How AMOLED facilitates seamless connectivity in IoT devices?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED in IoT Evolution
The evolution of AMOLED technology in IoT devices marks a significant shift in the landscape of connected devices. AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays have emerged as a game-changing component in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, offering unique advantages that enhance connectivity and user experience.
Initially, IoT devices relied on basic LCD screens or simple LED indicators for visual feedback. As the IoT market expanded, the demand for more sophisticated display solutions grew. AMOLED technology, with its superior color reproduction, high contrast ratios, and energy efficiency, began to find its way into high-end IoT devices around 2015.
The integration of AMOLED displays in IoT devices has progressed through several key stages. The first phase focused on improving visual quality and energy efficiency in smart home devices and wearables. This was followed by the development of flexible and foldable AMOLED displays, opening up new form factors for IoT devices and enabling seamless integration into various environments.
A crucial milestone in AMOLED's IoT evolution was the development of always-on display capabilities. This feature allowed IoT devices to continuously display essential information without significant battery drain, a critical factor for devices that need to maintain constant connectivity and provide real-time data.
The latest advancements in AMOLED technology have focused on enhancing touch sensitivity and reducing latency, crucial for IoT devices that require quick and precise user interactions. Additionally, improvements in durability and outdoor visibility have made AMOLED displays more suitable for a wider range of IoT applications, from industrial sensors to smart city infrastructure.
Looking forward, the evolution of AMOLED in IoT is expected to continue with the development of transparent and stretchable displays. These innovations will further blur the line between the digital and physical worlds, enabling new paradigms of human-machine interaction in IoT ecosystems.
The impact of AMOLED on IoT connectivity goes beyond mere visual enhancements. By providing more intuitive and informative interfaces, AMOLED displays have significantly improved the way users interact with and manage their IoT devices. This has led to increased adoption and more seamless integration of IoT solutions in both consumer and industrial applications.
Initially, IoT devices relied on basic LCD screens or simple LED indicators for visual feedback. As the IoT market expanded, the demand for more sophisticated display solutions grew. AMOLED technology, with its superior color reproduction, high contrast ratios, and energy efficiency, began to find its way into high-end IoT devices around 2015.
The integration of AMOLED displays in IoT devices has progressed through several key stages. The first phase focused on improving visual quality and energy efficiency in smart home devices and wearables. This was followed by the development of flexible and foldable AMOLED displays, opening up new form factors for IoT devices and enabling seamless integration into various environments.
A crucial milestone in AMOLED's IoT evolution was the development of always-on display capabilities. This feature allowed IoT devices to continuously display essential information without significant battery drain, a critical factor for devices that need to maintain constant connectivity and provide real-time data.
The latest advancements in AMOLED technology have focused on enhancing touch sensitivity and reducing latency, crucial for IoT devices that require quick and precise user interactions. Additionally, improvements in durability and outdoor visibility have made AMOLED displays more suitable for a wider range of IoT applications, from industrial sensors to smart city infrastructure.
Looking forward, the evolution of AMOLED in IoT is expected to continue with the development of transparent and stretchable displays. These innovations will further blur the line between the digital and physical worlds, enabling new paradigms of human-machine interaction in IoT ecosystems.
The impact of AMOLED on IoT connectivity goes beyond mere visual enhancements. By providing more intuitive and informative interfaces, AMOLED displays have significantly improved the way users interact with and manage their IoT devices. This has led to increased adoption and more seamless integration of IoT solutions in both consumer and industrial applications.
IoT Connectivity Demands
The Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the increasing demand for seamless connectivity among devices. This surge in IoT adoption has created a pressing need for advanced display technologies that can facilitate efficient and reliable communication between various smart devices. AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has emerged as a promising solution to address these connectivity demands in IoT devices.
IoT devices require displays that can provide clear, real-time information while consuming minimal power. AMOLED displays offer superior energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD screens, making them ideal for battery-powered IoT devices that need to operate for extended periods without frequent recharging. This energy efficiency is crucial for maintaining constant connectivity in IoT networks, where devices often need to remain active and responsive 24/7.
