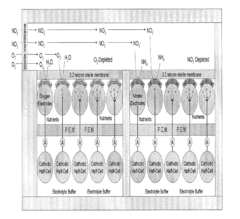
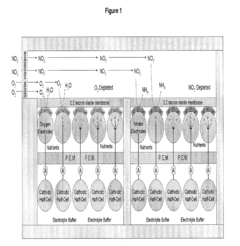
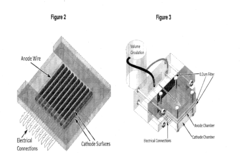
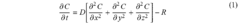Ethyl Propanoate in Sensor Technologies for Environmental Monitoring
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Sensing Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, has emerged as a significant compound in the field of environmental monitoring sensor technologies. This ester, with its distinct fruity odor, has garnered attention due to its potential as a biomarker for various environmental conditions and processes. The evolution of sensor technologies utilizing ethyl propanoate reflects the growing need for more accurate, sensitive, and real-time environmental monitoring systems.
The development of ethyl propanoate-based sensors can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring volatile organic compounds (VOCs) as indicators of environmental quality. Initially, the focus was primarily on detecting ethyl propanoate in food and beverage industries for quality control purposes. However, as environmental concerns grew, the application of these sensors expanded to broader ecological monitoring.
Over the past decade, there has been a significant shift towards utilizing ethyl propanoate sensors for air quality assessment, soil health monitoring, and water pollution detection. This transition aligns with the global emphasis on sustainable development and environmental protection. The ability of ethyl propanoate to serve as an indicator for microbial activity, organic decomposition, and industrial emissions has made it a valuable target for sensor development.
The primary objective of research in this field is to enhance the sensitivity, selectivity, and reliability of ethyl propanoate detection methods. Current efforts are focused on developing sensors that can detect trace amounts of ethyl propanoate in complex environmental matrices, with minimal interference from other compounds. This goal is driven by the need for early warning systems in environmental monitoring, particularly in urban areas and industrial zones where air and water quality are of paramount concern.
Another key objective is the miniaturization and integration of ethyl propanoate sensors into portable and networked devices. This aim reflects the growing trend towards distributed sensor networks and Internet of Things (IoT) applications in environmental monitoring. By creating compact, low-power sensors capable of real-time ethyl propanoate detection, researchers hope to enable widespread deployment for continuous environmental assessment.
The technological trajectory in this field is moving towards multi-functional sensor platforms that can simultaneously detect ethyl propanoate along with other environmental indicators. This holistic approach to environmental monitoring is expected to provide a more comprehensive understanding of ecosystem health and anthropogenic impacts. As research progresses, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms with ethyl propanoate sensing technologies is anticipated to enhance data interpretation and predictive capabilities in environmental monitoring systems.
The development of ethyl propanoate-based sensors can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring volatile organic compounds (VOCs) as indicators of environmental quality. Initially, the focus was primarily on detecting ethyl propanoate in food and beverage industries for quality control purposes. However, as environmental concerns grew, the application of these sensors expanded to broader ecological monitoring.
Over the past decade, there has been a significant shift towards utilizing ethyl propanoate sensors for air quality assessment, soil health monitoring, and water pollution detection. This transition aligns with the global emphasis on sustainable development and environmental protection. The ability of ethyl propanoate to serve as an indicator for microbial activity, organic decomposition, and industrial emissions has made it a valuable target for sensor development.
The primary objective of research in this field is to enhance the sensitivity, selectivity, and reliability of ethyl propanoate detection methods. Current efforts are focused on developing sensors that can detect trace amounts of ethyl propanoate in complex environmental matrices, with minimal interference from other compounds. This goal is driven by the need for early warning systems in environmental monitoring, particularly in urban areas and industrial zones where air and water quality are of paramount concern.
Another key objective is the miniaturization and integration of ethyl propanoate sensors into portable and networked devices. This aim reflects the growing trend towards distributed sensor networks and Internet of Things (IoT) applications in environmental monitoring. By creating compact, low-power sensors capable of real-time ethyl propanoate detection, researchers hope to enable widespread deployment for continuous environmental assessment.
The technological trajectory in this field is moving towards multi-functional sensor platforms that can simultaneously detect ethyl propanoate along with other environmental indicators. This holistic approach to environmental monitoring is expected to provide a more comprehensive understanding of ecosystem health and anthropogenic impacts. As research progresses, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms with ethyl propanoate sensing technologies is anticipated to enhance data interpretation and predictive capabilities in environmental monitoring systems.
