How AMOLED encourages eco-friendly smartphone manufacturing?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Evolution and Sustainability Goals
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception, with sustainability becoming an increasingly important focus in recent years. The development of AMOLED displays has been driven by the demand for more energy-efficient, thinner, and visually appealing screens in smartphones and other electronic devices.
The evolution of AMOLED technology can be traced through several key milestones. Initially, AMOLED displays faced challenges such as limited lifespan and high production costs. However, continuous research and development efforts have led to substantial improvements in both performance and manufacturing efficiency. These advancements have not only enhanced the visual quality of displays but also contributed to more sustainable smartphone production.
One of the primary sustainability goals in AMOLED technology is reducing energy consumption. AMOLED displays are inherently more energy-efficient than traditional LCD screens, as they do not require a backlight. Each pixel in an AMOLED display emits its own light, allowing for selective pixel illumination and true blacks when pixels are turned off. This characteristic has led to significant power savings, especially in devices with dark-themed user interfaces.
Another crucial sustainability objective is the reduction of harmful materials in the manufacturing process. Early AMOLED displays relied on heavy metals and other environmentally hazardous substances. However, ongoing research has focused on developing more eco-friendly materials and production methods. This includes the use of organic compounds and the exploration of alternative electrode materials that are less harmful to the environment.
Durability and longevity have also been key areas of improvement in AMOLED technology. Enhancing the lifespan of displays directly contributes to sustainability by reducing the frequency of device replacements and electronic waste. Researchers and manufacturers have made significant strides in addressing issues such as burn-in and color degradation, which were common problems in earlier AMOLED displays.
The pursuit of thinner and more flexible displays has indirectly contributed to sustainability goals. Thinner displays require fewer materials and potentially less energy to produce. Additionally, the development of flexible AMOLED technology opens up new possibilities for device design, potentially leading to more durable and longer-lasting products.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, sustainability remains a central focus. Future developments are likely to emphasize even greater energy efficiency, the use of biodegradable materials, and improved recycling processes for end-of-life displays. These advancements will play a crucial role in making smartphone manufacturing more environmentally friendly and aligning with global sustainability initiatives.
The evolution of AMOLED technology can be traced through several key milestones. Initially, AMOLED displays faced challenges such as limited lifespan and high production costs. However, continuous research and development efforts have led to substantial improvements in both performance and manufacturing efficiency. These advancements have not only enhanced the visual quality of displays but also contributed to more sustainable smartphone production.
One of the primary sustainability goals in AMOLED technology is reducing energy consumption. AMOLED displays are inherently more energy-efficient than traditional LCD screens, as they do not require a backlight. Each pixel in an AMOLED display emits its own light, allowing for selective pixel illumination and true blacks when pixels are turned off. This characteristic has led to significant power savings, especially in devices with dark-themed user interfaces.
Another crucial sustainability objective is the reduction of harmful materials in the manufacturing process. Early AMOLED displays relied on heavy metals and other environmentally hazardous substances. However, ongoing research has focused on developing more eco-friendly materials and production methods. This includes the use of organic compounds and the exploration of alternative electrode materials that are less harmful to the environment.
Durability and longevity have also been key areas of improvement in AMOLED technology. Enhancing the lifespan of displays directly contributes to sustainability by reducing the frequency of device replacements and electronic waste. Researchers and manufacturers have made significant strides in addressing issues such as burn-in and color degradation, which were common problems in earlier AMOLED displays.
The pursuit of thinner and more flexible displays has indirectly contributed to sustainability goals. Thinner displays require fewer materials and potentially less energy to produce. Additionally, the development of flexible AMOLED technology opens up new possibilities for device design, potentially leading to more durable and longer-lasting products.
As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, sustainability remains a central focus. Future developments are likely to emphasize even greater energy efficiency, the use of biodegradable materials, and improved recycling processes for end-of-life displays. These advancements will play a crucial role in making smartphone manufacturing more environmentally friendly and aligning with global sustainability initiatives.
