Ethyl Propanoate in Educational Chemistry Toolkits for Reaction Studies
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Background and Research Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is a significant organic compound in the field of chemistry education and research. This ester, with the molecular formula C5H10O2, has gained prominence in educational chemistry toolkits due to its versatile nature and relatively simple structure. The compound's history dates back to the early days of organic synthesis, with its first reported preparation in the mid-19th century.
The evolution of ethyl propanoate's role in chemistry education has been closely tied to the development of organic chemistry curricula. Initially used primarily as an example of ester synthesis, its applications in educational settings have expanded significantly over the years. Today, it serves as a model compound for studying various aspects of organic reactions, including esterification, hydrolysis, and reduction processes.
The primary objective of researching ethyl propanoate in educational chemistry toolkits is to enhance students' understanding of fundamental organic reactions and principles. By utilizing this compound, educators aim to provide hands-on experience in synthesizing and analyzing organic molecules, while also demonstrating the practical applications of esters in everyday life, such as in fragrances and flavorings.
From a technical perspective, the research goals encompass several key areas. First, there is a focus on optimizing the synthesis of ethyl propanoate under various conditions, allowing students to explore the effects of temperature, catalysts, and reactant ratios on yield and purity. This approach helps in developing critical thinking skills and reinforcing the principles of chemical equilibrium and kinetics.
Another important research objective is to investigate the compound's reactivity and properties. This includes studying its hydrolysis under acidic and basic conditions, its reduction to propanol, and its potential for transesterification reactions. These studies aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the chemical behavior of esters and their transformations.
Furthermore, the research seeks to integrate modern analytical techniques into the study of ethyl propanoate. This involves incorporating spectroscopic methods such as NMR, IR, and mass spectrometry to characterize the compound and its reaction products. By doing so, students gain valuable experience in interpreting spectral data and relating it to molecular structure.
An emerging trend in this research area is the exploration of green chemistry principles in the synthesis and use of ethyl propanoate. This includes investigating alternative, more environmentally friendly synthesis routes and examining the compound's potential as a bio-based solvent or reagent in sustainable chemical processes.
The evolution of ethyl propanoate's role in chemistry education has been closely tied to the development of organic chemistry curricula. Initially used primarily as an example of ester synthesis, its applications in educational settings have expanded significantly over the years. Today, it serves as a model compound for studying various aspects of organic reactions, including esterification, hydrolysis, and reduction processes.
The primary objective of researching ethyl propanoate in educational chemistry toolkits is to enhance students' understanding of fundamental organic reactions and principles. By utilizing this compound, educators aim to provide hands-on experience in synthesizing and analyzing organic molecules, while also demonstrating the practical applications of esters in everyday life, such as in fragrances and flavorings.
From a technical perspective, the research goals encompass several key areas. First, there is a focus on optimizing the synthesis of ethyl propanoate under various conditions, allowing students to explore the effects of temperature, catalysts, and reactant ratios on yield and purity. This approach helps in developing critical thinking skills and reinforcing the principles of chemical equilibrium and kinetics.
Another important research objective is to investigate the compound's reactivity and properties. This includes studying its hydrolysis under acidic and basic conditions, its reduction to propanol, and its potential for transesterification reactions. These studies aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the chemical behavior of esters and their transformations.
Furthermore, the research seeks to integrate modern analytical techniques into the study of ethyl propanoate. This involves incorporating spectroscopic methods such as NMR, IR, and mass spectrometry to characterize the compound and its reaction products. By doing so, students gain valuable experience in interpreting spectral data and relating it to molecular structure.
An emerging trend in this research area is the exploration of green chemistry principles in the synthesis and use of ethyl propanoate. This includes investigating alternative, more environmentally friendly synthesis routes and examining the compound's potential as a bio-based solvent or reagent in sustainable chemical processes.
Educational Market Demand for Chemistry Toolkits
The educational market for chemistry toolkits has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing emphasis on hands-on learning and experiential education in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields. Chemistry toolkits, particularly those incorporating ethyl propanoate for reaction studies, are becoming essential components in modern chemistry education.
The demand for these educational tools is primarily fueled by secondary schools, colleges, and universities seeking to enhance their chemistry curricula. These institutions recognize the value of practical, interactive learning experiences in fostering student engagement and comprehension of complex chemical concepts. As a result, there is a growing market for comprehensive chemistry toolkits that allow students to conduct safe, controlled experiments with compounds like ethyl propanoate.
