Analyzing Neopentane Safety Protocols for Industrial Use
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Neopentane Safety Overview and Objectives
Neopentane, also known as 2,2-dimethylpropane, is a highly volatile hydrocarbon compound with significant industrial applications. As its use in various sectors continues to grow, understanding and implementing robust safety protocols has become paramount. This technical preview aims to provide a comprehensive overview of neopentane safety considerations and establish clear objectives for its industrial use.
The development of neopentane safety protocols has evolved alongside the expansion of its applications in industries such as refrigeration, aerosols, and chemical manufacturing. Historical incidents involving similar hydrocarbons have underscored the importance of stringent safety measures. The primary goal of this analysis is to evaluate current safety practices, identify potential risks, and propose enhanced protocols to ensure the safe handling, storage, and use of neopentane in industrial settings.
Key safety concerns associated with neopentane include its high flammability, potential for rapid vaporization, and the risk of forming explosive mixtures with air. These properties necessitate careful consideration in all aspects of its industrial use, from transportation and storage to processing and disposal. The objectives of this technical preview encompass a thorough examination of existing safety guidelines, assessment of their effectiveness, and identification of areas for improvement.
One of the critical aspects of neopentane safety is the prevention of accidental releases and the mitigation of their consequences. This involves the design and implementation of robust containment systems, leak detection mechanisms, and emergency response procedures. Additionally, the review aims to explore advanced technologies and methodologies that can enhance safety measures, such as improved ventilation systems, state-of-the-art fire suppression techniques, and innovative personal protective equipment.
The analysis will also focus on the regulatory landscape surrounding neopentane use, including international standards, industry best practices, and regional regulations. By examining these frameworks, we aim to identify potential gaps in current safety protocols and propose harmonized approaches that can be adopted across different industrial sectors and geographical regions.
Furthermore, this technical preview will investigate the human factors involved in neopentane safety, including training requirements, risk awareness programs, and the development of a safety-first culture in industrial environments. The objective is to outline comprehensive strategies that address both technical and organizational aspects of safety management.
In conclusion, this overview sets the stage for a detailed exploration of neopentane safety protocols, with the ultimate goal of enhancing industrial safety standards and minimizing risks associated with its use. By combining technical analysis, regulatory insights, and practical recommendations, we aim to contribute to the continuous improvement of safety practices in neopentane-related industries.
The development of neopentane safety protocols has evolved alongside the expansion of its applications in industries such as refrigeration, aerosols, and chemical manufacturing. Historical incidents involving similar hydrocarbons have underscored the importance of stringent safety measures. The primary goal of this analysis is to evaluate current safety practices, identify potential risks, and propose enhanced protocols to ensure the safe handling, storage, and use of neopentane in industrial settings.
Key safety concerns associated with neopentane include its high flammability, potential for rapid vaporization, and the risk of forming explosive mixtures with air. These properties necessitate careful consideration in all aspects of its industrial use, from transportation and storage to processing and disposal. The objectives of this technical preview encompass a thorough examination of existing safety guidelines, assessment of their effectiveness, and identification of areas for improvement.
One of the critical aspects of neopentane safety is the prevention of accidental releases and the mitigation of their consequences. This involves the design and implementation of robust containment systems, leak detection mechanisms, and emergency response procedures. Additionally, the review aims to explore advanced technologies and methodologies that can enhance safety measures, such as improved ventilation systems, state-of-the-art fire suppression techniques, and innovative personal protective equipment.
The analysis will also focus on the regulatory landscape surrounding neopentane use, including international standards, industry best practices, and regional regulations. By examining these frameworks, we aim to identify potential gaps in current safety protocols and propose harmonized approaches that can be adopted across different industrial sectors and geographical regions.
Furthermore, this technical preview will investigate the human factors involved in neopentane safety, including training requirements, risk awareness programs, and the development of a safety-first culture in industrial environments. The objective is to outline comprehensive strategies that address both technical and organizational aspects of safety management.
