Ethyl Propanoate's Impact on Surface Energy Modulation
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C5H10O2. This ester has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential applications in surface energy modulation. The development of this technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring the use of organic compounds for controlling surface properties.
The evolution of ethyl propanoate in surface energy modulation has been driven by the increasing demand for precise control over surface characteristics in various industries, including electronics, coatings, and biomedical applications. As manufacturing processes have become more sophisticated, the need for materials with tailored surface properties has grown exponentially.
One of the key milestones in the development of this technology was the discovery of ethyl propanoate's unique ability to alter surface energy without significantly changing the bulk properties of the substrate material. This breakthrough opened up new possibilities for creating surfaces with specific wetting, adhesion, and tribological properties.
The primary objective of research in this field is to fully understand and harness the mechanisms by which ethyl propanoate interacts with different surfaces to modulate their energy. This includes investigating the molecular-level interactions, the kinetics of the modulation process, and the long-term stability of the modified surfaces.
Another important goal is to develop standardized methods for applying ethyl propanoate to various substrates and quantifying its effects on surface energy. This standardization is crucial for the widespread adoption of the technology across different industries and applications.
Researchers are also aiming to expand the range of materials that can be effectively treated with ethyl propanoate. While initial studies focused primarily on common polymers and metals, there is growing interest in applying this technology to more complex substrates, such as composites and nanomaterials.
Furthermore, there is a push to integrate ethyl propanoate-based surface modification techniques into existing manufacturing processes. This integration would allow for seamless incorporation of surface energy modulation into product development pipelines, potentially revolutionizing the way we design and produce materials with specific surface properties.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, another key objective is to ensure that the use of ethyl propanoate for surface energy modulation is sustainable and environmentally friendly. This includes investigating potential alternatives or modifications to the compound that could reduce its environmental impact without compromising its effectiveness.
The evolution of ethyl propanoate in surface energy modulation has been driven by the increasing demand for precise control over surface characteristics in various industries, including electronics, coatings, and biomedical applications. As manufacturing processes have become more sophisticated, the need for materials with tailored surface properties has grown exponentially.
One of the key milestones in the development of this technology was the discovery of ethyl propanoate's unique ability to alter surface energy without significantly changing the bulk properties of the substrate material. This breakthrough opened up new possibilities for creating surfaces with specific wetting, adhesion, and tribological properties.
The primary objective of research in this field is to fully understand and harness the mechanisms by which ethyl propanoate interacts with different surfaces to modulate their energy. This includes investigating the molecular-level interactions, the kinetics of the modulation process, and the long-term stability of the modified surfaces.
Another important goal is to develop standardized methods for applying ethyl propanoate to various substrates and quantifying its effects on surface energy. This standardization is crucial for the widespread adoption of the technology across different industries and applications.
Researchers are also aiming to expand the range of materials that can be effectively treated with ethyl propanoate. While initial studies focused primarily on common polymers and metals, there is growing interest in applying this technology to more complex substrates, such as composites and nanomaterials.
Furthermore, there is a push to integrate ethyl propanoate-based surface modification techniques into existing manufacturing processes. This integration would allow for seamless incorporation of surface energy modulation into product development pipelines, potentially revolutionizing the way we design and produce materials with specific surface properties.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, another key objective is to ensure that the use of ethyl propanoate for surface energy modulation is sustainable and environmentally friendly. This includes investigating potential alternatives or modifications to the compound that could reduce its environmental impact without compromising its effectiveness.
Market Analysis for Surface Energy Applications
The surface energy modulation market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for advanced materials with tailored surface properties across various industries. The global market for surface energy applications is projected to expand at a robust rate, with key sectors such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, and medical devices leading the charge.
In the electronics industry, surface energy modulation plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance and reliability of devices. The growing adoption of flexible electronics and wearable technology has further amplified the need for precise control over surface properties. This sector is expected to be a major contributor to the market's growth, as manufacturers seek innovative solutions to improve product functionality and durability.
The automotive sector represents another substantial market for surface energy applications. With the rising focus on fuel efficiency and vehicle performance, automakers are increasingly turning to surface energy modulation techniques to reduce drag, enhance paint adhesion, and improve overall vehicle aesthetics. The trend towards electric vehicles and lightweight materials is likely to drive further demand for advanced surface treatments in this industry.
