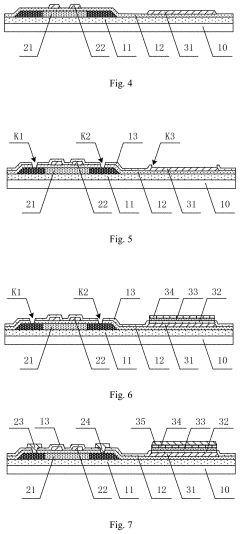
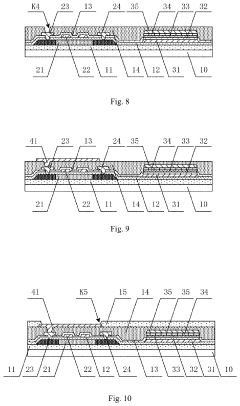
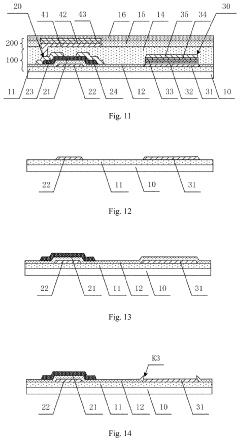
Innovations in AMOLED protective film materials.
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Film Evolution
The evolution of AMOLED protective film materials has been a critical factor in the advancement of display technology. Initially, these films were primarily designed for basic protection against scratches and minor impacts. However, as AMOLED displays became more prevalent in consumer electronics, the demands on protective films increased significantly.
In the early stages of AMOLED technology, protective films were often simple polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyurethane (PU) layers. These materials provided basic scratch resistance but offered limited protection against more severe impacts or environmental factors. As AMOLED displays became thinner and more flexible, the need for more advanced protective materials became apparent.
The next phase of evolution saw the introduction of multi-layer film structures. These composite films combined different materials to address various protection needs simultaneously. For instance, a typical multi-layer film might include a hard coat for scratch resistance, an anti-reflective layer to improve visibility, and a shock-absorbing layer to protect against impacts.
A significant milestone in AMOLED film evolution was the development of ultra-thin glass films. These films, often less than 100 micrometers thick, offered superior scratch resistance and optical clarity compared to plastic alternatives. However, their brittleness initially limited their application in flexible displays.
The pursuit of flexibility led to innovations in polymer-based films with glass-like properties. Materials such as polyimide and specialized acrylics were developed to provide a balance between durability and flexibility. These advanced polymers allowed for the creation of foldable and rollable AMOLED displays while maintaining adequate protection.
Recent advancements have focused on enhancing the functional properties of protective films. Self-healing materials, capable of repairing minor scratches, have been introduced. Additionally, films with improved optical properties, such as reduced glare and enhanced color accuracy, have been developed to optimize the visual experience of AMOLED displays.
The latest trend in AMOLED film evolution is the integration of smart functionalities. Films with embedded sensors for touch sensitivity, pressure detection, or even biometric authentication are being explored. These innovations aim to expand the capabilities of AMOLED displays beyond mere visual output, transforming them into more interactive and versatile interfaces.
In the early stages of AMOLED technology, protective films were often simple polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyurethane (PU) layers. These materials provided basic scratch resistance but offered limited protection against more severe impacts or environmental factors. As AMOLED displays became thinner and more flexible, the need for more advanced protective materials became apparent.
The next phase of evolution saw the introduction of multi-layer film structures. These composite films combined different materials to address various protection needs simultaneously. For instance, a typical multi-layer film might include a hard coat for scratch resistance, an anti-reflective layer to improve visibility, and a shock-absorbing layer to protect against impacts.
A significant milestone in AMOLED film evolution was the development of ultra-thin glass films. These films, often less than 100 micrometers thick, offered superior scratch resistance and optical clarity compared to plastic alternatives. However, their brittleness initially limited their application in flexible displays.
The pursuit of flexibility led to innovations in polymer-based films with glass-like properties. Materials such as polyimide and specialized acrylics were developed to provide a balance between durability and flexibility. These advanced polymers allowed for the creation of foldable and rollable AMOLED displays while maintaining adequate protection.
