How AMOLED complements edge-to-edge display solutions?
JUL 17, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED and Edge Display Evolution
The evolution of AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology and edge-to-edge display solutions has been a significant driver in the advancement of mobile device aesthetics and functionality. AMOLED displays have progressed from their initial introduction in the early 2000s to become a dominant force in high-end smartphones and other consumer electronics.
In the early stages, AMOLED displays were limited by manufacturing challenges and high costs. However, as production techniques improved, AMOLED panels began to offer superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD screens. This technological maturation coincided with the growing demand for larger, more immersive displays in mobile devices.
The concept of edge-to-edge displays emerged as manufacturers sought to maximize screen real estate without increasing device dimensions. Early attempts at reducing bezels were hindered by the need for physical buttons and front-facing cameras. However, the flexibility and thinness of AMOLED panels proved to be a perfect complement to this design goal.
AMOLED's ability to selectively illuminate pixels allowed for innovative solutions such as under-display fingerprint sensors and cameras, further enabling the reduction of bezels. The technology's flexibility also permitted the creation of curved and waterfall displays, pushing the boundaries of what was possible in edge-to-edge design.
As AMOLED production costs decreased and yield rates improved, the technology became more accessible to a broader range of devices. This democratization of AMOLED displays accelerated the adoption of edge-to-edge designs across various price points in the smartphone market.
The synergy between AMOLED and edge-to-edge displays has led to several key innovations. Foldable and rollable displays, made possible by AMOLED's flexible nature, have opened up new form factors and use cases for mobile devices. Additionally, the development of variable refresh rate AMOLED panels has addressed concerns about power consumption in large, high-resolution displays.
Looking forward, the co-evolution of AMOLED and edge-to-edge display solutions is expected to continue. Advancements in micro-LED technology may further enhance the benefits of AMOLED in edge-to-edge implementations, potentially offering even higher brightness, lower power consumption, and improved durability.
In the early stages, AMOLED displays were limited by manufacturing challenges and high costs. However, as production techniques improved, AMOLED panels began to offer superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD screens. This technological maturation coincided with the growing demand for larger, more immersive displays in mobile devices.
The concept of edge-to-edge displays emerged as manufacturers sought to maximize screen real estate without increasing device dimensions. Early attempts at reducing bezels were hindered by the need for physical buttons and front-facing cameras. However, the flexibility and thinness of AMOLED panels proved to be a perfect complement to this design goal.
AMOLED's ability to selectively illuminate pixels allowed for innovative solutions such as under-display fingerprint sensors and cameras, further enabling the reduction of bezels. The technology's flexibility also permitted the creation of curved and waterfall displays, pushing the boundaries of what was possible in edge-to-edge design.
As AMOLED production costs decreased and yield rates improved, the technology became more accessible to a broader range of devices. This democratization of AMOLED displays accelerated the adoption of edge-to-edge designs across various price points in the smartphone market.
The synergy between AMOLED and edge-to-edge displays has led to several key innovations. Foldable and rollable displays, made possible by AMOLED's flexible nature, have opened up new form factors and use cases for mobile devices. Additionally, the development of variable refresh rate AMOLED panels has addressed concerns about power consumption in large, high-resolution displays.
Looking forward, the co-evolution of AMOLED and edge-to-edge display solutions is expected to continue. Advancements in micro-LED technology may further enhance the benefits of AMOLED in edge-to-edge implementations, potentially offering even higher brightness, lower power consumption, and improved durability.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for edge-to-edge display solutions has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by consumer preferences for sleek, modern designs and immersive viewing experiences. AMOLED technology has emerged as a key enabler in this trend, offering several advantages that complement edge-to-edge display solutions.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have recognized the growing demand for devices with larger screens and minimal bezels. Smartphones, tablets, and laptops are increasingly adopting edge-to-edge displays to maximize screen real estate without increasing overall device dimensions. This trend is particularly evident in the premium smartphone segment, where edge-to-edge displays have become a standard feature.
AMOLED technology plays a crucial role in meeting this market demand by offering superior flexibility and thinness compared to traditional LCD displays. The ability of AMOLED panels to be curved or bent allows for innovative form factors, such as wraparound displays and foldable devices, which further enhance the edge-to-edge experience.