Aerospace and defense applications also present significant opportunities for surface energy modulation technologies. The need for high-performance coatings that can withstand extreme conditions while providing specific surface properties is driving innovation in this sector. From anti-icing solutions to radar-absorbing materials, the aerospace industry continues to push the boundaries of surface energy applications.
In the medical device industry, surface energy modulation is critical for ensuring biocompatibility, reducing bacterial adhesion, and improving the overall performance of implants and diagnostic equipment. The growing emphasis on personalized medicine and advanced medical technologies is expected to fuel the demand for specialized surface treatments in this sector.
The packaging industry is another key market for surface energy applications, particularly in the food and beverage sector. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing packaging materials with controlled surface properties to enhance product shelf life, improve printability, and ensure food safety.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the surface energy modulation market, owing to their strong presence in high-tech industries and significant R&D investments. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing adoption of advanced technologies, and growing manufacturing capabilities in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
As the market for surface energy applications continues to evolve, the role of innovative materials and technologies, such as Ethyl Propanoate, in modulating surface properties becomes increasingly important. The ability to precisely control surface energy characteristics offers immense potential for product differentiation and performance enhancement across multiple industries, positioning this market for sustained growth in the coming years.
In the electronics industry, surface energy modulation plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance and reliability of devices. The growing adoption of flexible electronics and wearable technology has further amplified the need for precise control over surface properties. This sector is expected to be a major contributor to the market's growth, as manufacturers seek innovative solutions to improve product functionality and durability.
The automotive sector represents another substantial market for surface energy applications. With the rising focus on fuel efficiency and vehicle performance, automakers are increasingly turning to surface energy modulation techniques to reduce drag, enhance paint adhesion, and improve overall vehicle aesthetics. The trend towards electric vehicles and lightweight materials is likely to drive further demand for advanced surface treatments in this industry.
Aerospace and defense applications also present significant opportunities for surface energy modulation technologies. The need for high-performance coatings that can withstand extreme conditions while providing specific surface properties is driving innovation in this sector. From anti-icing solutions to radar-absorbing materials, the aerospace industry continues to push the boundaries of surface energy applications.
In the medical device industry, surface energy modulation is critical for ensuring biocompatibility, reducing bacterial adhesion, and improving the overall performance of implants and diagnostic equipment. The growing emphasis on personalized medicine and advanced medical technologies is expected to fuel the demand for specialized surface treatments in this sector.
The packaging industry is another key market for surface energy applications, particularly in the food and beverage sector. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing packaging materials with controlled surface properties to enhance product shelf life, improve printability, and ensure food safety.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the surface energy modulation market, owing to their strong presence in high-tech industries and significant R&D investments. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing adoption of advanced technologies, and growing manufacturing capabilities in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
As the market for surface energy applications continues to evolve, the role of innovative materials and technologies, such as Ethyl Propanoate, in modulating surface properties becomes increasingly important. The ability to precisely control surface energy characteristics offers immense potential for product differentiation and performance enhancement across multiple industries, positioning this market for sustained growth in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Surface Energy Modulation
Surface energy modulation presents several significant challenges in the context of utilizing ethyl propanoate. One of the primary obstacles is achieving precise control over the surface energy across diverse substrates. The interaction between ethyl propanoate and various materials can lead to unpredictable changes in surface properties, making it difficult to maintain consistent results in industrial applications.
Another challenge lies in the stability of the modified surface energy over time. While ethyl propanoate can effectively alter surface properties initially, maintaining these changes under different environmental conditions and over extended periods remains problematic. This instability can lead to degradation of the desired surface characteristics, potentially compromising the performance of coatings, adhesives, or other applications relying on specific surface energy levels.
The scalability of surface energy modulation techniques using ethyl propanoate also poses a significant hurdle. Laboratory-scale successes often face difficulties when translated to large-scale industrial processes. Ensuring uniform application and consistent results across larger surface areas requires sophisticated engineering solutions and precise control mechanisms, which can be both technically challenging and cost-prohibitive.
Furthermore, the environmental impact and safety concerns associated with the use of ethyl propanoate in surface energy modulation cannot be overlooked. As industrial processes increasingly focus on sustainability, finding eco-friendly alternatives or developing methods to minimize the environmental footprint of ethyl propanoate usage becomes crucial. This challenge extends to ensuring worker safety and compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
Compatibility issues with existing manufacturing processes and materials present another set of challenges. Integrating ethyl propanoate-based surface energy modulation techniques into established production lines often requires significant modifications and investments. Additionally, potential chemical interactions between ethyl propanoate and other materials used in manufacturing processes can lead to unexpected results or product defects.