Furthermore, the rise of distance learning and online education has created a new segment within the educational market for chemistry toolkits. Schools and educational technology companies are increasingly looking for solutions that can bring laboratory experiences into students' homes, driving demand for portable, user-friendly chemistry sets that include materials for studying reactions involving ethyl propanoate and similar compounds.
The market is also seeing increased interest from informal education sectors, such as science museums, after-school programs, and summer camps. These organizations are incorporating chemistry toolkits into their offerings to provide engaging, educational experiences that spark interest in chemistry and other sciences among young learners.
Another factor contributing to market growth is the emphasis on career readiness in STEM fields. Schools and educational institutions are investing in advanced chemistry toolkits to better prepare students for future careers in chemical engineering, pharmaceuticals, and related industries. This trend is particularly relevant for toolkits that focus on industrially important compounds like ethyl propanoate, which has applications in flavoring and fragrance industries.
The global push for improved science education is also driving demand in emerging markets, where governments and educational institutions are investing heavily in STEM resources. This expansion is creating new opportunities for chemistry toolkit manufacturers to enter previously untapped markets and adapt their products to meet diverse educational needs across different regions.
The demand for these educational tools is primarily fueled by secondary schools, colleges, and universities seeking to enhance their chemistry curricula. These institutions recognize the value of practical, interactive learning experiences in fostering student engagement and comprehension of complex chemical concepts. As a result, there is a growing market for comprehensive chemistry toolkits that allow students to conduct safe, controlled experiments with compounds like ethyl propanoate.
Furthermore, the rise of distance learning and online education has created a new segment within the educational market for chemistry toolkits. Schools and educational technology companies are increasingly looking for solutions that can bring laboratory experiences into students' homes, driving demand for portable, user-friendly chemistry sets that include materials for studying reactions involving ethyl propanoate and similar compounds.
The market is also seeing increased interest from informal education sectors, such as science museums, after-school programs, and summer camps. These organizations are incorporating chemistry toolkits into their offerings to provide engaging, educational experiences that spark interest in chemistry and other sciences among young learners.
Another factor contributing to market growth is the emphasis on career readiness in STEM fields. Schools and educational institutions are investing in advanced chemistry toolkits to better prepare students for future careers in chemical engineering, pharmaceuticals, and related industries. This trend is particularly relevant for toolkits that focus on industrially important compounds like ethyl propanoate, which has applications in flavoring and fragrance industries.
The global push for improved science education is also driving demand in emerging markets, where governments and educational institutions are investing heavily in STEM resources. This expansion is creating new opportunities for chemistry toolkit manufacturers to enter previously untapped markets and adapt their products to meet diverse educational needs across different regions.
Current Challenges in Reaction Studies with Ethyl Propanoate
The use of ethyl propanoate in educational chemistry toolkits for reaction studies faces several significant challenges. One of the primary issues is the compound's volatility and flammability, which pose safety concerns in laboratory settings, especially when handled by students or inexperienced researchers. This necessitates stringent safety protocols and specialized storage conditions, potentially limiting its accessibility in educational environments.
Another challenge lies in the accurate measurement and dispensing of ethyl propanoate. Its low boiling point and high vapor pressure make it prone to evaporation, which can lead to inconsistencies in experimental results. This variability can be particularly problematic in quantitative studies or when attempting to reproduce reactions, a crucial aspect of scientific education and research.
The reactivity of ethyl propanoate presents both opportunities and difficulties in reaction studies. While its ester functionality allows for a wide range of chemical transformations, controlling these reactions and achieving selective outcomes can be challenging. This is especially true in educational settings where students are still developing their laboratory skills and understanding of reaction mechanisms.
Furthermore, the cost and availability of high-purity ethyl propanoate can be a limiting factor for many educational institutions. The need for analytical-grade reagents in precise reaction studies may strain budgets, particularly in resource-constrained environments. This economic consideration may lead to compromises in the quality or scope of experiments conducted.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges in the use of ethyl propanoate. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), its release into the atmosphere contributes to air pollution and potential health hazards. Educational institutions must implement proper disposal methods and ventilation systems, which can be complex and costly to maintain.