The automotive industry has also shown significant interest in edge-to-edge display solutions, particularly for infotainment systems and digital instrument clusters. AMOLED displays are well-suited for these applications due to their high contrast ratios, wide color gamut, and ability to produce true blacks, resulting in improved visibility and aesthetics in various lighting conditions.
Market research indicates that the global AMOLED display market is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, driven by increasing adoption in smartphones, televisions, and automotive applications. This growth is closely tied to the demand for edge-to-edge display solutions across various product categories.
The wearable technology sector, including smartwatches and fitness trackers, has also contributed to the rising demand for AMOLED-based edge-to-edge displays. These devices benefit from AMOLED's power efficiency and ability to produce vibrant colors in compact form factors, aligning with consumer preferences for stylish and functional wearables.
As consumers become more accustomed to edge-to-edge displays in their daily devices, there is a growing expectation for this feature across a wider range of products. This has led to increased research and development efforts in AMOLED technology to further improve its performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness in edge-to-edge applications.
The market demand analysis suggests that the combination of AMOLED technology and edge-to-edge display solutions will continue to drive innovation in the consumer electronics industry. Manufacturers are likely to invest heavily in these technologies to differentiate their products and meet evolving consumer expectations for immersive and visually appealing devices.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have recognized the growing demand for devices with larger screens and minimal bezels. Smartphones, tablets, and laptops are increasingly adopting edge-to-edge displays to maximize screen real estate without increasing overall device dimensions. This trend is particularly evident in the premium smartphone segment, where edge-to-edge displays have become a standard feature.
AMOLED technology plays a crucial role in meeting this market demand by offering superior flexibility and thinness compared to traditional LCD displays. The ability of AMOLED panels to be curved or bent allows for innovative form factors, such as wraparound displays and foldable devices, which further enhance the edge-to-edge experience.
The automotive industry has also shown significant interest in edge-to-edge display solutions, particularly for infotainment systems and digital instrument clusters. AMOLED displays are well-suited for these applications due to their high contrast ratios, wide color gamut, and ability to produce true blacks, resulting in improved visibility and aesthetics in various lighting conditions.
Market research indicates that the global AMOLED display market is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, driven by increasing adoption in smartphones, televisions, and automotive applications. This growth is closely tied to the demand for edge-to-edge display solutions across various product categories.
The wearable technology sector, including smartwatches and fitness trackers, has also contributed to the rising demand for AMOLED-based edge-to-edge displays. These devices benefit from AMOLED's power efficiency and ability to produce vibrant colors in compact form factors, aligning with consumer preferences for stylish and functional wearables.
As consumers become more accustomed to edge-to-edge displays in their daily devices, there is a growing expectation for this feature across a wider range of products. This has led to increased research and development efforts in AMOLED technology to further improve its performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness in edge-to-edge applications.
The market demand analysis suggests that the combination of AMOLED technology and edge-to-edge display solutions will continue to drive innovation in the consumer electronics industry. Manufacturers are likely to invest heavily in these technologies to differentiate their products and meet evolving consumer expectations for immersive and visually appealing devices.
Technical Challenges
AMOLED technology, while offering significant advantages for edge-to-edge display solutions, faces several technical challenges in its implementation. One of the primary hurdles is the integration of touch sensors directly into the AMOLED panel. Traditional capacitive touch sensors can interfere with the display's light emission, potentially compromising image quality and increasing power consumption.
Another significant challenge lies in the manufacturing process of curved or flexible AMOLED displays for edge-to-edge designs. Achieving consistent pixel density and color accuracy across curved surfaces requires advanced production techniques and quality control measures. The bending of the display also puts stress on the organic materials, potentially reducing the lifespan of the screen if not properly addressed.
Power management presents a unique set of challenges for AMOLED in edge-to-edge configurations. As each pixel emits its own light, power consumption can vary significantly based on the content displayed. Implementing efficient power management systems that can dynamically adjust brightness and power distribution across the expanded screen area is crucial for maintaining battery life without compromising visual quality.
