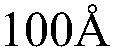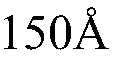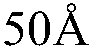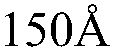The role of AMOLED in next-gen transparent displays.
JUL 17, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED Transparent Display Evolution
The evolution of AMOLED technology in transparent displays represents a significant leap forward in display technology. AMOLED, or Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode, has emerged as a key player in the development of next-generation transparent displays due to its unique properties and capabilities.
The journey of AMOLED in transparent displays began with the introduction of OLED technology in the late 1980s. Initially, OLED displays were opaque and primarily used in small electronic devices. As research progressed, the potential for creating transparent OLED displays became apparent, leading to increased focus on this application.
In the early 2000s, the first prototypes of transparent OLED displays were demonstrated, showcasing the technology's potential for creating see-through screens. However, these early versions suffered from low transparency and poor durability, limiting their practical applications.
The breakthrough came with the development of AMOLED technology, which offered improved efficiency, brightness, and color reproduction compared to passive-matrix OLED displays. This advancement paved the way for more robust and higher-quality transparent displays.
Over the past decade, AMOLED technology has undergone rapid improvements in transparency, power efficiency, and manufacturing processes. These advancements have enabled the creation of increasingly transparent displays with better image quality and longer lifespans.
Recent years have seen the integration of AMOLED transparent displays in various applications, from automotive head-up displays to smart windows in buildings. The technology has also found its way into consumer electronics, with concept devices featuring transparent screens gaining attention at tech exhibitions.
Looking ahead, the evolution of AMOLED in transparent displays is expected to continue at a rapid pace. Researchers are working on enhancing transparency levels while maintaining high image quality and energy efficiency. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve the flexibility of these displays, potentially leading to rollable or foldable transparent screens.
The future of AMOLED transparent displays also involves addressing challenges such as reducing production costs, improving durability, and expanding the color gamut. As these hurdles are overcome, we can anticipate wider adoption of this technology across various industries, revolutionizing how we interact with digital information in our physical environment.
The journey of AMOLED in transparent displays began with the introduction of OLED technology in the late 1980s. Initially, OLED displays were opaque and primarily used in small electronic devices. As research progressed, the potential for creating transparent OLED displays became apparent, leading to increased focus on this application.
In the early 2000s, the first prototypes of transparent OLED displays were demonstrated, showcasing the technology's potential for creating see-through screens. However, these early versions suffered from low transparency and poor durability, limiting their practical applications.
The breakthrough came with the development of AMOLED technology, which offered improved efficiency, brightness, and color reproduction compared to passive-matrix OLED displays. This advancement paved the way for more robust and higher-quality transparent displays.
Over the past decade, AMOLED technology has undergone rapid improvements in transparency, power efficiency, and manufacturing processes. These advancements have enabled the creation of increasingly transparent displays with better image quality and longer lifespans.
Recent years have seen the integration of AMOLED transparent displays in various applications, from automotive head-up displays to smart windows in buildings. The technology has also found its way into consumer electronics, with concept devices featuring transparent screens gaining attention at tech exhibitions.
Looking ahead, the evolution of AMOLED in transparent displays is expected to continue at a rapid pace. Researchers are working on enhancing transparency levels while maintaining high image quality and energy efficiency. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve the flexibility of these displays, potentially leading to rollable or foldable transparent screens.
The future of AMOLED transparent displays also involves addressing challenges such as reducing production costs, improving durability, and expanding the color gamut. As these hurdles are overcome, we can anticipate wider adoption of this technology across various industries, revolutionizing how we interact with digital information in our physical environment.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for next-generation transparent displays incorporating AMOLED technology is experiencing significant growth, driven by various factors across multiple industries. The automotive sector stands out as a key driver, with increasing interest in integrating transparent displays into windshields and windows for enhanced driver information systems and augmented reality applications. This trend is expected to revolutionize the driving experience, providing real-time navigation, safety alerts, and entertainment features without obstructing the driver's view.
In the consumer electronics market, there is a growing appetite for innovative display solutions that can seamlessly blend into everyday environments. Transparent AMOLED displays offer the potential for smart mirrors, interactive shop windows, and futuristic home appliances. The retail industry is particularly keen on adopting these displays for immersive and interactive shopping experiences, allowing customers to visualize products and access information through transparent interfaces.
