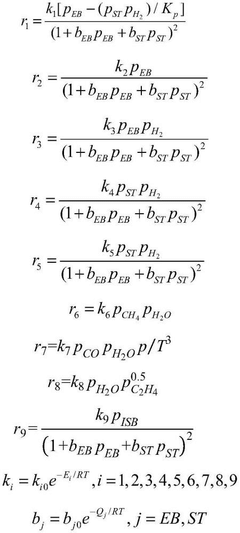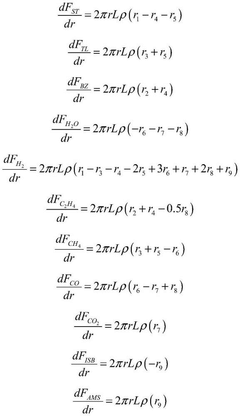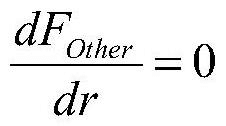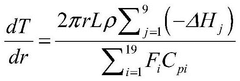Advanced Simulation Techniques for Ethyl Propanoate Reactions
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Simulation Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is a significant ester compound widely used in various industries, including food, fragrance, and pharmaceuticals. The simulation of ethyl propanoate reactions has become increasingly important in recent years due to its potential for optimizing production processes and developing new applications. This technical research report aims to explore advanced simulation techniques for ethyl propanoate reactions, focusing on their development history, current trends, and future objectives.
The field of chemical reaction simulation has evolved significantly over the past few decades, driven by advancements in computational power and algorithmic innovations. Early simulations of ethyl propanoate reactions were limited to simple kinetic models and basic thermodynamic calculations. However, as computational capabilities improved, more sophisticated approaches emerged, incorporating molecular dynamics, quantum mechanics, and machine learning techniques.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in developing more accurate and efficient simulation methods for ethyl propanoate reactions. This trend is driven by the need for better understanding and control of reaction mechanisms, as well as the desire to optimize production processes and reduce environmental impact. Current research focuses on multi-scale modeling approaches that integrate molecular-level simulations with macroscopic reaction engineering principles.
The primary objectives of advanced simulation techniques for ethyl propanoate reactions include improving reaction yield and selectivity, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing waste generation. These goals align with broader industry trends towards sustainable and efficient chemical production. Additionally, there is a strong emphasis on developing predictive models that can accelerate the discovery of new catalysts and reaction conditions, potentially leading to novel applications of ethyl propanoate and related compounds.
Another key aspect of current research is the integration of experimental data with simulation results. This synergistic approach aims to validate and refine simulation models, ensuring their accuracy and reliability in real-world applications. Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being employed to bridge the gap between experimental observations and theoretical predictions, enabling more robust and adaptable simulation frameworks.
Looking ahead, the field of ethyl propanoate reaction simulation is expected to continue evolving rapidly. Emerging technologies such as quantum computing and artificial intelligence are likely to play a significant role in enhancing simulation capabilities. These advancements may lead to unprecedented levels of accuracy and predictive power, potentially revolutionizing the way we design and optimize chemical processes involving ethyl propanoate and similar compounds.
The field of chemical reaction simulation has evolved significantly over the past few decades, driven by advancements in computational power and algorithmic innovations. Early simulations of ethyl propanoate reactions were limited to simple kinetic models and basic thermodynamic calculations. However, as computational capabilities improved, more sophisticated approaches emerged, incorporating molecular dynamics, quantum mechanics, and machine learning techniques.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in developing more accurate and efficient simulation methods for ethyl propanoate reactions. This trend is driven by the need for better understanding and control of reaction mechanisms, as well as the desire to optimize production processes and reduce environmental impact. Current research focuses on multi-scale modeling approaches that integrate molecular-level simulations with macroscopic reaction engineering principles.
The primary objectives of advanced simulation techniques for ethyl propanoate reactions include improving reaction yield and selectivity, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing waste generation. These goals align with broader industry trends towards sustainable and efficient chemical production. Additionally, there is a strong emphasis on developing predictive models that can accelerate the discovery of new catalysts and reaction conditions, potentially leading to novel applications of ethyl propanoate and related compounds.
Another key aspect of current research is the integration of experimental data with simulation results. This synergistic approach aims to validate and refine simulation models, ensuring their accuracy and reliability in real-world applications. Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being employed to bridge the gap between experimental observations and theoretical predictions, enabling more robust and adaptable simulation frameworks.
