Ethical considerations in AMOLED production sustainability.
JUL 17, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Sustainability Background and Objectives
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has revolutionized the display industry with its superior image quality, energy efficiency, and design flexibility. However, as the demand for AMOLED displays continues to grow, so does the concern for sustainable production practices. The ethical considerations in AMOLED production sustainability have become a critical focus for manufacturers, researchers, and policymakers alike.
The evolution of AMOLED technology can be traced back to the late 1980s with the development of organic electroluminescent materials. Over the years, significant advancements have been made in materials science, manufacturing processes, and device architectures, leading to the widespread adoption of AMOLED displays in smartphones, televisions, and other electronic devices. As the technology matures, the industry is now at a crucial juncture where sustainability must be integrated into every aspect of AMOLED production.
The primary objective of addressing ethical considerations in AMOLED production sustainability is to minimize the environmental impact of manufacturing processes while ensuring fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of materials. This involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses the entire lifecycle of AMOLED displays, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal and recycling.
One of the key challenges in AMOLED production is the use of rare earth elements and precious metals, which are essential for the fabrication of high-performance displays. The ethical sourcing of these materials, particularly from conflict-free zones, has become a priority for manufacturers seeking to align their practices with global sustainability standards.
Energy consumption during the production process is another critical area of focus. AMOLED manufacturing requires precise control of environmental conditions and complex deposition processes, which can be energy-intensive. The industry is actively exploring ways to optimize energy usage and transition to renewable energy sources to reduce the carbon footprint of AMOLED production.
Water usage and chemical waste management are also significant concerns in AMOLED manufacturing. The production of OLED panels involves various chemical processes that generate potentially hazardous waste. Developing closed-loop systems for water recycling and implementing advanced waste treatment technologies are essential steps towards more sustainable production practices.
As the AMOLED industry continues to expand, there is a growing emphasis on worker safety and fair labor practices. Ensuring safe working conditions, fair wages, and proper training for employees involved in the production process is crucial for the ethical sustainability of AMOLED manufacturing.
Looking ahead, the AMOLED industry aims to achieve a balance between technological innovation and sustainable practices. This includes developing new materials that are more environmentally friendly, improving manufacturing efficiency to reduce resource consumption, and designing products with longer lifespans and easier recyclability. By addressing these ethical considerations, the AMOLED industry can pave the way for a more sustainable future in display technology.
The evolution of AMOLED technology can be traced back to the late 1980s with the development of organic electroluminescent materials. Over the years, significant advancements have been made in materials science, manufacturing processes, and device architectures, leading to the widespread adoption of AMOLED displays in smartphones, televisions, and other electronic devices. As the technology matures, the industry is now at a crucial juncture where sustainability must be integrated into every aspect of AMOLED production.
The primary objective of addressing ethical considerations in AMOLED production sustainability is to minimize the environmental impact of manufacturing processes while ensuring fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of materials. This involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses the entire lifecycle of AMOLED displays, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal and recycling.
One of the key challenges in AMOLED production is the use of rare earth elements and precious metals, which are essential for the fabrication of high-performance displays. The ethical sourcing of these materials, particularly from conflict-free zones, has become a priority for manufacturers seeking to align their practices with global sustainability standards.
Energy consumption during the production process is another critical area of focus. AMOLED manufacturing requires precise control of environmental conditions and complex deposition processes, which can be energy-intensive. The industry is actively exploring ways to optimize energy usage and transition to renewable energy sources to reduce the carbon footprint of AMOLED production.
Water usage and chemical waste management are also significant concerns in AMOLED manufacturing. The production of OLED panels involves various chemical processes that generate potentially hazardous waste. Developing closed-loop systems for water recycling and implementing advanced waste treatment technologies are essential steps towards more sustainable production practices.
As the AMOLED industry continues to expand, there is a growing emphasis on worker safety and fair labor practices. Ensuring safe working conditions, fair wages, and proper training for employees involved in the production process is crucial for the ethical sustainability of AMOLED manufacturing.
Looking ahead, the AMOLED industry aims to achieve a balance between technological innovation and sustainable practices. This includes developing new materials that are more environmentally friendly, improving manufacturing efficiency to reduce resource consumption, and designing products with longer lifespans and easier recyclability. By addressing these ethical considerations, the AMOLED industry can pave the way for a more sustainable future in display technology.