The aerospace and defense sectors are also showing interest in transparent AMOLED technology for advanced cockpit displays and heads-up displays in military applications. These displays can provide critical information to pilots and soldiers while maintaining situational awareness, a crucial factor in high-stakes environments.
In the architectural and interior design fields, transparent AMOLED displays are gaining traction for their ability to transform ordinary glass surfaces into dynamic, interactive screens. This opens up new possibilities for smart buildings, where windows can double as information displays or entertainment systems, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics.
The healthcare industry is another sector where transparent AMOLED displays show promise, particularly in surgical environments and medical imaging. These displays can overlay vital patient information or imaging data onto transparent surfaces, allowing medical professionals to access critical information without losing sight of the patient or procedure.
Market analysts predict robust growth for transparent display technologies, with AMOLED playing a crucial role due to its superior image quality, flexibility, and energy efficiency compared to other display technologies. The global transparent display market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, with Asia-Pacific region leading in terms of both production and adoption.
However, challenges remain in terms of manufacturing costs and scalability, which currently limit widespread adoption. As technology advances and production processes improve, these barriers are expected to diminish, potentially leading to a surge in market demand across various sectors. The convergence of AMOLED technology with transparent displays represents a significant opportunity for innovation and market disruption in the display industry.
In the consumer electronics market, there is a growing appetite for innovative display solutions that can seamlessly blend into everyday environments. Transparent AMOLED displays offer the potential for smart mirrors, interactive shop windows, and futuristic home appliances. The retail industry is particularly keen on adopting these displays for immersive and interactive shopping experiences, allowing customers to visualize products and access information through transparent interfaces.
The aerospace and defense sectors are also showing interest in transparent AMOLED technology for advanced cockpit displays and heads-up displays in military applications. These displays can provide critical information to pilots and soldiers while maintaining situational awareness, a crucial factor in high-stakes environments.
In the architectural and interior design fields, transparent AMOLED displays are gaining traction for their ability to transform ordinary glass surfaces into dynamic, interactive screens. This opens up new possibilities for smart buildings, where windows can double as information displays or entertainment systems, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics.
The healthcare industry is another sector where transparent AMOLED displays show promise, particularly in surgical environments and medical imaging. These displays can overlay vital patient information or imaging data onto transparent surfaces, allowing medical professionals to access critical information without losing sight of the patient or procedure.
Market analysts predict robust growth for transparent display technologies, with AMOLED playing a crucial role due to its superior image quality, flexibility, and energy efficiency compared to other display technologies. The global transparent display market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, with Asia-Pacific region leading in terms of both production and adoption.
However, challenges remain in terms of manufacturing costs and scalability, which currently limit widespread adoption. As technology advances and production processes improve, these barriers are expected to diminish, potentially leading to a surge in market demand across various sectors. The convergence of AMOLED technology with transparent displays represents a significant opportunity for innovation and market disruption in the display industry.
Technical Challenges
AMOLED technology, while promising for next-generation transparent displays, faces several significant technical challenges. One of the primary hurdles is achieving high transparency without compromising display quality. Current AMOLED panels struggle to maintain optimal brightness and color accuracy when designed for transparency, as the light-emitting components must be sufficiently sparse to allow light transmission.
Another critical challenge lies in the power efficiency of transparent AMOLED displays. The need for increased brightness to compensate for light loss through transparency results in higher energy consumption. This issue is particularly problematic for mobile and wearable devices where battery life is a crucial factor.
Durability and lifespan present additional concerns. Transparent AMOLED displays are more susceptible to environmental factors such as UV radiation and moisture, which can accelerate degradation of organic materials. Developing robust encapsulation techniques to protect the sensitive organic layers without impacting transparency is a complex engineering task.
Manufacturing scalability poses a significant obstacle. Producing large-scale transparent AMOLED displays with consistent quality and yield rates comparable to traditional opaque displays remains challenging. The intricate processes required for transparency often result in higher defect rates and increased production costs.
Color management in transparent AMOLEDs is another area requiring innovation. Achieving accurate color reproduction is complicated by the varying backgrounds visible through the display, which can affect perceived colors. Developing adaptive color correction algorithms to compensate for these environmental variations is essential for maintaining display fidelity.