Looking ahead, the field of ethyl propanoate reaction simulation is expected to continue evolving rapidly. Emerging technologies such as quantum computing and artificial intelligence are likely to play a significant role in enhancing simulation capabilities. These advancements may lead to unprecedented levels of accuracy and predictive power, potentially revolutionizing the way we design and optimize chemical processes involving ethyl propanoate and similar compounds.
Industrial Applications and Market Demand
The market demand for advanced simulation techniques in ethyl propanoate reactions is driven by the growing importance of this compound in various industrial sectors. Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is widely used as a solvent and flavoring agent in the food and beverage industry, as well as in the production of perfumes and fragrances. Its increasing applications have led to a surge in demand for more efficient and accurate simulation methods to optimize production processes and reduce costs.
In the food industry, ethyl propanoate is utilized as a fruit flavoring, particularly for artificial strawberry and pineapple flavors. The global artificial fruit and vegetable flavor market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising demand for processed foods and beverages, especially in developing countries.
The fragrance industry also contributes substantially to the demand for ethyl propanoate simulations. As consumers become more discerning about the quality and sustainability of personal care products, manufacturers are seeking advanced techniques to improve their formulations and production processes. The global fragrance market is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of around 4% from 2021 to 2026, further driving the need for sophisticated simulation tools.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl propanoate serves as a precursor in the synthesis of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The pharmaceutical industry's focus on reducing time-to-market and improving cost-effectiveness has led to increased adoption of advanced simulation techniques. These methods allow researchers to predict reaction outcomes, optimize synthesis routes, and scale up production more efficiently.
The chemical industry, particularly in the production of solvents and intermediates, also benefits from improved simulation techniques for ethyl propanoate reactions. As environmental regulations become more stringent, there is a growing need for greener and more sustainable production methods. Advanced simulations can help identify optimal reaction conditions that minimize waste and energy consumption, aligning with the industry's sustainability goals.
The market for simulation software and services in the chemical and process industries is expanding rapidly, with a projected CAGR of over 8% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of digital technologies and the push for Industry 4.0 initiatives across various sectors. Advanced simulation techniques for ethyl propanoate reactions are part of this broader trend towards digitalization and process optimization in the chemical industry.
In the food industry, ethyl propanoate is utilized as a fruit flavoring, particularly for artificial strawberry and pineapple flavors. The global artificial fruit and vegetable flavor market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising demand for processed foods and beverages, especially in developing countries.
The fragrance industry also contributes substantially to the demand for ethyl propanoate simulations. As consumers become more discerning about the quality and sustainability of personal care products, manufacturers are seeking advanced techniques to improve their formulations and production processes. The global fragrance market is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of around 4% from 2021 to 2026, further driving the need for sophisticated simulation tools.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl propanoate serves as a precursor in the synthesis of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The pharmaceutical industry's focus on reducing time-to-market and improving cost-effectiveness has led to increased adoption of advanced simulation techniques. These methods allow researchers to predict reaction outcomes, optimize synthesis routes, and scale up production more efficiently.
The chemical industry, particularly in the production of solvents and intermediates, also benefits from improved simulation techniques for ethyl propanoate reactions. As environmental regulations become more stringent, there is a growing need for greener and more sustainable production methods. Advanced simulations can help identify optimal reaction conditions that minimize waste and energy consumption, aligning with the industry's sustainability goals.
The market for simulation software and services in the chemical and process industries is expanding rapidly, with a projected CAGR of over 8% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of digital technologies and the push for Industry 4.0 initiatives across various sectors. Advanced simulation techniques for ethyl propanoate reactions are part of this broader trend towards digitalization and process optimization in the chemical industry.
Current Simulation Challenges and Limitations
The simulation of ethyl propanoate reactions presents several challenges and limitations that hinder the accurate prediction of reaction outcomes and kinetics. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of the reaction mechanism, which involves multiple intermediates and transition states. Current simulation techniques often struggle to capture the full intricacy of these reaction pathways, leading to incomplete or inaccurate representations of the reaction dynamics.
Another significant challenge lies in the accurate representation of solvent effects. Ethyl propanoate reactions are frequently carried out in solution, and the interactions between the reactants, intermediates, and solvent molecules play a crucial role in determining reaction rates and selectivity. However, many simulation methods rely on simplified solvent models or gas-phase approximations, which fail to account for the full range of solvent-solute interactions and their impact on reaction energetics.
