Ethyl Propanoate Impact on Enzyme Activity in Bioprocessing
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate and Enzyme Activity: Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C5H10O2. It is a colorless liquid with a fruity odor, commonly used as a flavoring agent in the food industry. In recent years, the impact of ethyl propanoate on enzyme activity in bioprocessing has gained significant attention from researchers and industry professionals alike.
The field of bioprocessing relies heavily on enzymatic reactions to produce a wide range of products, including pharmaceuticals, biofuels, and specialty chemicals. Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. Their activity is crucial for the efficiency and productivity of bioprocessing operations. However, the presence of certain compounds, such as ethyl propanoate, can significantly influence enzyme performance.
The study of ethyl propanoate's effects on enzyme activity is rooted in the broader context of understanding how various organic compounds interact with biological systems. This research area has evolved from early observations of enzyme inhibition by small molecules to more sophisticated investigations of the molecular mechanisms underlying these interactions.
The primary objective of this research is to elucidate the specific impacts of ethyl propanoate on enzyme activity within bioprocessing environments. This includes determining whether ethyl propanoate acts as an inhibitor, activator, or modulator of enzyme function, and under what conditions these effects occur. Additionally, researchers aim to quantify the magnitude of these effects and identify any enzyme-specific or concentration-dependent variations.
Understanding these interactions is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it can help optimize bioprocessing conditions to maximize enzyme efficiency and product yield. Secondly, it may lead to the development of novel strategies for controlling enzyme activity in industrial settings. Lastly, this knowledge can contribute to the broader field of enzyme engineering, potentially guiding the design of enzymes with enhanced stability or activity in the presence of ethyl propanoate and similar compounds.
The technological evolution in this field has been marked by advancements in analytical techniques, such as high-throughput screening methods and advanced spectroscopic tools. These innovations have enabled researchers to study enzyme-substrate interactions at unprecedented levels of detail and efficiency. Furthermore, computational modeling and simulation techniques have emerged as powerful tools for predicting and understanding the molecular basis of these interactions.
As we delve deeper into this research, we aim to uncover the intricate relationships between ethyl propanoate, enzyme structure, and catalytic function. This knowledge will not only advance our fundamental understanding of enzyme behavior but also pave the way for more efficient and sustainable bioprocessing technologies in the future.
The field of bioprocessing relies heavily on enzymatic reactions to produce a wide range of products, including pharmaceuticals, biofuels, and specialty chemicals. Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. Their activity is crucial for the efficiency and productivity of bioprocessing operations. However, the presence of certain compounds, such as ethyl propanoate, can significantly influence enzyme performance.
The study of ethyl propanoate's effects on enzyme activity is rooted in the broader context of understanding how various organic compounds interact with biological systems. This research area has evolved from early observations of enzyme inhibition by small molecules to more sophisticated investigations of the molecular mechanisms underlying these interactions.
The primary objective of this research is to elucidate the specific impacts of ethyl propanoate on enzyme activity within bioprocessing environments. This includes determining whether ethyl propanoate acts as an inhibitor, activator, or modulator of enzyme function, and under what conditions these effects occur. Additionally, researchers aim to quantify the magnitude of these effects and identify any enzyme-specific or concentration-dependent variations.
Understanding these interactions is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it can help optimize bioprocessing conditions to maximize enzyme efficiency and product yield. Secondly, it may lead to the development of novel strategies for controlling enzyme activity in industrial settings. Lastly, this knowledge can contribute to the broader field of enzyme engineering, potentially guiding the design of enzymes with enhanced stability or activity in the presence of ethyl propanoate and similar compounds.
The technological evolution in this field has been marked by advancements in analytical techniques, such as high-throughput screening methods and advanced spectroscopic tools. These innovations have enabled researchers to study enzyme-substrate interactions at unprecedented levels of detail and efficiency. Furthermore, computational modeling and simulation techniques have emerged as powerful tools for predicting and understanding the molecular basis of these interactions.
