Ethyl Propanoate-Derived Materials in Biodegradable Packaging
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C5H10O2. It is a colorless liquid with a fruity odor, commonly used as a flavoring agent in the food industry. In recent years, there has been growing interest in exploring the potential of ethyl propanoate-derived materials for biodegradable packaging applications, driven by the urgent need to address environmental concerns associated with conventional plastic packaging.
The development of biodegradable packaging materials has gained significant momentum in response to the global plastic pollution crisis. As consumers and governments increasingly demand sustainable alternatives, researchers and industry players have been exploring various bio-based and biodegradable materials. Ethyl propanoate-derived materials have emerged as a promising candidate due to their potential for biodegradability and renewable sourcing.
The primary objective of research in this field is to develop packaging materials that can effectively replace traditional petroleum-based plastics while maintaining comparable performance characteristics. This includes investigating the mechanical properties, barrier properties, and overall durability of ethyl propanoate-derived materials in various packaging applications. Additionally, researchers aim to optimize the production processes to ensure economic viability and scalability for commercial adoption.
One of the key advantages of ethyl propanoate-derived materials is their potential for biodegradability. Unlike conventional plastics that persist in the environment for hundreds of years, these materials are designed to break down naturally under specific conditions, reducing their environmental impact. This aligns with the growing trend towards circular economy principles and sustainable packaging solutions.
The research on ethyl propanoate-derived materials for biodegradable packaging is part of a broader technological evolution in the packaging industry. It builds upon previous advancements in bioplastics and biodegradable polymers, seeking to address limitations and improve overall performance. The goal is to create packaging materials that not only meet environmental standards but also satisfy the functional requirements of various industries, including food, cosmetics, and consumer goods.
As the field progresses, researchers are exploring various aspects of ethyl propanoate-derived materials, including their synthesis, modification, and integration with other biodegradable components. This comprehensive approach aims to develop a new generation of packaging materials that can effectively compete with traditional plastics in terms of cost, performance, and environmental sustainability.
The development of biodegradable packaging materials has gained significant momentum in response to the global plastic pollution crisis. As consumers and governments increasingly demand sustainable alternatives, researchers and industry players have been exploring various bio-based and biodegradable materials. Ethyl propanoate-derived materials have emerged as a promising candidate due to their potential for biodegradability and renewable sourcing.
The primary objective of research in this field is to develop packaging materials that can effectively replace traditional petroleum-based plastics while maintaining comparable performance characteristics. This includes investigating the mechanical properties, barrier properties, and overall durability of ethyl propanoate-derived materials in various packaging applications. Additionally, researchers aim to optimize the production processes to ensure economic viability and scalability for commercial adoption.
One of the key advantages of ethyl propanoate-derived materials is their potential for biodegradability. Unlike conventional plastics that persist in the environment for hundreds of years, these materials are designed to break down naturally under specific conditions, reducing their environmental impact. This aligns with the growing trend towards circular economy principles and sustainable packaging solutions.
The research on ethyl propanoate-derived materials for biodegradable packaging is part of a broader technological evolution in the packaging industry. It builds upon previous advancements in bioplastics and biodegradable polymers, seeking to address limitations and improve overall performance. The goal is to create packaging materials that not only meet environmental standards but also satisfy the functional requirements of various industries, including food, cosmetics, and consumer goods.
As the field progresses, researchers are exploring various aspects of ethyl propanoate-derived materials, including their synthesis, modification, and integration with other biodegradable components. This comprehensive approach aims to develop a new generation of packaging materials that can effectively compete with traditional plastics in terms of cost, performance, and environmental sustainability.
Market Analysis for Biodegradable Packaging
The biodegradable packaging market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures to reduce plastic waste. The global market for biodegradable packaging is projected to reach $21.7 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.4% from 2020 to 2025. This growth is primarily fueled by the rising demand for sustainable packaging solutions across various industries, including food and beverage, personal care, and healthcare.
Consumer awareness and preferences play a crucial role in shaping the market demand for biodegradable packaging. A recent survey indicates that 74% of consumers are willing to pay more for sustainable packaging options. This shift in consumer behavior has prompted major brands and retailers to adopt eco-friendly packaging solutions, further driving market growth.