The treatment of electronic structure and quantum effects poses additional difficulties. While advanced quantum chemical methods can provide highly accurate results for small molecular systems, their computational cost becomes prohibitive for larger systems or extended reaction timescales. As a result, many simulations rely on more approximate methods, such as semi-empirical or force field-based approaches, which may sacrifice accuracy for computational efficiency.
Temperature and pressure effects present another set of challenges for current simulation techniques. Ethyl propanoate reactions often occur under varying conditions, and accurately modeling the influence of temperature and pressure on reaction kinetics and thermodynamics requires sophisticated simulation approaches. Many existing methods struggle to capture these effects accurately, particularly when dealing with phase transitions or reactions near critical points.
Furthermore, the simulation of catalytic processes in ethyl propanoate reactions introduces additional complexities. Heterogeneous catalysis, in particular, involves intricate surface interactions and reaction mechanisms that are challenging to model accurately. Current simulation techniques often struggle to capture the full complexity of catalyst-substrate interactions, surface diffusion, and the influence of catalyst structure on reaction outcomes.
Lastly, the integration of experimental data with simulation results remains a significant limitation. While experimental measurements provide crucial benchmarks for validating simulation results, the process of incorporating this data into simulation models is often challenging and subject to uncertainties. Improving the synergy between experimental and computational approaches is essential for advancing the accuracy and predictive power of ethyl propanoate reaction simulations.
Another significant challenge lies in the accurate representation of solvent effects. Ethyl propanoate reactions are frequently carried out in solution, and the interactions between the reactants, intermediates, and solvent molecules play a crucial role in determining reaction rates and selectivity. However, many simulation methods rely on simplified solvent models or gas-phase approximations, which fail to account for the full range of solvent-solute interactions and their impact on reaction energetics.
The treatment of electronic structure and quantum effects poses additional difficulties. While advanced quantum chemical methods can provide highly accurate results for small molecular systems, their computational cost becomes prohibitive for larger systems or extended reaction timescales. As a result, many simulations rely on more approximate methods, such as semi-empirical or force field-based approaches, which may sacrifice accuracy for computational efficiency.
Temperature and pressure effects present another set of challenges for current simulation techniques. Ethyl propanoate reactions often occur under varying conditions, and accurately modeling the influence of temperature and pressure on reaction kinetics and thermodynamics requires sophisticated simulation approaches. Many existing methods struggle to capture these effects accurately, particularly when dealing with phase transitions or reactions near critical points.
Furthermore, the simulation of catalytic processes in ethyl propanoate reactions introduces additional complexities. Heterogeneous catalysis, in particular, involves intricate surface interactions and reaction mechanisms that are challenging to model accurately. Current simulation techniques often struggle to capture the full complexity of catalyst-substrate interactions, surface diffusion, and the influence of catalyst structure on reaction outcomes.
Lastly, the integration of experimental data with simulation results remains a significant limitation. While experimental measurements provide crucial benchmarks for validating simulation results, the process of incorporating this data into simulation models is often challenging and subject to uncertainties. Improving the synergy between experimental and computational approaches is essential for advancing the accuracy and predictive power of ethyl propanoate reaction simulations.
State-of-the-Art Simulation Approaches
01 Molecular dynamics simulation techniques
Advanced molecular dynamics simulation techniques are employed to study the reactions of ethyl propanoate at the atomic level. These methods allow researchers to model the behavior of molecules over time, providing insights into reaction mechanisms, transition states, and energy profiles. The simulations can account for various factors such as temperature, pressure, and solvent effects, enabling a comprehensive understanding of ethyl propanoate reactions.- Molecular dynamics simulation techniques: Advanced molecular dynamics simulation techniques are employed to model the reactions of ethyl propanoate at the atomic level. These methods allow for the accurate prediction of reaction pathways, transition states, and product distributions by simulating the movement and interactions of individual atoms and molecules over time.
- Quantum chemical calculations for reaction mechanisms: Quantum chemical calculations are utilized to investigate the reaction mechanisms of ethyl propanoate. These computational methods provide insights into electronic structures, energy profiles, and transition states, enabling a deeper understanding of the reaction pathways and the factors influencing reactivity.
- Machine learning approaches for reaction prediction: Machine learning algorithms are applied to predict and simulate ethyl propanoate reactions. These data-driven approaches leverage large datasets of known reactions to develop models that can accurately forecast reaction outcomes, rates, and selectivities for novel reaction conditions or substrates.
