Integration of biometric sensors in AMOLED displays.
JUL 17, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Biometrics Evolution
The integration of biometric sensors in AMOLED displays represents a significant technological evolution in mobile device security and user experience. This journey began with the introduction of fingerprint sensors on smartphones, initially as separate hardware components. As display technology advanced, particularly with the widespread adoption of AMOLED screens, manufacturers sought ways to seamlessly incorporate biometric sensors into the display itself.
The first major milestone in this evolution was the development of under-display fingerprint sensors. These optical sensors, placed beneath the AMOLED panel, could capture fingerprint data through the display pixels. This innovation eliminated the need for a separate fingerprint sensor, allowing for sleeker device designs and larger screen-to-body ratios.
As the technology progressed, manufacturers explored more advanced biometric solutions. Facial recognition became a popular alternative, with some high-end devices incorporating sophisticated 3D facial mapping technologies. However, these systems often required dedicated hardware, including infrared cameras and dot projectors, which occupied space in the device's bezel or notch.
The next significant leap came with the integration of facial recognition capabilities directly into the AMOLED display. This was achieved through the development of under-display cameras, which could capture images through specially designed transparent areas of the screen. While initially facing challenges with image quality, advancements in both display and camera technologies have steadily improved the performance of these systems.
Concurrent with these developments, researchers began exploring the potential of using the AMOLED display itself as a biometric sensor. This led to the concept of "screen fingerprinting," where the entire display surface could potentially act as a fingerprint scanner. This technology utilizes the light-emitting properties of AMOLED pixels to detect the unique patterns of a user's fingerprint when placed anywhere on the screen.
More recently, the integration of other biometric sensors into AMOLED displays has gained traction. Heart rate monitors and blood oxygen sensors, traditionally found in wearable devices, are now being incorporated into smartphone displays. These sensors utilize the light-emitting and detecting capabilities of AMOLED pixels to measure physiological parameters, offering users health monitoring features without the need for additional hardware.
The latest frontier in this evolution is the development of multi-modal biometric systems integrated within AMOLED displays. These systems combine multiple biometric measurements, such as fingerprint, facial features, and even behavioral patterns like typing rhythm, to create a more secure and versatile authentication method. This approach not only enhances security but also provides users with flexible authentication options suited to different situations and preferences.
The first major milestone in this evolution was the development of under-display fingerprint sensors. These optical sensors, placed beneath the AMOLED panel, could capture fingerprint data through the display pixels. This innovation eliminated the need for a separate fingerprint sensor, allowing for sleeker device designs and larger screen-to-body ratios.
As the technology progressed, manufacturers explored more advanced biometric solutions. Facial recognition became a popular alternative, with some high-end devices incorporating sophisticated 3D facial mapping technologies. However, these systems often required dedicated hardware, including infrared cameras and dot projectors, which occupied space in the device's bezel or notch.
The next significant leap came with the integration of facial recognition capabilities directly into the AMOLED display. This was achieved through the development of under-display cameras, which could capture images through specially designed transparent areas of the screen. While initially facing challenges with image quality, advancements in both display and camera technologies have steadily improved the performance of these systems.
Concurrent with these developments, researchers began exploring the potential of using the AMOLED display itself as a biometric sensor. This led to the concept of "screen fingerprinting," where the entire display surface could potentially act as a fingerprint scanner. This technology utilizes the light-emitting properties of AMOLED pixels to detect the unique patterns of a user's fingerprint when placed anywhere on the screen.
More recently, the integration of other biometric sensors into AMOLED displays has gained traction. Heart rate monitors and blood oxygen sensors, traditionally found in wearable devices, are now being incorporated into smartphone displays. These sensors utilize the light-emitting and detecting capabilities of AMOLED pixels to measure physiological parameters, offering users health monitoring features without the need for additional hardware.
The latest frontier in this evolution is the development of multi-modal biometric systems integrated within AMOLED displays. These systems combine multiple biometric measurements, such as fingerprint, facial features, and even behavioral patterns like typing rhythm, to create a more secure and versatile authentication method. This approach not only enhances security but also provides users with flexible authentication options suited to different situations and preferences.