Recent advancements have focused on enhancing the functional properties of protective films. Self-healing materials, capable of repairing minor scratches, have been introduced. Additionally, films with improved optical properties, such as reduced glare and enhanced color accuracy, have been developed to optimize the visual experience of AMOLED displays.
The latest trend in AMOLED film evolution is the integration of smart functionalities. Films with embedded sensors for touch sensitivity, pressure detection, or even biometric authentication are being explored. These innovations aim to expand the capabilities of AMOLED displays beyond mere visual output, transforming them into more interactive and versatile interfaces.
Market Demand Analysis
The AMOLED protective film materials market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing adoption of AMOLED displays in smartphones, tablets, and other consumer electronics. As AMOLED technology continues to evolve and expand into new applications, the demand for innovative protective film materials is expected to surge.
The global AMOLED display market is projected to reach a substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) outpacing that of traditional LCD displays. This growth is primarily fueled by the superior performance characteristics of AMOLED displays, including better color reproduction, higher contrast ratios, and improved energy efficiency. As a result, the demand for protective film materials that can enhance and preserve these qualities is also on the rise.
One of the key drivers of market demand for AMOLED protective film materials is the increasing focus on device durability and longevity. Consumers are seeking devices that can withstand daily wear and tear, accidental drops, and environmental factors. This has led to a growing need for advanced protective films that offer superior scratch resistance, impact protection, and anti-fingerprint properties.
The automotive industry is emerging as a significant market for AMOLED displays and, consequently, protective film materials. As vehicle manufacturers integrate larger and more sophisticated displays into their dashboards and infotainment systems, the demand for protective films that can withstand harsh automotive environments is increasing. These materials must offer resistance to temperature fluctuations, UV radiation, and chemical exposure while maintaining optical clarity.
Another factor driving market demand is the trend towards flexible and foldable AMOLED displays. As manufacturers push the boundaries of display technology, there is a growing need for protective film materials that can accommodate bending and folding without compromising display quality or durability. This presents both challenges and opportunities for material innovators to develop solutions that can maintain flexibility while providing adequate protection.
The increasing awareness of environmental issues and sustainability is also influencing market demand for AMOLED protective film materials. Consumers and manufacturers alike are seeking eco-friendly alternatives that reduce the environmental impact of electronic devices. This has led to a growing interest in biodegradable or recyclable protective film materials that can meet performance requirements while aligning with sustainability goals.
In the healthcare and medical device sectors, there is a rising demand for AMOLED displays in diagnostic equipment and patient monitoring systems. This application requires protective film materials that not only offer durability and clarity but also meet stringent hygiene and sterilization standards. The ability to withstand frequent cleaning and disinfection without degradation is becoming a crucial factor in material selection for these applications.
The global AMOLED display market is projected to reach a substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) outpacing that of traditional LCD displays. This growth is primarily fueled by the superior performance characteristics of AMOLED displays, including better color reproduction, higher contrast ratios, and improved energy efficiency. As a result, the demand for protective film materials that can enhance and preserve these qualities is also on the rise.
One of the key drivers of market demand for AMOLED protective film materials is the increasing focus on device durability and longevity. Consumers are seeking devices that can withstand daily wear and tear, accidental drops, and environmental factors. This has led to a growing need for advanced protective films that offer superior scratch resistance, impact protection, and anti-fingerprint properties.
The automotive industry is emerging as a significant market for AMOLED displays and, consequently, protective film materials. As vehicle manufacturers integrate larger and more sophisticated displays into their dashboards and infotainment systems, the demand for protective films that can withstand harsh automotive environments is increasing. These materials must offer resistance to temperature fluctuations, UV radiation, and chemical exposure while maintaining optical clarity.
Another factor driving market demand is the trend towards flexible and foldable AMOLED displays. As manufacturers push the boundaries of display technology, there is a growing need for protective film materials that can accommodate bending and folding without compromising display quality or durability. This presents both challenges and opportunities for material innovators to develop solutions that can maintain flexibility while providing adequate protection.