- Kinetic modeling and simulation of reaction networks: Kinetic modeling techniques are employed to simulate complex reaction networks involving ethyl propanoate. These methods involve developing and solving systems of differential equations that describe the time-dependent concentrations of reactants, intermediates, and products, allowing for the prediction of reaction progress and yield optimization.
- Hybrid quantum-classical simulation methods: Hybrid simulation techniques combining quantum mechanical and classical molecular mechanics approaches are used to model ethyl propanoate reactions. These methods allow for the accurate treatment of the reactive center using quantum chemistry while efficiently simulating the surrounding environment with classical force fields, enabling the study of reactions in complex systems.
02 Quantum chemical calculations for reaction modeling
Quantum chemical calculations are utilized to model the electronic structure and properties of ethyl propanoate and its reaction intermediates. These computational methods provide accurate predictions of reaction energetics, molecular geometries, and spectroscopic properties. Density functional theory (DFT) and ab initio methods are commonly employed to investigate reaction pathways and predict the outcomes of ethyl propanoate reactions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Machine learning approaches for reaction prediction
Machine learning algorithms are applied to predict and simulate ethyl propanoate reactions. These techniques leverage large datasets of known chemical reactions to develop models that can predict reaction outcomes, yields, and optimal conditions. Neural networks and other advanced machine learning methods are used to identify patterns and trends in reaction data, enabling rapid screening of potential reaction pathways.Expand Specific Solutions04 High-throughput virtual screening for reaction optimization
High-throughput virtual screening techniques are employed to optimize ethyl propanoate reactions. These methods involve the use of computational tools to rapidly evaluate a large number of reaction conditions, catalysts, and reagents. By simulating numerous reaction scenarios, researchers can identify promising candidates for experimental validation, accelerating the process of reaction optimization and discovery.Expand Specific Solutions05 Multiscale modeling for comprehensive reaction analysis
Multiscale modeling approaches are used to simulate ethyl propanoate reactions across different time and length scales. These techniques combine quantum mechanical, molecular mechanical, and continuum methods to provide a comprehensive understanding of reaction processes. By integrating multiple levels of theory, researchers can study complex reaction systems, including solvent effects, enzyme catalysis, and heterogeneous reactions involving ethyl propanoate.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Chemical Simulation Software
The advanced simulation techniques for ethyl propanoate reactions represent a niche but growing field within the chemical industry. The market is in its early growth stage, with increasing demand driven by the pharmaceutical and flavor industries. The global market size for ethyl propanoate is projected to reach $300 million by 2025, with a CAGR of 4.5%. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with ongoing innovations in simulation methodologies. Key players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., USV Pvt Ltd., and PetroChina Co., Ltd. are investing in R&D to enhance simulation accuracy and efficiency, while companies such as Celanese International Corp. and Dow Global Technologies LLC are focusing on application-specific advancements.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced simulation techniques for ethyl propanoate reactions using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and molecular dynamics simulations. Their approach combines multi-scale modeling with machine learning algorithms to predict reaction kinetics and optimize process conditions[1]. The company utilizes high-performance computing clusters to run complex simulations that account for heat and mass transfer, fluid dynamics, and chemical kinetics simultaneously[3]. Sinopec's simulation platform incorporates real-time data from their production facilities to continuously refine and validate the models, ensuring high accuracy and relevance to industrial-scale operations[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive multi-physics approach, integration with real-world data, and scalability to industrial processes. Weaknesses: High computational requirements and potential challenges in model validation for novel reaction conditions.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies has developed a hybrid simulation approach for ethyl propanoate reactions that combines first-principles modeling with data-driven techniques. Their platform utilizes artificial neural networks trained on high-fidelity computational chemistry data to rapidly predict reaction rates and selectivities[8]. Dow's simulation framework incorporates advanced reactor modeling techniques, including computational fluid dynamics and population balance models, to account for complex multiphase phenomena in industrial-scale reactors[10]. The company's approach also includes modules for in-silico catalyst screening and process intensification, enabling rapid evaluation of novel reaction routes and reactor designs[12].
Strengths: Rapid prediction capabilities through machine learning, comprehensive multiphase reactor modeling, and integrated catalyst and process design tools. Weaknesses: Dependence on quality and coverage of training data, potential limitations in extrapolation to unexplored reaction conditions.