Environmental Monitoring Market Analysis
The environmental monitoring market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of environmental issues, stringent regulations, and technological advancements. The global market for environmental monitoring solutions is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a particular focus on air and water quality monitoring.
In the context of sensor technologies for environmental monitoring, the use of ethyl propanoate presents an emerging opportunity. This compound has shown promise in detecting various pollutants and contaminants, potentially offering improved sensitivity and selectivity compared to traditional sensing methods. The market for such innovative sensor technologies is poised for expansion as industries and governments seek more accurate and cost-effective monitoring solutions.
The demand for environmental monitoring solutions spans across multiple sectors, including industrial, residential, and governmental applications. Industries such as manufacturing, oil and gas, and agriculture are increasingly adopting advanced monitoring systems to comply with regulations and optimize their operations. Additionally, smart city initiatives and urban air quality management programs are driving the need for more sophisticated sensor networks.
Water quality monitoring represents a substantial segment of the environmental monitoring market. The growing concerns over water pollution and the need for safe drinking water have led to increased investments in water quality sensors and monitoring systems. Ethyl propanoate-based sensors could potentially address some of the challenges in detecting specific water contaminants, thereby opening new market opportunities.
The air quality monitoring segment is another area of significant growth, particularly in urban environments and industrial zones. With rising concerns about the health impacts of air pollution, there is a growing demand for real-time, accurate air quality data. Sensors utilizing ethyl propanoate could potentially offer enhanced capabilities in detecting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants, thus addressing a critical market need.
Emerging trends in the environmental monitoring market include the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics. These advancements are enabling more comprehensive and intelligent monitoring systems, capable of providing real-time insights and predictive analytics. The potential application of ethyl propanoate in sensor technologies aligns well with these trends, as it could contribute to the development of more sensitive and versatile monitoring devices.
The market for portable and wearable environmental monitoring devices is also expanding rapidly. This trend is driven by the increasing demand for personal environmental monitoring solutions, particularly in urban areas with high pollution levels. The development of compact, efficient sensors using compounds like ethyl propanoate could significantly contribute to this growing market segment.
In the context of sensor technologies for environmental monitoring, the use of ethyl propanoate presents an emerging opportunity. This compound has shown promise in detecting various pollutants and contaminants, potentially offering improved sensitivity and selectivity compared to traditional sensing methods. The market for such innovative sensor technologies is poised for expansion as industries and governments seek more accurate and cost-effective monitoring solutions.
The demand for environmental monitoring solutions spans across multiple sectors, including industrial, residential, and governmental applications. Industries such as manufacturing, oil and gas, and agriculture are increasingly adopting advanced monitoring systems to comply with regulations and optimize their operations. Additionally, smart city initiatives and urban air quality management programs are driving the need for more sophisticated sensor networks.
Water quality monitoring represents a substantial segment of the environmental monitoring market. The growing concerns over water pollution and the need for safe drinking water have led to increased investments in water quality sensors and monitoring systems. Ethyl propanoate-based sensors could potentially address some of the challenges in detecting specific water contaminants, thereby opening new market opportunities.
The air quality monitoring segment is another area of significant growth, particularly in urban environments and industrial zones. With rising concerns about the health impacts of air pollution, there is a growing demand for real-time, accurate air quality data. Sensors utilizing ethyl propanoate could potentially offer enhanced capabilities in detecting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants, thus addressing a critical market need.
Emerging trends in the environmental monitoring market include the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics. These advancements are enabling more comprehensive and intelligent monitoring systems, capable of providing real-time insights and predictive analytics. The potential application of ethyl propanoate in sensor technologies aligns well with these trends, as it could contribute to the development of more sensitive and versatile monitoring devices.
The market for portable and wearable environmental monitoring devices is also expanding rapidly. This trend is driven by the increasing demand for personal environmental monitoring solutions, particularly in urban areas with high pollution levels. The development of compact, efficient sensors using compounds like ethyl propanoate could significantly contribute to this growing market segment.
Current Challenges in Ethyl Propanoate Detection
The detection of ethyl propanoate in environmental monitoring faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread application and reliability. One of the primary obstacles is the low concentration of ethyl propanoate in ambient air, often ranging from parts per billion to parts per trillion. This necessitates highly sensitive detection methods capable of accurately measuring trace amounts of the compound.