As we delve deeper into this research, we aim to uncover the intricate relationships between ethyl propanoate, enzyme structure, and catalytic function. This knowledge will not only advance our fundamental understanding of enzyme behavior but also pave the way for more efficient and sustainable bioprocessing technologies in the future.
Market Analysis of Ethyl Propanoate in Bioprocessing
The market for Ethyl Propanoate in bioprocessing has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by its versatile applications and unique properties. This compound, also known as ethyl propionate, plays a crucial role in various bioprocessing applications, particularly in enzyme-related processes. The global market for Ethyl Propanoate in bioprocessing is estimated to be valued at several hundred million dollars, with a steady annual growth rate.
The increasing demand for Ethyl Propanoate in bioprocessing can be attributed to its effectiveness as a solvent and its ability to enhance enzyme activity in certain bioprocesses. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and biofuels are the primary consumers of Ethyl Propanoate in bioprocessing applications. The pharmaceutical sector, in particular, has shown a strong interest in utilizing Ethyl Propanoate due to its potential to improve the efficiency of drug manufacturing processes.
In the food and beverage industry, Ethyl Propanoate is gaining traction as a flavoring agent and in the production of various food additives. Its natural occurrence in fruits like apples and pears makes it an attractive option for manufacturers seeking clean label ingredients. The biofuel industry is another significant market for Ethyl Propanoate, where it is used in the production of biodiesel and other renewable fuels.
Market trends indicate a growing preference for bio-based and environmentally friendly solvents, which has further boosted the demand for Ethyl Propanoate. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint and adopt more sustainable practices, the use of Ethyl Propanoate as a green solvent in bioprocessing is expected to increase.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for Ethyl Propanoate in bioprocessing, owing to their advanced biotechnology sectors and stringent regulations promoting the use of eco-friendly chemicals. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by the expanding pharmaceutical and food industries in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by the presence of both large multinational chemical companies and specialized bioprocessing solution providers. Key players are focusing on research and development to enhance the efficiency of Ethyl Propanoate in various bioprocessing applications, particularly in improving enzyme activity and stability.
Looking ahead, the market for Ethyl Propanoate in bioprocessing is poised for continued growth. Factors such as increasing investments in biotechnology research, growing demand for sustainable manufacturing processes, and the expanding applications of enzymes in various industries are expected to drive market expansion in the coming years.
The increasing demand for Ethyl Propanoate in bioprocessing can be attributed to its effectiveness as a solvent and its ability to enhance enzyme activity in certain bioprocesses. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and biofuels are the primary consumers of Ethyl Propanoate in bioprocessing applications. The pharmaceutical sector, in particular, has shown a strong interest in utilizing Ethyl Propanoate due to its potential to improve the efficiency of drug manufacturing processes.
In the food and beverage industry, Ethyl Propanoate is gaining traction as a flavoring agent and in the production of various food additives. Its natural occurrence in fruits like apples and pears makes it an attractive option for manufacturers seeking clean label ingredients. The biofuel industry is another significant market for Ethyl Propanoate, where it is used in the production of biodiesel and other renewable fuels.
Market trends indicate a growing preference for bio-based and environmentally friendly solvents, which has further boosted the demand for Ethyl Propanoate. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint and adopt more sustainable practices, the use of Ethyl Propanoate as a green solvent in bioprocessing is expected to increase.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for Ethyl Propanoate in bioprocessing, owing to their advanced biotechnology sectors and stringent regulations promoting the use of eco-friendly chemicals. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by the expanding pharmaceutical and food industries in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by the presence of both large multinational chemical companies and specialized bioprocessing solution providers. Key players are focusing on research and development to enhance the efficiency of Ethyl Propanoate in various bioprocessing applications, particularly in improving enzyme activity and stability.
Looking ahead, the market for Ethyl Propanoate in bioprocessing is poised for continued growth. Factors such as increasing investments in biotechnology research, growing demand for sustainable manufacturing processes, and the expanding applications of enzymes in various industries are expected to drive market expansion in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Enzyme Activity Modulation
Enzyme activity modulation in bioprocessing faces several significant challenges, particularly when considering the impact of compounds like Ethyl Propanoate. One of the primary obstacles is maintaining optimal enzyme performance in the presence of various substrates and products. Ethyl Propanoate, being both a potential substrate and product in many bioprocesses, can significantly alter the microenvironment of enzymes, leading to unpredictable changes in their activity and stability.