Market Demand for Eco-Friendly Smartphones
The market demand for eco-friendly smartphones has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing environmental awareness and consumer preferences for sustainable products. This trend aligns with the adoption of AMOLED technology in smartphone manufacturing, which offers several eco-friendly advantages.
Consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions, including the lifecycle of electronic devices. This has led to a surge in demand for smartphones that are not only high-performing but also environmentally responsible. AMOLED displays contribute to this demand by offering energy efficiency and potential for longer device lifespan, both key factors in reducing the overall environmental footprint of smartphones.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED displays is a significant driver of market demand. These displays consume less power compared to traditional LCD screens, especially when displaying darker content. This translates to longer battery life, reducing the frequency of charging cycles and potentially extending the overall lifespan of the device. Consumers value this feature not only for convenience but also for its positive environmental impact through reduced energy consumption.
AMOLED technology also enables the development of thinner and lighter smartphones. This aligns with the market demand for sleek, portable devices while simultaneously reducing the amount of materials used in manufacturing. The reduction in material usage contributes to the eco-friendly appeal of AMOLED-equipped smartphones, resonating with environmentally conscious consumers.
The potential for increased durability and longevity of AMOLED displays also meets the growing market demand for sustainable electronics. Consumers are increasingly seeking devices that last longer, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby minimizing electronic waste. AMOLED's resistance to screen burn-in and potential for longer operational life addresses this aspect of eco-friendly demand.
Furthermore, the superior color reproduction and contrast ratios of AMOLED displays cater to the market segment that values both environmental responsibility and high-quality user experience. This combination of eco-friendliness and premium features is particularly appealing to a growing demographic of tech-savvy, environmentally conscious consumers.
The market demand for eco-friendly smartphones is also influenced by corporate and governmental initiatives promoting sustainable technology. As regulations around electronic waste and energy efficiency become more stringent, manufacturers are incentivized to adopt technologies like AMOLED that align with these environmental goals. This regulatory push further stimulates consumer awareness and demand for eco-friendly options.
In conclusion, the market demand for eco-friendly smartphones incorporating AMOLED technology is robust and growing. This demand is driven by a combination of consumer environmental awareness, desire for energy efficiency, preference for durable and long-lasting devices, and the appeal of high-quality displays. As sustainability continues to be a key factor in consumer electronics, AMOLED technology is well-positioned to meet and drive this eco-friendly market demand in smartphone manufacturing.
Consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions, including the lifecycle of electronic devices. This has led to a surge in demand for smartphones that are not only high-performing but also environmentally responsible. AMOLED displays contribute to this demand by offering energy efficiency and potential for longer device lifespan, both key factors in reducing the overall environmental footprint of smartphones.
The energy efficiency of AMOLED displays is a significant driver of market demand. These displays consume less power compared to traditional LCD screens, especially when displaying darker content. This translates to longer battery life, reducing the frequency of charging cycles and potentially extending the overall lifespan of the device. Consumers value this feature not only for convenience but also for its positive environmental impact through reduced energy consumption.
AMOLED technology also enables the development of thinner and lighter smartphones. This aligns with the market demand for sleek, portable devices while simultaneously reducing the amount of materials used in manufacturing. The reduction in material usage contributes to the eco-friendly appeal of AMOLED-equipped smartphones, resonating with environmentally conscious consumers.
The potential for increased durability and longevity of AMOLED displays also meets the growing market demand for sustainable electronics. Consumers are increasingly seeking devices that last longer, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby minimizing electronic waste. AMOLED's resistance to screen burn-in and potential for longer operational life addresses this aspect of eco-friendly demand.
Furthermore, the superior color reproduction and contrast ratios of AMOLED displays cater to the market segment that values both environmental responsibility and high-quality user experience. This combination of eco-friendliness and premium features is particularly appealing to a growing demographic of tech-savvy, environmentally conscious consumers.