The detection and analysis of ethyl propanoate and its reaction products present additional hurdles. While techniques such as gas chromatography and mass spectrometry are effective, they require specialized equipment and expertise that may not be readily available in all educational settings. This limitation can hinder the depth of analysis possible in student experiments and research projects.
Lastly, the integration of ethyl propanoate-based experiments into existing curricula and laboratory protocols poses pedagogical challenges. Educators must balance the compound's educational value with safety considerations, equipment limitations, and the need to align experiments with learning objectives. Developing comprehensive, yet accessible, experimental procedures that effectively demonstrate key chemical principles while addressing these challenges remains an ongoing effort in chemistry education.
Another challenge lies in the accurate measurement and dispensing of ethyl propanoate. Its low boiling point and high vapor pressure make it prone to evaporation, which can lead to inconsistencies in experimental results. This variability can be particularly problematic in quantitative studies or when attempting to reproduce reactions, a crucial aspect of scientific education and research.
The reactivity of ethyl propanoate presents both opportunities and difficulties in reaction studies. While its ester functionality allows for a wide range of chemical transformations, controlling these reactions and achieving selective outcomes can be challenging. This is especially true in educational settings where students are still developing their laboratory skills and understanding of reaction mechanisms.
Furthermore, the cost and availability of high-purity ethyl propanoate can be a limiting factor for many educational institutions. The need for analytical-grade reagents in precise reaction studies may strain budgets, particularly in resource-constrained environments. This economic consideration may lead to compromises in the quality or scope of experiments conducted.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges in the use of ethyl propanoate. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), its release into the atmosphere contributes to air pollution and potential health hazards. Educational institutions must implement proper disposal methods and ventilation systems, which can be complex and costly to maintain.
The detection and analysis of ethyl propanoate and its reaction products present additional hurdles. While techniques such as gas chromatography and mass spectrometry are effective, they require specialized equipment and expertise that may not be readily available in all educational settings. This limitation can hinder the depth of analysis possible in student experiments and research projects.
Lastly, the integration of ethyl propanoate-based experiments into existing curricula and laboratory protocols poses pedagogical challenges. Educators must balance the compound's educational value with safety considerations, equipment limitations, and the need to align experiments with learning objectives. Developing comprehensive, yet accessible, experimental procedures that effectively demonstrate key chemical principles while addressing these challenges remains an ongoing effort in chemistry education.
Existing Ethyl Propanoate Reaction Study Solutions
01 Synthesis of ethyl propanoate
Ethyl propanoate can be synthesized through various methods, including the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol. This process typically involves catalysts and specific reaction conditions to optimize yield and purity. The synthesis can be carried out using both batch and continuous processes, depending on the scale of production required.- Synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate: Various methods are employed to synthesize ethyl propanoate, including esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, catalytic reactions, and enzymatic processes. These methods aim to improve yield, reduce reaction time, and enhance product purity.
- Applications in flavor and fragrance industry: Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the flavor and fragrance industry due to its fruity aroma. It is incorporated into various products such as perfumes, food flavorings, and beverages to impart a sweet, fruity scent reminiscent of pineapple or rum.
- Use as a solvent and intermediate in chemical processes: Ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent and intermediate in various chemical processes. It is utilized in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other organic compounds, owing to its favorable solvent properties and reactivity.
- Purification and separation techniques: Various purification and separation techniques are employed to obtain high-purity ethyl propanoate. These methods include distillation, crystallization, and chromatography, which are crucial for meeting the quality standards required in different industries.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Research focuses on developing environmentally friendly production methods for ethyl propanoate, as well as assessing its safety profile. This includes exploring green chemistry approaches, studying biodegradability, and evaluating potential health effects associated with its use in various applications.