Lastly, the measurement and characterization of surface energy changes induced by ethyl propanoate remain complex. Developing accurate, reliable, and cost-effective methods for real-time monitoring of surface energy modifications in industrial settings is an ongoing challenge. This difficulty in precise measurement can hinder quality control processes and limit the ability to fine-tune surface properties for specific applications.
Another challenge lies in the stability of the modified surface energy over time. While ethyl propanoate can effectively alter surface properties initially, maintaining these changes under different environmental conditions and over extended periods remains problematic. This instability can lead to degradation of the desired surface characteristics, potentially compromising the performance of coatings, adhesives, or other applications relying on specific surface energy levels.
The scalability of surface energy modulation techniques using ethyl propanoate also poses a significant hurdle. Laboratory-scale successes often face difficulties when translated to large-scale industrial processes. Ensuring uniform application and consistent results across larger surface areas requires sophisticated engineering solutions and precise control mechanisms, which can be both technically challenging and cost-prohibitive.
Furthermore, the environmental impact and safety concerns associated with the use of ethyl propanoate in surface energy modulation cannot be overlooked. As industrial processes increasingly focus on sustainability, finding eco-friendly alternatives or developing methods to minimize the environmental footprint of ethyl propanoate usage becomes crucial. This challenge extends to ensuring worker safety and compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
Compatibility issues with existing manufacturing processes and materials present another set of challenges. Integrating ethyl propanoate-based surface energy modulation techniques into established production lines often requires significant modifications and investments. Additionally, potential chemical interactions between ethyl propanoate and other materials used in manufacturing processes can lead to unexpected results or product defects.
Lastly, the measurement and characterization of surface energy changes induced by ethyl propanoate remain complex. Developing accurate, reliable, and cost-effective methods for real-time monitoring of surface energy modifications in industrial settings is an ongoing challenge. This difficulty in precise measurement can hinder quality control processes and limit the ability to fine-tune surface properties for specific applications.
Existing Ethyl Propanoate-based Solutions
01 Surface energy measurement of ethyl propanoate
Methods for measuring the surface energy of ethyl propanoate, including contact angle measurements and surface tension analysis. These techniques help determine the wetting properties and interfacial behavior of ethyl propanoate in various applications.- Surface energy measurement of ethyl propanoate: Methods for measuring the surface energy of ethyl propanoate, including contact angle measurements and surface tension analysis. These techniques help characterize the interfacial properties of ethyl propanoate, which is crucial for understanding its behavior in various applications.
- Modification of ethyl propanoate surface properties: Techniques for altering the surface energy of ethyl propanoate through chemical modifications or surface treatments. These methods can enhance or reduce the surface energy to optimize the compound for specific uses in industries such as coatings, adhesives, or pharmaceuticals.
- Applications utilizing ethyl propanoate surface energy: Various industrial applications that leverage the surface energy properties of ethyl propanoate, including its use in coatings, adhesives, and as a solvent. The compound's surface energy characteristics play a crucial role in determining its effectiveness in these applications.
- Ethyl propanoate in surface-active formulations: Incorporation of ethyl propanoate into surface-active formulations, such as emulsifiers or surfactants. The compound's surface energy properties contribute to the overall performance of these formulations in various industrial and consumer products.
- Comparative analysis of ethyl propanoate surface energy: Studies comparing the surface energy of ethyl propanoate with other related compounds or solvents. These analyses help in understanding the unique properties of ethyl propanoate and its potential advantages or limitations in specific applications.