The increasing awareness of environmental issues and sustainability is also influencing market demand for AMOLED protective film materials. Consumers and manufacturers alike are seeking eco-friendly alternatives that reduce the environmental impact of electronic devices. This has led to a growing interest in biodegradable or recyclable protective film materials that can meet performance requirements while aligning with sustainability goals.
In the healthcare and medical device sectors, there is a rising demand for AMOLED displays in diagnostic equipment and patient monitoring systems. This application requires protective film materials that not only offer durability and clarity but also meet stringent hygiene and sterilization standards. The ability to withstand frequent cleaning and disinfection without degradation is becoming a crucial factor in material selection for these applications.
Technical Challenges
AMOLED protective film materials face several significant technical challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and optimal performance. One of the primary issues is achieving a balance between flexibility and durability. As AMOLED displays are increasingly used in flexible and foldable devices, the protective films must maintain their integrity under repeated bending and folding stress while still providing adequate protection against external damage.
Another critical challenge lies in enhancing the optical properties of these films. The protective layer must maintain high transparency to ensure the vibrant colors and deep blacks characteristic of AMOLED displays are not compromised. Additionally, reducing reflectivity and glare remains a persistent issue, particularly for outdoor use scenarios where ambient light can significantly impact display visibility.
The development of thin yet robust films poses another technical hurdle. As device manufacturers strive for sleeker designs, the protective films must become increasingly thinner without sacrificing their protective qualities. This requires innovative material compositions and manufacturing processes to create ultra-thin films that can withstand impact, scratches, and environmental factors.
Thermal management is a growing concern in AMOLED protective films. As displays become more powerful and energy-intensive, the films must effectively dissipate heat to prevent damage to the sensitive OLED components beneath. This challenge is compounded by the need to maintain the film's other protective properties while incorporating thermal management features.
Chemical resistance presents another significant challenge. AMOLED displays are susceptible to degradation from exposure to oxygen and moisture. Protective films must create an effective barrier against these elements without compromising the display's functionality or aesthetic appeal. Developing materials that provide long-term protection against environmental factors while remaining optically clear and flexible is an ongoing area of research.
The manufacturing process for these advanced protective films also faces technical challenges. Ensuring uniform application and adhesion across large display areas, particularly for curved or flexible screens, requires precise control and innovative production techniques. The industry must develop scalable manufacturing methods that can produce these high-performance films consistently and cost-effectively.
Lastly, the environmental impact and sustainability of AMOLED protective film materials have become increasingly important considerations. Developing eco-friendly materials that maintain the required protective properties while being recyclable or biodegradable presents a significant technical challenge. This aspect is crucial as the electronics industry faces growing pressure to reduce its environmental footprint.
Another critical challenge lies in enhancing the optical properties of these films. The protective layer must maintain high transparency to ensure the vibrant colors and deep blacks characteristic of AMOLED displays are not compromised. Additionally, reducing reflectivity and glare remains a persistent issue, particularly for outdoor use scenarios where ambient light can significantly impact display visibility.
The development of thin yet robust films poses another technical hurdle. As device manufacturers strive for sleeker designs, the protective films must become increasingly thinner without sacrificing their protective qualities. This requires innovative material compositions and manufacturing processes to create ultra-thin films that can withstand impact, scratches, and environmental factors.
Thermal management is a growing concern in AMOLED protective films. As displays become more powerful and energy-intensive, the films must effectively dissipate heat to prevent damage to the sensitive OLED components beneath. This challenge is compounded by the need to maintain the film's other protective properties while incorporating thermal management features.
Chemical resistance presents another significant challenge. AMOLED displays are susceptible to degradation from exposure to oxygen and moisture. Protective films must create an effective barrier against these elements without compromising the display's functionality or aesthetic appeal. Developing materials that provide long-term protection against environmental factors while remaining optically clear and flexible is an ongoing area of research.