The food and beverage industry remains the largest end-user segment for biodegradable packaging, accounting for approximately 60% of the market share. This dominance is attributed to the increasing use of biodegradable materials in food service disposables, fresh produce packaging, and beverage containers. The personal care and cosmetics industry is also emerging as a significant market for biodegradable packaging, with a projected CAGR of 20.5% from 2020 to 2025.
Geographically, Europe leads the biodegradable packaging market, followed by North America and Asia-Pacific. Europe's dominance is largely due to stringent regulations on single-use plastics and strong government support for sustainable packaging initiatives. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental awareness in countries like China and India.
The market for ethyl propanoate-derived materials in biodegradable packaging is still in its nascent stage but shows promising potential. These materials offer advantages such as improved barrier properties, enhanced biodegradability, and compatibility with existing packaging manufacturing processes. As research and development in this area progress, ethyl propanoate-derived materials are expected to capture a growing share of the biodegradable packaging market, particularly in applications requiring high-performance barrier properties.
Key market drivers for ethyl propanoate-derived biodegradable packaging include the increasing demand for bio-based and compostable materials, the need for extended shelf life in food packaging, and the push for circular economy solutions. However, challenges such as higher production costs compared to conventional plastics and the need for specialized waste management infrastructure may initially limit market penetration.
In conclusion, the biodegradable packaging market presents significant opportunities for ethyl propanoate-derived materials. As technology advances and economies of scale are achieved, these materials are poised to play an increasingly important role in meeting the growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions across various industries.
Consumer awareness and preferences play a crucial role in shaping the market demand for biodegradable packaging. A recent survey indicates that 74% of consumers are willing to pay more for sustainable packaging options. This shift in consumer behavior has prompted major brands and retailers to adopt eco-friendly packaging solutions, further driving market growth.
The food and beverage industry remains the largest end-user segment for biodegradable packaging, accounting for approximately 60% of the market share. This dominance is attributed to the increasing use of biodegradable materials in food service disposables, fresh produce packaging, and beverage containers. The personal care and cosmetics industry is also emerging as a significant market for biodegradable packaging, with a projected CAGR of 20.5% from 2020 to 2025.
Geographically, Europe leads the biodegradable packaging market, followed by North America and Asia-Pacific. Europe's dominance is largely due to stringent regulations on single-use plastics and strong government support for sustainable packaging initiatives. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental awareness in countries like China and India.
The market for ethyl propanoate-derived materials in biodegradable packaging is still in its nascent stage but shows promising potential. These materials offer advantages such as improved barrier properties, enhanced biodegradability, and compatibility with existing packaging manufacturing processes. As research and development in this area progress, ethyl propanoate-derived materials are expected to capture a growing share of the biodegradable packaging market, particularly in applications requiring high-performance barrier properties.
Key market drivers for ethyl propanoate-derived biodegradable packaging include the increasing demand for bio-based and compostable materials, the need for extended shelf life in food packaging, and the push for circular economy solutions. However, challenges such as higher production costs compared to conventional plastics and the need for specialized waste management infrastructure may initially limit market penetration.
In conclusion, the biodegradable packaging market presents significant opportunities for ethyl propanoate-derived materials. As technology advances and economies of scale are achieved, these materials are poised to play an increasingly important role in meeting the growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions across various industries.
Current Challenges in Ethyl Propanoate Materials
Despite the promising potential of ethyl propanoate-derived materials in biodegradable packaging, several significant challenges currently hinder their widespread adoption and commercial viability. These obstacles span across technical, economic, and regulatory domains, requiring a multifaceted approach to overcome.
One of the primary technical challenges is the optimization of material properties. While ethyl propanoate-based materials show promising biodegradability, they often fall short in terms of mechanical strength, barrier properties, and thermal stability compared to conventional plastics. This limitation restricts their application in certain packaging scenarios that demand high performance, such as long-shelf-life products or those requiring robust protection during transportation.
The scalability of production processes presents another hurdle. Current manufacturing methods for ethyl propanoate-derived materials are often limited to laboratory or small-scale production. Scaling up these processes to meet industrial demands while maintaining consistent quality and properties is a complex task that requires significant investment in research and development.
Cost-effectiveness remains a critical challenge. The production of ethyl propanoate-based materials is generally more expensive than that of traditional plastics, primarily due to higher raw material costs and more complex processing requirements. This price disparity makes it difficult for these materials to compete in a market where cost is often a decisive factor for both manufacturers and consumers.