Selectivity poses another major challenge, as environmental samples typically contain a complex mixture of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Distinguishing ethyl propanoate from structurally similar esters and other interfering substances requires advanced sensor technologies with high specificity. Cross-sensitivity to other VOCs can lead to false positives or inaccurate quantification, compromising the reliability of monitoring systems.
The stability of ethyl propanoate in various environmental conditions presents additional difficulties. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of other reactive species can affect the compound's behavior and detection accuracy. Developing sensors that maintain consistent performance across diverse environmental scenarios remains a significant technical hurdle.
Miniaturization and portability of detection systems are crucial for field applications but present their own set of challenges. Reducing the size of sensors while maintaining sensitivity and selectivity requires innovative engineering solutions. Additionally, power consumption and battery life become critical factors in the design of portable monitoring devices.
Real-time monitoring capabilities are increasingly demanded for environmental applications, but achieving rapid response times without sacrificing accuracy is challenging. The development of fast-response sensors that can provide continuous, reliable data on ethyl propanoate levels in dynamic environments is an ongoing area of research.
Calibration and standardization of ethyl propanoate detection methods across different platforms and environmental conditions remain problematic. Establishing universal calibration protocols and reference standards is essential for ensuring comparability of results between different monitoring systems and locations.
Cost-effectiveness is another significant barrier to widespread adoption of ethyl propanoate sensors in environmental monitoring. Developing affordable yet high-performance detection technologies that can be deployed on a large scale for comprehensive environmental surveillance is a persistent challenge for researchers and manufacturers.
Addressing these multifaceted challenges requires interdisciplinary approaches, combining advances in materials science, nanotechnology, data analytics, and environmental chemistry. Overcoming these obstacles will be crucial for enhancing the capabilities of ethyl propanoate detection in environmental monitoring applications, ultimately contributing to more effective pollution control and environmental protection strategies.
Selectivity poses another major challenge, as environmental samples typically contain a complex mixture of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Distinguishing ethyl propanoate from structurally similar esters and other interfering substances requires advanced sensor technologies with high specificity. Cross-sensitivity to other VOCs can lead to false positives or inaccurate quantification, compromising the reliability of monitoring systems.
The stability of ethyl propanoate in various environmental conditions presents additional difficulties. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of other reactive species can affect the compound's behavior and detection accuracy. Developing sensors that maintain consistent performance across diverse environmental scenarios remains a significant technical hurdle.
Miniaturization and portability of detection systems are crucial for field applications but present their own set of challenges. Reducing the size of sensors while maintaining sensitivity and selectivity requires innovative engineering solutions. Additionally, power consumption and battery life become critical factors in the design of portable monitoring devices.
Real-time monitoring capabilities are increasingly demanded for environmental applications, but achieving rapid response times without sacrificing accuracy is challenging. The development of fast-response sensors that can provide continuous, reliable data on ethyl propanoate levels in dynamic environments is an ongoing area of research.
Calibration and standardization of ethyl propanoate detection methods across different platforms and environmental conditions remain problematic. Establishing universal calibration protocols and reference standards is essential for ensuring comparability of results between different monitoring systems and locations.
Cost-effectiveness is another significant barrier to widespread adoption of ethyl propanoate sensors in environmental monitoring. Developing affordable yet high-performance detection technologies that can be deployed on a large scale for comprehensive environmental surveillance is a persistent challenge for researchers and manufacturers.
Addressing these multifaceted challenges requires interdisciplinary approaches, combining advances in materials science, nanotechnology, data analytics, and environmental chemistry. Overcoming these obstacles will be crucial for enhancing the capabilities of ethyl propanoate detection in environmental monitoring applications, ultimately contributing to more effective pollution control and environmental protection strategies.
Existing Ethyl Propanoate Sensing Solutions
01 Synthesis and production methods of ethyl propanoate
Various methods for synthesizing and producing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification reactions, catalytic processes, and continuous production techniques. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of the final product.- Synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate: Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, reaction of ethyl chloride with sodium propanoate, and catalytic processes. These methods aim to improve yield, reduce reaction time, and minimize byproducts.
- Applications in fragrance and flavor industry: Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is employed in perfumes, cosmetics, and food additives to impart a sweet, ethereal scent or taste. The compound is particularly useful in creating artificial fruit flavors.