Market Demand for Sustainable AMOLED Displays
The market demand for sustainable AMOLED displays has been growing rapidly in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and corporate sustainability initiatives. This trend is particularly evident in the consumer electronics sector, where manufacturers are under pressure to reduce their environmental footprint and meet stringent sustainability standards.
AMOLED technology, known for its superior image quality and energy efficiency, has already established a strong presence in the smartphone and television markets. However, the production processes for AMOLED displays have traditionally involved the use of environmentally harmful materials and energy-intensive manufacturing techniques. This has created a significant market opportunity for sustainable AMOLED production methods that can address these environmental concerns while maintaining the technology's performance advantages.
Major electronics manufacturers have recognized this demand and are investing heavily in research and development to create more sustainable AMOLED displays. These efforts are focused on reducing energy consumption during production, minimizing the use of rare earth elements and toxic chemicals, and improving the recyclability of display components.
The automotive industry has emerged as a key growth area for sustainable AMOLED displays. As electric vehicles gain market share, there is an increasing demand for advanced, energy-efficient display technologies that align with the overall sustainability goals of these vehicles. Sustainable AMOLED displays are seen as an ideal solution for in-vehicle infotainment systems and digital dashboards.
Consumer demand for sustainable electronics has also led to the development of eco-rating systems and certifications for display technologies. These ratings are becoming increasingly important in purchasing decisions, particularly in markets with high environmental awareness. As a result, manufacturers who can demonstrate the sustainability of their AMOLED production processes are likely to gain a competitive advantage.
The healthcare and medical device sectors represent another growing market for sustainable AMOLED displays. The need for high-quality, energy-efficient displays in medical imaging and diagnostic equipment is driving demand for AMOLED technology that meets strict environmental and ethical standards.
Despite the clear market demand, challenges remain in scaling up sustainable AMOLED production. The industry must balance the need for sustainability with cost considerations and performance requirements. This has led to increased collaboration between display manufacturers, materials scientists, and environmental experts to develop innovative solutions that can meet market demands while addressing ethical and sustainability concerns.
As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental regulations, the demand for sustainable AMOLED displays is expected to accelerate further. This regulatory pressure, combined with consumer preferences, is likely to reshape the competitive landscape of the display industry, favoring companies that can successfully integrate sustainability into their AMOLED production processes.
AMOLED technology, known for its superior image quality and energy efficiency, has already established a strong presence in the smartphone and television markets. However, the production processes for AMOLED displays have traditionally involved the use of environmentally harmful materials and energy-intensive manufacturing techniques. This has created a significant market opportunity for sustainable AMOLED production methods that can address these environmental concerns while maintaining the technology's performance advantages.
Major electronics manufacturers have recognized this demand and are investing heavily in research and development to create more sustainable AMOLED displays. These efforts are focused on reducing energy consumption during production, minimizing the use of rare earth elements and toxic chemicals, and improving the recyclability of display components.
The automotive industry has emerged as a key growth area for sustainable AMOLED displays. As electric vehicles gain market share, there is an increasing demand for advanced, energy-efficient display technologies that align with the overall sustainability goals of these vehicles. Sustainable AMOLED displays are seen as an ideal solution for in-vehicle infotainment systems and digital dashboards.
Consumer demand for sustainable electronics has also led to the development of eco-rating systems and certifications for display technologies. These ratings are becoming increasingly important in purchasing decisions, particularly in markets with high environmental awareness. As a result, manufacturers who can demonstrate the sustainability of their AMOLED production processes are likely to gain a competitive advantage.
The healthcare and medical device sectors represent another growing market for sustainable AMOLED displays. The need for high-quality, energy-efficient displays in medical imaging and diagnostic equipment is driving demand for AMOLED technology that meets strict environmental and ethical standards.
Despite the clear market demand, challenges remain in scaling up sustainable AMOLED production. The industry must balance the need for sustainability with cost considerations and performance requirements. This has led to increased collaboration between display manufacturers, materials scientists, and environmental experts to develop innovative solutions that can meet market demands while addressing ethical and sustainability concerns.
As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental regulations, the demand for sustainable AMOLED displays is expected to accelerate further. This regulatory pressure, combined with consumer preferences, is likely to reshape the competitive landscape of the display industry, favoring companies that can successfully integrate sustainability into their AMOLED production processes.
Ethical Challenges in AMOLED Production
The production of AMOLED displays raises several ethical concerns that demand careful consideration. One of the primary issues is the environmental impact of the manufacturing process. AMOLED production involves the use of rare earth elements and toxic chemicals, which can lead to significant environmental degradation if not properly managed. The extraction of these materials often occurs in developing countries, raising questions about fair labor practices and the exploitation of local communities.