The manufacturing process for these advanced protective films also faces technical challenges. Ensuring uniform application and adhesion across large display areas, particularly for curved or flexible screens, requires precise control and innovative production techniques. The industry must develop scalable manufacturing methods that can produce these high-performance films consistently and cost-effectively.
Lastly, the environmental impact and sustainability of AMOLED protective film materials have become increasingly important considerations. Developing eco-friendly materials that maintain the required protective properties while being recyclable or biodegradable presents a significant technical challenge. This aspect is crucial as the electronics industry faces growing pressure to reduce its environmental footprint.
Current Solutions
01 Protective film materials for AMOLED displays
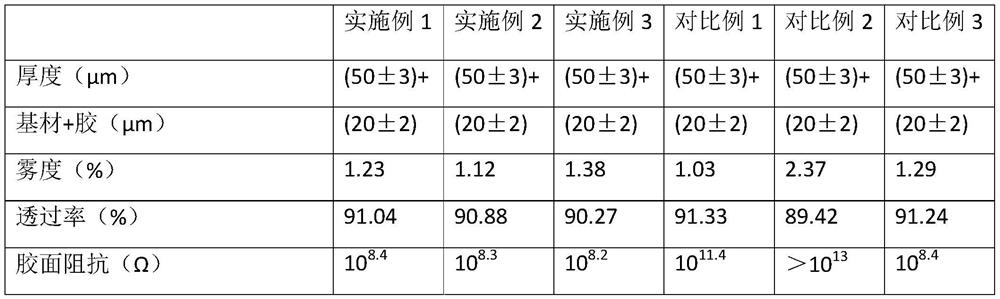
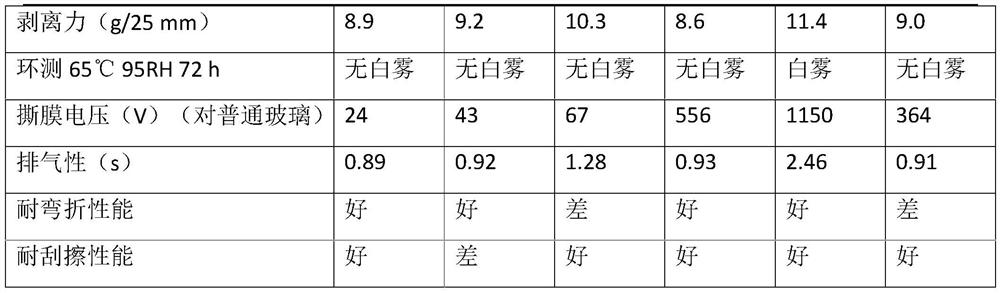
Various materials are used to create protective films for AMOLED displays, including organic and inorganic compounds. These films serve to protect the sensitive OLED layers from environmental factors such as moisture and oxygen, while maintaining the display's flexibility and optical properties. Common materials include silicon nitride, aluminum oxide, and organic polymers.- Protective film materials for AMOLED displays: Various materials are used to create protective films for AMOLED displays, including organic and inorganic compounds. These films serve to protect the sensitive OLED layers from environmental factors such as moisture and oxygen, while also enhancing the display's durability and longevity. The materials are often applied using thin-film deposition techniques to ensure uniform coverage and optimal protection.
- Encapsulation layers for AMOLED devices: Encapsulation layers play a crucial role in protecting AMOLED devices from degradation. These layers typically consist of alternating organic and inorganic materials, creating a multi-layer barrier that effectively prevents the ingress of moisture and oxygen. Advanced encapsulation techniques, such as thin-film encapsulation (TFE), are employed to achieve superior protection while maintaining the flexibility and thinness of AMOLED displays.
- Transparent conductive films for AMOLED screens: Transparent conductive films are essential components of AMOLED displays, serving as electrodes while maintaining optical transparency. Materials such as indium tin oxide (ITO) and more recently developed alternatives like graphene and silver nanowires are used to create these films. These materials offer a balance between conductivity, transparency, and flexibility, which is crucial for the performance and durability of AMOLED screens.