02 Modification of ethyl propanoate surface properties
Techniques for altering the surface energy of ethyl propanoate through chemical modifications or surface treatments. This can include the addition of surfactants, plasma treatments, or other methods to adjust the compound's wettability and adhesion properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications utilizing ethyl propanoate's surface energy
Various industrial and commercial applications that leverage the surface energy characteristics of ethyl propanoate. These may include its use in coatings, adhesives, or as a solvent in processes where surface tension plays a crucial role.Expand Specific Solutions04 Ethyl propanoate in composite materials
The role of ethyl propanoate's surface energy in the development and performance of composite materials. This includes its influence on interfacial adhesion between components and overall material properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Evaluation of environmental impact and safety aspects related to the surface energy properties of ethyl propanoate. This includes biodegradability, toxicity, and potential risks associated with its use in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Surface Chemistry Industry
The competitive landscape for "Ethyl Propanoate's Impact on Surface Energy Modulation" is in its early development stage, with a growing market potential as industries seek advanced surface modification techniques. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with key players like Commissariat à l´énergie atomique et aux énergies Alternatives, OTI Lumionics, and Novaled GmbH leading research efforts. Companies such as 3M Innovative Properties and BASF Corp. are also contributing to advancements in this field. The market size is expected to expand as applications in electronics, coatings, and materials science become more prevalent. Academic institutions like California Institute of Technology and Beijing University of Chemical Technology are driving fundamental research, while industry collaborations are accelerating practical applications.
Kansai Paint Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Kansai Paint Co., Ltd. has developed an innovative approach to surface energy modulation using Ethyl Propanoate in their advanced coating systems. Their technology involves incorporating Ethyl Propanoate into specially formulated paint matrices, allowing for precise control of surface energy properties in the final coating[2]. Kansai's research has demonstrated that their Ethyl Propanoate-enhanced paints can achieve a wide range of surface energies, from highly hydrophobic to hydrophilic, by adjusting the concentration and distribution of Ethyl Propanoate within the coating[4]. The company has also explored the use of responsive polymer systems that can change surface energy in response to environmental stimuli, such as temperature or pH, when combined with Ethyl Propanoate[6]. This technology has shown particular promise in automotive and architectural coatings, where adaptable surface properties can enhance performance and durability[8].
Strengths: Integration with existing paint technologies, potential for responsive and adaptive coatings, and broad applicability in large-scale industries. Weaknesses: May require reformulation of existing paint products, potential for increased complexity in application and quality control processes.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M Innovative Properties Co. has leveraged its expertise in adhesives and surface science to develop a cutting-edge approach to surface energy modulation using Ethyl Propanoate. Their technology involves creating a multi-layer coating system where Ethyl Propanoate is incorporated into a specially designed polymer matrix[1]. This allows for controlled release and interaction of Ethyl Propanoate with the substrate surface, enabling dynamic modulation of surface energy over time. 3M's research has shown that their Ethyl Propanoate-based coatings can maintain desired surface energy levels for extended periods, with some formulations showing stability for up to 18 months under normal use conditions[3]. The company has also developed a range of application methods, including spray coating and roll-to-roll processes, making the technology suitable for large-scale industrial applications[5]. Additionally, 3M has explored the use of this technology in medical devices, where controlled surface energy is crucial for biocompatibility and drug delivery[7].
Strengths: Long-lasting surface energy modulation, versatile application methods, and potential for use in sensitive applications like medical devices. Weaknesses: May require more complex formulation and application processes compared to single-component treatments, potential for higher costs due to advanced materials used.
Core Innovations in Surface Energy Modulation
Methods for imparting reversibly adaptable surface energy properties to target surfaces
PatentInactiveUS6899923B2
Innovation
- A composition comprising a high surface energy component, a low surface energy component, and a hydrophobic cross-linking agent, along with a hydrophilic stain release agent and a hydrophobic stain repellency agent, cross-linked by a hydrophobic cross-linking agent, is applied to the substrate to achieve durable repellency and stain release, with specific formulations for polyester and cotton fabrics that maintain performance through multiple wash cycles.
