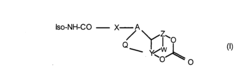
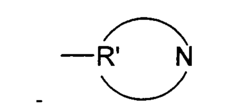
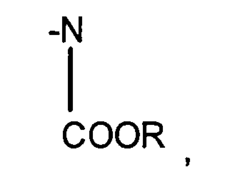
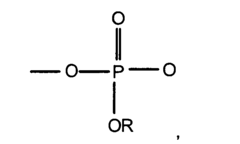
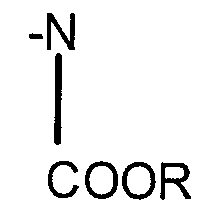Advancements in Isocyanate Reaction Control Techniques
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Chemistry Evolution and Objectives
Isocyanate chemistry has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. The discovery of isocyanates by Wurtz in 1848 laid the foundation for a revolutionary field in polymer science. Initially, the focus was on understanding the basic reactivity of isocyanates with various nucleophiles, particularly alcohols and amines, which led to the development of polyurethanes in the 1930s by Otto Bayer and his team at I.G. Farben.
The post-World War II era saw rapid advancements in isocyanate chemistry, driven by the growing demand for versatile materials in various industries. Researchers began exploring the complex kinetics and mechanisms of isocyanate reactions, leading to a deeper understanding of factors influencing reaction rates and product properties. This period marked the beginning of systematic efforts to control isocyanate reactions for tailored material properties.
By the 1960s and 1970s, the focus shifted towards developing more sophisticated catalysts and additives to fine-tune isocyanate reactions. This era saw the introduction of delayed-action catalysts and blowing agents, enabling better control over foam formation in polyurethane production. Concurrently, environmental and health concerns began to shape research directions, prompting the development of safer isocyanate handling techniques and alternative chemistries.
The advent of computer modeling and advanced analytical techniques in the 1980s and 1990s revolutionized isocyanate reaction control. These tools allowed for more precise prediction of reaction outcomes and enabled the design of complex formulations with specific performance characteristics. This period also saw increased efforts in developing low-VOC and water-based systems, addressing growing environmental regulations.
In recent years, the objectives of isocyanate reaction control have expanded beyond traditional performance metrics. Current research aims to achieve precise control over reaction kinetics, enabling the production of materials with highly specific properties. There is a growing emphasis on developing "smart" isocyanate systems that can respond to external stimuli, opening up new applications in fields such as biomedicine and adaptive materials.
Looking forward, the objectives in isocyanate reaction control techniques are multifaceted. Key goals include developing more environmentally friendly and sustainable isocyanate chemistries, improving worker safety through advanced handling and processing methods, and pushing the boundaries of material performance through nanoscale control of reaction processes. Additionally, there is a strong focus on integrating isocyanate chemistry with emerging technologies such as 3D printing and self-healing materials, aiming to create next-generation adaptive and responsive polymeric systems.
The post-World War II era saw rapid advancements in isocyanate chemistry, driven by the growing demand for versatile materials in various industries. Researchers began exploring the complex kinetics and mechanisms of isocyanate reactions, leading to a deeper understanding of factors influencing reaction rates and product properties. This period marked the beginning of systematic efforts to control isocyanate reactions for tailored material properties.
By the 1960s and 1970s, the focus shifted towards developing more sophisticated catalysts and additives to fine-tune isocyanate reactions. This era saw the introduction of delayed-action catalysts and blowing agents, enabling better control over foam formation in polyurethane production. Concurrently, environmental and health concerns began to shape research directions, prompting the development of safer isocyanate handling techniques and alternative chemistries.
The advent of computer modeling and advanced analytical techniques in the 1980s and 1990s revolutionized isocyanate reaction control. These tools allowed for more precise prediction of reaction outcomes and enabled the design of complex formulations with specific performance characteristics. This period also saw increased efforts in developing low-VOC and water-based systems, addressing growing environmental regulations.
In recent years, the objectives of isocyanate reaction control have expanded beyond traditional performance metrics. Current research aims to achieve precise control over reaction kinetics, enabling the production of materials with highly specific properties. There is a growing emphasis on developing "smart" isocyanate systems that can respond to external stimuli, opening up new applications in fields such as biomedicine and adaptive materials.