- Flexible substrate materials for AMOLED displays: Flexible substrates are increasingly used in AMOLED displays to enable bendable and foldable devices. Materials such as polyimide and ultra-thin glass are employed as substrates, providing the necessary flexibility while maintaining structural integrity. These materials must be compatible with the OLED fabrication process and offer sufficient barrier properties to protect the sensitive organic layers.
- Light-emitting materials for AMOLED pixels: The light-emitting materials used in AMOLED pixels are crucial for display performance. Organic compounds, including small molecules and polymers, are carefully designed and synthesized to emit light of specific colors when electrically stimulated. These materials are often protected by additional layers to prevent degradation and ensure long-term stability of the display.
02 Encapsulation techniques for AMOLED displays
Advanced encapsulation techniques are employed to protect AMOLED displays from degradation. These methods often involve multi-layer structures combining inorganic barrier layers with organic planarization layers. Thin-film encapsulation (TFE) is a popular approach, utilizing alternating layers of organic and inorganic materials to create an effective barrier against moisture and oxygen ingress.Expand Specific Solutions03 Flexible protective films for foldable AMOLED displays
Specialized protective films are developed for foldable AMOLED displays to maintain flexibility while providing adequate protection. These films often incorporate materials with high elastic modulus and low glass transition temperatures. Composite structures combining polymeric materials with inorganic nanoparticles are used to enhance both flexibility and barrier properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Optical enhancement films for AMOLED displays
Protective films for AMOLED displays often incorporate optical enhancement features. These may include anti-reflection coatings, polarizers, and color filters integrated into the protective layer structure. Such films help improve display visibility, color accuracy, and overall visual performance while maintaining the protective function.Expand Specific Solutions05 Self-healing protective films for AMOLED displays
Innovative self-healing materials are being developed for AMOLED protective films to address the issue of minor scratches and damage. These materials typically contain microcapsules filled with healing agents or utilize reversible chemical bonds that can reform after being broken. Self-healing films aim to extend the lifespan of AMOLED displays by automatically repairing minor surface damage.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The AMOLED protective film materials market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for high-quality displays in smartphones, wearables, and other electronic devices. The market size is expanding rapidly, with major players like BOE Technology, Samsung Electronics, and LG Chem investing heavily in research and development. Technological maturity varies among companies, with industry leaders like Samsung and LG demonstrating advanced capabilities in AMOLED technology. Emerging players such as Tianma Microelectronics and Everdisplay Optronics are making significant strides in innovation. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established electronics giants and specialized materials companies, each contributing to the evolution of AMOLED protective film technology.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has made significant strides in AMOLED protective film materials, focusing on enhancing durability and optical performance. Their latest innovation involves a multi-functional protective film that combines high hardness (9H on the Mohs scale) with excellent light transmission (>93%) [5]. BOE's film incorporates nanoparticles to improve scratch resistance while maintaining flexibility for curved and foldable displays. The company has also developed a proprietary anti-reflection coating that reduces glare by up to 98%, enhancing display visibility in bright environments [6]. Furthermore, BOE has introduced a novel self-healing polymer layer that can repair minor scratches within 24 hours at room temperature, significantly extending the lifespan of AMOLED displays [7].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, strong presence in the Chinese market, and diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Relatively new to OLED technology compared to some competitors, potential challenges in global market expansion.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed innovative AMOLED protective film materials using advanced polymer technology. Their latest solution incorporates a multi-layer structure with a hard coating on top for scratch resistance, an anti-fingerprint layer, and a flexible base film [1]. The company has also introduced a new material called 'UTG' (Ultra Thin Glass) for foldable displays, which offers improved durability and flexibility compared to traditional plastic films [2]. Samsung's protective films utilize nano-coating technology to enhance light transmission and reduce reflectivity, resulting in improved display brightness and outdoor visibility [3]. Additionally, they have implemented a self-healing polymer layer that can recover from minor scratches, extending the lifespan of the display [4].
Strengths: Industry-leading technology in flexible displays, strong R&D capabilities, and vertical integration. Weaknesses: High production costs and potential supply chain dependencies.