In conclusion, this overview sets the stage for a detailed exploration of neopentane safety protocols, with the ultimate goal of enhancing industrial safety standards and minimizing risks associated with its use. By combining technical analysis, regulatory insights, and practical recommendations, we aim to contribute to the continuous improvement of safety practices in neopentane-related industries.
Industrial Demand for Neopentane
Neopentane, a highly volatile hydrocarbon, has seen a significant increase in industrial demand over the past decade. This surge is primarily driven by its unique properties that make it valuable in various applications across multiple sectors. In the refrigeration industry, neopentane has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional refrigerants due to its low global warming potential and excellent thermodynamic properties. The automotive sector has also shown growing interest in neopentane as a blowing agent for foam insulation in vehicle manufacturing, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
The chemical industry represents another major source of demand for neopentane. Its use as a raw material in the production of specialty chemicals, particularly in the synthesis of high-performance polymers and resins, has expanded considerably. The electronics industry has also begun to utilize neopentane in the manufacturing of semiconductor devices, where its purity and controlled evaporation characteristics are highly valued.
Market analysis indicates that the global neopentane market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% in the coming years. This growth is largely attributed to the increasing adoption of environmentally friendly technologies and stricter regulations on greenhouse gas emissions in developed economies. Developing countries, particularly in Asia-Pacific, are also contributing to this growth as their industrial sectors expand and modernize.
The oil and gas industry has shown renewed interest in neopentane as a component in enhanced oil recovery techniques. Its use in gas injection methods has proven effective in improving oil extraction rates from mature fields, potentially extending the lifespan of existing reservoirs. This application is particularly relevant in regions with declining conventional oil production.
Despite the growing demand, the neopentane market faces challenges related to supply chain stability and price volatility. The production of neopentane is closely tied to the petrochemical industry, making it susceptible to fluctuations in crude oil prices and geopolitical factors affecting oil-producing regions. Additionally, the handling and transportation of neopentane require specialized equipment and safety protocols due to its high flammability and volatility, which can impact its accessibility and cost-effectiveness for some industrial users.
As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and energy efficiency, the demand for neopentane is expected to remain strong. However, this growth will likely be tempered by ongoing research into alternative materials and technologies that may compete with neopentane in specific applications. The development of new safety protocols and handling technologies will be crucial in facilitating the wider adoption of neopentane across various industrial sectors, ensuring its continued growth in the global market.
The chemical industry represents another major source of demand for neopentane. Its use as a raw material in the production of specialty chemicals, particularly in the synthesis of high-performance polymers and resins, has expanded considerably. The electronics industry has also begun to utilize neopentane in the manufacturing of semiconductor devices, where its purity and controlled evaporation characteristics are highly valued.
Market analysis indicates that the global neopentane market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% in the coming years. This growth is largely attributed to the increasing adoption of environmentally friendly technologies and stricter regulations on greenhouse gas emissions in developed economies. Developing countries, particularly in Asia-Pacific, are also contributing to this growth as their industrial sectors expand and modernize.
The oil and gas industry has shown renewed interest in neopentane as a component in enhanced oil recovery techniques. Its use in gas injection methods has proven effective in improving oil extraction rates from mature fields, potentially extending the lifespan of existing reservoirs. This application is particularly relevant in regions with declining conventional oil production.
Despite the growing demand, the neopentane market faces challenges related to supply chain stability and price volatility. The production of neopentane is closely tied to the petrochemical industry, making it susceptible to fluctuations in crude oil prices and geopolitical factors affecting oil-producing regions. Additionally, the handling and transportation of neopentane require specialized equipment and safety protocols due to its high flammability and volatility, which can impact its accessibility and cost-effectiveness for some industrial users.
As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and energy efficiency, the demand for neopentane is expected to remain strong. However, this growth will likely be tempered by ongoing research into alternative materials and technologies that may compete with neopentane in specific applications. The development of new safety protocols and handling technologies will be crucial in facilitating the wider adoption of neopentane across various industrial sectors, ensuring its continued growth in the global market.