Integration of touch functionality without compromising transparency or display performance adds another layer of complexity. Traditional touch sensors can reduce transparency and affect visual quality, necessitating the development of new, highly transparent touch-sensing technologies compatible with AMOLED structures.
Addressing image retention and burn-in issues, which are inherent to OLED technology, becomes more critical in transparent displays. These artifacts are potentially more noticeable against varying backgrounds, requiring advanced compensation techniques and possibly new materials to mitigate long-term image persistence.
Lastly, the challenge of uniform light distribution across the entire display area is amplified in transparent AMOLEDs. Achieving consistent brightness and color across all viewing angles while maintaining transparency demands innovative pixel designs and light management strategies.
Another critical challenge lies in the power efficiency of transparent AMOLED displays. The need for increased brightness to compensate for light loss through transparency results in higher energy consumption. This issue is particularly problematic for mobile and wearable devices where battery life is a crucial factor.
Durability and lifespan present additional concerns. Transparent AMOLED displays are more susceptible to environmental factors such as UV radiation and moisture, which can accelerate degradation of organic materials. Developing robust encapsulation techniques to protect the sensitive organic layers without impacting transparency is a complex engineering task.
Manufacturing scalability poses a significant obstacle. Producing large-scale transparent AMOLED displays with consistent quality and yield rates comparable to traditional opaque displays remains challenging. The intricate processes required for transparency often result in higher defect rates and increased production costs.
Color management in transparent AMOLEDs is another area requiring innovation. Achieving accurate color reproduction is complicated by the varying backgrounds visible through the display, which can affect perceived colors. Developing adaptive color correction algorithms to compensate for these environmental variations is essential for maintaining display fidelity.
Integration of touch functionality without compromising transparency or display performance adds another layer of complexity. Traditional touch sensors can reduce transparency and affect visual quality, necessitating the development of new, highly transparent touch-sensing technologies compatible with AMOLED structures.
Addressing image retention and burn-in issues, which are inherent to OLED technology, becomes more critical in transparent displays. These artifacts are potentially more noticeable against varying backgrounds, requiring advanced compensation techniques and possibly new materials to mitigate long-term image persistence.
Lastly, the challenge of uniform light distribution across the entire display area is amplified in transparent AMOLEDs. Achieving consistent brightness and color across all viewing angles while maintaining transparency demands innovative pixel designs and light management strategies.
Current AMOLED Solutions
01 Transparent AMOLED display structure
AMOLED displays can be designed with transparent structures, allowing light to pass through the display. This is achieved by using transparent materials for electrodes and organic layers, and optimizing the arrangement of opaque components to maximize light transmission. The resulting displays can be used in applications requiring see-through capabilities, such as augmented reality devices or smart windows.- Transparent AMOLED display structure: AMOLED displays can be designed with transparent structures, allowing light to pass through the display. This is achieved by using transparent materials for electrodes and organic layers, and optimizing the arrangement of opaque components to maximize light transmission. These displays can be used in applications requiring see-through capabilities, such as augmented reality devices or smart windows.
- Pixel circuit design for transparent AMOLEDs: Specialized pixel circuits are developed for transparent AMOLED displays to maintain display performance while maximizing transparency. These circuits may include novel transistor arrangements, capacitor designs, and signal line layouts to minimize the opaque area within each pixel. The goal is to achieve high aperture ratios and uniform light transmission across the display.
- Transparent electrode materials and fabrication: Development of transparent electrode materials is crucial for AMOLED transparency. This includes the use of materials such as indium tin oxide (ITO), graphene, or metal nanowires. Advanced fabrication techniques are employed to deposit these materials with high transparency and conductivity, ensuring optimal display performance without compromising light transmission.
- Integration of transparent AMOLEDs in devices: Transparent AMOLED displays are integrated into various devices, including smartphones, wearables, and automotive applications. This integration involves addressing challenges such as power consumption, durability, and compatibility with other device components. Novel device architectures and manufacturing processes are developed to incorporate transparent displays effectively.