Environmental impact assessment poses another challenge. While biodegradability is a key advantage, comprehensive life cycle analyses are needed to fully understand the environmental footprint of these materials, including their production, use, and end-of-life phases. Ensuring that the overall environmental impact is indeed lower than conventional plastics is crucial for their long-term sustainability.
Regulatory hurdles and standardization issues also present significant challenges. The lack of universally accepted standards for biodegradability and compostability of packaging materials creates uncertainty in the market. Additionally, navigating the complex landscape of food contact regulations across different regions can be time-consuming and costly for manufacturers.
Consumer perception and behavior represent another set of challenges. While there is growing awareness and demand for sustainable packaging solutions, there is still a need for education regarding the proper disposal and recycling of biodegradable materials. Misconceptions about biodegradability and its implications can lead to improper disposal, potentially negating the environmental benefits of these materials.
Lastly, the integration of ethyl propanoate-derived materials into existing recycling and waste management infrastructures poses logistical challenges. Many current systems are not equipped to handle or properly process these new materials, which could lead to contamination of recycling streams or ineffective decomposition in landfills.
One of the primary technical challenges is the optimization of material properties. While ethyl propanoate-based materials show promising biodegradability, they often fall short in terms of mechanical strength, barrier properties, and thermal stability compared to conventional plastics. This limitation restricts their application in certain packaging scenarios that demand high performance, such as long-shelf-life products or those requiring robust protection during transportation.
The scalability of production processes presents another hurdle. Current manufacturing methods for ethyl propanoate-derived materials are often limited to laboratory or small-scale production. Scaling up these processes to meet industrial demands while maintaining consistent quality and properties is a complex task that requires significant investment in research and development.
Cost-effectiveness remains a critical challenge. The production of ethyl propanoate-based materials is generally more expensive than that of traditional plastics, primarily due to higher raw material costs and more complex processing requirements. This price disparity makes it difficult for these materials to compete in a market where cost is often a decisive factor for both manufacturers and consumers.
Environmental impact assessment poses another challenge. While biodegradability is a key advantage, comprehensive life cycle analyses are needed to fully understand the environmental footprint of these materials, including their production, use, and end-of-life phases. Ensuring that the overall environmental impact is indeed lower than conventional plastics is crucial for their long-term sustainability.
Regulatory hurdles and standardization issues also present significant challenges. The lack of universally accepted standards for biodegradability and compostability of packaging materials creates uncertainty in the market. Additionally, navigating the complex landscape of food contact regulations across different regions can be time-consuming and costly for manufacturers.
Consumer perception and behavior represent another set of challenges. While there is growing awareness and demand for sustainable packaging solutions, there is still a need for education regarding the proper disposal and recycling of biodegradable materials. Misconceptions about biodegradability and its implications can lead to improper disposal, potentially negating the environmental benefits of these materials.
Lastly, the integration of ethyl propanoate-derived materials into existing recycling and waste management infrastructures poses logistical challenges. Many current systems are not equipped to handle or properly process these new materials, which could lead to contamination of recycling streams or ineffective decomposition in landfills.
Existing Ethyl Propanoate-Based Solutions
01 Synthesis of ethyl propanoate derivatives
Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate derivatives are described. These processes involve different reaction conditions, catalysts, and starting materials to produce ethyl propanoate-based compounds with specific properties or functionalities.- Synthesis and production methods of ethyl propanoate derivatives: Various methods for synthesizing and producing ethyl propanoate-derived materials are described. These methods may involve different catalysts, reaction conditions, and starting materials to optimize yield and purity of the desired compounds.
- Applications of ethyl propanoate derivatives in fragrance and flavor industry: Ethyl propanoate-derived materials find extensive use in the fragrance and flavor industry due to their fruity and sweet odor profiles. These compounds are utilized in perfumes, cosmetics, and food additives to impart desirable scents and tastes.
- Ethyl propanoate derivatives as solvents and intermediates: Ethyl propanoate-derived materials serve as important solvents and chemical intermediates in various industrial processes. They are used in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other specialty chemicals due to their unique properties and reactivity.
- Purification and separation techniques for ethyl propanoate derivatives: Various purification and separation techniques are employed to obtain high-purity ethyl propanoate-derived materials. These methods may include distillation, crystallization, and chromatography, among others, to remove impurities and isolate desired compounds.
- Environmental and safety considerations in handling ethyl propanoate derivatives: The handling, storage, and disposal of ethyl propanoate-derived materials require careful consideration of environmental and safety factors. Proper containment, personal protective equipment, and waste management practices are essential to minimize risks associated with these compounds.