The market demand for eco-friendly smartphones is also influenced by corporate and governmental initiatives promoting sustainable technology. As regulations around electronic waste and energy efficiency become more stringent, manufacturers are incentivized to adopt technologies like AMOLED that align with these environmental goals. This regulatory push further stimulates consumer awareness and demand for eco-friendly options.
In conclusion, the market demand for eco-friendly smartphones incorporating AMOLED technology is robust and growing. This demand is driven by a combination of consumer environmental awareness, desire for energy efficiency, preference for durable and long-lasting devices, and the appeal of high-quality displays. As sustainability continues to be a key factor in consumer electronics, AMOLED technology is well-positioned to meet and drive this eco-friendly market demand in smartphone manufacturing.
AMOLED Technology: Current State and Challenges
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology has made significant strides in recent years, revolutionizing smartphone displays. However, it still faces several challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and eco-friendly implementation.
One of the primary challenges is the complexity of the manufacturing process. AMOLED displays require precise deposition of organic materials, which is a delicate and time-consuming procedure. This complexity often leads to lower yield rates and higher production costs compared to traditional LCD technology, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits.
The lifespan of AMOLED displays presents another hurdle. While improvements have been made, AMOLED screens are still prone to burn-in and color degradation over time, especially in areas of static content. This reduced longevity can lead to more frequent device replacements, contradicting the principles of sustainable manufacturing.
Power efficiency remains a double-edged sword for AMOLED technology. While it offers excellent power savings for dark content, displaying bright or white content can consume significantly more power than LCD alternatives. This variability in power consumption poses challenges for consistent energy efficiency across different usage scenarios.
The use of rare and precious metals in AMOLED production is another environmental concern. Materials like indium, which is essential for transparent electrodes, are in limited supply and their extraction can have significant environmental impacts. Finding sustainable alternatives or improving recycling processes for these materials is crucial for eco-friendly manufacturing.
Color accuracy and consistency across different viewing angles continue to be areas of improvement for AMOLED displays. While advancements have been made, achieving uniform color reproduction and maintaining accuracy under various lighting conditions remains challenging.
Scalability in production is another obstacle. As demand for larger AMOLED displays grows, manufacturers face difficulties in scaling up production while maintaining quality and yield rates. This challenge is particularly evident in the production of foldable and flexible AMOLED displays, which require even more sophisticated manufacturing techniques.
The environmental impact of AMOLED production, particularly the use of harmful chemicals and solvents, is a significant concern. Developing greener production methods and finding eco-friendly alternatives to these materials is essential for truly sustainable manufacturing.
Lastly, the recycling and disposal of AMOLED displays pose unique challenges due to their complex structure and the presence of organic materials. Developing efficient recycling processes that can recover valuable materials while safely disposing of harmful components is crucial for closing the loop in eco-friendly smartphone manufacturing.
One of the primary challenges is the complexity of the manufacturing process. AMOLED displays require precise deposition of organic materials, which is a delicate and time-consuming procedure. This complexity often leads to lower yield rates and higher production costs compared to traditional LCD technology, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits.
The lifespan of AMOLED displays presents another hurdle. While improvements have been made, AMOLED screens are still prone to burn-in and color degradation over time, especially in areas of static content. This reduced longevity can lead to more frequent device replacements, contradicting the principles of sustainable manufacturing.
Power efficiency remains a double-edged sword for AMOLED technology. While it offers excellent power savings for dark content, displaying bright or white content can consume significantly more power than LCD alternatives. This variability in power consumption poses challenges for consistent energy efficiency across different usage scenarios.
The use of rare and precious metals in AMOLED production is another environmental concern. Materials like indium, which is essential for transparent electrodes, are in limited supply and their extraction can have significant environmental impacts. Finding sustainable alternatives or improving recycling processes for these materials is crucial for eco-friendly manufacturing.
Color accuracy and consistency across different viewing angles continue to be areas of improvement for AMOLED displays. While advancements have been made, achieving uniform color reproduction and maintaining accuracy under various lighting conditions remains challenging.