Looking forward, the objectives in isocyanate reaction control techniques are multifaceted. Key goals include developing more environmentally friendly and sustainable isocyanate chemistries, improving worker safety through advanced handling and processing methods, and pushing the boundaries of material performance through nanoscale control of reaction processes. Additionally, there is a strong focus on integrating isocyanate chemistry with emerging technologies such as 3D printing and self-healing materials, aiming to create next-generation adaptive and responsive polymeric systems.
Market Demand for Controlled Isocyanate Reactions
The market demand for controlled isocyanate reactions has been steadily growing across various industries, driven by the increasing need for high-performance materials and advanced manufacturing processes. Isocyanates are crucial components in the production of polyurethanes, which find extensive applications in automotive, construction, furniture, and electronics sectors.
In the automotive industry, there is a rising demand for lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Controlled isocyanate reactions enable the production of high-strength, low-density polyurethane foams used in vehicle interiors, seating, and insulation. This trend is expected to continue as automakers strive to meet stringent environmental regulations and consumer preferences for eco-friendly vehicles.
The construction sector represents another significant market for controlled isocyanate reactions. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient buildings has led to increased adoption of polyurethane-based insulation materials. These materials offer superior thermal insulation properties, contributing to reduced energy consumption in both residential and commercial structures. As green building practices gain traction worldwide, the demand for advanced insulation solutions is projected to surge.
In the furniture industry, controlled isocyanate reactions play a vital role in producing durable and comfortable foam materials for mattresses, sofas, and chairs. The rising consumer focus on ergonomics and sleep quality has spurred innovation in this sector, driving the need for precisely controlled foam formulations that offer optimal support and comfort.
The electronics industry has also witnessed a growing demand for controlled isocyanate reactions, particularly in the production of protective coatings and encapsulants for electronic components. As electronic devices become more compact and sophisticated, the need for reliable protection against moisture, dust, and mechanical stress has intensified, boosting the market for specialized polyurethane-based solutions.
Furthermore, the medical and healthcare sectors have emerged as promising markets for controlled isocyanate reactions. The development of advanced wound dressings, prosthetics, and medical-grade foams relies heavily on precise control of isocyanate chemistry. As healthcare technologies continue to evolve, the demand for biocompatible and customizable materials is expected to drive further innovation in this field.
The global push towards sustainability has also influenced the market demand for controlled isocyanate reactions. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing bio-based isocyanates and environmentally friendly production processes to meet the growing consumer preference for sustainable products. This shift is likely to open up new opportunities and drive research into novel isocyanate chemistries and control techniques.
In the automotive industry, there is a rising demand for lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Controlled isocyanate reactions enable the production of high-strength, low-density polyurethane foams used in vehicle interiors, seating, and insulation. This trend is expected to continue as automakers strive to meet stringent environmental regulations and consumer preferences for eco-friendly vehicles.
The construction sector represents another significant market for controlled isocyanate reactions. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient buildings has led to increased adoption of polyurethane-based insulation materials. These materials offer superior thermal insulation properties, contributing to reduced energy consumption in both residential and commercial structures. As green building practices gain traction worldwide, the demand for advanced insulation solutions is projected to surge.
In the furniture industry, controlled isocyanate reactions play a vital role in producing durable and comfortable foam materials for mattresses, sofas, and chairs. The rising consumer focus on ergonomics and sleep quality has spurred innovation in this sector, driving the need for precisely controlled foam formulations that offer optimal support and comfort.
The electronics industry has also witnessed a growing demand for controlled isocyanate reactions, particularly in the production of protective coatings and encapsulants for electronic components. As electronic devices become more compact and sophisticated, the need for reliable protection against moisture, dust, and mechanical stress has intensified, boosting the market for specialized polyurethane-based solutions.
Furthermore, the medical and healthcare sectors have emerged as promising markets for controlled isocyanate reactions. The development of advanced wound dressings, prosthetics, and medical-grade foams relies heavily on precise control of isocyanate chemistry. As healthcare technologies continue to evolve, the demand for biocompatible and customizable materials is expected to drive further innovation in this field.
The global push towards sustainability has also influenced the market demand for controlled isocyanate reactions. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing bio-based isocyanates and environmentally friendly production processes to meet the growing consumer preference for sustainable products. This shift is likely to open up new opportunities and drive research into novel isocyanate chemistries and control techniques.