Market Demand Analysis
The integration of biometric sensors in AMOLED displays represents a significant technological advancement that is poised to revolutionize the smartphone and wearable device markets. This innovation addresses the growing consumer demand for enhanced security features and seamless user experiences in mobile devices.
Market research indicates a robust and expanding demand for biometric authentication technologies in consumer electronics. The global biometrics market is projected to experience substantial growth, driven primarily by the increasing adoption of fingerprint sensors, facial recognition systems, and other biometric modalities in smartphones and wearables.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards devices that offer both convenience and security. The integration of biometric sensors directly into AMOLED displays aligns perfectly with this trend, as it eliminates the need for separate hardware components while maintaining a sleek device design. This integration is particularly appealing to manufacturers seeking to maximize screen real estate and minimize bezels in their products.
The automotive industry is also showing interest in this technology for in-vehicle authentication and personalization. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, the demand for secure and user-friendly biometric interfaces is expected to rise significantly.
In the healthcare sector, wearable devices with integrated biometric sensors in displays could revolutionize patient monitoring and telemedicine applications. The ability to seamlessly capture vital signs and biometric data through a device's display opens up new possibilities for remote health monitoring and personalized medicine.
The enterprise market presents another significant opportunity for this technology. With the increasing prevalence of bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, organizations are seeking more secure and convenient ways to authenticate users and protect sensitive data. Integrated biometric sensors in displays offer a robust solution to these security challenges.
However, market adoption may face some initial hurdles. Privacy concerns and data security issues need to be addressed to gain consumer trust. Additionally, the cost of implementing this technology may initially be high, potentially limiting its adoption to premium devices before becoming more widespread.
Despite these challenges, the overall market trajectory for integrated biometric sensors in AMOLED displays appears highly promising. As the technology matures and production costs decrease, it is expected to become a standard feature in a wide range of consumer electronics, driving innovation and creating new opportunities across multiple industries.
Market research indicates a robust and expanding demand for biometric authentication technologies in consumer electronics. The global biometrics market is projected to experience substantial growth, driven primarily by the increasing adoption of fingerprint sensors, facial recognition systems, and other biometric modalities in smartphones and wearables.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards devices that offer both convenience and security. The integration of biometric sensors directly into AMOLED displays aligns perfectly with this trend, as it eliminates the need for separate hardware components while maintaining a sleek device design. This integration is particularly appealing to manufacturers seeking to maximize screen real estate and minimize bezels in their products.
The automotive industry is also showing interest in this technology for in-vehicle authentication and personalization. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, the demand for secure and user-friendly biometric interfaces is expected to rise significantly.
In the healthcare sector, wearable devices with integrated biometric sensors in displays could revolutionize patient monitoring and telemedicine applications. The ability to seamlessly capture vital signs and biometric data through a device's display opens up new possibilities for remote health monitoring and personalized medicine.
The enterprise market presents another significant opportunity for this technology. With the increasing prevalence of bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, organizations are seeking more secure and convenient ways to authenticate users and protect sensitive data. Integrated biometric sensors in displays offer a robust solution to these security challenges.
However, market adoption may face some initial hurdles. Privacy concerns and data security issues need to be addressed to gain consumer trust. Additionally, the cost of implementing this technology may initially be high, potentially limiting its adoption to premium devices before becoming more widespread.
Despite these challenges, the overall market trajectory for integrated biometric sensors in AMOLED displays appears highly promising. As the technology matures and production costs decrease, it is expected to become a standard feature in a wide range of consumer electronics, driving innovation and creating new opportunities across multiple industries.
Technical Challenges
The integration of biometric sensors into AMOLED displays presents several significant technical challenges that researchers and manufacturers must overcome. One of the primary obstacles is maintaining display quality while incorporating sensor components. The addition of sensors can potentially interfere with pixel density, color accuracy, and overall visual performance of the display.
Another major challenge lies in the miniaturization of biometric sensors to fit within the thin profile of modern AMOLED displays. This requires advanced manufacturing techniques and materials to create sensors that are both compact and highly sensitive. The integration process must also ensure that the sensors do not compromise the structural integrity or flexibility of the display.