Another ethical challenge lies in the energy-intensive nature of AMOLED production. The high energy consumption contributes to increased carbon emissions, exacerbating climate change concerns. This raises the question of whether the benefits of AMOLED technology outweigh its environmental costs, and how manufacturers can balance technological advancement with ecological responsibility.
The issue of worker safety in AMOLED production facilities is also a critical ethical consideration. Employees may be exposed to hazardous materials and working conditions, necessitating stringent safety protocols and fair labor practices. Ensuring proper training, protective equipment, and adequate compensation for workers in potentially dangerous environments is an ethical imperative for manufacturers.
Furthermore, the rapid obsolescence of electronic devices containing AMOLED displays contributes to the growing problem of e-waste. The ethical responsibility of manufacturers extends beyond production to the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. Developing sustainable end-of-life strategies for AMOLED displays is crucial to mitigate environmental impact and resource depletion.
The global supply chain for AMOLED production also presents ethical challenges. Ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain is essential to prevent human rights abuses, such as child labor or forced labor, in the sourcing of raw materials. Manufacturers must implement robust due diligence processes to verify the ethical standards of their suppliers and subcontractors.
Intellectual property rights and technology transfer pose additional ethical dilemmas in AMOLED production. Balancing the protection of proprietary technologies with the need for innovation and fair competition requires careful consideration. Ethical concerns arise when companies engage in aggressive patent litigation or restrict access to essential technologies, potentially hindering industry-wide advancements in sustainability.
Lastly, the ethical implications of planned obsolescence in AMOLED technology must be addressed. As manufacturers continually develop new and improved displays, there is a risk of artificially shortening the lifespan of existing products to drive consumer demand. This practice raises questions about corporate responsibility, consumer rights, and the broader societal impact of unsustainable consumption patterns.
Another ethical challenge lies in the energy-intensive nature of AMOLED production. The high energy consumption contributes to increased carbon emissions, exacerbating climate change concerns. This raises the question of whether the benefits of AMOLED technology outweigh its environmental costs, and how manufacturers can balance technological advancement with ecological responsibility.
The issue of worker safety in AMOLED production facilities is also a critical ethical consideration. Employees may be exposed to hazardous materials and working conditions, necessitating stringent safety protocols and fair labor practices. Ensuring proper training, protective equipment, and adequate compensation for workers in potentially dangerous environments is an ethical imperative for manufacturers.
Furthermore, the rapid obsolescence of electronic devices containing AMOLED displays contributes to the growing problem of e-waste. The ethical responsibility of manufacturers extends beyond production to the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. Developing sustainable end-of-life strategies for AMOLED displays is crucial to mitigate environmental impact and resource depletion.
The global supply chain for AMOLED production also presents ethical challenges. Ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain is essential to prevent human rights abuses, such as child labor or forced labor, in the sourcing of raw materials. Manufacturers must implement robust due diligence processes to verify the ethical standards of their suppliers and subcontractors.
Intellectual property rights and technology transfer pose additional ethical dilemmas in AMOLED production. Balancing the protection of proprietary technologies with the need for innovation and fair competition requires careful consideration. Ethical concerns arise when companies engage in aggressive patent litigation or restrict access to essential technologies, potentially hindering industry-wide advancements in sustainability.
Lastly, the ethical implications of planned obsolescence in AMOLED technology must be addressed. As manufacturers continually develop new and improved displays, there is a risk of artificially shortening the lifespan of existing products to drive consumer demand. This practice raises questions about corporate responsibility, consumer rights, and the broader societal impact of unsustainable consumption patterns.
Current Sustainable AMOLED Production Methods
01 Energy-efficient AMOLED production
AMOLED production processes are being optimized for energy efficiency, reducing power consumption during manufacturing. This includes improvements in display driver circuits, pixel structures, and power management systems. These advancements contribute to more sustainable production practices and reduced environmental impact.- Energy-efficient AMOLED production: AMOLED production processes are being optimized for energy efficiency, reducing power consumption during manufacturing. This includes improvements in display driver circuits, pixel structures, and power management systems to minimize energy waste and enhance overall sustainability in production.
- Sustainable materials for AMOLED displays: Research is focused on developing and incorporating eco-friendly materials in AMOLED production. This includes the use of recyclable substrates, organic light-emitting materials, and reducing the reliance on rare earth elements. These efforts aim to minimize environmental impact and improve the sustainability of AMOLED technology.