Scalability in production is another obstacle. As demand for larger AMOLED displays grows, manufacturers face difficulties in scaling up production while maintaining quality and yield rates. This challenge is particularly evident in the production of foldable and flexible AMOLED displays, which require even more sophisticated manufacturing techniques.
The environmental impact of AMOLED production, particularly the use of harmful chemicals and solvents, is a significant concern. Developing greener production methods and finding eco-friendly alternatives to these materials is essential for truly sustainable manufacturing.
Lastly, the recycling and disposal of AMOLED displays pose unique challenges due to their complex structure and the presence of organic materials. Developing efficient recycling processes that can recover valuable materials while safely disposing of harmful components is crucial for closing the loop in eco-friendly smartphone manufacturing.
Eco-Friendly AMOLED Manufacturing Processes
01 Energy-efficient AMOLED display technology
AMOLED displays are inherently more energy-efficient compared to traditional LCD displays. They consume less power by selectively illuminating only the required pixels, leading to improved battery life in devices. This energy efficiency contributes to the eco-friendliness of AMOLED technology by reducing overall power consumption.- Energy-efficient AMOLED display technology: AMOLED displays are inherently more energy-efficient compared to traditional LCD displays. They consume less power by selectively illuminating only the required pixels, leading to improved battery life in devices. This energy efficiency contributes to the eco-friendliness of AMOLED technology by reducing overall power consumption.
- Eco-friendly materials in AMOLED production: Manufacturers are developing and implementing eco-friendly materials in AMOLED production processes. This includes the use of organic compounds and recyclable components, reducing the environmental impact of display manufacturing. These materials often require less energy to produce and can be more easily recycled at the end of the product's life cycle.
- Improved AMOLED lifespan and durability: Advancements in AMOLED technology have led to increased lifespan and durability of displays. This improvement reduces the frequency of device replacements, thereby minimizing electronic waste. Longer-lasting displays contribute to sustainability by reducing the overall environmental impact of consumer electronics.
- AMOLED color accuracy and reduced eye strain: AMOLED displays offer superior color accuracy and contrast ratios, potentially reducing eye strain for users. This can lead to lower brightness settings, further conserving energy. The improved visual experience may also contribute to user satisfaction and potentially extend device usage periods, indirectly supporting eco-friendliness through reduced consumption.
- Sustainable manufacturing processes for AMOLED: Efforts are being made to develop more sustainable manufacturing processes for AMOLED displays. This includes optimizing production techniques to reduce waste, implementing recycling systems for production materials, and utilizing renewable energy sources in manufacturing facilities. These initiatives aim to minimize the environmental footprint of AMOLED production.
02 Eco-friendly materials in AMOLED production
Advancements in AMOLED manufacturing processes focus on using more environmentally friendly materials. This includes the development of organic compounds and substrates that are less harmful to the environment, both during production and disposal. These eco-friendly materials contribute to reducing the overall environmental impact of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions03 Improved AMOLED lifespan and durability
Enhancing the lifespan and durability of AMOLED displays contributes to their eco-friendliness by reducing the frequency of device replacements. Techniques to improve pixel longevity, prevent burn-in, and enhance overall display durability are being developed, which in turn reduces electronic waste and the need for frequent upgrades.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and sustainable disposal of AMOLED components
Research is being conducted on methods to recycle and sustainably dispose of AMOLED display components. This includes developing processes to recover valuable materials from old displays and finding ways to break down organic compounds in an environmentally friendly manner. These efforts aim to reduce the environmental impact of AMOLED technology at the end of its lifecycle.Expand Specific Solutions05 Optimization of AMOLED manufacturing processes
Efforts are being made to optimize AMOLED manufacturing processes to reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and decrease the use of harmful chemicals. This includes developing more efficient production techniques, implementing cleaner technologies, and improving overall manufacturing sustainability. These optimizations contribute to making AMOLED production more eco-friendly.Expand Specific Solutions
Key AMOLED Manufacturers and Innovators
The AMOLED technology market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for high-quality displays in smartphones and other electronic devices. The global AMOLED market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with major players like Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE Technology Group leading the competition. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to improve AMOLED technology, focusing on energy efficiency and eco-friendly manufacturing processes. The technology's maturity is advancing rapidly, with companies like Applied Materials and Tianma Microelectronics developing innovative production techniques to reduce environmental impact and enhance sustainability in smartphone manufacturing.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has made significant progress in eco-friendly AMOLED manufacturing. They have developed a low-temperature polysilicon (LTPS) backplane technology that reduces energy consumption during production by up to 20%[7]. BOE has also implemented an advanced material recycling system that recovers over 90% of waste solvents used in the OLED manufacturing process[8]. Additionally, they have introduced flexible AMOLED displays that use plastic substrates, reducing the overall weight and material usage in smartphone production[9].