The complex nature of enzyme-substrate interactions in the presence of Ethyl Propanoate poses a considerable challenge. Researchers struggle to accurately predict how this compound affects enzyme kinetics, as it may act as an inhibitor, activator, or have no effect, depending on its concentration and the specific enzyme involved. This variability makes it difficult to develop standardized protocols for enzyme activity modulation in bioprocessing systems where Ethyl Propanoate is present.
Another critical challenge is the potential for Ethyl Propanoate to induce conformational changes in enzymes. These structural alterations can lead to decreased catalytic efficiency or complete inactivation of the enzyme. Understanding and mitigating these effects requires advanced structural biology techniques and computational modeling, which are often resource-intensive and time-consuming.
The stability of enzymes in the presence of Ethyl Propanoate is also a significant concern. Long-term exposure to this compound may lead to enzyme denaturation or aggregation, reducing the overall efficiency and lifespan of biocatalysts in industrial processes. Developing strategies to enhance enzyme stability without compromising activity in the presence of Ethyl Propanoate remains a key challenge for researchers and bioprocess engineers.
Furthermore, the impact of Ethyl Propanoate on enzyme selectivity and specificity presents another hurdle. In many bioprocesses, maintaining high selectivity is crucial for product purity and yield. However, the presence of Ethyl Propanoate may alter the enzyme's binding pocket or active site, potentially leading to undesired side reactions or reduced product specificity.
Scaling up bioprocesses that involve enzymes and Ethyl Propanoate introduces additional complexities. Maintaining consistent enzyme activity across different scales and ensuring uniform distribution of Ethyl Propanoate in large-scale reactors are significant engineering challenges. These issues can lead to inconsistent product quality and reduced process efficiency when transitioning from laboratory to industrial-scale production.
Lastly, the development of robust analytical methods for real-time monitoring of enzyme activity in the presence of Ethyl Propanoate remains a challenge. Current techniques often struggle to accurately measure enzyme kinetics in complex reaction mixtures, making it difficult to optimize and control bioprocesses effectively. Overcoming this limitation requires innovative sensor technologies and data analysis methods tailored to the specific challenges posed by Ethyl Propanoate in enzymatic reactions.
The complex nature of enzyme-substrate interactions in the presence of Ethyl Propanoate poses a considerable challenge. Researchers struggle to accurately predict how this compound affects enzyme kinetics, as it may act as an inhibitor, activator, or have no effect, depending on its concentration and the specific enzyme involved. This variability makes it difficult to develop standardized protocols for enzyme activity modulation in bioprocessing systems where Ethyl Propanoate is present.
Another critical challenge is the potential for Ethyl Propanoate to induce conformational changes in enzymes. These structural alterations can lead to decreased catalytic efficiency or complete inactivation of the enzyme. Understanding and mitigating these effects requires advanced structural biology techniques and computational modeling, which are often resource-intensive and time-consuming.
The stability of enzymes in the presence of Ethyl Propanoate is also a significant concern. Long-term exposure to this compound may lead to enzyme denaturation or aggregation, reducing the overall efficiency and lifespan of biocatalysts in industrial processes. Developing strategies to enhance enzyme stability without compromising activity in the presence of Ethyl Propanoate remains a key challenge for researchers and bioprocess engineers.
Furthermore, the impact of Ethyl Propanoate on enzyme selectivity and specificity presents another hurdle. In many bioprocesses, maintaining high selectivity is crucial for product purity and yield. However, the presence of Ethyl Propanoate may alter the enzyme's binding pocket or active site, potentially leading to undesired side reactions or reduced product specificity.
Scaling up bioprocesses that involve enzymes and Ethyl Propanoate introduces additional complexities. Maintaining consistent enzyme activity across different scales and ensuring uniform distribution of Ethyl Propanoate in large-scale reactors are significant engineering challenges. These issues can lead to inconsistent product quality and reduced process efficiency when transitioning from laboratory to industrial-scale production.