Power consumption is a critical concern in mobile devices, and the addition of biometric sensors can significantly impact battery life. Developing energy-efficient sensor technologies that can operate seamlessly with AMOLED displays without draining excessive power is a complex engineering task. This challenge is compounded by the need for continuous or frequent biometric monitoring in certain applications.
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of biometric readings in various environmental conditions poses another substantial challenge. Factors such as ambient light, temperature fluctuations, and physical stress on the display can affect sensor performance. Engineers must develop robust algorithms and calibration techniques to maintain consistent and precise biometric measurements across diverse usage scenarios.
The integration of biometric sensors also raises concerns about data security and privacy. Protecting sensitive biometric information collected through the display requires advanced encryption methods and secure data processing architectures. This challenge extends to the development of tamper-resistant hardware designs that prevent unauthorized access to biometric data.
Manufacturing scalability presents another hurdle in the widespread adoption of this technology. Current production processes for AMOLED displays may need significant modifications to accommodate the integration of biometric sensors. Achieving high yields while maintaining cost-effectiveness is crucial for commercial viability.
Lastly, the challenge of cross-compatibility and standardization cannot be overlooked. As different manufacturers develop proprietary solutions, ensuring interoperability between devices and applications becomes increasingly complex. Establishing industry standards for biometric sensor integration in AMOLED displays is essential for widespread adoption and seamless user experiences across different platforms and devices.
Another major challenge lies in the miniaturization of biometric sensors to fit within the thin profile of modern AMOLED displays. This requires advanced manufacturing techniques and materials to create sensors that are both compact and highly sensitive. The integration process must also ensure that the sensors do not compromise the structural integrity or flexibility of the display.
Power consumption is a critical concern in mobile devices, and the addition of biometric sensors can significantly impact battery life. Developing energy-efficient sensor technologies that can operate seamlessly with AMOLED displays without draining excessive power is a complex engineering task. This challenge is compounded by the need for continuous or frequent biometric monitoring in certain applications.
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of biometric readings in various environmental conditions poses another substantial challenge. Factors such as ambient light, temperature fluctuations, and physical stress on the display can affect sensor performance. Engineers must develop robust algorithms and calibration techniques to maintain consistent and precise biometric measurements across diverse usage scenarios.
The integration of biometric sensors also raises concerns about data security and privacy. Protecting sensitive biometric information collected through the display requires advanced encryption methods and secure data processing architectures. This challenge extends to the development of tamper-resistant hardware designs that prevent unauthorized access to biometric data.
Manufacturing scalability presents another hurdle in the widespread adoption of this technology. Current production processes for AMOLED displays may need significant modifications to accommodate the integration of biometric sensors. Achieving high yields while maintaining cost-effectiveness is crucial for commercial viability.
Lastly, the challenge of cross-compatibility and standardization cannot be overlooked. As different manufacturers develop proprietary solutions, ensuring interoperability between devices and applications becomes increasingly complex. Establishing industry standards for biometric sensor integration in AMOLED displays is essential for widespread adoption and seamless user experiences across different platforms and devices.
Current Integration Methods
01 Integration of biometric sensors in AMOLED displays
AMOLED displays can be integrated with biometric sensors, such as fingerprint sensors, to provide enhanced security features. These sensors can be embedded beneath the display, allowing for a seamless user experience without compromising screen real estate. The integration enables secure authentication methods directly on the display surface.- Integration of biometric sensors in AMOLED displays: AMOLED displays can be integrated with biometric sensors, such as fingerprint sensors, to provide enhanced security features in devices. These sensors can be embedded beneath the display, allowing for a seamless and unobtrusive user experience while maintaining the display's visual quality.
- Optical sensing technology in AMOLED displays: Optical sensing technology can be incorporated into AMOLED displays to enable biometric authentication. This technology uses light emitted by the display pixels to capture fingerprints or other biometric data, eliminating the need for separate sensor hardware and allowing for a larger sensing area.
- Display driver integration for biometric sensing: Display drivers can be designed to support biometric sensing functionality in AMOLED displays. These integrated drivers can control both display operations and biometric sensor functions, improving overall system efficiency and reducing component count.