- Optical enhancements for transparent AMOLEDs: Various optical enhancements are implemented to improve the performance of transparent AMOLED displays. These may include anti-reflection coatings, polarizers, and light management films. Such enhancements aim to reduce glare, improve contrast, and optimize visibility in different lighting conditions while maintaining transparency.
02 Pixel circuit design for transparent AMOLEDs
Specialized pixel circuits are developed for transparent AMOLED displays to maintain display performance while maximizing transparency. These circuits may include novel transistor arrangements, capacitor designs, and signal line layouts to minimize the opaque area within each pixel. The goal is to achieve high aperture ratios while preserving the display's electrical characteristics and image quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Transparent electrode materials and fabrication
Development of transparent electrode materials is crucial for AMOLED transparency. This includes the use of materials such as indium tin oxide (ITO), graphene, or metal nanowires. Advanced fabrication techniques are employed to deposit these materials with high transparency and conductivity, balancing the trade-off between optical and electrical properties to achieve optimal display performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of transparent AMOLEDs in devices
Transparent AMOLED displays are integrated into various devices, including smartphones, wearables, and automotive applications. This integration involves addressing challenges such as power management, touch functionality, and environmental protection. Novel device architectures and packaging solutions are developed to incorporate transparent displays while maintaining overall device functionality and durability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Driving methods for transparent AMOLED displays
Specialized driving methods are developed for transparent AMOLED displays to optimize image quality and power efficiency. These methods may include compensation techniques for non-uniform light transmission, adaptive brightness control based on ambient light conditions, and algorithms to enhance contrast and visibility in various lighting environments. The driving schemes aim to maintain display performance while leveraging the unique characteristics of transparent AMOLEDs.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The AMOLED technology for next-generation transparent displays is in a rapidly evolving phase, with significant market potential and growing technological maturity. The industry is transitioning from research and development to early commercialization, driven by increasing demand for innovative display solutions. Major players like BOE Technology, TCL China Star Optoelectronics, and Innolux Corp are investing heavily in AMOLED technology, pushing the boundaries of transparency and performance. The market size is expected to expand substantially as applications in automotive, wearables, and smart home devices gain traction. While challenges remain in scaling production and reducing costs, advancements by companies such as Tianma Microelectronics and Everdisplay Optronics are accelerating the technology's readiness for mass-market adoption.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has been at the forefront of AMOLED technology for transparent displays. They have developed a 55-inch transparent AMOLED display with a transmittance of up to 38%[1]. This display utilizes advanced pixel design and driving techniques to achieve high transparency while maintaining vibrant colors and contrast. BOE's transparent AMOLED technology incorporates a unique electrode structure that allows light to pass through the display, creating a see-through effect. They have also implemented a proprietary light management system that optimizes the balance between transparency and image quality[2]. Additionally, BOE has developed flexible transparent AMOLED displays that can be curved or bent, opening up new possibilities for innovative product designs[3].
Strengths: High transmittance, advanced pixel design, flexible display capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential for higher power consumption compared to traditional displays, challenges in mass production scalability.
TCL China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: TCL CSOT has been actively developing transparent AMOLED technology for next-generation displays. They have showcased a 31-inch 4K transparent AMOLED display with a transmittance of over 50%[8]. TCL CSOT's approach focuses on optimizing the OLED material stack and employing advanced optical designs to achieve high transparency without compromising display performance. They have developed a proprietary light management system that enhances contrast and color reproduction in transparent mode. TCL CSOT has also implemented a unique electrode structure that minimizes light reflection and improves overall transparency[9]. Their technology incorporates adaptive brightness control to optimize visibility in various lighting conditions.
Strengths: Large-size transparent AMOLED capability, high resolution, advanced light management. Weaknesses: Potential for high production costs, challenges in maintaining uniform transparency across large areas.