Current Challenges in Isocyanate Reaction Control
Despite significant advancements in isocyanate reaction control techniques, several challenges persist in this field, hindering optimal performance and efficiency in various applications. One of the primary obstacles is the precise control of reaction kinetics, particularly in complex polyurethane systems. The highly reactive nature of isocyanates makes it difficult to achieve consistent and predictable reaction rates, especially when dealing with multiple components and varying environmental conditions.
Temperature management remains a critical challenge in isocyanate reactions. The exothermic nature of these reactions can lead to localized hot spots, resulting in uneven curing, degradation of materials, and potential safety hazards. Developing effective heat dissipation methods and temperature control systems is crucial for maintaining reaction stability and product quality.
Another significant hurdle is the sensitivity of isocyanate reactions to moisture. Even trace amounts of water can lead to unwanted side reactions, forming carbon dioxide and compromising the final product's properties. This necessitates stringent moisture control measures throughout the entire production process, from raw material storage to the final application.
The toxicity and potential health hazards associated with isocyanates pose ongoing challenges in terms of worker safety and environmental protection. Developing safer handling procedures, improved personal protective equipment, and more effective emission control systems are essential for mitigating these risks.
Catalyst optimization remains a complex issue in isocyanate reaction control. Balancing the need for rapid cure times with the desire for extended pot life and workability is a delicate process. Furthermore, the interaction between catalysts and other additives in formulations can lead to unexpected results, requiring extensive research and fine-tuning.
The increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly materials presents new challenges in isocyanate chemistry. Developing bio-based isocyanates or finding alternative chemistries that can match the performance of traditional isocyanate systems while reducing environmental impact is an ongoing area of research and development.
Lastly, achieving consistent quality in large-scale production remains challenging. Scaling up laboratory-optimized processes to industrial levels often reveals unforeseen issues related to mixing efficiency, heat transfer, and reaction homogeneity. Addressing these scale-up challenges requires innovative reactor designs and advanced process control strategies.
Temperature management remains a critical challenge in isocyanate reactions. The exothermic nature of these reactions can lead to localized hot spots, resulting in uneven curing, degradation of materials, and potential safety hazards. Developing effective heat dissipation methods and temperature control systems is crucial for maintaining reaction stability and product quality.
Another significant hurdle is the sensitivity of isocyanate reactions to moisture. Even trace amounts of water can lead to unwanted side reactions, forming carbon dioxide and compromising the final product's properties. This necessitates stringent moisture control measures throughout the entire production process, from raw material storage to the final application.
The toxicity and potential health hazards associated with isocyanates pose ongoing challenges in terms of worker safety and environmental protection. Developing safer handling procedures, improved personal protective equipment, and more effective emission control systems are essential for mitigating these risks.
Catalyst optimization remains a complex issue in isocyanate reaction control. Balancing the need for rapid cure times with the desire for extended pot life and workability is a delicate process. Furthermore, the interaction between catalysts and other additives in formulations can lead to unexpected results, requiring extensive research and fine-tuning.
The increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly materials presents new challenges in isocyanate chemistry. Developing bio-based isocyanates or finding alternative chemistries that can match the performance of traditional isocyanate systems while reducing environmental impact is an ongoing area of research and development.
Lastly, achieving consistent quality in large-scale production remains challenging. Scaling up laboratory-optimized processes to industrial levels often reveals unforeseen issues related to mixing efficiency, heat transfer, and reaction homogeneity. Addressing these scale-up challenges requires innovative reactor designs and advanced process control strategies.
Existing Isocyanate Reaction Control Methods
01 Temperature control in isocyanate reactions
Controlling the temperature during isocyanate reactions is crucial for achieving desired product properties and reaction rates. This can be accomplished through various cooling or heating methods, such as using jacketed reactors or heat exchangers. Proper temperature control helps prevent side reactions and ensures consistent product quality.- Temperature control in isocyanate reactions: Controlling the temperature during isocyanate reactions is crucial for achieving desired product properties and reaction rates. This can be accomplished through various cooling or heating methods, as well as by carefully monitoring and adjusting reaction conditions. Proper temperature control helps prevent side reactions and ensures consistent product quality.