02 Applications in fragrance and flavor industry
Ethyl propanoate-derived materials find extensive use in the fragrance and flavor industry. These compounds are utilized as aroma chemicals, flavor enhancers, or as building blocks for creating complex fragrances and flavors in various consumer products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Pharmaceutical applications
Ethyl propanoate-derived materials are employed in pharmaceutical applications. They serve as intermediates or precursors in the synthesis of various drug molecules, active pharmaceutical ingredients, or as excipients in drug formulations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Industrial and chemical applications
Ethyl propanoate-derived materials find use in various industrial and chemical applications. These include their use as solvents, plasticizers, or as intermediates in the production of polymers, resins, and other industrial chemicals.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl propanoate-derived materials. This includes developing eco-friendly production methods, studying biodegradability, and assessing potential health effects of these compounds.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Biodegradable Packaging Industry
The research on ethyl propanoate-derived materials in biodegradable packaging is in an emerging stage, with growing market potential driven by increasing environmental concerns. The global biodegradable packaging market is expanding rapidly, expected to reach $21.6 billion by 2025. Major players like DuPont, BASF, and Novozymes are investing heavily in R&D, leveraging their expertise in biochemistry and materials science. Smaller companies such as Tipa Corp. and Innovative Bottles are also making significant strides, focusing on niche applications. The technology is progressing, but challenges remain in scaling production and improving material properties to match conventional plastics.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed a range of biodegradable packaging materials derived from ethyl propanoate. Their approach involves the polymerization of ethyl propanoate to create a biodegradable polymer with enhanced mechanical properties. The resulting material, known as Bio-PDO (bio-based 1,3-propanediol), is used in the production of Sorona® fibers and other biodegradable packaging solutions[1]. DuPont's process utilizes renewable resources and enzymatic catalysis to produce ethyl propanoate, which is then converted into the final biodegradable material. This method results in a reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by up to 40% compared to traditional petroleum-based materials[2]. The company has also developed proprietary additives to enhance the material's barrier properties and extend shelf life for food packaging applications.
Strengths: Utilizes renewable resources, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and offers enhanced mechanical properties. Weaknesses: May have higher production costs compared to conventional plastics and limited scalability for mass production.
Novozymes A/S
Technical Solution: Novozymes has pioneered enzymatic processes for the production of ethyl propanoate-derived biodegradable materials. Their technology involves the use of specialized enzymes to catalyze the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, resulting in high-purity ethyl propanoate[3]. This bio-based precursor is then polymerized using proprietary biocatalysts to create biodegradable polymers suitable for packaging applications. Novozymes' approach allows for milder reaction conditions, reducing energy consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional chemical synthesis methods[4]. The company has also developed enzyme cocktails that can break down these materials at end-of-life, ensuring complete biodegradability in industrial composting facilities within 12 weeks[5].
Strengths: Energy-efficient production process, high-purity precursors, and enhanced biodegradability. Weaknesses: Reliance on specific enzyme availability and potentially higher material costs.
Core Innovations in Ethyl Propanoate Materials
Biodegradable packaging material, use and method for manufacturing thereof
PatentPendingUS20250229963A1
Innovation
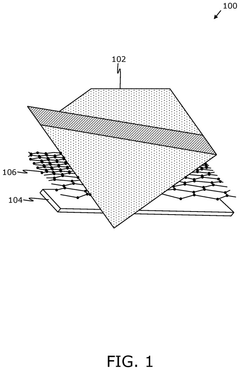
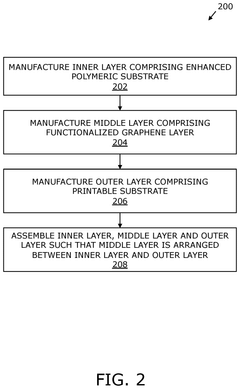
- A biodegradable packaging material comprising an inner layer of enhanced polymeric substrate, a middle layer of functionalized graphene, and an outer layer of printable substrate, which provides enhanced barrier and mechanical properties, and is suitable for anaerobic digestion.