- Power management for AMOLED displays with biometric sensors: Efficient power management techniques can be implemented to optimize the performance of AMOLED displays with integrated biometric sensors. These techniques may include selective pixel activation, low-power sensing modes, and intelligent power distribution between display and sensing functions.
- Image processing for biometric data in AMOLED displays: Advanced image processing algorithms can be employed to enhance the quality and accuracy of biometric data captured through AMOLED displays. These algorithms may include noise reduction, feature extraction, and pattern matching techniques specifically designed for display-integrated biometric sensors.
02 Optical sensing technology for AMOLED displays
Optical sensing technology can be incorporated into AMOLED displays to enable biometric authentication. This technology uses light emitted by the display pixels to capture fingerprints or other biometric data. The integration of optical sensors allows for improved accuracy and reliability in biometric recognition while maintaining the display's visual quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Touch and biometric sensing in flexible AMOLED displays
Flexible AMOLED displays can be designed to incorporate both touch and biometric sensing capabilities. This integration allows for the development of curved or foldable devices with advanced security features. The flexibility of the display does not compromise the accuracy of biometric sensors, enabling secure authentication in various form factors.Expand Specific Solutions04 Power efficiency in AMOLED displays with biometric sensors
AMOLED displays with integrated biometric sensors can be optimized for power efficiency. This involves implementing intelligent power management techniques that activate the biometric sensors only when needed, reducing overall power consumption. The integration of low-power sensing technologies ensures that the addition of biometric features does not significantly impact battery life.Expand Specific Solutions05 Display driver integration for biometric sensing
Display drivers for AMOLED screens can be designed to support integrated biometric sensing capabilities. These drivers manage both display functions and biometric sensor operations, enabling seamless coordination between the two systems. The integration of display and biometric functions at the driver level allows for improved performance and reduced complexity in device design.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The integration of biometric sensors in AMOLED displays is an emerging technology in the early stages of development, with a growing market potential driven by increasing demand for secure and seamless user authentication in mobile devices. The market is characterized by intense competition among major players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology, and LG Display, who are investing heavily in R&D to advance this technology. While still evolving, the integration of biometric sensors with displays shows promise for enhancing user experience and device security, with companies like Fingerprint Cards and Goodix Technology focusing on developing specialized sensors and algorithms for this application.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed an innovative in-display fingerprint sensor technology for AMOLED displays. Their solution utilizes ultrasonic technology, which creates a 3D map of the fingerprint by bouncing soundwaves off the finger[1]. This allows for improved accuracy and security compared to traditional optical sensors. Samsung has integrated this technology into their flagship smartphones, such as the Galaxy S and Note series. The ultrasonic sensor can work through thicker glass and is less affected by contaminants on the finger[2]. Samsung has also been exploring the integration of other biometric sensors, such as heart rate monitors and blood oxygen sensors, into their AMOLED displays for future devices[3].
Strengths: High accuracy and security, works with thicker glass, less affected by contaminants. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to optical sensors, limited to high-end devices currently.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has made significant strides in integrating biometric sensors into AMOLED displays. They have developed an optical in-display fingerprint sensing technology that uses a thin-film sensor array embedded within the AMOLED panel[4]. This approach allows for a larger sensing area compared to traditional solutions. BOE's technology utilizes specialized OLED pixels that can both emit light and detect reflected light from the finger, enabling fingerprint recognition across a substantial portion of the display[5]. Additionally, BOE has been working on integrating other biometric sensors, such as facial recognition cameras and iris scanners, directly into the display panel, potentially eliminating the need for notches or punch-holes in future smartphone designs[6].
Strengths: Large sensing area, potential for full-screen biometric sensing, versatile integration of multiple biometric technologies. Weaknesses: Optical technology may be less secure than ultrasonic solutions, potential impact on display quality in sensing areas.