- Catalyst selection and concentration: The choice and concentration of catalysts play a significant role in controlling isocyanate reactions. Different catalysts can be used to promote specific reaction pathways, control reaction rates, and influence product properties. Optimizing catalyst selection and concentration helps achieve desired reaction outcomes and product characteristics.
- Reactant ratio and feed rate control: Controlling the ratio of reactants and their feed rates is essential for managing isocyanate reactions. This involves carefully metering and mixing the components to achieve the desired stoichiometry and reaction kinetics. Proper control of reactant ratios and feed rates helps optimize product properties and reaction efficiency.
- Solvent selection and concentration: The choice and concentration of solvents can significantly impact isocyanate reactions. Solvents can affect reaction rates, product solubility, and heat transfer. Selecting appropriate solvents and controlling their concentration helps manage reaction kinetics and product properties.
- Monitoring and control systems: Implementing advanced monitoring and control systems is crucial for managing isocyanate reactions. These systems can include real-time analysis of reaction parameters, automated feedback loops, and process optimization algorithms. Such systems help maintain consistent product quality and improve overall reaction control.
02 Catalyst selection and concentration
The choice and concentration of catalysts play a significant role in controlling isocyanate reactions. Different catalysts can be used to promote specific reaction pathways or control reaction rates. Adjusting catalyst concentrations allows for fine-tuning of reaction kinetics and product properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Reactant ratio and feed rate control
Controlling the ratio of reactants and their feed rates into the reaction system is essential for managing isocyanate reactions. This approach helps maintain stoichiometric balance, control reaction rates, and influence product characteristics. Precise metering and mixing systems are often employed to achieve accurate reactant ratios.Expand Specific Solutions04 Solvent selection and concentration
The choice and concentration of solvents can significantly impact isocyanate reactions. Solvents affect reaction rates, product solubility, and heat transfer. Selecting appropriate solvents and adjusting their concentrations helps control reaction kinetics and product properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Pressure control and inert atmosphere
Controlling pressure and maintaining an inert atmosphere are important factors in managing isocyanate reactions. Pressure control can influence reaction rates and product properties, while an inert atmosphere helps prevent unwanted side reactions with atmospheric components. These techniques are often used in conjunction with other control methods to optimize reaction outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isocyanate Chemistry Industry
The isocyanate reaction control techniques market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand in polyurethane applications across various industries. The global market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, fueled by advancements in automotive, construction, and electronics sectors. Technologically, the field is evolving rapidly, with companies like Wanhua Chemical Group, Covestro, and BASF leading innovation. These firms are developing sophisticated control methods to enhance reaction efficiency, product quality, and environmental sustainability. Emerging players such as Vencorex and Asahi Kasei are also contributing to technological advancements, intensifying competition and driving further innovation in isocyanate reaction control techniques.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group has developed advanced isocyanate reaction control techniques, focusing on improving the efficiency and selectivity of isocyanate production. Their approach involves using novel catalysts and optimized reaction conditions to enhance the conversion of amine precursors to isocyanates. The company has implemented a continuous flow reactor system that allows for precise temperature and pressure control, resulting in improved product quality and reduced side reactions[1]. Additionally, Wanhua has developed a proprietary purification process that removes trace impurities, leading to higher-grade isocyanates suitable for demanding applications in polyurethane manufacturing[2].
Strengths: High-efficiency production, improved product purity, and reduced environmental impact. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial investment costs and the need for specialized equipment and expertise.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro has made significant advancements in isocyanate reaction control techniques, particularly in the field of aliphatic isocyanates. Their innovative approach involves the use of microreactor technology, which allows for precise control of reaction parameters and improved heat transfer[3]. This technology enables the production of isocyanates with enhanced purity and reduced side products. Covestro has also developed a novel gas-phase phosgenation process that significantly reduces solvent usage and improves overall process efficiency[4]. Furthermore, the company has implemented advanced process analytical technology (PAT) to monitor and control isocyanate reactions in real-time, ensuring consistent product quality and optimizing production yields[5].
Strengths: Improved product quality, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced process efficiency. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs and the need for specialized equipment and expertise.