Current Safety Challenges in Neopentane Handling
Neopentane, a highly flammable and volatile hydrocarbon, presents significant safety challenges in industrial settings. The primary concern is its low boiling point and high vapor pressure, which make it prone to rapid vaporization and potential formation of explosive atmospheres. This characteristic necessitates stringent containment measures and specialized handling procedures to prevent accidental releases.
One of the most pressing challenges is the prevention of leaks and spills. Neopentane's low molecular weight and small molecule size make it particularly prone to permeating through seals and gaskets, even those typically considered adequate for other hydrocarbons. This requires the use of specialized materials and frequent inspection and maintenance of storage and transfer equipment to ensure integrity.
Fire and explosion risks pose another major safety concern. Neopentane has a wide flammability range and a low autoignition temperature, making it susceptible to ignition from various sources, including static electricity. Implementing comprehensive grounding and bonding systems, as well as utilizing explosion-proof electrical equipment, is crucial but can be complex and costly in large industrial settings.
The potential for rapid pressure buildup in confined spaces presents a significant challenge. Temperature fluctuations can cause dramatic pressure changes in neopentane storage vessels, necessitating robust pressure relief systems and careful monitoring. Designing and maintaining these systems to handle worst-case scenarios while preventing unnecessary releases is a delicate balance.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) selection and use pose unique challenges due to neopentane's properties. Standard PPE may not provide adequate protection against its rapid permeation through materials. Identifying and implementing appropriate PPE that offers sufficient protection while allowing workers to perform their tasks efficiently is an ongoing challenge.
Environmental concerns add another layer of complexity to neopentane handling. Its high volatility means that any release can quickly disperse into the atmosphere, potentially contributing to air pollution and posing risks to surrounding communities. Developing effective containment and recovery systems for both liquid and vapor phases is essential but technically challenging.
Training and emergency response preparedness represent ongoing challenges in neopentane handling. The unique properties of neopentane require specialized knowledge and skills for safe handling, which must be continually updated as best practices evolve. Ensuring that all personnel, including emergency responders, are adequately trained and equipped to handle neopentane-related incidents is a critical but resource-intensive task.
One of the most pressing challenges is the prevention of leaks and spills. Neopentane's low molecular weight and small molecule size make it particularly prone to permeating through seals and gaskets, even those typically considered adequate for other hydrocarbons. This requires the use of specialized materials and frequent inspection and maintenance of storage and transfer equipment to ensure integrity.
Fire and explosion risks pose another major safety concern. Neopentane has a wide flammability range and a low autoignition temperature, making it susceptible to ignition from various sources, including static electricity. Implementing comprehensive grounding and bonding systems, as well as utilizing explosion-proof electrical equipment, is crucial but can be complex and costly in large industrial settings.
The potential for rapid pressure buildup in confined spaces presents a significant challenge. Temperature fluctuations can cause dramatic pressure changes in neopentane storage vessels, necessitating robust pressure relief systems and careful monitoring. Designing and maintaining these systems to handle worst-case scenarios while preventing unnecessary releases is a delicate balance.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) selection and use pose unique challenges due to neopentane's properties. Standard PPE may not provide adequate protection against its rapid permeation through materials. Identifying and implementing appropriate PPE that offers sufficient protection while allowing workers to perform their tasks efficiently is an ongoing challenge.
Environmental concerns add another layer of complexity to neopentane handling. Its high volatility means that any release can quickly disperse into the atmosphere, potentially contributing to air pollution and posing risks to surrounding communities. Developing effective containment and recovery systems for both liquid and vapor phases is essential but technically challenging.
Training and emergency response preparedness represent ongoing challenges in neopentane handling. The unique properties of neopentane require specialized knowledge and skills for safe handling, which must be continually updated as best practices evolve. Ensuring that all personnel, including emergency responders, are adequately trained and equipped to handle neopentane-related incidents is a critical but resource-intensive task.