Innovative AMOLED Patents
Array substrate, display device, and method for manufacturing array substrate
PatentActiveUS20170148862A1
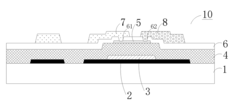
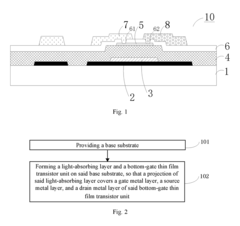
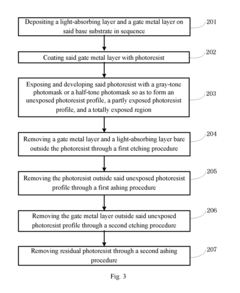
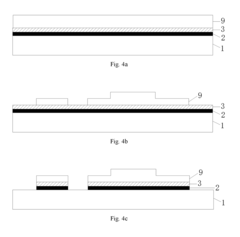
Innovation
- An array substrate with a light-absorbing layer covering the gate, source, and drain metal layers of a bottom-gate thin film transistor unit, preventing ambient light irradiation while allowing useful light to pass through.
Light-emitting diode, array substrate, and method of making the same
PatentWO2018223647A1
Innovation
- Introducing a substantially transparent protective layer between the second electrode and a transparent conductive layer to enhance device stability while maintaining transparency.
- Implementing a transparent conductive layer electrically connected to the second electrode through vias, addressing the IR drop issue in large AMOLED displays.
- Utilizing a dual-layer structure (second electrode + transparent conductive layer) to balance transparency and conductivity requirements in AMOLED displays.
Supply Chain Analysis
The supply chain for AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays in next-generation transparent displays is complex and involves multiple key players across various stages of production. At the core of this supply chain are the manufacturers of organic materials, which are essential for the light-emitting layers of AMOLED displays. Companies like Universal Display Corporation and Idemitsu Kosan are major suppliers of these critical components.
Panel manufacturers form another crucial link in the chain. Industry leaders such as Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE Technology Group are at the forefront of AMOLED panel production for transparent displays. These companies invest heavily in research and development to improve the transparency, efficiency, and durability of AMOLED panels.
The production of thin-film transistors (TFTs) is another vital aspect of the supply chain. Companies specializing in semiconductor manufacturing, like TSMC and GlobalFoundries, play a significant role in producing the high-performance, low-temperature polysilicon (LTPS) TFTs required for AMOLED displays.
Glass and substrate manufacturers are also integral to the supply chain. Corning, AGC, and Schott are among the leading suppliers of ultra-thin, flexible glass substrates that are crucial for achieving transparency in next-gen displays. These companies continually innovate to produce glass that is not only transparent but also durable and suitable for various applications.
The integration of touch sensors and other functional layers adds another dimension to the supply chain. Companies like TPK Holding and Nissha specialize in producing touch sensors and integrating them with display panels. Their expertise is crucial for creating interactive transparent displays.
Finally, the supply chain extends to equipment manufacturers who provide the specialized machinery needed for AMOLED production. Companies like Applied Materials, Canon Tokki, and Coherent offer cutting-edge deposition and patterning equipment essential for manufacturing high-quality AMOLED panels.
As the demand for transparent displays grows, the supply chain is likely to evolve, with increased focus on scalability, cost reduction, and sustainability. Collaboration between different players in the supply chain will be crucial for addressing challenges and driving innovation in this emerging field.
Panel manufacturers form another crucial link in the chain. Industry leaders such as Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE Technology Group are at the forefront of AMOLED panel production for transparent displays. These companies invest heavily in research and development to improve the transparency, efficiency, and durability of AMOLED panels.
The production of thin-film transistors (TFTs) is another vital aspect of the supply chain. Companies specializing in semiconductor manufacturing, like TSMC and GlobalFoundries, play a significant role in producing the high-performance, low-temperature polysilicon (LTPS) TFTs required for AMOLED displays.
Glass and substrate manufacturers are also integral to the supply chain. Corning, AGC, and Schott are among the leading suppliers of ultra-thin, flexible glass substrates that are crucial for achieving transparency in next-gen displays. These companies continually innovate to produce glass that is not only transparent but also durable and suitable for various applications.
The integration of touch sensors and other functional layers adds another dimension to the supply chain. Companies like TPK Holding and Nissha specialize in producing touch sensors and integrating them with display panels. Their expertise is crucial for creating interactive transparent displays.
Finally, the supply chain extends to equipment manufacturers who provide the specialized machinery needed for AMOLED production. Companies like Applied Materials, Canon Tokki, and Coherent offer cutting-edge deposition and patterning equipment essential for manufacturing high-quality AMOLED panels.