Innovative Approaches to Isocyanate Control
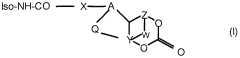
Modified isocyanates
PatentInactiveEP1382626A1
Innovation
- Development of modified isocyanate derivatives with a crosslinking functional group that remains stable at low temperatures and only reacts at high temperatures, allowing for controlled crosslinking reactions without the need for masking agents, using cyclic carbonates to form stable polyisocyanates that can react with nucleophilic compounds to form coatings and polymers.
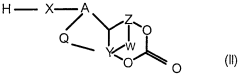
Modified isocyanates
PatentWO2000020477A1
Innovation
- Development of modified isocyanate derivatives with a crosslinking functional group that remains stable and reacts only under specific conditions, allowing for controlled crosslinking reactions without releasing isocyanate functions prematurely, using cyclic carbonates to form stable polyisocyanates that can react with nucleophilic compounds to create coatings and foams.
Environmental Impact of Isocyanate Technologies
The environmental impact of isocyanate technologies has become a critical concern in recent years, as the industry strives to balance the benefits of these versatile compounds with their potential ecological consequences. Isocyanates, widely used in the production of polyurethanes, have significant applications across various sectors, including construction, automotive, and consumer goods. However, their production and use can lead to environmental challenges that require careful consideration and mitigation strategies.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with isocyanate technologies is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during manufacturing processes and product use. These emissions can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone, potentially impacting both human health and ecosystems. Additionally, the production of isocyanates often involves the use of fossil fuel-derived raw materials, contributing to carbon dioxide emissions and the depletion of non-renewable resources.
Water pollution is another significant environmental issue related to isocyanate technologies. Improper disposal of isocyanate-containing waste or accidental spills can lead to contamination of water bodies, posing risks to aquatic life and potentially entering the food chain. The persistence of certain isocyanate compounds in the environment further exacerbates these concerns, as they may not readily degrade and can accumulate in ecosystems over time.
The industry has responded to these environmental challenges by developing and implementing various mitigation strategies. These include the adoption of closed-loop production systems to minimize emissions, the use of water-based and solvent-free formulations to reduce VOC emissions, and the implementation of advanced waste treatment technologies to prevent water contamination. Furthermore, there is a growing focus on developing bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources, which could potentially reduce the carbon footprint associated with their production.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide have also evolved to address the environmental impact of isocyanate technologies. Stringent emission standards, waste management regulations, and occupational safety guidelines have been implemented in many countries to minimize the ecological footprint of isocyanate production and use. These regulations have driven innovation in the industry, leading to the development of more environmentally friendly processes and products.
As the demand for polyurethane products continues to grow, the industry faces the ongoing challenge of balancing economic interests with environmental stewardship. Research and development efforts are increasingly focused on creating sustainable alternatives and improving existing technologies to minimize environmental impact. This includes exploring novel catalysts and reaction control techniques that can enhance efficiency and reduce waste generation in isocyanate production processes.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with isocyanate technologies is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during manufacturing processes and product use. These emissions can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone, potentially impacting both human health and ecosystems. Additionally, the production of isocyanates often involves the use of fossil fuel-derived raw materials, contributing to carbon dioxide emissions and the depletion of non-renewable resources.
Water pollution is another significant environmental issue related to isocyanate technologies. Improper disposal of isocyanate-containing waste or accidental spills can lead to contamination of water bodies, posing risks to aquatic life and potentially entering the food chain. The persistence of certain isocyanate compounds in the environment further exacerbates these concerns, as they may not readily degrade and can accumulate in ecosystems over time.
The industry has responded to these environmental challenges by developing and implementing various mitigation strategies. These include the adoption of closed-loop production systems to minimize emissions, the use of water-based and solvent-free formulations to reduce VOC emissions, and the implementation of advanced waste treatment technologies to prevent water contamination. Furthermore, there is a growing focus on developing bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources, which could potentially reduce the carbon footprint associated with their production.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide have also evolved to address the environmental impact of isocyanate technologies. Stringent emission standards, waste management regulations, and occupational safety guidelines have been implemented in many countries to minimize the ecological footprint of isocyanate production and use. These regulations have driven innovation in the industry, leading to the development of more environmentally friendly processes and products.
As the demand for polyurethane products continues to grow, the industry faces the ongoing challenge of balancing economic interests with environmental stewardship. Research and development efforts are increasingly focused on creating sustainable alternatives and improving existing technologies to minimize environmental impact. This includes exploring novel catalysts and reaction control techniques that can enhance efficiency and reduce waste generation in isocyanate production processes.