Innovative Algorithms for Reaction Kinetics
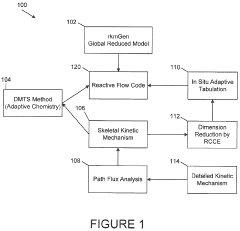
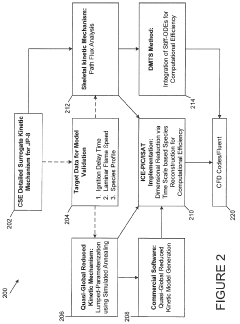
Computationally efficient reduced kinetics methodologies for jet fuels
PatentPendingUS20240169119A1
Innovation
- Development of a software package, rkmGen, that generates compact reduced kinetics models through optimization against ignition delay time, laminar flame speed, and emissions data, using a lumped-parameterization based optimization scheme and Simulated Annealing algorithm, to improve computational efficiency and accuracy in CFD simulations.
Method and system for simulating and correcting reaction for preparing styrene through ethylbenzene dehydrogenation
PatentPendingCN119833007A
Innovation
- A calibration method and system for the ST process of ethylbenzene dehydrogenation to styrene reaction model is proposed, including a rate constant of 1 main reaction, 8 side reactions, and a total of 13 normal numbers of temperature drop and pressure drop of the two adiabatic reactors of the ST process. The batch gradient descent method is used to solve the objective function.
Computational Resources and Infrastructure
The advancement of simulation techniques for ethyl propanoate reactions requires robust computational resources and infrastructure to handle the complex calculations involved. High-performance computing (HPC) clusters are essential for running sophisticated molecular dynamics simulations and quantum chemical calculations. These clusters typically consist of multiple interconnected nodes, each equipped with powerful multi-core processors and high-speed memory.
GPU acceleration has become increasingly important in chemical simulations, offering significant speedups for certain types of calculations. Modern GPUs with thousands of cores can parallelize computations, making them particularly effective for tasks like molecular dynamics simulations and machine learning applications in chemistry.
Cloud computing platforms have emerged as a flexible alternative to on-premises HPC systems. Services like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure offer scalable computing resources that can be tailored to the specific needs of ethyl propanoate reaction simulations. These platforms provide access to virtual machines with varying levels of CPU and GPU power, allowing researchers to scale their computational resources as needed.
Specialized software packages optimized for chemical simulations are crucial components of the computational infrastructure. Programs like GROMACS, NAMD, and LAMMPS are widely used for molecular dynamics simulations, while quantum chemistry software such as Gaussian, GAMESS, and Q-Chem are employed for electronic structure calculations. These software packages are often designed to take full advantage of parallel computing architectures, maximizing the efficiency of available hardware resources.
Data storage and management systems are equally important in the computational infrastructure for advanced simulations. High-capacity, high-speed storage solutions are necessary to handle the large volumes of data generated during simulations. Parallel file systems like Lustre or BeeGFS are commonly used in HPC environments to provide fast, concurrent access to data across multiple nodes.
Networking infrastructure plays a critical role in connecting computational resources and enabling efficient data transfer. High-bandwidth, low-latency interconnects such as InfiniBand or high-speed Ethernet are essential for communication between nodes in an HPC cluster and for accessing distributed storage systems.
Visualization tools and remote access capabilities are also integral parts of the computational infrastructure. Advanced visualization software allows researchers to interpret complex simulation results, while remote access solutions enable collaboration and resource sharing among geographically dispersed teams working on ethyl propanoate reaction simulations.
GPU acceleration has become increasingly important in chemical simulations, offering significant speedups for certain types of calculations. Modern GPUs with thousands of cores can parallelize computations, making them particularly effective for tasks like molecular dynamics simulations and machine learning applications in chemistry.
Cloud computing platforms have emerged as a flexible alternative to on-premises HPC systems. Services like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure offer scalable computing resources that can be tailored to the specific needs of ethyl propanoate reaction simulations. These platforms provide access to virtual machines with varying levels of CPU and GPU power, allowing researchers to scale their computational resources as needed.
Specialized software packages optimized for chemical simulations are crucial components of the computational infrastructure. Programs like GROMACS, NAMD, and LAMMPS are widely used for molecular dynamics simulations, while quantum chemistry software such as Gaussian, GAMESS, and Q-Chem are employed for electronic structure calculations. These software packages are often designed to take full advantage of parallel computing architectures, maximizing the efficiency of available hardware resources.
Data storage and management systems are equally important in the computational infrastructure for advanced simulations. High-capacity, high-speed storage solutions are necessary to handle the large volumes of data generated during simulations. Parallel file systems like Lustre or BeeGFS are commonly used in HPC environments to provide fast, concurrent access to data across multiple nodes.