The increased screen-to-body ratio in edge-to-edge designs also poses challenges for integrating other essential components, such as front-facing cameras and sensors. Manufacturers must develop innovative solutions, such as under-display cameras or pop-up mechanisms, which add complexity to the overall device design and potentially impact durability.
Color accuracy and uniformity across the entire display surface remain ongoing challenges, particularly in edge-to-edge implementations. The organic nature of AMOLED materials can lead to color shifts over time, and maintaining consistent color reproduction from the center to the edges of the display requires sophisticated calibration techniques and compensation algorithms.
Durability is another critical concern, especially for curved or flexible AMOLED displays used in edge-to-edge designs. The organic materials are susceptible to degradation from exposure to oxygen and moisture, necessitating advanced encapsulation technologies to protect the display and ensure longevity.
Lastly, the cost of production for high-quality AMOLED panels suitable for edge-to-edge applications remains a significant challenge. The complex manufacturing processes, coupled with the need for specialized materials and equipment, contribute to higher production costs compared to traditional LCD technologies. Balancing these costs with market demands for affordable devices presents an ongoing challenge for manufacturers and may impact the widespread adoption of AMOLED in edge-to-edge display solutions across all market segments.
Another significant challenge lies in the manufacturing process of curved or flexible AMOLED displays for edge-to-edge designs. Achieving consistent pixel density and color accuracy across curved surfaces requires advanced production techniques and quality control measures. The bending of the display also puts stress on the organic materials, potentially reducing the lifespan of the screen if not properly addressed.
Power management presents a unique set of challenges for AMOLED in edge-to-edge configurations. As each pixel emits its own light, power consumption can vary significantly based on the content displayed. Implementing efficient power management systems that can dynamically adjust brightness and power distribution across the expanded screen area is crucial for maintaining battery life without compromising visual quality.
The increased screen-to-body ratio in edge-to-edge designs also poses challenges for integrating other essential components, such as front-facing cameras and sensors. Manufacturers must develop innovative solutions, such as under-display cameras or pop-up mechanisms, which add complexity to the overall device design and potentially impact durability.
Color accuracy and uniformity across the entire display surface remain ongoing challenges, particularly in edge-to-edge implementations. The organic nature of AMOLED materials can lead to color shifts over time, and maintaining consistent color reproduction from the center to the edges of the display requires sophisticated calibration techniques and compensation algorithms.
Durability is another critical concern, especially for curved or flexible AMOLED displays used in edge-to-edge designs. The organic materials are susceptible to degradation from exposure to oxygen and moisture, necessitating advanced encapsulation technologies to protect the display and ensure longevity.
Lastly, the cost of production for high-quality AMOLED panels suitable for edge-to-edge applications remains a significant challenge. The complex manufacturing processes, coupled with the need for specialized materials and equipment, contribute to higher production costs compared to traditional LCD technologies. Balancing these costs with market demands for affordable devices presents an ongoing challenge for manufacturers and may impact the widespread adoption of AMOLED in edge-to-edge display solutions across all market segments.
Current Edge Display Solutions
01 Edge-to-edge AMOLED display design
AMOLED displays are designed to extend to the edges of the device, maximizing screen real estate and providing a seamless, immersive viewing experience. This design eliminates bezels and creates a more visually appealing device with an increased screen-to-body ratio.- Edge-to-edge AMOLED display design: AMOLED displays are designed to cover the entire front surface of devices, maximizing screen-to-body ratio. This edge-to-edge design eliminates bezels and provides an immersive viewing experience. The display can be curved or flat, extending to the edges of the device.
- Flexible AMOLED display technology: Flexible AMOLED displays allow for curved or bendable screens, enabling innovative form factors and edge-to-edge designs. These displays can conform to various shapes and contours, enhancing the overall aesthetics and functionality of devices.
- Under-display sensors and components: To achieve a true edge-to-edge display, various sensors and components are integrated beneath the AMOLED screen. This includes under-display cameras, fingerprint sensors, and other essential elements, allowing for a seamless and uninterrupted display surface.
- Display driver and control circuitry: Advanced display driver ICs and control circuitry are developed to manage the edge-to-edge AMOLED display effectively. These components ensure proper signal distribution, power management, and image quality across the entire screen, including the curved or edge areas.
