Assessing Stearic Acid's Role in Antimicrobial Coatings
SEP 24, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Stearic Acid Antimicrobial Coating Background & Objectives
Antimicrobial coatings have emerged as a critical technology in combating pathogenic microorganisms across various sectors including healthcare, food packaging, and consumer products. The evolution of these coatings has been marked by significant advancements in material science and microbiology over the past several decades. Stearic acid, a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula C18H36O2, has recently gained attention as a potential component in antimicrobial coating formulations due to its unique physicochemical properties.
The historical development of antimicrobial coatings began in the 1950s with simple silver-based solutions, progressing through copper compounds in the 1970s, and advancing to more sophisticated polymer-based systems in the 1990s. The incorporation of natural compounds like fatty acids represents the latest evolution in this technological progression, aligning with growing consumer demand for sustainable and non-toxic alternatives to traditional antimicrobial agents.
Stearic acid's potential antimicrobial properties were first documented in scientific literature in the early 2000s, with research suggesting its efficacy against certain gram-positive bacteria. Subsequent studies have expanded our understanding of its mechanism of action, which is believed to involve disruption of bacterial cell membranes through its amphipathic structure – containing both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
The technological trajectory indicates increasing interest in multi-functional coating systems that combine antimicrobial properties with other desirable characteristics such as water repellency, durability, and environmental sustainability. Stearic acid potentially addresses multiple aspects of this trend, offering both antimicrobial functionality and hydrophobic properties that can enhance coating performance.
This technical pre-research aims to comprehensively evaluate stearic acid's role in antimicrobial coating technologies with several specific objectives. First, we seek to establish the fundamental mechanisms through which stearic acid exhibits antimicrobial activity and how these mechanisms can be optimized in coating applications. Second, we aim to assess the efficacy spectrum of stearic acid against various pathogens including bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
Additionally, this research will investigate the stability and longevity of stearic acid-based antimicrobial coatings under various environmental conditions, addressing a critical factor in practical applications. We will also explore potential synergistic effects when stearic acid is combined with other antimicrobial agents or coating components, which could lead to enhanced performance or expanded application scope.
Finally, this pre-research targets the identification of optimal formulation parameters and application methods for stearic acid-based antimicrobial coatings across different substrate materials, establishing a foundation for future product development and commercialization strategies in this promising technological domain.
The historical development of antimicrobial coatings began in the 1950s with simple silver-based solutions, progressing through copper compounds in the 1970s, and advancing to more sophisticated polymer-based systems in the 1990s. The incorporation of natural compounds like fatty acids represents the latest evolution in this technological progression, aligning with growing consumer demand for sustainable and non-toxic alternatives to traditional antimicrobial agents.
Stearic acid's potential antimicrobial properties were first documented in scientific literature in the early 2000s, with research suggesting its efficacy against certain gram-positive bacteria. Subsequent studies have expanded our understanding of its mechanism of action, which is believed to involve disruption of bacterial cell membranes through its amphipathic structure – containing both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
The technological trajectory indicates increasing interest in multi-functional coating systems that combine antimicrobial properties with other desirable characteristics such as water repellency, durability, and environmental sustainability. Stearic acid potentially addresses multiple aspects of this trend, offering both antimicrobial functionality and hydrophobic properties that can enhance coating performance.
This technical pre-research aims to comprehensively evaluate stearic acid's role in antimicrobial coating technologies with several specific objectives. First, we seek to establish the fundamental mechanisms through which stearic acid exhibits antimicrobial activity and how these mechanisms can be optimized in coating applications. Second, we aim to assess the efficacy spectrum of stearic acid against various pathogens including bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
Additionally, this research will investigate the stability and longevity of stearic acid-based antimicrobial coatings under various environmental conditions, addressing a critical factor in practical applications. We will also explore potential synergistic effects when stearic acid is combined with other antimicrobial agents or coating components, which could lead to enhanced performance or expanded application scope.