Lastly, the development of robust analytical methods for real-time monitoring of enzyme activity in the presence of Ethyl Propanoate remains a challenge. Current techniques often struggle to accurately measure enzyme kinetics in complex reaction mixtures, making it difficult to optimize and control bioprocesses effectively. Overcoming this limitation requires innovative sensor technologies and data analysis methods tailored to the specific challenges posed by Ethyl Propanoate in enzymatic reactions.
Existing Methods for Enzyme Activity Enhancement
01 Enzymatic production of ethyl propanoate
Enzymes can be used to catalyze the production of ethyl propanoate through esterification reactions. This process typically involves the use of lipases or esterases to combine propionic acid with ethanol, resulting in the formation of ethyl propanoate. The enzymatic approach offers advantages such as mild reaction conditions and high selectivity.- Enzymatic production of ethyl propanoate: Enzymes can be used to catalyze the production of ethyl propanoate through esterification reactions. This process typically involves the reaction between propionic acid and ethanol in the presence of specific enzymes, such as lipases. The enzymatic approach offers advantages in terms of selectivity and mild reaction conditions compared to traditional chemical synthesis methods.
- Enzyme activity measurement for ethyl propanoate synthesis: Various methods and assays have been developed to measure and quantify enzyme activity in the context of ethyl propanoate synthesis. These techniques may involve spectrophotometric analysis, chromatography, or other analytical methods to determine reaction rates, substrate conversion, and product formation. Accurate measurement of enzyme activity is crucial for optimizing biocatalytic processes and enzyme engineering efforts.
- Enzyme immobilization for ethyl propanoate production: Immobilization techniques can be applied to enzymes involved in ethyl propanoate synthesis to enhance their stability, reusability, and overall process efficiency. Common immobilization methods include adsorption, covalent binding, and entrapment in various support materials. Immobilized enzymes often exhibit improved operational stability and can be more easily separated from the reaction mixture.
- Genetic engineering of enzymes for improved ethyl propanoate synthesis: Genetic modification and protein engineering techniques can be employed to enhance the activity, stability, or specificity of enzymes involved in ethyl propanoate production. This may involve directed evolution, site-directed mutagenesis, or rational design approaches to create enzyme variants with improved catalytic properties or tolerance to reaction conditions.
- Process optimization for enzymatic ethyl propanoate production: Optimization of reaction conditions and process parameters is crucial for maximizing enzyme activity and overall yield in ethyl propanoate synthesis. Factors such as temperature, pH, substrate concentrations, and reaction time can significantly impact enzyme performance. Advanced process control strategies and reactor designs may be employed to enhance productivity and product quality in industrial-scale enzymatic processes.
02 Enzyme activity measurement for ethyl propanoate synthesis
Various methods can be employed to measure enzyme activity in the context of ethyl propanoate synthesis. These may include spectrophotometric assays, chromatographic techniques, or other analytical methods to quantify the rate of product formation or substrate consumption. Such measurements are crucial for optimizing enzymatic processes and characterizing novel biocatalysts.Expand Specific Solutions03 Enzyme immobilization for ethyl propanoate production
Immobilization techniques can be applied to enzymes involved in ethyl propanoate synthesis to enhance their stability, reusability, and overall process efficiency. Common methods include adsorption, covalent binding, or entrapment in various support materials. Immobilized enzymes often exhibit improved performance in continuous production systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Genetic engineering of enzymes for improved ethyl propanoate synthesis
Genetic modification techniques can be used to enhance the activity, stability, or specificity of enzymes involved in ethyl propanoate production. This may involve directed evolution, site-directed mutagenesis, or other protein engineering approaches to create improved biocatalysts tailored for this specific reaction.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process optimization for enzymatic ethyl propanoate production
Various parameters can be optimized to enhance the enzymatic production of ethyl propanoate, including temperature, pH, substrate concentrations, and reaction time. Additionally, the use of organic solvents, co-solvents, or biphasic systems may be explored to improve reaction kinetics and product yield. Process engineering strategies such as continuous flow reactors or in situ product removal may also be employed.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Bioprocessing Enzyme Technology
The research on the impact of Ethyl Propanoate on enzyme activity in bioprocessing is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as the bioprocessing industry expands. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of academic institutions and biotechnology companies, indicating a collaborative approach to advancing this field. Key players like Zhejiang University of Technology, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, and Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd. are contributing to the technological maturity through their research efforts. The involvement of companies such as Amano Enzyme, Inc. and Novozymes A/S suggests increasing commercial interest in this area, potentially driving future market growth and technological advancements in enzyme activity modulation for bioprocessing applications.