Strengths: Rapidly growing AMOLED production capacity, strong government support. Weaknesses: Less experience in high-end AMOLED production, catching up with Korean competitors in technology.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has pioneered eco-friendly AMOLED manufacturing through several innovative approaches. They have developed a soluble organic material that allows for inkjet printing of OLED displays, reducing material waste by up to 90% compared to traditional methods[1]. Additionally, Samsung has implemented a closed-loop recycling system for OLED production, recovering and reusing over 95% of the indium used in the manufacturing process[2]. The company has also invested in energy-efficient production facilities, with their A3 OLED production line using 30% less energy per unit area compared to previous generations[3].
Strengths: Industry leader in AMOLED technology, significant R&D resources, vertical integration. Weaknesses: High production costs, potential supply chain vulnerabilities.
AMOLED Patents for Sustainable Production
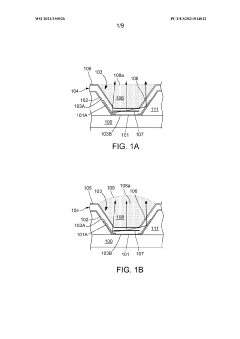
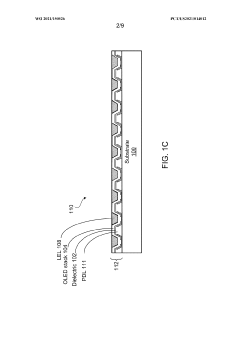
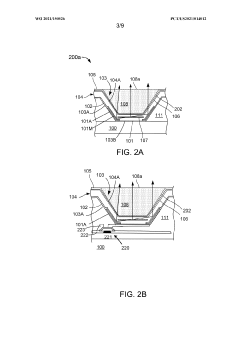
Organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display devices with mirror and method for making the same
PatentWO2021150526A1
Innovation
- The method involves forming an OLED structure with a well structure and mirrors on the sidewalls, using a single deposition and lithography patterning step to create a reflective lower electrode and surrounding mirror, and incorporating a UV-blocking layer to enable the use of UV-curable inks for the light extraction layer, which improves external quantum efficiency and simplifies manufacturing.
Array substrate, display device, and method for manufacturing array substrate
PatentActiveUS20170148862A1
Innovation
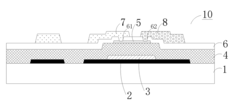
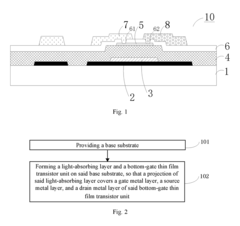
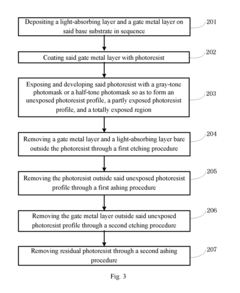
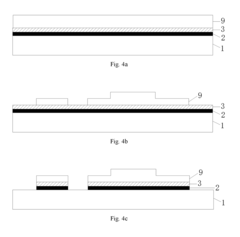
- An array substrate with a light-absorbing layer covering the gate, source, and drain metal layers of a bottom-gate thin film transistor unit, preventing ambient light irradiation while allowing useful light to pass through.