Networking infrastructure plays a critical role in connecting computational resources and enabling efficient data transfer. High-bandwidth, low-latency interconnects such as InfiniBand or high-speed Ethernet are essential for communication between nodes in an HPC cluster and for accessing distributed storage systems.
Visualization tools and remote access capabilities are also integral parts of the computational infrastructure. Advanced visualization software allows researchers to interpret complex simulation results, while remote access solutions enable collaboration and resource sharing among geographically dispersed teams working on ethyl propanoate reaction simulations.
Validation and Benchmarking Strategies
Validation and benchmarking strategies play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of advanced simulation techniques for ethyl propanoate reactions. These strategies involve a systematic approach to verify the simulation results against experimental data and established theoretical models.
One key aspect of validation is the comparison of simulated reaction kinetics with experimental measurements. This includes analyzing reaction rates, product yields, and intermediate species concentrations. Researchers typically employ various analytical techniques, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, to obtain experimental data for comparison. The simulation results are then evaluated based on their ability to reproduce these experimental observations within acceptable margins of error.
Benchmarking against other simulation methods is another essential strategy. This involves comparing the results of the advanced simulation techniques with those obtained from well-established computational methods, such as density functional theory (DFT) calculations or molecular dynamics simulations. By doing so, researchers can assess the relative performance and accuracy of their new simulation approaches.
Sensitivity analysis is a critical component of the validation process. This involves systematically varying input parameters and examining their impact on the simulation outcomes. By identifying the most influential parameters, researchers can focus on refining these aspects of the simulation to improve overall accuracy. Additionally, this analysis helps in understanding the robustness of the simulation technique under different conditions.
Cross-validation techniques are often employed to assess the generalizability of the simulation method. This involves dividing the available data into training and testing sets, allowing researchers to evaluate how well the simulation performs on unseen data. This approach helps in identifying potential overfitting issues and ensures that the simulation technique is applicable across a wide range of reaction conditions.
Statistical analysis of simulation results is crucial for quantifying the accuracy and precision of the advanced techniques. This includes calculating metrics such as mean absolute error, root mean square error, and correlation coefficients between simulated and experimental data. These statistical measures provide a quantitative basis for comparing different simulation methods and assessing their reliability.
Lastly, the validation and benchmarking process often involves collaboration with experimental chemists and other computational experts. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that the simulation techniques are grounded in practical relevance and can effectively address real-world challenges in ethyl propanoate reactions. By combining diverse expertise, researchers can refine their simulation methods and enhance their applicability to complex reaction systems.
One key aspect of validation is the comparison of simulated reaction kinetics with experimental measurements. This includes analyzing reaction rates, product yields, and intermediate species concentrations. Researchers typically employ various analytical techniques, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, to obtain experimental data for comparison. The simulation results are then evaluated based on their ability to reproduce these experimental observations within acceptable margins of error.
Benchmarking against other simulation methods is another essential strategy. This involves comparing the results of the advanced simulation techniques with those obtained from well-established computational methods, such as density functional theory (DFT) calculations or molecular dynamics simulations. By doing so, researchers can assess the relative performance and accuracy of their new simulation approaches.
Sensitivity analysis is a critical component of the validation process. This involves systematically varying input parameters and examining their impact on the simulation outcomes. By identifying the most influential parameters, researchers can focus on refining these aspects of the simulation to improve overall accuracy. Additionally, this analysis helps in understanding the robustness of the simulation technique under different conditions.
Cross-validation techniques are often employed to assess the generalizability of the simulation method. This involves dividing the available data into training and testing sets, allowing researchers to evaluate how well the simulation performs on unseen data. This approach helps in identifying potential overfitting issues and ensures that the simulation technique is applicable across a wide range of reaction conditions.
Statistical analysis of simulation results is crucial for quantifying the accuracy and precision of the advanced techniques. This includes calculating metrics such as mean absolute error, root mean square error, and correlation coefficients between simulated and experimental data. These statistical measures provide a quantitative basis for comparing different simulation methods and assessing their reliability.
Lastly, the validation and benchmarking process often involves collaboration with experimental chemists and other computational experts. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that the simulation techniques are grounded in practical relevance and can effectively address real-world challenges in ethyl propanoate reactions. By combining diverse expertise, researchers can refine their simulation methods and enhance their applicability to complex reaction systems.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!