Furthermore, AMOLED displays offer faster refresh rates and better color reproduction, enabling IoT devices to present complex data visualizations and alerts more effectively. This enhanced visual performance is particularly valuable in industrial IoT applications, where operators need to quickly interpret and respond to critical information from multiple connected devices and sensors.
The flexibility of AMOLED displays also plays a significant role in meeting IoT connectivity demands. As IoT devices come in various form factors, from wearables to smart home appliances, AMOLED's ability to be manufactured in flexible and curved formats allows for seamless integration into diverse device designs. This adaptability ensures that connectivity interfaces can be incorporated into a wide range of IoT products without compromising on form or function.
AMOLED's superior contrast ratios and deep blacks contribute to improved readability in various lighting conditions, a crucial factor for IoT devices deployed in challenging environments. Whether it's a smart thermostat in a brightly lit room or an outdoor sensor display, AMOLED ensures that connectivity status and data remain visible and accessible.
The technology's capability to support always-on displays is another key feature addressing IoT connectivity needs. Always-on displays allow devices to continuously show essential information, such as connection status, notifications, or critical data points, without significant battery drain. This constant availability of information enhances the user experience and ensures that IoT devices remain responsive and connected at all times.
As IoT networks become more complex, the need for displays that can handle multi-device interactions and data visualization becomes increasingly important. AMOLED's high pixel density and color accuracy make it well-suited for displaying intricate network topologies, real-time data flows, and interactive control interfaces, facilitating more intuitive management of IoT ecosystems.
IoT devices require displays that can provide clear, real-time information while consuming minimal power. AMOLED displays offer superior energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD screens, making them ideal for battery-powered IoT devices that need to operate for extended periods without frequent recharging. This energy efficiency is crucial for maintaining constant connectivity in IoT networks, where devices often need to remain active and responsive 24/7.
Furthermore, AMOLED displays offer faster refresh rates and better color reproduction, enabling IoT devices to present complex data visualizations and alerts more effectively. This enhanced visual performance is particularly valuable in industrial IoT applications, where operators need to quickly interpret and respond to critical information from multiple connected devices and sensors.
The flexibility of AMOLED displays also plays a significant role in meeting IoT connectivity demands. As IoT devices come in various form factors, from wearables to smart home appliances, AMOLED's ability to be manufactured in flexible and curved formats allows for seamless integration into diverse device designs. This adaptability ensures that connectivity interfaces can be incorporated into a wide range of IoT products without compromising on form or function.
AMOLED's superior contrast ratios and deep blacks contribute to improved readability in various lighting conditions, a crucial factor for IoT devices deployed in challenging environments. Whether it's a smart thermostat in a brightly lit room or an outdoor sensor display, AMOLED ensures that connectivity status and data remain visible and accessible.
The technology's capability to support always-on displays is another key feature addressing IoT connectivity needs. Always-on displays allow devices to continuously show essential information, such as connection status, notifications, or critical data points, without significant battery drain. This constant availability of information enhances the user experience and ensures that IoT devices remain responsive and connected at all times.
As IoT networks become more complex, the need for displays that can handle multi-device interactions and data visualization becomes increasingly important. AMOLED's high pixel density and color accuracy make it well-suited for displaying intricate network topologies, real-time data flows, and interactive control interfaces, facilitating more intuitive management of IoT ecosystems.
AMOLED Tech Challenges
AMOLED technology, while offering numerous advantages for IoT devices, faces several significant challenges in its implementation and widespread adoption. One of the primary hurdles is the high production cost associated with AMOLED displays. The complex manufacturing process and the need for specialized equipment contribute to elevated expenses, making it difficult for manufacturers to integrate AMOLED screens into cost-sensitive IoT devices.
Another critical challenge is the limited lifespan of AMOLED displays, particularly when compared to traditional LCD technology. The organic compounds used in AMOLED screens are susceptible to degradation over time, leading to issues such as burn-in and color shift. This poses a significant concern for IoT devices that are expected to operate continuously for extended periods without frequent replacements.
Power consumption remains a double-edged sword for AMOLED technology in IoT applications. While AMOLED displays can be more energy-efficient when displaying darker content, they tend to consume more power when displaying brighter or white backgrounds. This variability in power consumption can be problematic for IoT devices with limited battery capacity or those relying on energy harvesting techniques.