Environmental Impact Assessment of AMOLED
The environmental impact assessment of AMOLED technology in smartphone manufacturing reveals significant eco-friendly advantages compared to traditional LCD displays. AMOLED screens consume less power, particularly when displaying darker content, leading to improved energy efficiency and extended battery life. This reduction in power consumption translates to lower carbon emissions over the device's lifecycle.
AMOLED displays also contribute to material conservation. They are thinner and lighter than LCD screens, reducing the overall weight and size of smartphones. This allows for more compact device designs, potentially decreasing the amount of materials used in manufacturing and packaging. Additionally, AMOLED panels require fewer components, simplifying the production process and reducing waste.
The production of AMOLED displays involves fewer harmful chemicals compared to LCD manufacturing. While both technologies use some hazardous substances, AMOLED production generally requires less toxic materials, reducing the environmental impact of the manufacturing process. This aspect is particularly important in the context of responsible waste management and recycling efforts.
AMOLED technology also offers potential benefits in terms of device longevity. The ability to selectively illuminate pixels can help prevent screen burn-in, potentially extending the usable life of smartphones. This longevity contributes to a reduction in electronic waste, as consumers may keep their devices for longer periods before upgrading.
However, it's important to note that AMOLED production does have some environmental challenges. The manufacturing process can be energy-intensive, and some rare materials used in AMOLED displays may have limited availability. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues, exploring more sustainable production methods and alternative materials.
In terms of end-of-life considerations, AMOLED displays present both opportunities and challenges. While their simpler structure may facilitate easier recycling of some components, the organic materials used in AMOLED screens can be more difficult to recycle than traditional LCD components. This highlights the need for continued innovation in recycling technologies specific to AMOLED displays.
Overall, the adoption of AMOLED technology in smartphone manufacturing represents a step towards more eco-friendly practices in the electronics industry. Its benefits in energy efficiency, material conservation, and reduced use of harmful chemicals contribute to a lower environmental footprint. As the technology continues to evolve, further improvements in sustainability are expected, reinforcing AMOLED's role in promoting greener smartphone production.
AMOLED displays also contribute to material conservation. They are thinner and lighter than LCD screens, reducing the overall weight and size of smartphones. This allows for more compact device designs, potentially decreasing the amount of materials used in manufacturing and packaging. Additionally, AMOLED panels require fewer components, simplifying the production process and reducing waste.
The production of AMOLED displays involves fewer harmful chemicals compared to LCD manufacturing. While both technologies use some hazardous substances, AMOLED production generally requires less toxic materials, reducing the environmental impact of the manufacturing process. This aspect is particularly important in the context of responsible waste management and recycling efforts.
AMOLED technology also offers potential benefits in terms of device longevity. The ability to selectively illuminate pixels can help prevent screen burn-in, potentially extending the usable life of smartphones. This longevity contributes to a reduction in electronic waste, as consumers may keep their devices for longer periods before upgrading.
However, it's important to note that AMOLED production does have some environmental challenges. The manufacturing process can be energy-intensive, and some rare materials used in AMOLED displays may have limited availability. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues, exploring more sustainable production methods and alternative materials.
In terms of end-of-life considerations, AMOLED displays present both opportunities and challenges. While their simpler structure may facilitate easier recycling of some components, the organic materials used in AMOLED screens can be more difficult to recycle than traditional LCD components. This highlights the need for continued innovation in recycling technologies specific to AMOLED displays.
Overall, the adoption of AMOLED technology in smartphone manufacturing represents a step towards more eco-friendly practices in the electronics industry. Its benefits in energy efficiency, material conservation, and reduced use of harmful chemicals contribute to a lower environmental footprint. As the technology continues to evolve, further improvements in sustainability are expected, reinforcing AMOLED's role in promoting greener smartphone production.