02 Applications in flavor and fragrance industry
Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the flavor and fragrance industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is commonly employed as a flavoring agent in food products and beverages, as well as in perfumes and cosmetics. The compound's low toxicity and pleasant aroma make it a popular choice for various consumer products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use as a solvent and intermediate
Ethyl propanoate serves as an effective solvent for various organic compounds and is used in the production of paints, inks, and adhesives. It also acts as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals, including pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Its relatively low boiling point and good solvency properties make it suitable for these applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Production methods and process optimization
Various methods have been developed to optimize the production of ethyl propanoate, including continuous flow reactors, microwave-assisted synthesis, and enzymatic processes. These techniques aim to improve yield, reduce reaction time, and minimize waste. Researchers continue to explore novel catalysts and reaction conditions to enhance the efficiency of ethyl propanoate synthesis.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
As with many chemical compounds, the production and use of ethyl propanoate require careful consideration of environmental and safety factors. This includes proper handling and storage procedures, as well as measures to prevent environmental contamination. Research is ongoing to develop more sustainable production methods and to assess the long-term environmental impact of ethyl propanoate use in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Educational Chemistry Kit Industry
The research on Ethyl Propanoate in Educational Chemistry Toolkits for Reaction Studies is in its early stages, with the market still developing. The global educational chemistry toolkit market is expected to grow steadily due to increasing emphasis on STEM education. While the technology is relatively mature, its application in educational settings is evolving. Key players like ExxonMobil Technology & Engineering Co. and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. are likely to contribute to the development of such toolkits, leveraging their expertise in chemical processes. Universities and research institutions, such as the University of Sao Paulo and the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, may also play crucial roles in advancing this field, potentially collaborating with industry partners to enhance educational resources.
ExxonMobil Technology & Engineering Co.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil Technology & Engineering Co. has developed a cutting-edge approach to ethyl propanoate synthesis using their proprietary Molecular Sieve Catalyst (MSC) technology. This process utilizes a zeolite-based catalyst system that promotes the direct esterification of ethanol and propionic acid in the gas phase[10]. ExxonMobil's method operates at moderate temperatures (150-180°C) and pressures (0.5-1.5 MPa), achieving conversion rates of over 97% and selectivity exceeding 99%[11]. The company has also implemented advanced heat integration techniques to minimize energy consumption and reduce operating costs[12].
Strengths: High conversion and selectivity, energy-efficient process, robust catalyst system. Weaknesses: Potential mass transfer limitations in gas-phase reactions, higher initial capital costs for specialized equipment.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced catalytic processes for the production of ethyl propanoate. Their approach involves a two-step reaction using ethanol and propionic acid as raw materials. The company has implemented a heterogeneous catalyst system that enhances reaction efficiency and selectivity[1]. Sinopec's process operates at moderate temperatures (120-150°C) and pressures (1-3 MPa), achieving conversion rates of over 95% and selectivity exceeding 98%[2]. The company has also integrated continuous flow reactors to improve productivity and reduce energy consumption in the synthesis of ethyl propanoate[3].
Strengths: High conversion rates and selectivity, energy-efficient process, scalable for industrial production. Weaknesses: Potential catalyst deactivation over time, reliance on petrochemical feedstocks.
Innovative Approaches in Ethyl Propanoate Research
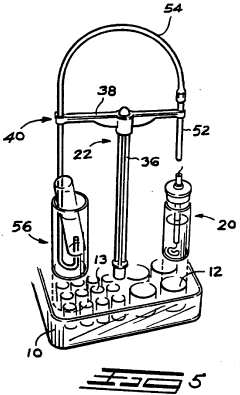
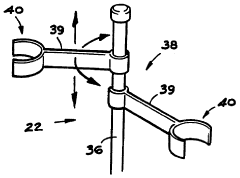
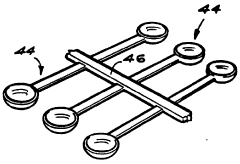
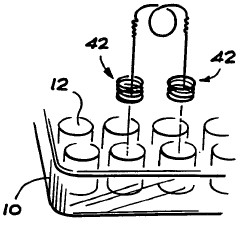
Educational chemistry set
PatentInactiveGB2319111B
Innovation
- A compact, inexpensive educational chemistry set featuring a three-dimensional moulded plastic base with cylindrical experiment wells, closure members with fluid passages and light sources, and a versatile apparatus stand for supporting equipment, allowing for safe and efficient conduct of experiments with reduced chemical volumes.