- Touch sensitivity and palm rejection: Edge-to-edge AMOLED displays incorporate enhanced touch sensitivity and palm rejection technologies. These features allow for accurate touch input across the entire screen surface while minimizing accidental touches on the edges, improving user experience and device usability.
02 Flexible AMOLED display technology
Flexible AMOLED displays allow for curved or bendable screens, enabling manufacturers to create devices with unique form factors and edge-to-edge displays that wrap around the sides of the device. This technology enhances both aesthetics and functionality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Under-display sensors and components
To achieve a true edge-to-edge display, various sensors and components are integrated beneath the AMOLED screen. This includes under-display cameras, fingerprint sensors, and proximity sensors, allowing for a seamless front surface without interruptions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Display driver and power management
Specialized display drivers and power management systems are developed to efficiently control and power edge-to-edge AMOLED displays. These systems optimize performance, reduce power consumption, and ensure uniform brightness across the entire screen.Expand Specific Solutions05 Touch sensitivity and palm rejection
Edge-to-edge AMOLED displays incorporate advanced touch sensitivity and palm rejection technologies to prevent accidental inputs along the edges of the screen. This ensures accurate touch response while maintaining the seamless edge-to-edge design.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The AMOLED technology for edge-to-edge display solutions is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and advancing technical maturity. Major players like Samsung Display, BOE Technology, and Tianma Microelectronics are driving innovation in this field. The market is characterized by intense competition among established manufacturers and emerging companies, particularly from China. As AMOLED technology continues to evolve, we see a trend towards thinner, more flexible displays with improved energy efficiency and color accuracy. The integration of AMOLED with edge-to-edge designs is becoming increasingly important for smartphones, wearables, and other consumer electronics, indicating a promising future for this technology in the display industry.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed flexible AMOLED displays that complement edge-to-edge solutions. Their technology includes on-cell touch AMOLED displays, reducing the overall thickness of the panel[4]. BOE's AMOLED screens feature high color gamut (100% DCI-P3) and contrast ratios exceeding 100,000:1, enhancing visual quality on edge-to-edge displays[5]. They've also introduced 1Hz-120Hz variable refresh rate technology for AMOLED, optimizing power consumption in edge-to-edge implementations[6]. BOE's recent advancements include under-display camera technology, further enabling full-screen edge-to-edge designs.
Strengths: Rapid advancement in AMOLED technology, competitive pricing. Weaknesses: Still catching up to Samsung in some advanced features, less experience with foldable displays.
TCL China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: TCL CSOT has made significant strides in AMOLED technology for edge-to-edge displays. They've developed a 6.67-inch AMOLED display with a 120Hz refresh rate and 1080x2400 resolution, suitable for edge-to-edge smartphone designs[7]. Their AMOLED panels feature in-cell touch technology, reducing thickness and enabling sleeker edge-to-edge form factors. TCL CSOT has also introduced inkjet-printed AMOLED displays, potentially lowering production costs for edge-to-edge screens[8]. Their recent focus includes developing foldable and rollable AMOLED displays to expand edge-to-edge possibilities.
Strengths: Innovative printing techniques, cost-effective production. Weaknesses: Less market share compared to leaders, still developing some cutting-edge features.
AMOLED Innovations
Organic light emitting display
PatentInactiveEP3098804A3
Innovation
- The proposed solution involves a pixel structure with a driving transistor, multiple transistors, and a capacitor to control the flow of current and compensate for threshold voltage changes, using an initial voltage lower than the low-level driving voltage to minimize unnecessary light emission and leakage current, and ensuring a sufficient sampling period for accurate compensation.