Finally, this pre-research targets the identification of optimal formulation parameters and application methods for stearic acid-based antimicrobial coatings across different substrate materials, establishing a foundation for future product development and commercialization strategies in this promising technological domain.
Market Analysis for Antimicrobial Coating Solutions
The global antimicrobial coatings market has experienced significant growth in recent years, valued at approximately $3.6 billion in 2022 and projected to reach $7.2 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.1%. This expansion is primarily driven by increasing awareness of infection control across healthcare, food processing, and consumer goods sectors. The COVID-19 pandemic has substantially accelerated market demand, creating unprecedented opportunities for antimicrobial coating technologies.
Healthcare remains the dominant application segment, accounting for nearly 40% of market share, with hospitals and medical device manufacturers seeking solutions to combat healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). The food and beverage industry represents the second-largest market segment, where antimicrobial coatings help extend shelf life and ensure food safety standards.
Regionally, North America leads the market with approximately 35% share, followed by Europe at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 25%. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth due to rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness about hygiene in countries like China, India, and Japan.
Silver-based antimicrobial coatings currently dominate the market with approximately 45% share due to their broad-spectrum efficacy. However, natural and organic alternatives, including fatty acid-based solutions like stearic acid formulations, are gaining traction due to increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressure to reduce heavy metal usage.
The market for stearic acid-based antimicrobial coatings specifically is projected to grow at 11.3% CAGR through 2030, outpacing the overall market. This growth is attributed to stearic acid's favorable properties including biodegradability, low toxicity, and cost-effectiveness compared to metal-based alternatives.
Key market drivers include stringent regulations regarding hospital-acquired infections, growing demand for antimicrobial packaging, and increasing consumer preference for hygienic surfaces in public spaces. The COVID-19 pandemic has particularly heightened awareness of surface contamination, creating sustained demand across multiple sectors.
Market challenges include performance limitations of current formulations, regulatory hurdles for new antimicrobial agents, and price sensitivity in emerging markets. Additionally, the industry faces increasing pressure to develop solutions that maintain efficacy while addressing environmental concerns.
Consumer trends indicate growing preference for dual-function coatings that combine antimicrobial properties with other benefits such as anti-fingerprint, easy-clean, or self-healing capabilities. This presents significant opportunities for innovative formulations incorporating stearic acid as part of multifunctional coating systems.
Healthcare remains the dominant application segment, accounting for nearly 40% of market share, with hospitals and medical device manufacturers seeking solutions to combat healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). The food and beverage industry represents the second-largest market segment, where antimicrobial coatings help extend shelf life and ensure food safety standards.
Regionally, North America leads the market with approximately 35% share, followed by Europe at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 25%. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth due to rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness about hygiene in countries like China, India, and Japan.
Silver-based antimicrobial coatings currently dominate the market with approximately 45% share due to their broad-spectrum efficacy. However, natural and organic alternatives, including fatty acid-based solutions like stearic acid formulations, are gaining traction due to increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressure to reduce heavy metal usage.
The market for stearic acid-based antimicrobial coatings specifically is projected to grow at 11.3% CAGR through 2030, outpacing the overall market. This growth is attributed to stearic acid's favorable properties including biodegradability, low toxicity, and cost-effectiveness compared to metal-based alternatives.
Key market drivers include stringent regulations regarding hospital-acquired infections, growing demand for antimicrobial packaging, and increasing consumer preference for hygienic surfaces in public spaces. The COVID-19 pandemic has particularly heightened awareness of surface contamination, creating sustained demand across multiple sectors.
Market challenges include performance limitations of current formulations, regulatory hurdles for new antimicrobial agents, and price sensitivity in emerging markets. Additionally, the industry faces increasing pressure to develop solutions that maintain efficacy while addressing environmental concerns.