Biodegradable packaging material comprising a biodegradable polymeric composite lamina material having an increased oxygen and fat/oil barrier
PatentWO2024165595A1
Innovation
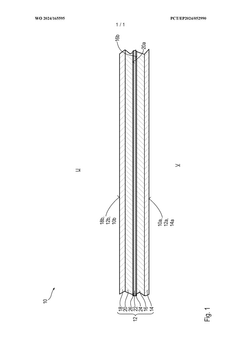
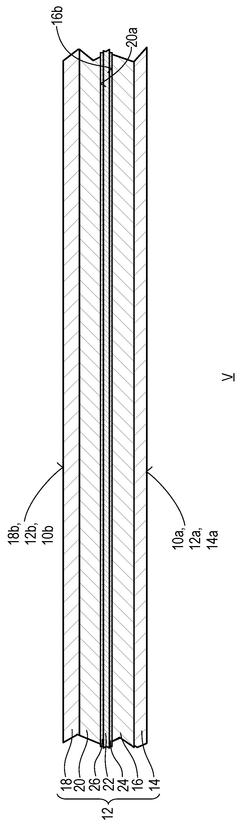
- A biodegradable polymer composite sheet material with layers of biodegradable polymers such as PLA, PBS, PHB, and PVOH, designed to provide enhanced oxygen and fat/oil barriers through coextrusion, ensuring compliance with EN 13432 standards for biodegradability and incorporating adhesion promoter layers for improved adhesion and barrier performance.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of ethyl propanoate-derived materials in biodegradable packaging reveals both promising benefits and potential concerns. These materials offer significant advantages in terms of biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional petroleum-based plastics.
Ethyl propanoate-derived packaging materials demonstrate faster decomposition rates in various environmental conditions, including soil, water, and composting facilities. This rapid biodegradation helps mitigate the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and marine ecosystems, addressing one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time.
The production process of these materials generally requires less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional plastic manufacturing. This contributes to a lower overall carbon footprint throughout the product lifecycle. Additionally, the use of renewable resources in the production of ethyl propanoate-derived materials reduces dependence on finite fossil fuel resources.
However, the environmental impact assessment also highlights some potential drawbacks. The cultivation of crops for raw material production may lead to increased land use and potential competition with food crops. This raises concerns about indirect land-use change and its associated environmental impacts, including deforestation and loss of biodiversity.
Water consumption and potential pollution from agricultural practices used to grow feedstock crops are additional environmental considerations. The use of pesticides and fertilizers in crop cultivation may have negative impacts on soil and water quality if not managed sustainably.
The end-of-life management of these biodegradable materials presents both opportunities and challenges. While they offer improved biodegradability, proper waste management infrastructure is crucial to ensure these materials are disposed of in environments where they can effectively biodegrade. Improper disposal may lead to unintended consequences, such as methane emissions in landfills.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) of ethyl propanoate-derived packaging materials show varying results depending on specific production methods and disposal scenarios. Generally, these materials demonstrate lower environmental impacts in categories such as global warming potential and fossil resource depletion. However, they may show higher impacts in categories related to land use and eutrophication potential.
In conclusion, while ethyl propanoate-derived materials in biodegradable packaging offer significant environmental benefits, particularly in addressing plastic pollution and reducing reliance on fossil fuels, their widespread adoption requires careful consideration of the entire life cycle impacts. Continued research and development are necessary to optimize production processes, improve material properties, and establish effective end-of-life management strategies to maximize the environmental benefits of these innovative packaging solutions.
Ethyl propanoate-derived packaging materials demonstrate faster decomposition rates in various environmental conditions, including soil, water, and composting facilities. This rapid biodegradation helps mitigate the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and marine ecosystems, addressing one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time.
The production process of these materials generally requires less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional plastic manufacturing. This contributes to a lower overall carbon footprint throughout the product lifecycle. Additionally, the use of renewable resources in the production of ethyl propanoate-derived materials reduces dependence on finite fossil fuel resources.
However, the environmental impact assessment also highlights some potential drawbacks. The cultivation of crops for raw material production may lead to increased land use and potential competition with food crops. This raises concerns about indirect land-use change and its associated environmental impacts, including deforestation and loss of biodiversity.
Water consumption and potential pollution from agricultural practices used to grow feedstock crops are additional environmental considerations. The use of pesticides and fertilizers in crop cultivation may have negative impacts on soil and water quality if not managed sustainably.