The complexity of AMOLED driver circuits presents another technical challenge. These circuits require precise control to manage the individual pixels effectively, adding to the overall complexity and potential points of failure in IoT devices. This complexity can impact the reliability and durability of AMOLED-equipped IoT products, especially in harsh environmental conditions.
Color accuracy and consistency across different AMOLED panels remain ongoing concerns. Variations in manufacturing processes can lead to discrepancies in color reproduction between devices, potentially affecting the user experience and the reliability of visual data in IoT applications. Achieving uniform color performance across a range of AMOLED-equipped IoT devices is a significant technical hurdle.
Scalability is another challenge facing AMOLED technology in the IoT sector. While AMOLED displays excel in certain size ranges, producing very small or very large AMOLED panels for diverse IoT applications can be technically challenging and cost-prohibitive. This limitation may restrict the types of IoT devices that can effectively utilize AMOLED technology.
Lastly, the integration of touch functionality with AMOLED displays presents its own set of challenges. Ensuring accurate and responsive touch detection without compromising the display quality or increasing the overall thickness of the device is a complex task. This is particularly crucial for IoT devices that rely heavily on touch-based interactions for user input and control.
Another critical challenge is the limited lifespan of AMOLED displays, particularly when compared to traditional LCD technology. The organic compounds used in AMOLED screens are susceptible to degradation over time, leading to issues such as burn-in and color shift. This poses a significant concern for IoT devices that are expected to operate continuously for extended periods without frequent replacements.
Power consumption remains a double-edged sword for AMOLED technology in IoT applications. While AMOLED displays can be more energy-efficient when displaying darker content, they tend to consume more power when displaying brighter or white backgrounds. This variability in power consumption can be problematic for IoT devices with limited battery capacity or those relying on energy harvesting techniques.
The complexity of AMOLED driver circuits presents another technical challenge. These circuits require precise control to manage the individual pixels effectively, adding to the overall complexity and potential points of failure in IoT devices. This complexity can impact the reliability and durability of AMOLED-equipped IoT products, especially in harsh environmental conditions.
Color accuracy and consistency across different AMOLED panels remain ongoing concerns. Variations in manufacturing processes can lead to discrepancies in color reproduction between devices, potentially affecting the user experience and the reliability of visual data in IoT applications. Achieving uniform color performance across a range of AMOLED-equipped IoT devices is a significant technical hurdle.
Scalability is another challenge facing AMOLED technology in the IoT sector. While AMOLED displays excel in certain size ranges, producing very small or very large AMOLED panels for diverse IoT applications can be technically challenging and cost-prohibitive. This limitation may restrict the types of IoT devices that can effectively utilize AMOLED technology.
Lastly, the integration of touch functionality with AMOLED displays presents its own set of challenges. Ensuring accurate and responsive touch detection without compromising the display quality or increasing the overall thickness of the device is a complex task. This is particularly crucial for IoT devices that rely heavily on touch-based interactions for user input and control.
Current AMOLED Solutions
01 AMOLED display connectivity and control
AMOLED displays require specialized connectivity and control mechanisms to manage pixel illumination, color reproduction, and power efficiency. This includes advanced driver circuits, data transmission protocols, and timing controllers to ensure proper display performance and integration with other device components.- AMOLED display connectivity and control: This category focuses on the connectivity and control mechanisms for AMOLED displays. It includes technologies for driving and controlling AMOLED panels, such as data line driving circuits, scan line driving circuits, and pixel circuits. These innovations aim to improve display performance, reduce power consumption, and enhance overall display quality.
- AMOLED panel structure and fabrication: This category covers advancements in AMOLED panel structure and fabrication techniques. It includes innovations in thin-film transistor (TFT) designs, pixel layouts, and manufacturing processes for AMOLED displays. These technologies aim to improve display efficiency, increase resolution, and enhance overall panel performance.
- Touch integration in AMOLED displays: This category focuses on integrating touch functionality into AMOLED displays. It includes technologies for in-cell and on-cell touch sensors, as well as methods for improving touch sensitivity and accuracy in AMOLED panels. These innovations aim to create more responsive and interactive display experiences while maintaining the benefits of AMOLED technology.