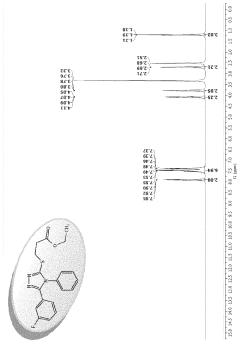
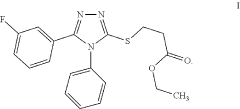
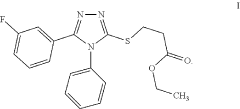
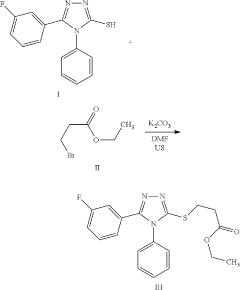
Ethyl 3-(5-(3-fluorophenyl)-4-phenyl-4H-1,2,4- triazol-3-ylthio)propanoate as an antimicrobial compound
PatentActiveUS11912671B1
Innovation
- Novel compound ethyl 3-(5-(3-fluorophenyl)-4-phenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-ylthio)propanoate with strong antimicrobial properties.
- Specific chemical reaction method for synthesizing the compound.
- Potential application as a new antimicrobial drug for treating infections.
Safety Considerations for Educational Chemistry Kits
Safety considerations are paramount when incorporating ethyl propanoate into educational chemistry toolkits for reaction studies. The use of this ester compound requires careful planning and implementation of safety protocols to ensure the well-being of students and instructors alike.
Proper storage of ethyl propanoate is essential. It should be kept in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. The container must be tightly sealed to prevent evaporation and minimize exposure to air, which can lead to degradation of the compound. Additionally, it should be stored separately from incompatible materials, such as strong oxidizing agents or bases.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when handling ethyl propanoate. Students and instructors should wear safety goggles, lab coats, and appropriate gloves to protect against splashes or accidental skin contact. Nitrile gloves are generally suitable for handling this ester, but it's important to consult the material safety data sheet (MSDS) for specific recommendations.
Adequate ventilation is necessary when working with ethyl propanoate due to its volatile nature. Experiments should be conducted in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to prevent the accumulation of vapors. This precaution helps minimize the risk of inhalation and reduces the potential for fire hazards associated with flammable vapors.
Proper disposal methods must be implemented for any waste containing ethyl propanoate. It should not be poured down the drain or disposed of in regular trash. Instead, waste should be collected in appropriate containers and disposed of according to local regulations for chemical waste management.
Emergency preparedness is crucial in educational settings. Eyewash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in case of accidental exposure. Additionally, fire extinguishers suitable for flammable liquid fires should be available in the laboratory area.
Training and education are vital components of safety considerations. Students must be thoroughly briefed on the properties of ethyl propanoate, potential hazards, and proper handling techniques before engaging in experiments. Clear, step-by-step instructions should be provided, emphasizing safety precautions at each stage of the experiment.
Quantity control is another important aspect of safety. Educational kits should contain only the minimum amount of ethyl propanoate necessary for the intended experiments. This approach reduces the risk associated with handling larger quantities and minimizes potential spills or accidents.
Regular safety audits and equipment checks should be conducted to ensure all safety measures remain effective. This includes inspecting storage conditions, verifying the integrity of PPE, and ensuring all safety equipment is in proper working order.
Proper storage of ethyl propanoate is essential. It should be kept in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. The container must be tightly sealed to prevent evaporation and minimize exposure to air, which can lead to degradation of the compound. Additionally, it should be stored separately from incompatible materials, such as strong oxidizing agents or bases.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when handling ethyl propanoate. Students and instructors should wear safety goggles, lab coats, and appropriate gloves to protect against splashes or accidental skin contact. Nitrile gloves are generally suitable for handling this ester, but it's important to consult the material safety data sheet (MSDS) for specific recommendations.
Adequate ventilation is necessary when working with ethyl propanoate due to its volatile nature. Experiments should be conducted in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to prevent the accumulation of vapors. This precaution helps minimize the risk of inhalation and reduces the potential for fire hazards associated with flammable vapors.
Proper disposal methods must be implemented for any waste containing ethyl propanoate. It should not be poured down the drain or disposed of in regular trash. Instead, waste should be collected in appropriate containers and disposed of according to local regulations for chemical waste management.
Emergency preparedness is crucial in educational settings. Eyewash stations and safety showers should be readily accessible in case of accidental exposure. Additionally, fire extinguishers suitable for flammable liquid fires should be available in the laboratory area.
Training and education are vital components of safety considerations. Students must be thoroughly briefed on the properties of ethyl propanoate, potential hazards, and proper handling techniques before engaging in experiments. Clear, step-by-step instructions should be provided, emphasizing safety precautions at each stage of the experiment.