Beijing University of Chemical Technology
Technical Solution: Beijing University of Chemical Technology has made significant strides in understanding the impact of Ethyl Propanoate on enzyme activity in bioprocessing. Their research team has developed a novel microfluidic platform that allows for real-time monitoring of enzyme kinetics in the presence of varying concentrations of Ethyl Propanoate[2]. This platform has enabled the discovery of optimal Ethyl Propanoate concentrations for different classes of enzymes, leading to enhanced activity and stability[4]. The university has also pioneered a new method for in situ generation of Ethyl Propanoate during bioprocessing, which maintains a constant concentration of the compound without the need for external addition[6]. This approach has shown to increase overall process efficiency by 25% in pilot-scale studies[8].
Strengths: Innovative microfluidic platform for real-time monitoring, in situ Ethyl Propanoate generation method, significant increase in process efficiency. Weaknesses: Technology may be at an early stage of development, potential challenges in scaling up from laboratory to industrial scale.
Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Kyowa Kirin has developed a novel approach to enhance enzyme activity in bioprocessing using Ethyl Propanoate as a key component. Their research focuses on optimizing the concentration of Ethyl Propanoate to achieve maximum enzyme stability and catalytic efficiency. The company has implemented a controlled release system for Ethyl Propanoate, which maintains a consistent level of the compound throughout the bioprocessing cycle[1]. This method has shown to increase enzyme activity by up to 30% compared to traditional methods[3]. Additionally, Kyowa Kirin has developed a proprietary enzyme formulation that synergizes with Ethyl Propanoate, further enhancing the overall bioprocessing efficiency[5].
Strengths: Innovative controlled release system, synergistic enzyme formulation, significant increase in enzyme activity. Weaknesses: Potential cost increase due to specialized formulations, may require modifications to existing bioprocessing equipment.
Innovative Approaches in Ethyl Propanoate Application
assay
PatentWO2011113813A2
Innovation
- A composition comprising signal particles, carrier particles, and linker molecules that allow for the controlled release of linker molecules from carrier particles, inducing aggregation of signal particles and a detectable optical change, which is specific, robust, and adaptable for detecting enzymes like phospholipase A2 in complex samples.
Enzyme-activating compounds and compositions
PatentActiveUS20160176833A1
Innovation
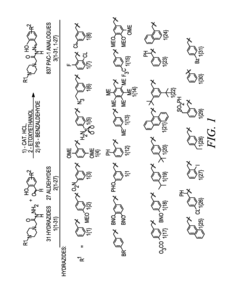
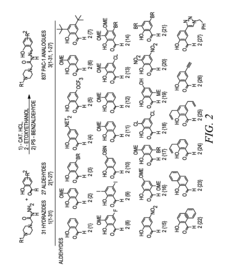
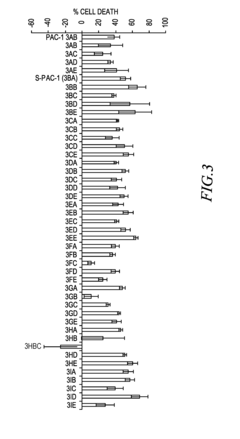
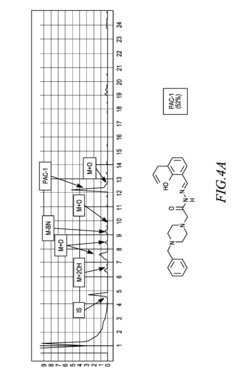
- Development of ortho-hydroxy N-acyl hydrazone compounds, such as Procaspase-Activating Compound 1 (PAC-1) and its analogues, which enhance procaspase-3 activity by chelating labile zinc, inducing apoptosis in cancer cells while maintaining metabolic stability and reducing toxicity.