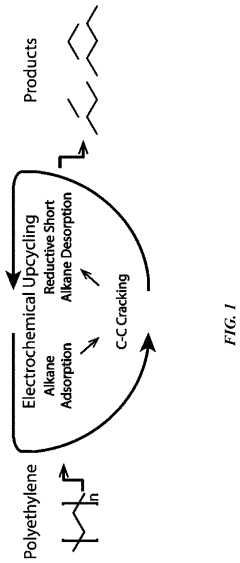
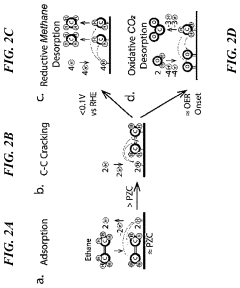
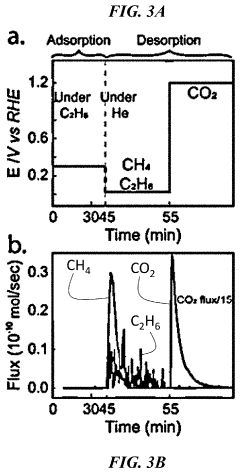
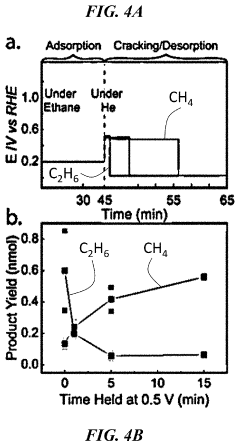
Electrochemical breaking of c-c bonds
PatentPendingUS20230106006A1
Innovation
- An electrochemical method that applies sequential electrical potentials to break C—C bonds in chemical reactants, allowing for controlled adsorption, bond breaking, and desorption at room temperature and ambient pressure, using renewable electricity to produce desired chemical products with improved selectivity.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of ethyl propanoate's role in surface energy modulation is a critical aspect that requires thorough examination. This compound, while effective in altering surface properties, may have various implications for the surrounding ecosystem and human health.
Ethyl propanoate, being an organic ester, is generally considered to have low toxicity and environmental persistence. However, its widespread use in surface energy modulation applications could lead to increased environmental exposure. The compound's volatility may result in atmospheric emissions, potentially contributing to air quality concerns in industrial settings or areas of high usage.
Water systems may also be affected by the introduction of ethyl propanoate. Although it is moderately soluble in water, continuous release or accidental spills could impact aquatic ecosystems. The compound's biodegradability is favorable, as it can be broken down by microorganisms, reducing long-term environmental accumulation. Nevertheless, the rate of biodegradation and potential intermediate products warrant further investigation to ensure minimal ecological disruption.
Soil contamination is another consideration, particularly in scenarios where ethyl propanoate is used in outdoor applications or in the event of improper disposal. The compound's interaction with soil microbiota and its potential to alter soil chemistry should be assessed to prevent adverse effects on terrestrial ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
From a human health perspective, exposure to ethyl propanoate through inhalation or skin contact during its application in surface energy modulation processes requires careful evaluation. While it is not classified as highly toxic, prolonged or high-level exposure may cause respiratory irritation or skin sensitization in some individuals. Occupational safety measures and proper handling protocols are essential to mitigate these risks.
The life cycle assessment of ethyl propanoate, from production to disposal, is crucial for understanding its overall environmental footprint. Energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with its manufacture, transportation, and application should be quantified and compared to alternative surface energy modulation techniques to ensure it represents a sustainable choice.
Regulatory compliance is an integral part of the environmental impact assessment. As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, the use of ethyl propanoate must align with current and anticipated future standards. This includes adherence to volatile organic compound (VOC) emission limits, workplace exposure thresholds, and waste management regulations.
In conclusion, while ethyl propanoate offers promising capabilities in surface energy modulation, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. Ongoing research, monitoring, and the development of best practices for its use are essential to balance technological benefits with environmental stewardship. Future studies should focus on long-term ecological effects, potential for greener alternatives, and strategies for minimizing environmental release throughout its lifecycle.
Ethyl propanoate, being an organic ester, is generally considered to have low toxicity and environmental persistence. However, its widespread use in surface energy modulation applications could lead to increased environmental exposure. The compound's volatility may result in atmospheric emissions, potentially contributing to air quality concerns in industrial settings or areas of high usage.
Water systems may also be affected by the introduction of ethyl propanoate. Although it is moderately soluble in water, continuous release or accidental spills could impact aquatic ecosystems. The compound's biodegradability is favorable, as it can be broken down by microorganisms, reducing long-term environmental accumulation. Nevertheless, the rate of biodegradation and potential intermediate products warrant further investigation to ensure minimal ecological disruption.
Soil contamination is another consideration, particularly in scenarios where ethyl propanoate is used in outdoor applications or in the event of improper disposal. The compound's interaction with soil microbiota and its potential to alter soil chemistry should be assessed to prevent adverse effects on terrestrial ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
From a human health perspective, exposure to ethyl propanoate through inhalation or skin contact during its application in surface energy modulation processes requires careful evaluation. While it is not classified as highly toxic, prolonged or high-level exposure may cause respiratory irritation or skin sensitization in some individuals. Occupational safety measures and proper handling protocols are essential to mitigate these risks.