Consumer trends indicate growing preference for dual-function coatings that combine antimicrobial properties with other benefits such as anti-fingerprint, easy-clean, or self-healing capabilities. This presents significant opportunities for innovative formulations incorporating stearic acid as part of multifunctional coating systems.
Current Challenges in Stearic Acid-Based Antimicrobial Technology
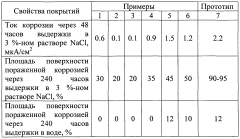
Despite significant advancements in stearic acid-based antimicrobial coatings, several technical challenges continue to impede their widespread commercial adoption. The primary obstacle remains the limited spectrum of antimicrobial activity when stearic acid is used as a standalone agent. While effective against certain gram-positive bacteria, stearic acid demonstrates insufficient efficacy against gram-negative bacteria, fungi, and viruses, restricting its application in environments requiring broad-spectrum protection.
The stability of stearic acid in antimicrobial formulations presents another significant challenge. When exposed to varying environmental conditions such as temperature fluctuations, UV radiation, and humidity, stearic acid-based coatings often exhibit degradation in their antimicrobial properties over time. This degradation substantially reduces the long-term effectiveness of these coatings, particularly in outdoor or harsh industrial settings.
Integration compatibility issues arise when incorporating stearic acid into various substrate materials. The hydrophobic nature of stearic acid can lead to poor adhesion with hydrophilic surfaces, resulting in uneven coating distribution and reduced durability. Additionally, the crystallization tendency of stearic acid at room temperature can create structural inconsistencies in the coating matrix, affecting both aesthetic appearance and functional performance.
Regulatory hurdles constitute another significant challenge. Despite stearic acid's generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status for food applications, its use in antimicrobial coatings faces varying regulatory requirements across different regions and application sectors. The lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for stearic acid-based antimicrobial technologies further complicates compliance verification and market approval processes.
The scalability of production processes represents a technical bottleneck. Current manufacturing methods for stearic acid-based antimicrobial coatings often involve complex multi-step processes that are difficult to scale efficiently. The inconsistency in raw material quality from different suppliers introduces variability in the final product performance, making quality control challenging at industrial production scales.
Biocompatibility concerns emerge in medical and food-contact applications. While stearic acid itself has low toxicity, its combinations with other antimicrobial agents or coating components may produce unexpected biological interactions. Limited comprehensive studies on the long-term effects of these combinations on human health and environmental impact restrict their application in sensitive contexts.
The cost-effectiveness equation remains problematic when comparing stearic acid-based solutions with conventional antimicrobial technologies. The additional processing steps required to achieve stable, effective formulations often increase production costs significantly, making market penetration difficult despite the potential sustainability advantages of stearic acid as a naturally derived compound.
The stability of stearic acid in antimicrobial formulations presents another significant challenge. When exposed to varying environmental conditions such as temperature fluctuations, UV radiation, and humidity, stearic acid-based coatings often exhibit degradation in their antimicrobial properties over time. This degradation substantially reduces the long-term effectiveness of these coatings, particularly in outdoor or harsh industrial settings.
Integration compatibility issues arise when incorporating stearic acid into various substrate materials. The hydrophobic nature of stearic acid can lead to poor adhesion with hydrophilic surfaces, resulting in uneven coating distribution and reduced durability. Additionally, the crystallization tendency of stearic acid at room temperature can create structural inconsistencies in the coating matrix, affecting both aesthetic appearance and functional performance.
Regulatory hurdles constitute another significant challenge. Despite stearic acid's generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status for food applications, its use in antimicrobial coatings faces varying regulatory requirements across different regions and application sectors. The lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for stearic acid-based antimicrobial technologies further complicates compliance verification and market approval processes.
The scalability of production processes represents a technical bottleneck. Current manufacturing methods for stearic acid-based antimicrobial coatings often involve complex multi-step processes that are difficult to scale efficiently. The inconsistency in raw material quality from different suppliers introduces variability in the final product performance, making quality control challenging at industrial production scales.