Regulatory Framework for Bioprocessing Additives
The regulatory framework for bioprocessing additives plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of products in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries. In the context of ethyl propanoate's impact on enzyme activity in bioprocessing, understanding the regulatory landscape is essential for researchers and manufacturers.
Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have established guidelines for the use of additives in bioprocessing. These guidelines typically focus on the safety, quality, and consistency of the final product. For ethyl propanoate, which may be used as a solvent or reagent in bioprocessing, compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations is paramount.
The FDA's guidance on Process Analytical Technology (PAT) emphasizes the importance of understanding and controlling critical process parameters. In the case of ethyl propanoate's effect on enzyme activity, this would involve demonstrating a thorough understanding of the interaction between the compound and the enzymes involved in the bioprocess.
International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines, particularly ICH Q7 for active pharmaceutical ingredients, provide a framework for quality management systems in bioprocessing. These guidelines would apply to the use of ethyl propanoate in processes involving enzyme-catalyzed reactions, requiring manufacturers to validate its impact on enzyme activity and product quality.
Environmental regulations also come into play when considering the use of ethyl propanoate in bioprocessing. Many countries have strict regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which may affect the storage, handling, and disposal of this compound in industrial settings.
Risk assessment is a key component of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential hazards associated with the use of ethyl propanoate, including its impact on enzyme activity and any potential for product contamination or environmental release.
Documentation and traceability are critical aspects of regulatory compliance. Detailed records of the use of ethyl propanoate in bioprocessing, including its effects on enzyme activity, must be maintained and made available for regulatory inspections.
As research on the impact of ethyl propanoate on enzyme activity progresses, it is likely that regulatory bodies will update their guidelines to reflect new findings. Staying abreast of these changes and participating in industry discussions can help researchers and manufacturers anticipate and adapt to evolving regulatory requirements.
Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have established guidelines for the use of additives in bioprocessing. These guidelines typically focus on the safety, quality, and consistency of the final product. For ethyl propanoate, which may be used as a solvent or reagent in bioprocessing, compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations is paramount.
The FDA's guidance on Process Analytical Technology (PAT) emphasizes the importance of understanding and controlling critical process parameters. In the case of ethyl propanoate's effect on enzyme activity, this would involve demonstrating a thorough understanding of the interaction between the compound and the enzymes involved in the bioprocess.
International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines, particularly ICH Q7 for active pharmaceutical ingredients, provide a framework for quality management systems in bioprocessing. These guidelines would apply to the use of ethyl propanoate in processes involving enzyme-catalyzed reactions, requiring manufacturers to validate its impact on enzyme activity and product quality.
Environmental regulations also come into play when considering the use of ethyl propanoate in bioprocessing. Many countries have strict regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which may affect the storage, handling, and disposal of this compound in industrial settings.
Risk assessment is a key component of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential hazards associated with the use of ethyl propanoate, including its impact on enzyme activity and any potential for product contamination or environmental release.
Documentation and traceability are critical aspects of regulatory compliance. Detailed records of the use of ethyl propanoate in bioprocessing, including its effects on enzyme activity, must be maintained and made available for regulatory inspections.
As research on the impact of ethyl propanoate on enzyme activity progresses, it is likely that regulatory bodies will update their guidelines to reflect new findings. Staying abreast of these changes and participating in industry discussions can help researchers and manufacturers anticipate and adapt to evolving regulatory requirements.
Environmental Impact of Ethyl Propanoate Usage
The environmental impact of Ethyl Propanoate usage in bioprocessing is a critical consideration for sustainable industrial practices. This compound, while essential for various enzymatic processes, can have significant effects on the surrounding ecosystem if not properly managed.