Active matrix organic light emitting diode pixel
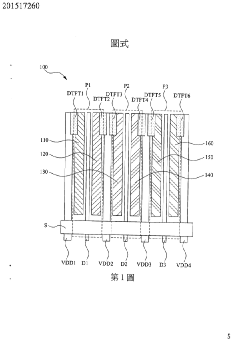
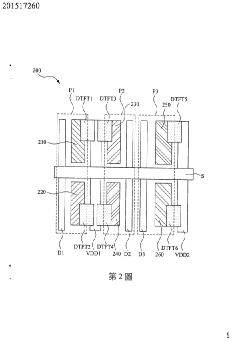
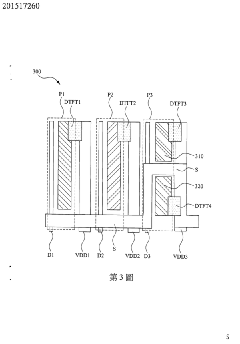
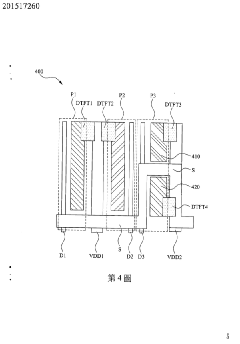
PatentInactiveTW201517260A
Innovation
- Dividing at least one sub-pixel into two secondary pixels with different organic light emitting materials, enabling emission of different lights.
- Improving display ability by mixing lights emitted from secondary pixels within a single sub-pixel.
- Enhancing AMOLED display performance through innovative pixel structure design.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing processes for AMOLED displays that complement edge-to-edge solutions involve several sophisticated steps. The process begins with the preparation of a glass substrate, which is meticulously cleaned and coated with a thin film transistor (TFT) array. This array serves as the foundation for controlling individual pixels.
Next, the organic light-emitting materials are deposited onto the TFT array. This is typically done through a process called vacuum thermal evaporation, where organic molecules are heated and evaporated in a vacuum chamber, allowing them to condense on the substrate in precise patterns. For edge-to-edge displays, this step requires extreme precision to ensure uniform deposition up to the very edges of the panel.
Following the organic layer deposition, a cathode layer is applied. This is often done using a sputtering technique, which allows for a thin, even layer of metal to be deposited across the entire surface. To achieve the edge-to-edge effect, special masking techniques are employed to ensure the cathode extends to the panel's edges without compromising the display's integrity.
Encapsulation is a critical step in AMOLED manufacturing, especially for edge-to-edge displays. Advanced thin-film encapsulation (TFE) technologies are used to protect the organic materials from moisture and oxygen. This process involves depositing alternating layers of inorganic and organic materials, creating a barrier that extends to the edges of the display.
To accommodate the edge-to-edge design, manufacturers have developed innovative techniques for integrating touch sensors. In-cell or on-cell touch technologies are often employed, where touch sensors are embedded within the display layers rather than added as a separate component on top. This approach maintains the sleek profile of the edge-to-edge display while ensuring touch functionality extends to the very edges.
The final stages of manufacturing involve attaching flexible printed circuits (FPCs) and driver ICs. For edge-to-edge displays, these components are carefully positioned to minimize bezel size. Advanced bonding techniques, such as chip-on-glass (COG) or chip-on-film (COF), are used to attach these components with minimal impact on the display's edge-to-edge aesthetics.
Throughout the manufacturing process, stringent quality control measures are implemented. These include high-resolution optical inspections and electrical tests to ensure pixel uniformity, color accuracy, and touch responsiveness, particularly at the edges of the display where defects could be more noticeable in an edge-to-edge design.
Next, the organic light-emitting materials are deposited onto the TFT array. This is typically done through a process called vacuum thermal evaporation, where organic molecules are heated and evaporated in a vacuum chamber, allowing them to condense on the substrate in precise patterns. For edge-to-edge displays, this step requires extreme precision to ensure uniform deposition up to the very edges of the panel.
Following the organic layer deposition, a cathode layer is applied. This is often done using a sputtering technique, which allows for a thin, even layer of metal to be deposited across the entire surface. To achieve the edge-to-edge effect, special masking techniques are employed to ensure the cathode extends to the panel's edges without compromising the display's integrity.
Encapsulation is a critical step in AMOLED manufacturing, especially for edge-to-edge displays. Advanced thin-film encapsulation (TFE) technologies are used to protect the organic materials from moisture and oxygen. This process involves depositing alternating layers of inorganic and organic materials, creating a barrier that extends to the edges of the display.
To accommodate the edge-to-edge design, manufacturers have developed innovative techniques for integrating touch sensors. In-cell or on-cell touch technologies are often employed, where touch sensors are embedded within the display layers rather than added as a separate component on top. This approach maintains the sleek profile of the edge-to-edge display while ensuring touch functionality extends to the very edges.