- Improved manufacturing processes for sustainability: Advancements in AMOLED manufacturing processes are being made to reduce waste, improve yield rates, and minimize resource consumption. This includes the development of more efficient deposition techniques, optimized production line layouts, and the implementation of smart manufacturing systems to enhance overall sustainability in AMOLED production.
- Recycling and circular economy in AMOLED production: Efforts are being made to implement recycling programs and circular economy principles in AMOLED production. This includes developing methods for recovering and reusing valuable materials from end-of-life displays, as well as designing products with easier disassembly and recycling in mind to promote sustainability throughout the product lifecycle.
- Life cycle assessment and sustainability metrics: The AMOLED industry is focusing on developing comprehensive life cycle assessments and sustainability metrics to evaluate and improve the environmental impact of production processes. This includes analyzing factors such as carbon footprint, water usage, and chemical emissions throughout the entire production chain to identify areas for sustainability improvements.
02 Sustainable materials in AMOLED displays
Researchers are developing eco-friendly materials for AMOLED displays, focusing on biodegradable and recyclable components. This includes organic light-emitting materials, substrate materials, and encapsulation layers. The use of sustainable materials helps reduce the environmental footprint of AMOLED production and improves end-of-life recyclability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Improved manufacturing processes for AMOLED
Advancements in AMOLED manufacturing processes aim to reduce waste, improve yield rates, and minimize resource consumption. This includes innovations in deposition techniques, patterning methods, and quality control systems. These improvements contribute to more sustainable production by optimizing material usage and reducing energy consumption.Expand Specific Solutions04 Longevity and durability of AMOLED displays
Efforts are being made to enhance the lifespan and durability of AMOLED displays, reducing the need for frequent replacements. This includes developing more robust organic materials, improved encapsulation techniques, and advanced burn-in compensation algorithms. Longer-lasting displays contribute to sustainability by reducing electronic waste and conserving resources.Expand Specific Solutions05 Recycling and circular economy in AMOLED production
The AMOLED industry is exploring recycling technologies and circular economy principles to minimize waste and recover valuable materials. This includes developing processes for reclaiming rare earth elements, recycling organic materials, and designing displays for easier disassembly and material recovery. These initiatives aim to create a more sustainable lifecycle for AMOLED products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable AMOLED Manufacturing
The ethical considerations in AMOLED production sustainability are gaining prominence as the industry matures. The market for AMOLED displays is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing demand for high-quality displays in smartphones, TVs, and other consumer electronics. Key players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology, and Japan Display are investing heavily in AMOLED technology, indicating its growing importance. However, the industry faces challenges in sustainable production practices, including energy consumption, material sourcing, and waste management. Companies are exploring innovative solutions to address these issues, with some like BOE and Samsung leading efforts in eco-friendly manufacturing processes and recycling initiatives. As the technology advances, balancing production efficiency with environmental responsibility remains a critical focus for industry leaders.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has implemented a comprehensive sustainability strategy for AMOLED production, focusing on reducing environmental impact and improving resource efficiency. They have developed an innovative "Green Factory" concept, which incorporates advanced waste management systems and energy-efficient manufacturing processes[1]. BOE's approach includes the use of eco-friendly materials in AMOLED panels, such as low-emission organic compounds and recyclable components. The company has also invested in water recycling technologies, achieving a water reuse rate of over 90% in some of their production facilities[2]. Additionally, BOE has implemented strict supplier management policies to ensure ethical sourcing of raw materials, particularly focusing on conflict-free minerals[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive sustainability approach, high water reuse rate, and ethical sourcing policies. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs and challenges in maintaining consistent quality while using eco-friendly materials.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has been at the forefront of ethical considerations in AMOLED production sustainability. They have implemented a circular economy approach, focusing on reducing waste and maximizing resource efficiency. Samsung's "Galaxy Upcycling" program repurposes old Galaxy smartphones into IoT devices, extending product lifecycles[4]. For AMOLED production, Samsung has developed eco-friendly quantum dot technology that eliminates the use of toxic cadmium[5]. The company has also invested heavily in renewable energy, with a commitment to using 100% renewable energy in all its global operations by 2050[6]. Samsung's ethical sourcing policy ensures responsible mineral sourcing and fair labor practices throughout its supply chain.
Strengths: Industry-leading circular economy initiatives, innovative eco-friendly technologies, and strong commitment to renewable energy. Weaknesses: High investment costs for sustainability initiatives and potential challenges in scaling eco-friendly technologies across all product lines.
