization and economies of scale, it also makes the industry vulnerable to geopolitical tensions and supply disruptions, as seen in recent years with semiconductor shortages.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!