Existing Neopentane Safety Solutions
01 Storage and handling protocols
Neopentane requires specific storage and handling protocols due to its flammable nature. This includes using appropriate containers, maintaining proper temperature and pressure conditions, and implementing safety measures to prevent leaks or accidental ignition. Proper ventilation and the use of explosion-proof equipment are essential in areas where neopentane is stored or handled.- Storage and handling protocols: Neopentane requires specific storage and handling protocols due to its flammable nature. This includes using appropriate containers, maintaining proper temperature and pressure conditions, and implementing safety measures to prevent leaks or accidental releases. Proper ventilation and the use of explosion-proof equipment are essential in areas where neopentane is stored or handled.
- Fire safety and suppression systems: Given neopentane's high flammability, robust fire safety and suppression systems are crucial. This includes the installation of specialized fire detection and alarm systems, as well as appropriate fire extinguishing equipment. Training personnel in fire response procedures and conducting regular fire drills are also important components of neopentane safety protocols.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Workers handling neopentane must use appropriate personal protective equipment. This typically includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles or face shields, and flame-resistant clothing. In some cases, respiratory protection may also be necessary. Regular training on the proper use and maintenance of PPE is essential for ensuring worker safety.
- Emergency response and evacuation procedures: Comprehensive emergency response and evacuation procedures must be in place for facilities handling neopentane. This includes clear communication protocols, designated evacuation routes, and regular drills to ensure all personnel are familiar with the procedures. Emergency response teams should be trained in handling neopentane-specific incidents.
- Environmental protection and spill containment: Protocols for preventing and managing neopentane spills are crucial for environmental protection. This includes implementing proper containment systems, using spill-resistant equipment, and having absorbent materials readily available. Procedures for safe cleanup and disposal of spilled neopentane should be clearly defined and regularly practiced.
02 Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Workers handling neopentane should use appropriate personal protective equipment. This may include chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and flame-resistant clothing. In some cases, respiratory protection may be necessary. Regular training on the proper use of PPE and emergency procedures is crucial for maintaining safety when working with neopentane.Expand Specific Solutions03 Emergency response procedures
Establishing and maintaining emergency response procedures is critical for neopentane safety. This includes developing evacuation plans, installing fire suppression systems, and training personnel on how to respond to spills, leaks, or fires involving neopentane. Regular drills and simulations can help ensure that all staff are prepared for potential emergencies.Expand Specific Solutions04 Monitoring and detection systems
Implementing robust monitoring and detection systems is essential for neopentane safety. This may include gas detectors, pressure sensors, and temperature monitors to alert personnel to potential leaks or unsafe conditions. Regular calibration and maintenance of these systems are necessary to ensure their reliability and effectiveness in preventing accidents.Expand Specific Solutions05 Transportation safety measures
Transporting neopentane requires specific safety measures due to its hazardous nature. This includes using appropriate containers, following proper labeling and documentation procedures, and adhering to transportation regulations. Drivers and handlers should be trained in emergency procedures and equipped with necessary safety equipment. Route planning and risk assessments are also important aspects of neopentane transportation safety.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Neopentane Industry
The neopentane safety protocols for industrial use market is in a mature stage, with established players and well-defined safety standards. The market size is moderate, driven by the chemical and petrochemical industries' demand for safe handling of this flammable gas. Technologically, safety protocols are well-developed, with companies like ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc. and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. leading in innovation. Sinopec Shanghai Petrochemical Co., Ltd. and Hongbaoli Group Corp. Ltd. have also made significant contributions to safety practices. While the core technology is mature, ongoing research by institutions like North Carolina State University and The Chinese University of Hong Kong continues to refine and enhance safety measures, ensuring the industry stays current with evolving industrial needs and regulatory requirements.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed advanced safety protocols for handling neopentane in industrial settings. Their approach includes multi-layered containment systems, utilizing specialized pressure-resistant vessels and piping materials designed to withstand the unique properties of neopentane. The company has implemented state-of-the-art leak detection systems that employ infrared sensors and gas chromatography for real-time monitoring[1]. Additionally, ExxonMobil has developed proprietary software for risk assessment and emergency response planning specific to neopentane handling[2]. Their safety measures also incorporate innovative fire suppression systems tailored to neopentane's flammability characteristics, including the use of high-expansion foam and inert gas flooding systems[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach, cutting-edge technology, and industry-leading expertise. Weaknesses: Potentially high implementation costs and complexity in smaller-scale operations.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has implemented a robust safety protocol for neopentane handling in its industrial processes. Their approach focuses on a combination of engineering controls and operational procedures. Sinopec has developed specialized storage tanks with advanced pressure relief systems and inert gas blanketing to prevent explosive atmospheres[4]. The company utilizes a sophisticated process control system that incorporates real-time monitoring of temperature, pressure, and concentration levels. Sinopec has also implemented a comprehensive employee training program on neopentane safety, including regular drills and simulations[5]. Their safety measures extend to transportation, with custom-designed tankers and strict loading/unloading procedures to minimize risks during transit[6].