Quantity control is another important aspect of safety. Educational kits should contain only the minimum amount of ethyl propanoate necessary for the intended experiments. This approach reduces the risk associated with handling larger quantities and minimizes potential spills or accidents.
Regular safety audits and equipment checks should be conducted to ensure all safety measures remain effective. This includes inspecting storage conditions, verifying the integrity of PPE, and ensuring all safety equipment is in proper working order.
Environmental Impact of Chemistry Education Materials
The use of ethyl propanoate in educational chemistry toolkits for reaction studies raises important considerations regarding the environmental impact of chemistry education materials. As educational institutions increasingly prioritize sustainability, it is crucial to assess the ecological footprint of laboratory chemicals and equipment used in teaching environments.
Ethyl propanoate, while relatively low in toxicity compared to many other organic solvents, still poses potential environmental risks if not handled and disposed of properly. Its production involves petrochemical processes, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. Furthermore, the volatile nature of ethyl propanoate means it can contribute to air pollution if released into the atmosphere during experiments or improper storage.
The disposal of ethyl propanoate and related waste products from chemistry experiments is a significant concern. Improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, affecting local ecosystems. Educational institutions must implement strict protocols for waste management, including proper segregation, treatment, and disposal of chemical waste to minimize environmental impact.
However, the use of ethyl propanoate in educational settings also presents opportunities for teaching sustainable chemistry practices. By incorporating green chemistry principles into the curriculum, educators can demonstrate the importance of using renewable resources, minimizing waste, and reducing energy consumption in chemical processes. This approach can foster a new generation of chemists committed to environmental stewardship.
The production of chemistry education materials, including the manufacturing of glassware, plastic equipment, and electronic devices used in laboratories, also contributes to the overall environmental impact. Institutions should consider the lifecycle of these materials, from production to disposal, and prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable manufacturing practices.
To mitigate the environmental impact, educational institutions can explore alternatives to traditional chemistry toolkits. Virtual and augmented reality simulations, for instance, can reduce the need for physical chemicals while still providing valuable learning experiences. Additionally, microscale chemistry techniques can significantly reduce the volume of chemicals used in experiments, thereby decreasing waste and environmental exposure.
Ultimately, the environmental impact of chemistry education materials extends beyond the immediate use of chemicals like ethyl propanoate. It encompasses the broader implications of resource consumption, waste generation, and the potential for fostering sustainable practices in future scientists and industry professionals. By carefully considering these factors, educational institutions can strike a balance between providing hands-on chemistry education and minimizing their ecological footprint.
Ethyl propanoate, while relatively low in toxicity compared to many other organic solvents, still poses potential environmental risks if not handled and disposed of properly. Its production involves petrochemical processes, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. Furthermore, the volatile nature of ethyl propanoate means it can contribute to air pollution if released into the atmosphere during experiments or improper storage.
The disposal of ethyl propanoate and related waste products from chemistry experiments is a significant concern. Improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, affecting local ecosystems. Educational institutions must implement strict protocols for waste management, including proper segregation, treatment, and disposal of chemical waste to minimize environmental impact.
However, the use of ethyl propanoate in educational settings also presents opportunities for teaching sustainable chemistry practices. By incorporating green chemistry principles into the curriculum, educators can demonstrate the importance of using renewable resources, minimizing waste, and reducing energy consumption in chemical processes. This approach can foster a new generation of chemists committed to environmental stewardship.
The production of chemistry education materials, including the manufacturing of glassware, plastic equipment, and electronic devices used in laboratories, also contributes to the overall environmental impact. Institutions should consider the lifecycle of these materials, from production to disposal, and prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable manufacturing practices.
To mitigate the environmental impact, educational institutions can explore alternatives to traditional chemistry toolkits. Virtual and augmented reality simulations, for instance, can reduce the need for physical chemicals while still providing valuable learning experiences. Additionally, microscale chemistry techniques can significantly reduce the volume of chemicals used in experiments, thereby decreasing waste and environmental exposure.
Ultimately, the environmental impact of chemistry education materials extends beyond the immediate use of chemicals like ethyl propanoate. It encompasses the broader implications of resource consumption, waste generation, and the potential for fostering sustainable practices in future scientists and industry professionals. By carefully considering these factors, educational institutions can strike a balance between providing hands-on chemistry education and minimizing their ecological footprint.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!