Core Patents and Research
Active matrix organic light emitting diode pixel unit circuit, display panel and electronic product
PatentActiveUS9459721B2
Innovation
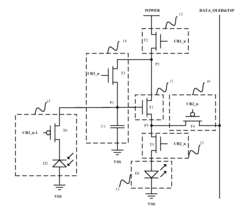
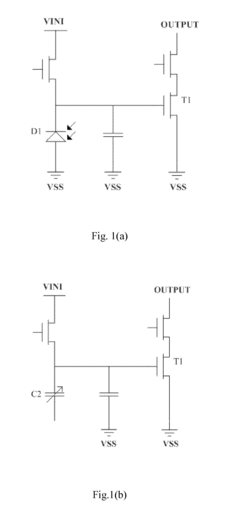
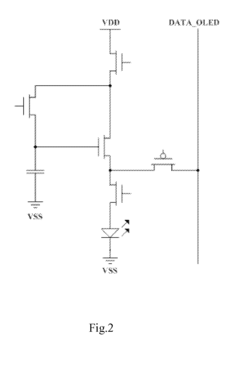
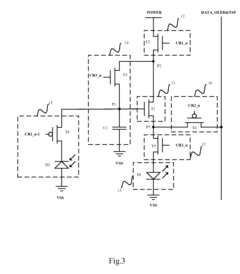
- The AMOLED pixel unit circuit is redesigned to include a light emitting module, a driving module, a threshold compensating module, a light emission controlling module, a touch sensing module, and an induction signal outputting module, which utilize existing data lines and control signals to integrate the TSP in Cell circuit, sharing circuit elements and control signals to minimize additional components.
Touch device integrated with amoled panel, and method of manufacturing the same
PatentActiveJP2016053934A
Innovation
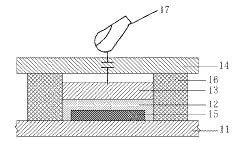
- A touch device integrated with an AMOLED panel that includes a thin film transistor array, organic light emitting diodes, a touch cover, and a light sensor positioned between the diode and the base, utilizing In-Cell optical touch technology to eliminate errors and enhance accuracy.
Display-Sensor Synergies
The integration of biometric sensors into AMOLED displays represents a significant advancement in display technology, offering numerous synergies that enhance both user experience and device functionality. This convergence of display and sensing technologies creates a seamless interface between users and their devices, enabling more intuitive and secure interactions.
One of the primary synergies lies in the optimization of device real estate. By incorporating biometric sensors directly into the display, manufacturers can eliminate the need for separate sensor components, resulting in sleeker device designs and potentially larger screen-to-body ratios. This integration also allows for more flexible placement of sensors across the display surface, enhancing the overall ergonomics of the device.
The combination of AMOLED display technology with biometric sensors offers unique advantages in terms of power efficiency. AMOLED displays can selectively activate individual pixels, allowing for partial screen activation during biometric sensing operations. This targeted approach minimizes power consumption while maintaining high-quality sensor performance, contributing to extended battery life in mobile devices.
From a user experience perspective, the integration of biometric sensors into displays enables more natural and intuitive interactions. For instance, in-display fingerprint sensors allow users to unlock their devices or authenticate transactions by simply touching the screen, eliminating the need for dedicated hardware buttons or sensors. This seamless interaction enhances the overall user experience and simplifies device usage.
The synergy between display and sensor technologies also opens up new possibilities for advanced security features. By leveraging the high-resolution capabilities of AMOLED displays, integrated biometric sensors can capture more detailed and accurate biometric data. This enhanced data quality can lead to improved authentication accuracy and reduced false acceptance rates, bolstering device security.
Furthermore, the integration of biometric sensors with displays enables multi-modal biometric authentication. By combining fingerprint sensing with facial recognition or iris scanning, devices can offer more robust and versatile security options. This multi-layered approach not only enhances security but also provides users with greater flexibility in how they choose to authenticate.
The display-sensor integration also facilitates advancements in health monitoring capabilities. By incorporating heart rate sensors or blood oxygen level detectors into the display, devices can offer continuous health tracking without the need for additional wearable accessories. This seamless integration of health monitoring features into everyday devices has the potential to revolutionize personal health management and preventive care.
One of the primary synergies lies in the optimization of device real estate. By incorporating biometric sensors directly into the display, manufacturers can eliminate the need for separate sensor components, resulting in sleeker device designs and potentially larger screen-to-body ratios. This integration also allows for more flexible placement of sensors across the display surface, enhancing the overall ergonomics of the device.