Key Innovations
Novel OLED screen protective film and preparation method and application thereof
PatentActiveCN112724852A
Innovation
- Use anti-UV and anti-static TPU film as the base material layer, and set anti-static PU glue and the first anti-static release film on it, combined with the hardened layer to ensure low static voltage, excellent exhaust performance, good weather resistance and no residue Glue characteristics, suitable for OLED screens.
Active matrix organic light emitting diode back plate, method for preparing the same, and display panel
PatentInactiveUS20200335558A1
Innovation
- An active matrix organic light emitting diode back plate is designed with a thin film transistor and a thin film battery integrated coplanarly on a substrate, allowing for a single preparation process and maximizing integration, which reduces module thickness, simplifies the preparation process, and lowers production costs.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of AMOLED protective film materials is a critical consideration in the development and adoption of these innovative technologies. As the demand for AMOLED displays continues to grow, the production and disposal of protective films have become increasingly significant environmental concerns.
One of the primary environmental challenges associated with AMOLED protective films is the use of non-biodegradable materials. Many current protective films are made from synthetic polymers that can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. This longevity contributes to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and oceans, posing threats to ecosystems and wildlife.
The manufacturing process of AMOLED protective films also raises environmental concerns. The production often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially harmful chemicals. These factors contribute to increased carbon emissions and the release of pollutants into the environment, affecting air and water quality in manufacturing regions.
However, recent innovations in AMOLED protective film materials are addressing these environmental challenges. Researchers are exploring bio-based and biodegradable alternatives that can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of these materials. For instance, some companies are developing protective films made from plant-based polymers that offer similar performance to traditional materials while being more environmentally friendly.
Another area of focus is the development of recyclable protective films. By designing materials that can be easily separated and recycled at the end of their lifecycle, manufacturers aim to reduce waste and promote a circular economy approach in the electronics industry. This shift towards recyclability not only reduces the environmental impact but also helps conserve resources.
Energy efficiency in the production process is also being improved through technological advancements. New manufacturing techniques are being developed that require less energy and fewer chemical inputs, thereby reducing the overall environmental impact of protective film production.
Furthermore, innovations in AMOLED protective film materials are contributing to the longevity of electronic devices. By providing better protection against scratches, impacts, and environmental factors, these advanced films can extend the lifespan of devices, potentially reducing electronic waste and the need for frequent replacements.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, the development of eco-friendly AMOLED protective film materials is likely to accelerate. This trend is expected to drive further innovations in material science and manufacturing processes, ultimately leading to more sustainable and environmentally responsible products in the consumer electronics industry.
One of the primary environmental challenges associated with AMOLED protective films is the use of non-biodegradable materials. Many current protective films are made from synthetic polymers that can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. This longevity contributes to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and oceans, posing threats to ecosystems and wildlife.
The manufacturing process of AMOLED protective films also raises environmental concerns. The production often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially harmful chemicals. These factors contribute to increased carbon emissions and the release of pollutants into the environment, affecting air and water quality in manufacturing regions.
However, recent innovations in AMOLED protective film materials are addressing these environmental challenges. Researchers are exploring bio-based and biodegradable alternatives that can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of these materials. For instance, some companies are developing protective films made from plant-based polymers that offer similar performance to traditional materials while being more environmentally friendly.
Another area of focus is the development of recyclable protective films. By designing materials that can be easily separated and recycled at the end of their lifecycle, manufacturers aim to reduce waste and promote a circular economy approach in the electronics industry. This shift towards recyclability not only reduces the environmental impact but also helps conserve resources.
Energy efficiency in the production process is also being improved through technological advancements. New manufacturing techniques are being developed that require less energy and fewer chemical inputs, thereby reducing the overall environmental impact of protective film production.
Furthermore, innovations in AMOLED protective film materials are contributing to the longevity of electronic devices. By providing better protection against scratches, impacts, and environmental factors, these advanced films can extend the lifespan of devices, potentially reducing electronic waste and the need for frequent replacements.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, the development of eco-friendly AMOLED protective film materials is likely to accelerate. This trend is expected to drive further innovations in material science and manufacturing processes, ultimately leading to more sustainable and environmentally responsible products in the consumer electronics industry.