Innovations in Eco-friendly AMOLED Materials
Active matrix organic light emitting diode panel
PatentInactiveUS20200185645A1
Innovation
- An AMOLED panel design featuring a hydrogel layer coated between two backing plates at the bent portion, which is then solidified with ultraviolet light, providing structural strength and toughness to the fillet formed when the panel is folded, thereby preventing deformation and breakage.
Array substrate, display device, and method for manufacturing array substrate
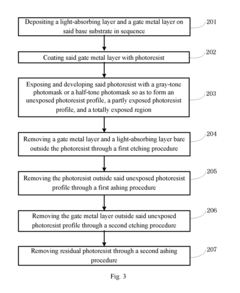
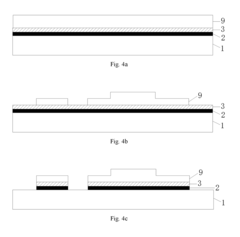
PatentActiveUS20170148862A1
Innovation
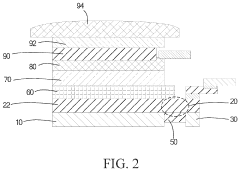
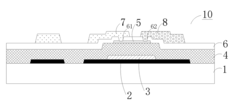
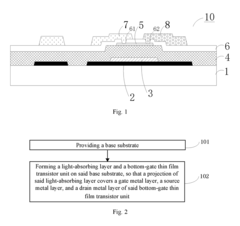
- An array substrate with a light-absorbing layer covering the gate, source, and drain metal layers of a bottom-gate thin film transistor unit, preventing ambient light irradiation while allowing useful light to pass through.
Environmental Regulations for Display Industry
The display industry, particularly in AMOLED production, is subject to a complex web of environmental regulations aimed at mitigating the ecological impact of manufacturing processes. These regulations vary across regions but generally focus on reducing emissions, managing hazardous materials, and promoting sustainable practices.
In the European Union, the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive plays a crucial role in limiting the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, including AMOLED displays. This directive restricts the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls (PBB), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) in electronic products.
The REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation in the EU further complements RoHS by requiring manufacturers to register and manage the risks associated with chemicals used in their products. This regulation has significant implications for AMOLED producers, as it necessitates careful consideration of the materials used in display production.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces regulations under the Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act that impact AMOLED manufacturing. These regulations set limits on air emissions and wastewater discharges from production facilities, requiring manufacturers to implement advanced pollution control technologies.
China, a major player in the display industry, has implemented its own set of environmental regulations. The Ministry of Ecology and Environment enforces standards for air and water quality, as well as hazardous waste management, which directly affect AMOLED production facilities operating within the country.
Global initiatives like the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) also influence the regulatory landscape. SDG 12, which focuses on responsible consumption and production, has led to increased pressure on the display industry to adopt more sustainable practices and circular economy principles.
The evolving nature of environmental regulations presents both challenges and opportunities for AMOLED producers. Compliance often requires significant investments in cleaner technologies and process improvements. However, it also drives innovation in sustainable manufacturing methods, potentially leading to long-term cost savings and improved brand reputation.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, it is likely that regulations will become increasingly stringent. AMOLED manufacturers must stay ahead of these changes by proactively adopting sustainable practices and investing in research and development of eco-friendly production methods. This approach not only ensures compliance but also positions companies as leaders in sustainable technology production.
In the European Union, the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive plays a crucial role in limiting the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, including AMOLED displays. This directive restricts the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls (PBB), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) in electronic products.
The REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation in the EU further complements RoHS by requiring manufacturers to register and manage the risks associated with chemicals used in their products. This regulation has significant implications for AMOLED producers, as it necessitates careful consideration of the materials used in display production.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces regulations under the Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act that impact AMOLED manufacturing. These regulations set limits on air emissions and wastewater discharges from production facilities, requiring manufacturers to implement advanced pollution control technologies.
China, a major player in the display industry, has implemented its own set of environmental regulations. The Ministry of Ecology and Environment enforces standards for air and water quality, as well as hazardous waste management, which directly affect AMOLED production facilities operating within the country.
Global initiatives like the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) also influence the regulatory landscape. SDG 12, which focuses on responsible consumption and production, has led to increased pressure on the display industry to adopt more sustainable practices and circular economy principles.