Strengths: Integrated approach covering storage, processing, and transportation; strong focus on employee training. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in adapting protocols to different regional regulations.
Innovative Safety Technologies for Neopentane
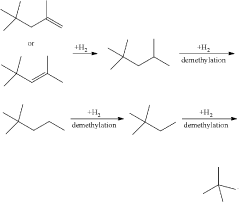
Production of Neopentane
PatentActiveUS20190177248A1
Innovation
- A process involving the dimerization of isobutylene to form diisobutylene, followed by demethylation using a catalyst in the presence of hydrogen, which utilizes readily available isobutylene from refinery raffinate streams to produce neopentane with high yield and selectivity.
Regulatory Framework for Neopentane Use
The regulatory framework for neopentane use in industrial settings is a complex and evolving landscape that requires careful consideration and adherence. At the international level, organizations such as the United Nations and the International Maritime Organization have established guidelines for the safe handling and transport of hazardous materials, including neopentane. These regulations often serve as a foundation for national and regional policies.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) plays a crucial role in regulating neopentane use in industrial environments. OSHA has set specific standards for permissible exposure limits, personal protective equipment requirements, and workplace safety protocols. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also contributes to the regulatory framework by enforcing emissions standards and waste management practices related to neopentane.
The European Union has implemented the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, which applies to neopentane and other chemical substances. This comprehensive framework requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with neopentane use, as well as to provide safety information to downstream users.
Many countries have adopted the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS), which standardizes hazard communication for chemical substances, including neopentane. This system ensures consistent labeling and safety data sheets across different jurisdictions, facilitating international trade and improving workplace safety.
Industry-specific regulations also play a significant role in shaping neopentane safety protocols. For instance, in the petrochemical industry, organizations like the American Petroleum Institute (API) have developed standards and recommended practices for handling volatile hydrocarbons, which include neopentane.
Local and regional authorities often impose additional requirements for neopentane use, storage, and transportation. These may include zoning restrictions, fire safety codes, and emergency response planning. Compliance with these local regulations is essential for industrial facilities using neopentane.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, many jurisdictions are implementing stricter regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions, which affect neopentane use. This trend is driving industries to adopt more efficient containment systems and explore alternative substances where possible.
The regulatory landscape for neopentane is not static, and ongoing research into its environmental and health impacts may lead to future regulatory changes. Industrial users must stay informed about these developments and be prepared to adapt their safety protocols accordingly.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) plays a crucial role in regulating neopentane use in industrial environments. OSHA has set specific standards for permissible exposure limits, personal protective equipment requirements, and workplace safety protocols. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also contributes to the regulatory framework by enforcing emissions standards and waste management practices related to neopentane.
The European Union has implemented the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, which applies to neopentane and other chemical substances. This comprehensive framework requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with neopentane use, as well as to provide safety information to downstream users.
Many countries have adopted the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS), which standardizes hazard communication for chemical substances, including neopentane. This system ensures consistent labeling and safety data sheets across different jurisdictions, facilitating international trade and improving workplace safety.