The combination of AMOLED display technology with biometric sensors offers unique advantages in terms of power efficiency. AMOLED displays can selectively activate individual pixels, allowing for partial screen activation during biometric sensing operations. This targeted approach minimizes power consumption while maintaining high-quality sensor performance, contributing to extended battery life in mobile devices.
From a user experience perspective, the integration of biometric sensors into displays enables more natural and intuitive interactions. For instance, in-display fingerprint sensors allow users to unlock their devices or authenticate transactions by simply touching the screen, eliminating the need for dedicated hardware buttons or sensors. This seamless interaction enhances the overall user experience and simplifies device usage.
The synergy between display and sensor technologies also opens up new possibilities for advanced security features. By leveraging the high-resolution capabilities of AMOLED displays, integrated biometric sensors can capture more detailed and accurate biometric data. This enhanced data quality can lead to improved authentication accuracy and reduced false acceptance rates, bolstering device security.
Furthermore, the integration of biometric sensors with displays enables multi-modal biometric authentication. By combining fingerprint sensing with facial recognition or iris scanning, devices can offer more robust and versatile security options. This multi-layered approach not only enhances security but also provides users with greater flexibility in how they choose to authenticate.
The display-sensor integration also facilitates advancements in health monitoring capabilities. By incorporating heart rate sensors or blood oxygen level detectors into the display, devices can offer continuous health tracking without the need for additional wearable accessories. This seamless integration of health monitoring features into everyday devices has the potential to revolutionize personal health management and preventive care.
Regulatory Considerations
The integration of biometric sensors in AMOLED displays is subject to a complex regulatory landscape that varies across different regions and jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating biometric devices, especially those used for medical purposes. Manufacturers must comply with FDA guidelines for medical devices, which may include premarket approval processes and ongoing quality control measures.
In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has significant implications for biometric data collection and processing. AMOLED displays with integrated biometric sensors must adhere to strict data protection principles, including user consent, data minimization, and robust security measures. Additionally, the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) may apply if the device is intended for medical use.
Privacy laws in various countries also impact the development and deployment of biometric sensors in displays. For instance, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States and the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) in Canada impose specific requirements on the collection and use of biometric data.
Standardization bodies such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have developed standards relevant to biometric technologies. These standards, including ISO/IEC 19794 for biometric data interchange formats and ISO/IEC 24745 for biometric information protection, provide guidelines for ensuring interoperability and security in biometric systems.
Manufacturers must also consider industry-specific regulations. For example, in the automotive sector, regulations such as the UN Regulation No. 79 on steering equipment may impact the integration of biometric sensors in vehicle displays for driver monitoring systems.
As the technology evolves, regulatory frameworks are likely to adapt. Emerging regulations around artificial intelligence and machine learning, which are often integral to biometric systems, may introduce new compliance requirements. Companies developing AMOLED displays with integrated biometric sensors must stay abreast of these evolving regulations and engage in proactive compliance strategies to ensure market access and user trust.
In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has significant implications for biometric data collection and processing. AMOLED displays with integrated biometric sensors must adhere to strict data protection principles, including user consent, data minimization, and robust security measures. Additionally, the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) may apply if the device is intended for medical use.
Privacy laws in various countries also impact the development and deployment of biometric sensors in displays. For instance, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States and the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) in Canada impose specific requirements on the collection and use of biometric data.
Standardization bodies such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have developed standards relevant to biometric technologies. These standards, including ISO/IEC 19794 for biometric data interchange formats and ISO/IEC 24745 for biometric information protection, provide guidelines for ensuring interoperability and security in biometric systems.
Manufacturers must also consider industry-specific regulations. For example, in the automotive sector, regulations such as the UN Regulation No. 79 on steering equipment may impact the integration of biometric sensors in vehicle displays for driver monitoring systems.
As the technology evolves, regulatory frameworks are likely to adapt. Emerging regulations around artificial intelligence and machine learning, which are often integral to biometric systems, may introduce new compliance requirements. Companies developing AMOLED displays with integrated biometric sensors must stay abreast of these evolving regulations and engage in proactive compliance strategies to ensure market access and user trust.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!