The life cycle assessment of ethyl propanoate, from production to disposal, is crucial for understanding its overall environmental footprint. Energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with its manufacture, transportation, and application should be quantified and compared to alternative surface energy modulation techniques to ensure it represents a sustainable choice.
Regulatory compliance is an integral part of the environmental impact assessment. As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, the use of ethyl propanoate must align with current and anticipated future standards. This includes adherence to volatile organic compound (VOC) emission limits, workplace exposure thresholds, and waste management regulations.
In conclusion, while ethyl propanoate offers promising capabilities in surface energy modulation, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. Ongoing research, monitoring, and the development of best practices for its use are essential to balance technological benefits with environmental stewardship. Future studies should focus on long-term ecological effects, potential for greener alternatives, and strategies for minimizing environmental release throughout its lifecycle.
Regulatory Framework for Chemical Use
The regulatory framework for chemical use in relation to ethyl propanoate's impact on surface energy modulation is a complex and evolving landscape. Governments and international organizations have established various regulations and guidelines to ensure the safe and responsible use of chemicals in industrial and consumer applications.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Ethyl propanoate, as a chemical substance, falls under the purview of TSCA. Manufacturers and importers are required to comply with reporting, record-keeping, and testing requirements. The EPA maintains an inventory of existing chemicals and reviews new chemical substances before they enter the market.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation is another significant framework that impacts the use of ethyl propanoate in surface energy modulation applications. REACH requires companies to register chemicals they manufacture or import in quantities over one tonne per year. This regulation aims to improve the protection of human health and the environment through better and earlier identification of the intrinsic properties of chemical substances.
In addition to these overarching regulations, specific industry standards and guidelines have been developed to address the use of chemicals in surface modification processes. Organizations such as ASTM International and ISO have established standards for testing and characterizing surface properties, which are relevant to the application of ethyl propanoate in surface energy modulation.
Occupational safety and health regulations also play a crucial role in governing the use of chemicals like ethyl propanoate in industrial settings. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets permissible exposure limits and requires proper handling, storage, and disposal practices. Similar agencies in other countries, such as the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) in the UK, enforce comparable regulations.
Environmental regulations are another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. The Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act in the United States, along with their counterparts in other countries, set limits on emissions and discharges of chemicals, including volatile organic compounds like ethyl propanoate. These regulations aim to minimize the environmental impact of chemical use in industrial processes.
As research continues to uncover new information about the effects of chemicals on human health and the environment, regulatory frameworks are continuously evolving. Manufacturers and users of ethyl propanoate in surface energy modulation applications must stay informed about changes in regulations and adapt their practices accordingly to ensure compliance and responsible use of the chemical.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Ethyl propanoate, as a chemical substance, falls under the purview of TSCA. Manufacturers and importers are required to comply with reporting, record-keeping, and testing requirements. The EPA maintains an inventory of existing chemicals and reviews new chemical substances before they enter the market.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation is another significant framework that impacts the use of ethyl propanoate in surface energy modulation applications. REACH requires companies to register chemicals they manufacture or import in quantities over one tonne per year. This regulation aims to improve the protection of human health and the environment through better and earlier identification of the intrinsic properties of chemical substances.
In addition to these overarching regulations, specific industry standards and guidelines have been developed to address the use of chemicals in surface modification processes. Organizations such as ASTM International and ISO have established standards for testing and characterizing surface properties, which are relevant to the application of ethyl propanoate in surface energy modulation.
Occupational safety and health regulations also play a crucial role in governing the use of chemicals like ethyl propanoate in industrial settings. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets permissible exposure limits and requires proper handling, storage, and disposal practices. Similar agencies in other countries, such as the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) in the UK, enforce comparable regulations.
Environmental regulations are another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. The Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act in the United States, along with their counterparts in other countries, set limits on emissions and discharges of chemicals, including volatile organic compounds like ethyl propanoate. These regulations aim to minimize the environmental impact of chemical use in industrial processes.
As research continues to uncover new information about the effects of chemicals on human health and the environment, regulatory frameworks are continuously evolving. Manufacturers and users of ethyl propanoate in surface energy modulation applications must stay informed about changes in regulations and adapt their practices accordingly to ensure compliance and responsible use of the chemical.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!