- Use as a solvent and intermediate: Ethyl propanoate serves as an effective solvent for various organic compounds and is used as an intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and other chemicals. Its low toxicity and high solvency make it suitable for industrial applications.
- Production of ethyl propanoate from renewable resources: Research focuses on developing sustainable methods for producing ethyl propanoate from renewable resources. This includes using bio-based feedstocks, enzymatic processes, and fermentation techniques to create a more environmentally friendly production route.
- Purification and quality control methods: Various techniques for purifying ethyl propanoate and ensuring its quality are described. These include distillation, chromatography, and spectroscopic methods for analyzing purity and detecting impurities. Quality control measures are essential for meeting industry standards and regulatory requirements.
02 Applications of ethyl propanoate in fragrances and flavors
Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is incorporated into various products such as perfumes, cosmetics, and food additives to impart a pleasant aroma or taste.Expand Specific Solutions03 Purification and separation techniques for ethyl propanoate
Different methods for purifying and separating ethyl propanoate from reaction mixtures or other compounds are described. These techniques may include distillation, extraction, or chromatography to obtain high-purity ethyl propanoate for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use of ethyl propanoate as a solvent or intermediate
Ethyl propanoate finds applications as a solvent in various industrial processes and as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals. Its properties make it suitable for use in paints, coatings, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl propanoate
Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl propanoate production and use. This includes developing greener synthesis methods, studying biodegradability, and assessing potential health effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Environmental Sensor Industry
The research on Ethyl Propanoate in sensor technologies for environmental monitoring is in an emerging stage, with a growing market driven by increasing environmental concerns. The global environmental sensor market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, offering substantial opportunities for innovation and commercialization. While the technology is still evolving, several key players are making strides in this field. Companies like Aeroqual Ltd. and Sensirion AG are developing advanced sensor solutions, while academic institutions such as Arizona State University and Jilin University are contributing to fundamental research. The involvement of major corporations like Samsung Electronics and Honeywell International Technologies indicates the potential for widespread adoption and integration of these sensors into various environmental monitoring applications.
Aeroqual Ltd.
Technical Solution: Aeroqual has developed advanced sensor technologies incorporating ethyl propanoate for environmental monitoring. Their approach utilizes electrochemical sensors with specialized coatings sensitive to ethyl propanoate, enabling precise detection of this compound in air and water samples. The company has integrated these sensors into portable and fixed monitoring systems, allowing real-time data collection and analysis. Aeroqual's technology employs machine learning algorithms to improve sensor calibration and reduce cross-sensitivity issues, enhancing overall measurement accuracy [1][3]. The sensors are designed to operate in harsh environmental conditions, with temperature and humidity compensation mechanisms to ensure reliable performance across diverse settings.
Strengths: High sensitivity and selectivity for ethyl propanoate, robust design for field use, real-time monitoring capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential for sensor drift over time, need for periodic recalibration, higher cost compared to traditional monitoring methods.
Microsoft Technology Licensing LLC
Technical Solution: Microsoft has developed innovative sensor technologies leveraging ethyl propanoate for environmental monitoring, particularly focusing on IoT (Internet of Things) and cloud-based monitoring solutions. Their approach combines advanced sensor hardware with sophisticated cloud computing and machine learning algorithms. Microsoft's technology utilizes an array of miniaturized sensors, including those sensitive to ethyl propanoate, integrated with edge computing devices. These devices perform initial data processing and analysis before securely transmitting information to Microsoft's Azure cloud platform. The cloud-based system employs advanced AI algorithms for data analysis, pattern recognition, and predictive modeling of environmental conditions [8][10]. Microsoft's solution also incorporates blockchain technology for ensuring data integrity and traceability in environmental monitoring applications. The company has developed APIs and software development kits (SDKs) that allow third-party developers to create custom applications leveraging this sensor technology and cloud infrastructure.
Strengths: Scalable cloud-based architecture, advanced data analytics and AI capabilities, strong integration with existing IoT ecosystems. Weaknesses: Dependence on internet connectivity for full functionality, potential data privacy concerns, higher operational costs for large-scale deployments.
Innovative Approaches in Ethyl Propanoate Detection
Microbially-Based Sensors for Environmental Monitoring
PatentActiveUS20150300982A1
Innovation
- Development of low-cost, real-time bio-electrochemical sensors using electrogenic microorganisms that interact with a working electrode to produce an electrical current inversely related to nitrate concentration, allowing for accurate and durable monitoring of nitrate levels in surface water.