Circular Economy Strategies for AMOLED Devices
Circular economy strategies for AMOLED devices focus on maximizing resource efficiency and minimizing waste throughout the product lifecycle. These strategies aim to extend the lifespan of AMOLED displays and their components, reduce environmental impact, and create value from waste materials.
One key approach is designing AMOLED devices for durability and repairability. Manufacturers can use modular designs that allow for easy replacement of individual components, such as the display panel or battery. This extends the device's overall lifespan and reduces the need for complete replacements. Additionally, using high-quality materials and robust construction techniques can improve the longevity of AMOLED displays, reducing the frequency of repairs and replacements.
Another important strategy is the implementation of efficient recycling processes for AMOLED devices. This involves developing advanced techniques to recover valuable materials from end-of-life displays, such as indium, silver, and organic compounds. By improving the recovery rates of these materials, manufacturers can reduce the demand for virgin resources and minimize the environmental impact of AMOLED production.
Refurbishment and remanufacturing programs also play a crucial role in circular economy strategies for AMOLED devices. These initiatives involve collecting used smartphones, repairing or upgrading their components, and reselling them as refurbished units. This approach not only extends the lifespan of AMOLED displays but also creates new business opportunities and reduces electronic waste.
Manufacturers can also explore the use of bio-based and biodegradable materials in AMOLED production. While challenges remain in achieving the necessary performance characteristics, research into sustainable alternatives for organic light-emitting materials and substrates shows promise for reducing the environmental footprint of AMOLED devices.
Implementing take-back programs and incentives for device return is another essential aspect of circular economy strategies. By encouraging consumers to return their old devices, manufacturers can ensure proper recycling and recovery of valuable materials. This can be achieved through trade-in programs, deposit systems, or partnerships with recycling facilities.
Lastly, adopting a product-as-a-service model for AMOLED devices can promote circularity by shifting the focus from ownership to usage. In this model, manufacturers retain ownership of the devices and provide them to consumers on a subscription or leasing basis. This approach incentivizes manufacturers to design for longevity and repairability, as they remain responsible for the device throughout its lifecycle.
One key approach is designing AMOLED devices for durability and repairability. Manufacturers can use modular designs that allow for easy replacement of individual components, such as the display panel or battery. This extends the device's overall lifespan and reduces the need for complete replacements. Additionally, using high-quality materials and robust construction techniques can improve the longevity of AMOLED displays, reducing the frequency of repairs and replacements.
Another important strategy is the implementation of efficient recycling processes for AMOLED devices. This involves developing advanced techniques to recover valuable materials from end-of-life displays, such as indium, silver, and organic compounds. By improving the recovery rates of these materials, manufacturers can reduce the demand for virgin resources and minimize the environmental impact of AMOLED production.
Refurbishment and remanufacturing programs also play a crucial role in circular economy strategies for AMOLED devices. These initiatives involve collecting used smartphones, repairing or upgrading their components, and reselling them as refurbished units. This approach not only extends the lifespan of AMOLED displays but also creates new business opportunities and reduces electronic waste.
Manufacturers can also explore the use of bio-based and biodegradable materials in AMOLED production. While challenges remain in achieving the necessary performance characteristics, research into sustainable alternatives for organic light-emitting materials and substrates shows promise for reducing the environmental footprint of AMOLED devices.
Implementing take-back programs and incentives for device return is another essential aspect of circular economy strategies. By encouraging consumers to return their old devices, manufacturers can ensure proper recycling and recovery of valuable materials. This can be achieved through trade-in programs, deposit systems, or partnerships with recycling facilities.
Lastly, adopting a product-as-a-service model for AMOLED devices can promote circularity by shifting the focus from ownership to usage. In this model, manufacturers retain ownership of the devices and provide them to consumers on a subscription or leasing basis. This approach incentivizes manufacturers to design for longevity and repairability, as they remain responsible for the device throughout its lifecycle.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!