- Power management and efficiency in AMOLED displays: This category covers technologies related to power management and efficiency improvements in AMOLED displays. It includes innovations in pixel driving schemes, voltage regulation, and power-saving techniques specific to AMOLED panels. These advancements aim to reduce power consumption and extend battery life in devices using AMOLED displays.
- AMOLED display image quality enhancement: This category focuses on technologies for enhancing image quality in AMOLED displays. It includes innovations in color management, contrast improvement, and compensation techniques for display uniformity. These advancements aim to provide better visual experiences and address challenges specific to AMOLED technology, such as color accuracy and burn-in prevention.
02 Touch integration in AMOLED displays
Integrating touch functionality into AMOLED displays involves developing techniques for seamless touch sensing without compromising display quality. This may include in-cell or on-cell touch solutions, specialized sensors, and signal processing algorithms to accurately detect and interpret touch inputs on the AMOLED screen.Expand Specific Solutions03 AMOLED panel structure and fabrication
The structure and fabrication of AMOLED panels involve innovative techniques to enhance display performance, durability, and manufacturing efficiency. This includes developing new materials, optimizing layer structures, and improving production processes to achieve better color accuracy, brightness, and longevity of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions04 Power management for AMOLED displays
Efficient power management is crucial for AMOLED displays to optimize battery life in mobile devices. This involves developing advanced power control circuits, implementing adaptive brightness techniques, and utilizing intelligent pixel management to reduce energy consumption without compromising display quality.Expand Specific Solutions05 AMOLED display driving techniques
Advanced driving techniques for AMOLED displays focus on improving image quality, reducing motion blur, and enhancing overall visual performance. This includes developing sophisticated algorithms for pixel compensation, implementing high refresh rate technologies, and optimizing voltage control for individual pixels to achieve uniform brightness and color across the display.Expand Specific Solutions
Key AMOLED-IoT Players
The AMOLED technology in IoT devices is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and improving technical maturity. The competitive landscape is characterized by major players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology, and TCL China Star Optoelectronics, who are driving innovation and expanding production capabilities. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to enhance AMOLED performance for IoT applications, focusing on energy efficiency, flexibility, and seamless connectivity. As the technology matures, we're seeing a broader adoption across various IoT sectors, from wearables to smart home devices, indicating a promising future for AMOLED in facilitating advanced IoT connectivity solutions.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed flexible AMOLED displays specifically designed for IoT applications. Their technology incorporates low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) backplanes with OLED frontplanes, allowing for ultra-thin and flexible form factors[2]. BOE's AMOLED displays for IoT devices feature integrated touch and force-sensing capabilities, enabling intuitive user interactions[4]. The company has also implemented power-saving technologies, such as partial-update modes and adaptive refresh rates, to extend battery life in IoT devices[6].
Strengths: Flexible display technology, integrated touch solutions, and power-efficient designs. Weaknesses: Less established in the global market compared to some competitors, and potential yield challenges with flexible displays.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed AMOLED displays with integrated IoT connectivity features. Their technology includes low-power AMOLED panels with built-in wireless communication modules, enabling direct connectivity to IoT networks[1]. The displays incorporate energy-efficient OLED pixels with thin-film transistor (TFT) backplanes, allowing for always-on display functionality while minimizing power consumption[3]. Samsung's AMOLED solutions for IoT devices also feature touch sensors integrated directly into the display stack, reducing overall device thickness and improving responsiveness[5].
Strengths: Industry-leading AMOLED technology, integrated connectivity solutions, and energy efficiency. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost compared to traditional display technologies, and limited compatibility with some existing IoT ecosystems.
AMOLED-IoT Innovations
Amoled double-side display
PatentActiveUS20200219957A1
Innovation
- An AMOLED double-sided display design featuring a substrate with alternating top-emitting and bottom-emitting OLED units, where the anode of top-emitting units is thicker and reflective, and the cathode of bottom-emitting units is thicker and light-transmissive, allowing for single IC control and eliminating mirrored images.