Industry-specific regulations also play a significant role in shaping neopentane safety protocols. For instance, in the petrochemical industry, organizations like the American Petroleum Institute (API) have developed standards and recommended practices for handling volatile hydrocarbons, which include neopentane.
Local and regional authorities often impose additional requirements for neopentane use, storage, and transportation. These may include zoning restrictions, fire safety codes, and emergency response planning. Compliance with these local regulations is essential for industrial facilities using neopentane.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, many jurisdictions are implementing stricter regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions, which affect neopentane use. This trend is driving industries to adopt more efficient containment systems and explore alternative substances where possible.
The regulatory landscape for neopentane is not static, and ongoing research into its environmental and health impacts may lead to future regulatory changes. Industrial users must stay informed about these developments and be prepared to adapt their safety protocols accordingly.
Environmental Impact of Neopentane
Neopentane, a highly volatile hydrocarbon, poses significant environmental concerns when used in industrial applications. Its release into the atmosphere can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a key component of smog. This photochemical reaction occurs when neopentane vapors interact with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight, leading to reduced air quality and potential health risks for both humans and ecosystems.
The global warming potential of neopentane is another critical environmental factor to consider. As a hydrocarbon, it acts as a greenhouse gas when released into the atmosphere, trapping heat and contributing to climate change. While its atmospheric lifetime is relatively short compared to carbon dioxide, its impact during that period is more intense, making proper containment and handling crucial for minimizing its environmental footprint.
Water pollution is an additional concern associated with neopentane use in industrial settings. Accidental spills or improper disposal can lead to contamination of water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. The low water solubility of neopentane means it can form a persistent layer on water surfaces, impeding oxygen transfer and disrupting aquatic life.
Industrial use of neopentane also raises concerns about soil contamination. Leaks or spills can result in the compound permeating soil layers, potentially reaching groundwater reserves. This contamination can have long-lasting effects on soil microorganisms, plant life, and ultimately, the entire ecosystem of affected areas.
The production and transportation of neopentane for industrial use contribute to its overall environmental impact. The energy-intensive processes involved in its manufacture and distribution result in additional carbon emissions, further exacerbating its climate change effects. Moreover, the risk of accidental releases during transportation poses threats to ecosystems along shipping routes.
To mitigate these environmental risks, stringent safety protocols and containment measures are essential in industrial settings using neopentane. Implementing closed-loop systems, improving leak detection technologies, and enhancing spill response capabilities can significantly reduce the potential for environmental contamination. Additionally, exploring alternative substances with lower environmental impacts could be a long-term strategy for industries reliant on neopentane.
The global warming potential of neopentane is another critical environmental factor to consider. As a hydrocarbon, it acts as a greenhouse gas when released into the atmosphere, trapping heat and contributing to climate change. While its atmospheric lifetime is relatively short compared to carbon dioxide, its impact during that period is more intense, making proper containment and handling crucial for minimizing its environmental footprint.
Water pollution is an additional concern associated with neopentane use in industrial settings. Accidental spills or improper disposal can lead to contamination of water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. The low water solubility of neopentane means it can form a persistent layer on water surfaces, impeding oxygen transfer and disrupting aquatic life.
Industrial use of neopentane also raises concerns about soil contamination. Leaks or spills can result in the compound permeating soil layers, potentially reaching groundwater reserves. This contamination can have long-lasting effects on soil microorganisms, plant life, and ultimately, the entire ecosystem of affected areas.
The production and transportation of neopentane for industrial use contribute to its overall environmental impact. The energy-intensive processes involved in its manufacture and distribution result in additional carbon emissions, further exacerbating its climate change effects. Moreover, the risk of accidental releases during transportation poses threats to ecosystems along shipping routes.
To mitigate these environmental risks, stringent safety protocols and containment measures are essential in industrial settings using neopentane. Implementing closed-loop systems, improving leak detection technologies, and enhancing spill response capabilities can significantly reduce the potential for environmental contamination. Additionally, exploring alternative substances with lower environmental impacts could be a long-term strategy for industries reliant on neopentane.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!