The end-of-life management of these biodegradable materials presents both opportunities and challenges. While they offer improved biodegradability, proper waste management infrastructure is crucial to ensure these materials are disposed of in environments where they can effectively biodegrade. Improper disposal may lead to unintended consequences, such as methane emissions in landfills.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) of ethyl propanoate-derived packaging materials show varying results depending on specific production methods and disposal scenarios. Generally, these materials demonstrate lower environmental impacts in categories such as global warming potential and fossil resource depletion. However, they may show higher impacts in categories related to land use and eutrophication potential.
In conclusion, while ethyl propanoate-derived materials in biodegradable packaging offer significant environmental benefits, particularly in addressing plastic pollution and reducing reliance on fossil fuels, their widespread adoption requires careful consideration of the entire life cycle impacts. Continued research and development are necessary to optimize production processes, improve material properties, and establish effective end-of-life management strategies to maximize the environmental benefits of these innovative packaging solutions.
Regulatory Framework for Bioplastics
The regulatory framework for bioplastics plays a crucial role in shaping the development and adoption of biodegradable packaging materials, including those derived from ethyl propanoate. As the global focus on sustainability intensifies, governments and international organizations are establishing guidelines and standards to ensure the safety, efficacy, and environmental impact of these innovative materials.
In the European Union, the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) has developed EN 13432, a harmonized standard for compostable and biodegradable packaging. This standard sets specific requirements for packaging recoverable through composting and biodegradation, including criteria for biodegradability, disintegration, and absence of ecotoxicity. Materials derived from ethyl propanoate must meet these stringent criteria to be certified as compostable in the EU market.
The United States has a more fragmented approach, with regulations varying at federal, state, and local levels. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) provides guidelines on environmental marketing claims, including those related to biodegradability and compostability. Additionally, states like California have enacted their own regulations, such as SB 567, which sets strict standards for labeling products as "biodegradable" or "compostable."
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have established certification systems for biodegradable plastics. Japan's BiomassPla mark and South Korea's EL724 standard provide frameworks for evaluating and certifying bioplastic materials, including those potentially derived from ethyl propanoate.
International standards, such as ISO 17088 for compostable plastics, provide a global benchmark for biodegradable materials. These standards ensure consistency in testing methods and performance criteria across different regions, facilitating international trade and adoption of innovative packaging solutions.
Regulatory bodies are also addressing the end-of-life management of bioplastics. The EU's Waste Framework Directive and Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive are being updated to include specific provisions for biodegradable and compostable plastics, emphasizing the importance of proper waste management infrastructure.
As research on ethyl propanoate-derived materials progresses, manufacturers must navigate this complex regulatory landscape. Compliance with these regulations not only ensures market access but also builds consumer trust in the environmental claims of biodegradable packaging products. The evolving nature of these regulations underscores the need for ongoing collaboration between researchers, industry stakeholders, and policymakers to create a supportive framework for sustainable packaging innovations.
In the European Union, the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) has developed EN 13432, a harmonized standard for compostable and biodegradable packaging. This standard sets specific requirements for packaging recoverable through composting and biodegradation, including criteria for biodegradability, disintegration, and absence of ecotoxicity. Materials derived from ethyl propanoate must meet these stringent criteria to be certified as compostable in the EU market.
The United States has a more fragmented approach, with regulations varying at federal, state, and local levels. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) provides guidelines on environmental marketing claims, including those related to biodegradability and compostability. Additionally, states like California have enacted their own regulations, such as SB 567, which sets strict standards for labeling products as "biodegradable" or "compostable."
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have established certification systems for biodegradable plastics. Japan's BiomassPla mark and South Korea's EL724 standard provide frameworks for evaluating and certifying bioplastic materials, including those potentially derived from ethyl propanoate.
International standards, such as ISO 17088 for compostable plastics, provide a global benchmark for biodegradable materials. These standards ensure consistency in testing methods and performance criteria across different regions, facilitating international trade and adoption of innovative packaging solutions.
Regulatory bodies are also addressing the end-of-life management of bioplastics. The EU's Waste Framework Directive and Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive are being updated to include specific provisions for biodegradable and compostable plastics, emphasizing the importance of proper waste management infrastructure.
As research on ethyl propanoate-derived materials progresses, manufacturers must navigate this complex regulatory landscape. Compliance with these regulations not only ensures market access but also builds consumer trust in the environmental claims of biodegradable packaging products. The evolving nature of these regulations underscores the need for ongoing collaboration between researchers, industry stakeholders, and policymakers to create a supportive framework for sustainable packaging innovations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!