Intellectual Property
The intellectual property landscape surrounding AMOLED protective film materials has seen significant developments in recent years. Major display manufacturers and materials companies have been actively filing patents to protect their innovations in this critical area of display technology.
Samsung Display, as a leading OLED panel manufacturer, holds a substantial patent portfolio related to protective film materials and structures. Their patents cover various aspects, including multi-layer film compositions, novel barrier materials, and manufacturing processes for enhancing durability and flexibility. LG Display has also been active in this space, with patents focusing on thin-film encapsulation technologies and moisture-resistant barrier films.
Materials suppliers like DuPont and 3M have made notable contributions to the field. DuPont's patents often relate to high-performance polymers and composite materials designed to protect OLED devices from environmental factors. 3M's intellectual property includes innovations in optical films and adhesive technologies specifically tailored for AMOLED applications.
Japanese companies such as Sumitomo Chemical and Konica Minolta have patented advanced barrier film technologies, emphasizing gas permeation resistance and optical properties. Their innovations often address the challenges of maintaining display quality while enhancing device longevity.
Chinese firms, including BOE Technology and Visionox, have been increasingly active in patent filings. Their intellectual property often focuses on cost-effective solutions for mass production and integration of protective films in flexible OLED displays.
Key areas of patent activity include ultra-thin glass technologies, hybrid organic-inorganic barrier layers, and self-healing materials. Patents related to roll-to-roll manufacturing processes for protective films have also gained prominence, reflecting the industry's push towards more efficient production methods.
Collaborations between display manufacturers and materials companies have resulted in joint patents, combining expertise in device architecture and materials science. These partnerships often yield innovations that address specific challenges in AMOLED protection, such as enhanced scratch resistance or improved optical characteristics.
The intellectual property landscape also reveals trends in emerging technologies. Patents related to quantum dot-enhanced barrier films and nanocomposite materials for superior barrier properties are becoming more prevalent. Additionally, there is growing interest in environmentally friendly and recyclable protective film materials, as evidenced by recent patent filings in this area.
Samsung Display, as a leading OLED panel manufacturer, holds a substantial patent portfolio related to protective film materials and structures. Their patents cover various aspects, including multi-layer film compositions, novel barrier materials, and manufacturing processes for enhancing durability and flexibility. LG Display has also been active in this space, with patents focusing on thin-film encapsulation technologies and moisture-resistant barrier films.
Materials suppliers like DuPont and 3M have made notable contributions to the field. DuPont's patents often relate to high-performance polymers and composite materials designed to protect OLED devices from environmental factors. 3M's intellectual property includes innovations in optical films and adhesive technologies specifically tailored for AMOLED applications.
Japanese companies such as Sumitomo Chemical and Konica Minolta have patented advanced barrier film technologies, emphasizing gas permeation resistance and optical properties. Their innovations often address the challenges of maintaining display quality while enhancing device longevity.
Chinese firms, including BOE Technology and Visionox, have been increasingly active in patent filings. Their intellectual property often focuses on cost-effective solutions for mass production and integration of protective films in flexible OLED displays.
Key areas of patent activity include ultra-thin glass technologies, hybrid organic-inorganic barrier layers, and self-healing materials. Patents related to roll-to-roll manufacturing processes for protective films have also gained prominence, reflecting the industry's push towards more efficient production methods.
Collaborations between display manufacturers and materials companies have resulted in joint patents, combining expertise in device architecture and materials science. These partnerships often yield innovations that address specific challenges in AMOLED protection, such as enhanced scratch resistance or improved optical characteristics.
The intellectual property landscape also reveals trends in emerging technologies. Patents related to quantum dot-enhanced barrier films and nanocomposite materials for superior barrier properties are becoming more prevalent. Additionally, there is growing interest in environmentally friendly and recyclable protective film materials, as evidenced by recent patent filings in this area.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!