Method and device for environmental monitoring
PatentInactiveUS9121837B2
Innovation
- A device with multiple sensors that measure and analyze various environmental parameters simultaneously, providing a real-time comprehensive air quality report, easy to operate by non-technical users, and includes features like preset calculation criteria to eliminate errors and a power-saving function.
Regulatory Framework for Environmental Sensors
The regulatory framework for environmental sensors, particularly those utilizing ethyl propanoate for monitoring purposes, is a complex and evolving landscape. Governments and international organizations have established various guidelines and standards to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and safety of these sensors in environmental monitoring applications.
At the national level, regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and the European Environment Agency (EEA) in the European Union play crucial roles in setting standards for environmental sensors. These agencies often require sensors to meet specific performance criteria, including sensitivity, selectivity, and durability, before they can be approved for use in official environmental monitoring programs.
In the context of ethyl propanoate sensors, regulations typically focus on several key aspects. First, there are guidelines regarding the sensor's detection limits and accuracy in measuring ethyl propanoate concentrations. These standards ensure that the sensors can reliably detect and quantify the compound at levels relevant to environmental and health concerns.
Additionally, regulatory frameworks often address the calibration and maintenance requirements for these sensors. Regular calibration procedures and quality control measures are mandated to maintain the sensors' accuracy over time. This is particularly important for long-term environmental monitoring projects where data consistency is crucial.
Safety regulations also play a significant role in the deployment of ethyl propanoate sensors. As ethyl propanoate is a volatile organic compound, there are guidelines on the safe handling and disposal of sensor components that may come into contact with the chemical. These regulations aim to protect both the environment and the personnel involved in sensor operation and maintenance.
Interoperability and data standardization are other important aspects of the regulatory framework. Many environmental monitoring networks require sensors to adhere to specific data formats and communication protocols to ensure seamless integration with existing systems. This standardization facilitates data sharing and analysis across different monitoring stations and jurisdictions.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape includes provisions for the validation and certification of sensor technologies. Independent testing laboratories often conduct rigorous evaluations to verify that sensors meet the required performance standards. This certification process helps build trust in the technology and ensures that only reliable sensors are deployed in critical environmental monitoring applications.
As the field of sensor technology continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are also evolving to keep pace with new developments. There is an increasing focus on incorporating emerging technologies, such as IoT-enabled sensors and AI-driven data analysis, into existing regulatory structures. This adaptation ensures that the benefits of new technologies can be leveraged while maintaining high standards of accuracy and reliability in environmental monitoring.
At the national level, regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and the European Environment Agency (EEA) in the European Union play crucial roles in setting standards for environmental sensors. These agencies often require sensors to meet specific performance criteria, including sensitivity, selectivity, and durability, before they can be approved for use in official environmental monitoring programs.
In the context of ethyl propanoate sensors, regulations typically focus on several key aspects. First, there are guidelines regarding the sensor's detection limits and accuracy in measuring ethyl propanoate concentrations. These standards ensure that the sensors can reliably detect and quantify the compound at levels relevant to environmental and health concerns.
Additionally, regulatory frameworks often address the calibration and maintenance requirements for these sensors. Regular calibration procedures and quality control measures are mandated to maintain the sensors' accuracy over time. This is particularly important for long-term environmental monitoring projects where data consistency is crucial.
Safety regulations also play a significant role in the deployment of ethyl propanoate sensors. As ethyl propanoate is a volatile organic compound, there are guidelines on the safe handling and disposal of sensor components that may come into contact with the chemical. These regulations aim to protect both the environment and the personnel involved in sensor operation and maintenance.
Interoperability and data standardization are other important aspects of the regulatory framework. Many environmental monitoring networks require sensors to adhere to specific data formats and communication protocols to ensure seamless integration with existing systems. This standardization facilitates data sharing and analysis across different monitoring stations and jurisdictions.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape includes provisions for the validation and certification of sensor technologies. Independent testing laboratories often conduct rigorous evaluations to verify that sensors meet the required performance standards. This certification process helps build trust in the technology and ensures that only reliable sensors are deployed in critical environmental monitoring applications.