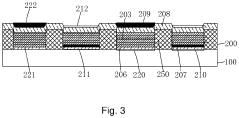
Active matrix organic light-emitting display and display apparatus
PatentActiveUS20160181348A1
Innovation
- The implementation of a planar power supply signal electrode that covers the entire display area, replacing traditional linear power supply signal lines, significantly reduces resistance and IR drop, and is designed to provide power supply voltage signals to pixel structures while maintaining normal operation and emission efficiency.
Energy Efficiency Impact
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology plays a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency for IoT devices, thereby facilitating seamless connectivity. The low power consumption characteristics of AMOLED displays significantly contribute to extending battery life, a critical factor in the widespread adoption and functionality of IoT devices.
AMOLED screens offer superior energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD displays. This is primarily due to their ability to selectively illuminate only the necessary pixels, allowing for true blacks and reducing overall power consumption. In IoT applications, where devices often need to operate for extended periods without frequent charging, this energy-saving feature becomes paramount.
The impact of AMOLED's energy efficiency on IoT connectivity is multifaceted. Firstly, it allows for longer operational times between charges, ensuring that devices remain connected and functional for extended periods. This is particularly crucial for remote or hard-to-reach IoT sensors and devices, where frequent battery replacements or recharging is impractical.
Moreover, the reduced power consumption of AMOLED displays enables IoT device manufacturers to allocate more energy resources to connectivity components. This reallocation can support more powerful wireless modules or more frequent data transmissions, enhancing the overall connectivity capabilities of IoT devices without compromising battery life.
In smart home applications, AMOLED-equipped IoT devices can maintain constant connectivity while displaying relevant information with minimal power drain. This is especially beneficial for devices like smart thermostats, security cameras, or home automation control panels, where continuous display and network connectivity are essential.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED also contributes to the miniaturization of IoT devices. With less power required for display functions, designers can opt for smaller batteries without sacrificing performance or connectivity. This reduction in size and weight makes AMOLED-based IoT devices more versatile and easier to integrate into various environments and applications.
Furthermore, the power savings from AMOLED displays can be leveraged to support more advanced connectivity features in IoT devices. For instance, it can enable the implementation of more sophisticated encryption protocols or support for multiple wireless standards, enhancing both the security and flexibility of IoT networks without significantly impacting battery life.
In conclusion, the energy efficiency impact of AMOLED technology on IoT devices is substantial. By reducing power consumption in display components, AMOLED enables longer-lasting, more capable, and better-connected IoT devices. This efficiency is a key factor in driving the expansion and improving the functionality of the IoT ecosystem, supporting the vision of ubiquitous and seamless connectivity across a wide range of applications and environments.
AMOLED screens offer superior energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD displays. This is primarily due to their ability to selectively illuminate only the necessary pixels, allowing for true blacks and reducing overall power consumption. In IoT applications, where devices often need to operate for extended periods without frequent charging, this energy-saving feature becomes paramount.
The impact of AMOLED's energy efficiency on IoT connectivity is multifaceted. Firstly, it allows for longer operational times between charges, ensuring that devices remain connected and functional for extended periods. This is particularly crucial for remote or hard-to-reach IoT sensors and devices, where frequent battery replacements or recharging is impractical.
Moreover, the reduced power consumption of AMOLED displays enables IoT device manufacturers to allocate more energy resources to connectivity components. This reallocation can support more powerful wireless modules or more frequent data transmissions, enhancing the overall connectivity capabilities of IoT devices without compromising battery life.
In smart home applications, AMOLED-equipped IoT devices can maintain constant connectivity while displaying relevant information with minimal power drain. This is especially beneficial for devices like smart thermostats, security cameras, or home automation control panels, where continuous display and network connectivity are essential.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED also contributes to the miniaturization of IoT devices. With less power required for display functions, designers can opt for smaller batteries without sacrificing performance or connectivity. This reduction in size and weight makes AMOLED-based IoT devices more versatile and easier to integrate into various environments and applications.
Furthermore, the power savings from AMOLED displays can be leveraged to support more advanced connectivity features in IoT devices. For instance, it can enable the implementation of more sophisticated encryption protocols or support for multiple wireless standards, enhancing both the security and flexibility of IoT networks without significantly impacting battery life.