Safety Regulations in Isocyanate Handling
Safety regulations in isocyanate handling have become increasingly stringent due to the potential health hazards associated with these chemicals. Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented comprehensive guidelines to ensure the safe use, storage, and transportation of isocyanates in industrial settings. These regulations typically cover various aspects, including exposure limits, personal protective equipment (PPE), engineering controls, and emergency response procedures.
One of the primary focuses of safety regulations is the establishment of occupational exposure limits (OELs) for isocyanates. These limits are designed to protect workers from both acute and chronic health effects. For instance, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States has set permissible exposure limits (PELs) for common isocyanates such as toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI). Similarly, the European Union has established binding occupational exposure limit values (BOELVs) for these substances under the Chemical Agents Directive.
Personal protective equipment requirements form a crucial component of isocyanate safety regulations. Workers handling isocyanates are typically required to wear appropriate respiratory protection, such as air-purifying respirators or supplied-air respirators, depending on the concentration and type of isocyanate present. Impervious gloves, protective clothing, and eye protection are also mandated to prevent skin and eye contact with these chemicals.
Engineering controls play a vital role in minimizing isocyanate exposure in the workplace. Regulations often require the implementation of closed systems, local exhaust ventilation, and containment measures to reduce the release of isocyanate vapors and aerosols into the work environment. Regular monitoring of air quality and the installation of alarm systems to detect leaks or elevated isocyanate levels are also commonly prescribed.
Storage and transportation regulations for isocyanates are designed to prevent accidental releases and ensure proper handling during transit. These regulations typically specify requirements for container design, labeling, and segregation from incompatible materials. Additionally, emergency response plans and spill containment procedures are mandated to address potential incidents involving isocyanates.
Training and education requirements are integral to isocyanate safety regulations. Workers involved in handling these chemicals must receive comprehensive training on the hazards associated with isocyanates, proper use of PPE, safe work practices, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher training is often required to ensure ongoing compliance and awareness.
As advancements in isocyanate reaction control techniques continue to evolve, safety regulations are likely to adapt to address new challenges and incorporate improved protective measures. This may include the integration of real-time monitoring technologies, enhanced exposure assessment methods, and more sophisticated engineering controls to further minimize the risks associated with isocyanate handling in industrial processes.
One of the primary focuses of safety regulations is the establishment of occupational exposure limits (OELs) for isocyanates. These limits are designed to protect workers from both acute and chronic health effects. For instance, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States has set permissible exposure limits (PELs) for common isocyanates such as toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI). Similarly, the European Union has established binding occupational exposure limit values (BOELVs) for these substances under the Chemical Agents Directive.
Personal protective equipment requirements form a crucial component of isocyanate safety regulations. Workers handling isocyanates are typically required to wear appropriate respiratory protection, such as air-purifying respirators or supplied-air respirators, depending on the concentration and type of isocyanate present. Impervious gloves, protective clothing, and eye protection are also mandated to prevent skin and eye contact with these chemicals.
Engineering controls play a vital role in minimizing isocyanate exposure in the workplace. Regulations often require the implementation of closed systems, local exhaust ventilation, and containment measures to reduce the release of isocyanate vapors and aerosols into the work environment. Regular monitoring of air quality and the installation of alarm systems to detect leaks or elevated isocyanate levels are also commonly prescribed.
Storage and transportation regulations for isocyanates are designed to prevent accidental releases and ensure proper handling during transit. These regulations typically specify requirements for container design, labeling, and segregation from incompatible materials. Additionally, emergency response plans and spill containment procedures are mandated to address potential incidents involving isocyanates.
Training and education requirements are integral to isocyanate safety regulations. Workers involved in handling these chemicals must receive comprehensive training on the hazards associated with isocyanates, proper use of PPE, safe work practices, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher training is often required to ensure ongoing compliance and awareness.
As advancements in isocyanate reaction control techniques continue to evolve, safety regulations are likely to adapt to address new challenges and incorporate improved protective measures. This may include the integration of real-time monitoring technologies, enhanced exposure assessment methods, and more sophisticated engineering controls to further minimize the risks associated with isocyanate handling in industrial processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!