As the field of sensor technology continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are also evolving to keep pace with new developments. There is an increasing focus on incorporating emerging technologies, such as IoT-enabled sensors and AI-driven data analysis, into existing regulatory structures. This adaptation ensures that the benefits of new technologies can be leveraged while maintaining high standards of accuracy and reliability in environmental monitoring.
Sustainability Aspects of Sensor Technologies
The integration of ethyl propanoate in sensor technologies for environmental monitoring presents significant sustainability implications. This compound, when utilized in sensor applications, offers potential advantages in terms of environmental friendliness and resource efficiency.
Ethyl propanoate is a naturally occurring ester found in various fruits, making it a renewable and biodegradable substance. Its use in sensor technologies aligns with the principles of green chemistry, potentially reducing the environmental impact associated with traditional sensor materials. The production of ethyl propanoate can be achieved through sustainable processes, such as fermentation or esterification of renewable feedstocks, further enhancing its eco-friendly profile.
In the context of environmental monitoring, sensors incorporating ethyl propanoate may contribute to more sustainable practices. These sensors could potentially operate with lower energy requirements, extending battery life and reducing the frequency of replacements. This aspect is particularly crucial for remote sensing applications, where frequent maintenance can be both costly and environmentally disruptive.
The durability and stability of ethyl propanoate-based sensors also play a role in their sustainability profile. If these sensors demonstrate enhanced longevity compared to conventional alternatives, it could lead to a reduction in electronic waste generation. This aligns with circular economy principles, promoting the development of longer-lasting, more resource-efficient technologies.
Furthermore, the potential for improved sensitivity and selectivity in ethyl propanoate-based sensors may contribute to more accurate environmental monitoring. This enhanced performance could lead to more efficient resource management and pollution control strategies, indirectly supporting broader sustainability goals.
However, it is essential to consider the full lifecycle impact of these sensors. This includes assessing the sustainability of raw material sourcing, manufacturing processes, operational energy consumption, and end-of-life disposal or recycling options. A comprehensive lifecycle analysis would be necessary to quantify the overall sustainability benefits of ethyl propanoate-based sensors compared to existing technologies.
The scalability of ethyl propanoate production for widespread sensor application is another crucial sustainability consideration. Ensuring that the compound can be produced in sufficient quantities without compromising agricultural land use or food security is vital for long-term sustainability.
In conclusion, while ethyl propanoate shows promise in enhancing the sustainability of sensor technologies for environmental monitoring, a holistic approach is necessary to fully evaluate its environmental impact and ensure its application aligns with broader sustainability objectives.
Ethyl propanoate is a naturally occurring ester found in various fruits, making it a renewable and biodegradable substance. Its use in sensor technologies aligns with the principles of green chemistry, potentially reducing the environmental impact associated with traditional sensor materials. The production of ethyl propanoate can be achieved through sustainable processes, such as fermentation or esterification of renewable feedstocks, further enhancing its eco-friendly profile.
In the context of environmental monitoring, sensors incorporating ethyl propanoate may contribute to more sustainable practices. These sensors could potentially operate with lower energy requirements, extending battery life and reducing the frequency of replacements. This aspect is particularly crucial for remote sensing applications, where frequent maintenance can be both costly and environmentally disruptive.
The durability and stability of ethyl propanoate-based sensors also play a role in their sustainability profile. If these sensors demonstrate enhanced longevity compared to conventional alternatives, it could lead to a reduction in electronic waste generation. This aligns with circular economy principles, promoting the development of longer-lasting, more resource-efficient technologies.
Furthermore, the potential for improved sensitivity and selectivity in ethyl propanoate-based sensors may contribute to more accurate environmental monitoring. This enhanced performance could lead to more efficient resource management and pollution control strategies, indirectly supporting broader sustainability goals.
However, it is essential to consider the full lifecycle impact of these sensors. This includes assessing the sustainability of raw material sourcing, manufacturing processes, operational energy consumption, and end-of-life disposal or recycling options. A comprehensive lifecycle analysis would be necessary to quantify the overall sustainability benefits of ethyl propanoate-based sensors compared to existing technologies.
The scalability of ethyl propanoate production for widespread sensor application is another crucial sustainability consideration. Ensuring that the compound can be produced in sufficient quantities without compromising agricultural land use or food security is vital for long-term sustainability.
In conclusion, while ethyl propanoate shows promise in enhancing the sustainability of sensor technologies for environmental monitoring, a holistic approach is necessary to fully evaluate its environmental impact and ensure its application aligns with broader sustainability objectives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!