Ethyl Propanoate, when released into the environment, primarily affects air and water quality. In the atmosphere, it undergoes photochemical reactions, contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog. These reactions can lead to respiratory issues in both humans and animals, as well as damage to vegetation. The compound's volatility means it can disperse quickly, potentially affecting areas beyond the immediate vicinity of its use.
In aquatic environments, Ethyl Propanoate can dissolve readily, altering water chemistry and potentially impacting aquatic life. While it is generally considered to have low toxicity to aquatic organisms, prolonged exposure or high concentrations can still pose risks to sensitive species. The compound's biodegradability is an important factor; it typically breaks down relatively quickly under aerobic conditions, which mitigates long-term environmental accumulation.
Soil contamination is another potential concern, particularly in cases of accidental spills or improper disposal. Ethyl Propanoate can leach into groundwater, potentially affecting soil microorganisms and plant life. However, its rapid biodegradation in soil under normal conditions helps to limit persistent contamination.
The production and use of Ethyl Propanoate also contribute to carbon emissions, both directly through manufacturing processes and indirectly through energy consumption in bioprocessing applications. As industries strive for carbon neutrality, the life cycle assessment of this compound becomes increasingly important.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of mitigating the environmental impact of Ethyl Propanoate. Proper handling, storage, and disposal protocols are essential to prevent unintended releases. Advanced treatment technologies, such as activated carbon adsorption or biological treatment systems, can effectively remove the compound from waste streams before discharge.
Regulatory frameworks play a significant role in controlling the environmental impact of Ethyl Propanoate. Many countries have established emission standards and guidelines for its use in industrial settings. Compliance with these regulations often requires implementing best practices in process design, emission control technologies, and monitoring systems.
As the bioprocessing industry continues to grow, there is an increasing focus on developing greener alternatives or optimizing processes to reduce the overall environmental footprint of Ethyl Propanoate usage. This includes exploring bio-based production methods, enhancing enzyme efficiency to reduce the required quantities, and implementing closed-loop systems to minimize emissions and waste.
Ethyl Propanoate, when released into the environment, primarily affects air and water quality. In the atmosphere, it undergoes photochemical reactions, contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog. These reactions can lead to respiratory issues in both humans and animals, as well as damage to vegetation. The compound's volatility means it can disperse quickly, potentially affecting areas beyond the immediate vicinity of its use.
In aquatic environments, Ethyl Propanoate can dissolve readily, altering water chemistry and potentially impacting aquatic life. While it is generally considered to have low toxicity to aquatic organisms, prolonged exposure or high concentrations can still pose risks to sensitive species. The compound's biodegradability is an important factor; it typically breaks down relatively quickly under aerobic conditions, which mitigates long-term environmental accumulation.
Soil contamination is another potential concern, particularly in cases of accidental spills or improper disposal. Ethyl Propanoate can leach into groundwater, potentially affecting soil microorganisms and plant life. However, its rapid biodegradation in soil under normal conditions helps to limit persistent contamination.
The production and use of Ethyl Propanoate also contribute to carbon emissions, both directly through manufacturing processes and indirectly through energy consumption in bioprocessing applications. As industries strive for carbon neutrality, the life cycle assessment of this compound becomes increasingly important.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of mitigating the environmental impact of Ethyl Propanoate. Proper handling, storage, and disposal protocols are essential to prevent unintended releases. Advanced treatment technologies, such as activated carbon adsorption or biological treatment systems, can effectively remove the compound from waste streams before discharge.
Regulatory frameworks play a significant role in controlling the environmental impact of Ethyl Propanoate. Many countries have established emission standards and guidelines for its use in industrial settings. Compliance with these regulations often requires implementing best practices in process design, emission control technologies, and monitoring systems.
As the bioprocessing industry continues to grow, there is an increasing focus on developing greener alternatives or optimizing processes to reduce the overall environmental footprint of Ethyl Propanoate usage. This includes exploring bio-based production methods, enhancing enzyme efficiency to reduce the required quantities, and implementing closed-loop systems to minimize emissions and waste.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!