As the demand for transparent displays grows, the supply chain is likely to evolve, with increased focus on scalability, cost reduction, and sustainability. Collaboration between different players in the supply chain will be crucial for addressing challenges and driving innovation in this emerging field.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of AMOLED technology in next-generation transparent displays is a crucial consideration as this technology gains prominence. AMOLED displays offer several environmental advantages over traditional LCD screens, primarily due to their energy efficiency and reduced material usage.
AMOLED screens consume less power than LCDs, particularly when displaying darker content, as they can selectively illuminate only the necessary pixels. This energy efficiency translates to reduced electricity consumption and, consequently, lower carbon emissions associated with device usage. As transparent displays become more prevalent in various applications, such as smart windows and augmented reality devices, the energy-saving potential of AMOLED technology becomes increasingly significant.
The manufacturing process of AMOLED displays also presents environmental benefits. These displays require fewer components than LCDs, resulting in a streamlined production process that consumes less energy and resources. Additionally, the absence of a backlight in AMOLED displays eliminates the need for mercury, a toxic substance commonly used in LCD backlights, thus reducing the environmental hazards associated with display production and disposal.
However, the environmental impact of AMOLED technology is not without challenges. The production of OLED materials involves the use of rare earth elements and other precious metals, which can lead to resource depletion and environmental degradation if not managed responsibly. The extraction and processing of these materials often have significant ecological footprints, including habitat destruction and water pollution.
End-of-life considerations for AMOLED displays also present environmental concerns. While these displays are generally thinner and lighter than LCDs, potentially reducing e-waste volume, the complex nature of OLED materials can make recycling more challenging. Developing efficient recycling processes for AMOLED displays is crucial to mitigate their environmental impact and recover valuable materials.
As transparent AMOLED displays become more widespread, their potential to replace traditional signage and screens could lead to reduced paper usage and associated environmental benefits. However, this shift may also result in increased electronic waste if not managed properly. Balancing the benefits of digital displays with responsible production and disposal practices will be essential for minimizing the overall environmental impact of this technology.
In conclusion, while AMOLED technology in next-generation transparent displays offers several environmental advantages, particularly in energy efficiency and reduced material usage, it also presents challenges related to resource extraction and end-of-life management. As this technology continues to evolve, addressing these environmental concerns will be crucial for ensuring its sustainable integration into future display applications.
AMOLED screens consume less power than LCDs, particularly when displaying darker content, as they can selectively illuminate only the necessary pixels. This energy efficiency translates to reduced electricity consumption and, consequently, lower carbon emissions associated with device usage. As transparent displays become more prevalent in various applications, such as smart windows and augmented reality devices, the energy-saving potential of AMOLED technology becomes increasingly significant.
The manufacturing process of AMOLED displays also presents environmental benefits. These displays require fewer components than LCDs, resulting in a streamlined production process that consumes less energy and resources. Additionally, the absence of a backlight in AMOLED displays eliminates the need for mercury, a toxic substance commonly used in LCD backlights, thus reducing the environmental hazards associated with display production and disposal.
However, the environmental impact of AMOLED technology is not without challenges. The production of OLED materials involves the use of rare earth elements and other precious metals, which can lead to resource depletion and environmental degradation if not managed responsibly. The extraction and processing of these materials often have significant ecological footprints, including habitat destruction and water pollution.
End-of-life considerations for AMOLED displays also present environmental concerns. While these displays are generally thinner and lighter than LCDs, potentially reducing e-waste volume, the complex nature of OLED materials can make recycling more challenging. Developing efficient recycling processes for AMOLED displays is crucial to mitigate their environmental impact and recover valuable materials.
As transparent AMOLED displays become more widespread, their potential to replace traditional signage and screens could lead to reduced paper usage and associated environmental benefits. However, this shift may also result in increased electronic waste if not managed properly. Balancing the benefits of digital displays with responsible production and disposal practices will be essential for minimizing the overall environmental impact of this technology.
In conclusion, while AMOLED technology in next-generation transparent displays offers several environmental advantages, particularly in energy efficiency and reduced material usage, it also presents challenges related to resource extraction and end-of-life management. As this technology continues to evolve, addressing these environmental concerns will be crucial for ensuring its sustainable integration into future display applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!