The evolving nature of environmental regulations presents both challenges and opportunities for AMOLED producers. Compliance often requires significant investments in cleaner technologies and process improvements. However, it also drives innovation in sustainable manufacturing methods, potentially leading to long-term cost savings and improved brand reputation.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, it is likely that regulations will become increasingly stringent. AMOLED manufacturers must stay ahead of these changes by proactively adopting sustainable practices and investing in research and development of eco-friendly production methods. This approach not only ensures compliance but also positions companies as leaders in sustainable technology production.
Socioeconomic Impact of AMOLED Manufacturing
The socioeconomic impact of AMOLED manufacturing extends far beyond the technological realm, influencing various aspects of society and the economy. As AMOLED technology continues to gain prominence in consumer electronics, its production has become a significant driver of economic growth in regions where manufacturing facilities are located.
The establishment of AMOLED production plants often leads to the creation of numerous high-skilled jobs, ranging from engineers and technicians to researchers and production line workers. This influx of employment opportunities can revitalize local economies, particularly in areas that may have experienced industrial decline. The ripple effect of these jobs extends to supporting industries, such as suppliers of raw materials, logistics, and services, further stimulating economic activity.
However, the concentration of AMOLED manufacturing in specific regions can also lead to economic disparities. Areas with established production facilities may experience rapid development and increased prosperity, while regions without such industries may fall behind. This uneven distribution of economic benefits can exacerbate existing socioeconomic inequalities both within and between countries.
The high-tech nature of AMOLED production necessitates substantial investments in education and training programs. This focus on skill development can lead to improvements in local educational systems and the creation of specialized academic programs, ultimately enhancing the overall human capital of the region. The transfer of knowledge and expertise from multinational corporations to local workforces can also contribute to long-term economic development and innovation capabilities.
From a global perspective, the AMOLED industry has become a key player in international trade and economic relations. Countries with strong AMOLED manufacturing capabilities often gain strategic advantages in negotiations and partnerships, influencing geopolitical dynamics. The competition for market share and technological supremacy in AMOLED production can drive international collaborations as well as tensions, shaping diplomatic and economic relationships between nations.
The environmental impact of AMOLED manufacturing also has significant socioeconomic implications. While the industry strives for more sustainable practices, the resource-intensive nature of production can strain local ecosystems and communities. Balancing economic growth with environmental stewardship remains a critical challenge, often requiring careful policy-making and corporate responsibility initiatives to mitigate negative externalities.
In conclusion, the socioeconomic impact of AMOLED manufacturing is multifaceted, encompassing job creation, regional development, educational advancements, and global economic dynamics. As the industry continues to evolve, careful consideration of these impacts will be crucial for ensuring sustainable and equitable growth in the AMOLED sector.
The establishment of AMOLED production plants often leads to the creation of numerous high-skilled jobs, ranging from engineers and technicians to researchers and production line workers. This influx of employment opportunities can revitalize local economies, particularly in areas that may have experienced industrial decline. The ripple effect of these jobs extends to supporting industries, such as suppliers of raw materials, logistics, and services, further stimulating economic activity.
However, the concentration of AMOLED manufacturing in specific regions can also lead to economic disparities. Areas with established production facilities may experience rapid development and increased prosperity, while regions without such industries may fall behind. This uneven distribution of economic benefits can exacerbate existing socioeconomic inequalities both within and between countries.
The high-tech nature of AMOLED production necessitates substantial investments in education and training programs. This focus on skill development can lead to improvements in local educational systems and the creation of specialized academic programs, ultimately enhancing the overall human capital of the region. The transfer of knowledge and expertise from multinational corporations to local workforces can also contribute to long-term economic development and innovation capabilities.
From a global perspective, the AMOLED industry has become a key player in international trade and economic relations. Countries with strong AMOLED manufacturing capabilities often gain strategic advantages in negotiations and partnerships, influencing geopolitical dynamics. The competition for market share and technological supremacy in AMOLED production can drive international collaborations as well as tensions, shaping diplomatic and economic relationships between nations.
The environmental impact of AMOLED manufacturing also has significant socioeconomic implications. While the industry strives for more sustainable practices, the resource-intensive nature of production can strain local ecosystems and communities. Balancing economic growth with environmental stewardship remains a critical challenge, often requiring careful policy-making and corporate responsibility initiatives to mitigate negative externalities.
In conclusion, the socioeconomic impact of AMOLED manufacturing is multifaceted, encompassing job creation, regional development, educational advancements, and global economic dynamics. As the industry continues to evolve, careful consideration of these impacts will be crucial for ensuring sustainable and equitable growth in the AMOLED sector.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!