The final stages of manufacturing involve attaching flexible printed circuits (FPCs) and driver ICs. For edge-to-edge displays, these components are carefully positioned to minimize bezel size. Advanced bonding techniques, such as chip-on-glass (COG) or chip-on-film (COF), are used to attach these components with minimal impact on the display's edge-to-edge aesthetics.
Throughout the manufacturing process, stringent quality control measures are implemented. These include high-resolution optical inspections and electrical tests to ensure pixel uniformity, color accuracy, and touch responsiveness, particularly at the edges of the display where defects could be more noticeable in an edge-to-edge design.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of AMOLED technology in edge-to-edge display solutions is a crucial consideration in the context of sustainable electronics manufacturing. AMOLED displays offer several advantages that contribute to reduced environmental footprint compared to traditional LCD technologies. Firstly, AMOLED panels are more energy-efficient, particularly when displaying darker content, as they only illuminate the necessary pixels. This energy efficiency translates to lower power consumption in devices, potentially extending battery life and reducing overall energy demand.
The manufacturing process of AMOLED displays also presents environmental benefits. These displays require fewer components and layers compared to LCDs, potentially reducing material usage and simplifying the production process. Additionally, AMOLED panels are typically thinner and lighter, which can lead to a decrease in transportation-related emissions when shipping finished products.
However, the environmental impact of AMOLED technology is not without challenges. The production of AMOLED displays involves the use of rare earth elements and other precious metals, which raises concerns about resource depletion and the environmental consequences of mining these materials. The disposal and recycling of AMOLED displays also present unique challenges due to the organic compounds used in their construction.
When considering edge-to-edge display solutions, AMOLED technology enables manufacturers to create devices with minimal bezels, potentially reducing the overall size and material requirements of devices. This design approach can lead to more compact and resource-efficient products, further contributing to environmental sustainability.
The longevity of AMOLED displays is another factor to consider. While these displays can suffer from burn-in over time, advancements in technology have improved their lifespan. Longer-lasting displays contribute to reduced electronic waste, as devices may need replacement less frequently.
As the technology continues to evolve, researchers and manufacturers are exploring ways to make AMOLED production more environmentally friendly. This includes developing more efficient manufacturing processes, investigating alternative materials that are more abundant and less harmful to extract, and improving recycling techniques for end-of-life displays.
In conclusion, while AMOLED technology in edge-to-edge display solutions offers several environmental benefits, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and potential material reduction, it also presents challenges that need to be addressed to ensure a truly sustainable approach to display technology. The ongoing research and development in this field are crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of these advanced display solutions.
The manufacturing process of AMOLED displays also presents environmental benefits. These displays require fewer components and layers compared to LCDs, potentially reducing material usage and simplifying the production process. Additionally, AMOLED panels are typically thinner and lighter, which can lead to a decrease in transportation-related emissions when shipping finished products.
However, the environmental impact of AMOLED technology is not without challenges. The production of AMOLED displays involves the use of rare earth elements and other precious metals, which raises concerns about resource depletion and the environmental consequences of mining these materials. The disposal and recycling of AMOLED displays also present unique challenges due to the organic compounds used in their construction.
When considering edge-to-edge display solutions, AMOLED technology enables manufacturers to create devices with minimal bezels, potentially reducing the overall size and material requirements of devices. This design approach can lead to more compact and resource-efficient products, further contributing to environmental sustainability.
The longevity of AMOLED displays is another factor to consider. While these displays can suffer from burn-in over time, advancements in technology have improved their lifespan. Longer-lasting displays contribute to reduced electronic waste, as devices may need replacement less frequently.
As the technology continues to evolve, researchers and manufacturers are exploring ways to make AMOLED production more environmentally friendly. This includes developing more efficient manufacturing processes, investigating alternative materials that are more abundant and less harmful to extract, and improving recycling techniques for end-of-life displays.
In conclusion, while AMOLED technology in edge-to-edge display solutions offers several environmental benefits, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and potential material reduction, it also presents challenges that need to be addressed to ensure a truly sustainable approach to display technology. The ongoing research and development in this field are crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of these advanced display solutions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!