In conclusion, the energy efficiency impact of AMOLED technology on IoT devices is substantial. By reducing power consumption in display components, AMOLED enables longer-lasting, more capable, and better-connected IoT devices. This efficiency is a key factor in driving the expansion and improving the functionality of the IoT ecosystem, supporting the vision of ubiquitous and seamless connectivity across a wide range of applications and environments.
AMOLED-IoT Security
AMOLED technology plays a crucial role in enhancing the security of IoT devices, addressing several key challenges in the rapidly evolving landscape of connected devices. The integration of AMOLED displays in IoT devices offers unique advantages that contribute to improved security measures and user authentication processes.
One of the primary security benefits of AMOLED technology in IoT devices is its ability to support advanced biometric authentication methods. The high contrast ratio and precise color reproduction of AMOLED displays enable more accurate fingerprint recognition directly on the screen. This on-screen fingerprint sensing technology, often referred to as in-display fingerprint scanning, provides a seamless and secure method for user authentication without the need for additional hardware components.
Furthermore, AMOLED displays facilitate the implementation of facial recognition systems in IoT devices. The superior image quality and fast response times of AMOLED screens allow for more accurate and reliable facial recognition, even in challenging lighting conditions. This enhances the overall security of IoT devices by providing an additional layer of user verification.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED displays also contributes to the security of IoT devices. By consuming less power compared to traditional LCD screens, AMOLED technology allows for longer battery life in IoT devices. This extended operational time ensures that security features remain active for longer periods, reducing the vulnerability window for potential attacks during power-saving modes or when devices are offline.
AMOLED displays also enable the implementation of dynamic security interfaces in IoT devices. The ability to selectively illuminate individual pixels allows for the creation of customizable and context-aware security prompts. This flexibility in display output can be leveraged to present users with unique security challenges or to display real-time security status information, enhancing the overall security awareness and interaction between users and their IoT devices.
Moreover, the high refresh rates and low latency of AMOLED screens contribute to the responsiveness of security-related user interfaces. This improved performance ensures that security prompts, alerts, and authentication processes are displayed quickly and smoothly, reducing the risk of user frustration or potential security bypasses due to delayed system responses.
In conclusion, AMOLED technology significantly enhances the security capabilities of IoT devices through its support for advanced biometric authentication, energy efficiency, dynamic security interfaces, and improved user interaction. As IoT ecosystems continue to expand, the integration of AMOLED displays will play an increasingly important role in safeguarding connected devices and user data.
One of the primary security benefits of AMOLED technology in IoT devices is its ability to support advanced biometric authentication methods. The high contrast ratio and precise color reproduction of AMOLED displays enable more accurate fingerprint recognition directly on the screen. This on-screen fingerprint sensing technology, often referred to as in-display fingerprint scanning, provides a seamless and secure method for user authentication without the need for additional hardware components.
Furthermore, AMOLED displays facilitate the implementation of facial recognition systems in IoT devices. The superior image quality and fast response times of AMOLED screens allow for more accurate and reliable facial recognition, even in challenging lighting conditions. This enhances the overall security of IoT devices by providing an additional layer of user verification.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED displays also contributes to the security of IoT devices. By consuming less power compared to traditional LCD screens, AMOLED technology allows for longer battery life in IoT devices. This extended operational time ensures that security features remain active for longer periods, reducing the vulnerability window for potential attacks during power-saving modes or when devices are offline.
AMOLED displays also enable the implementation of dynamic security interfaces in IoT devices. The ability to selectively illuminate individual pixels allows for the creation of customizable and context-aware security prompts. This flexibility in display output can be leveraged to present users with unique security challenges or to display real-time security status information, enhancing the overall security awareness and interaction between users and their IoT devices.
Moreover, the high refresh rates and low latency of AMOLED screens contribute to the responsiveness of security-related user interfaces. This improved performance ensures that security prompts, alerts, and authentication processes are displayed quickly and smoothly, reducing the risk of user frustration or potential security bypasses due to delayed system responses.
In conclusion, AMOLED technology significantly enhances the security capabilities of IoT devices through its support for advanced biometric authentication, energy efficiency, dynamic security interfaces, and improved user interaction. As IoT ecosystems continue to expand, the integration of AMOLED displays will play an increasingly important role in safeguarding connected devices and user data.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!