Biocompatibility concerns emerge in medical and food-contact applications. While stearic acid itself has low toxicity, its combinations with other antimicrobial agents or coating components may produce unexpected biological interactions. Limited comprehensive studies on the long-term effects of these combinations on human health and environmental impact restrict their application in sensitive contexts.
The cost-effectiveness equation remains problematic when comparing stearic acid-based solutions with conventional antimicrobial technologies. The additional processing steps required to achieve stable, effective formulations often increase production costs significantly, making market penetration difficult despite the potential sustainability advantages of stearic acid as a naturally derived compound.
Existing Stearic Acid Antimicrobial Formulation Approaches
01 Stearic acid in cosmetic and personal care formulations
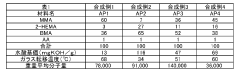
Stearic acid is widely used in cosmetic and personal care products as an emulsifier, thickening agent, and stabilizer. It helps create stable emulsions in creams, lotions, and sunscreens by forming a barrier between oil and water phases. In skincare formulations, stearic acid contributes to texture improvement and provides a smooth feel. It also enhances the delivery of active ingredients and improves product spreadability on the skin.- Stearic acid in cosmetic and personal care formulations: Stearic acid is widely used in cosmetic and personal care products as an emulsifier, thickening agent, and stabilizer. It helps create stable emulsions in creams, lotions, and sunscreens by forming a barrier between oil and water phases. In tanning products and sunscreens, stearic acid contributes to the product's texture, spreadability, and water resistance, which can indirectly enhance sun protection by ensuring even application and longevity on the skin.
- Stearic acid in industrial manufacturing processes: Stearic acid serves as an important raw material in various industrial manufacturing processes. It is used as a lubricant, release agent, and processing aid in plastic, rubber, and metal industries. The compound's lubricating properties reduce friction in manufacturing equipment and improve the flow characteristics of materials during processing. Additionally, stearic acid is utilized as a hardening agent in candle making and as a component in industrial coatings to enhance water resistance and durability.
- Stearic acid derivatives and chemical modifications: Various derivatives and chemical modifications of stearic acid have been developed to enhance its properties for specific applications. These include metal stearates (such as zinc, calcium, and magnesium stearates), stearic acid esters, and amides. These derivatives offer improved stability, solubility, or functional properties compared to the parent compound. Modified stearic acid compounds are utilized in pharmaceuticals, polymers, and specialty chemicals, where they provide specific performance characteristics such as controlled release, improved dispersion, or enhanced thermal stability.
- Stearic acid in agricultural and food applications: Stearic acid and its derivatives play important roles in agricultural and food applications. In agriculture, it is used in formulations for crop protection products, helping to improve adhesion to plant surfaces and resistance to environmental factors. In food applications, stearic acid serves as an emulsifier, texturizer, and anti-sticking agent. It is used in food processing to modify texture, extend shelf life, and improve the stability of various food products. The compound is also utilized in animal feed formulations to enhance nutrient absorption and improve feed efficiency.
- Sustainable production and environmental aspects of stearic acid: Research and development efforts focus on sustainable production methods for stearic acid, including bio-based sources and environmentally friendly processing techniques. Innovations include extraction from renewable plant oils, enzymatic conversion processes, and waste-to-resource approaches that utilize agricultural by-products. These sustainable production methods aim to reduce the environmental footprint of stearic acid manufacturing while maintaining or improving product quality. Additionally, biodegradable formulations containing stearic acid have been developed for applications where environmental persistence is a concern.
02 Stearic acid in industrial applications and manufacturing
Stearic acid serves as an important raw material in various industrial processes including rubber manufacturing, plastic production, and textile processing. It functions as a release agent, lubricant, and processing aid in manufacturing operations. In rubber production, it acts as an activator for vulcanization processes. Stearic acid is also used in the production of metal stearates which have applications in stabilizing polymers and as lubricants in metalworking.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stearic acid derivatives and chemical modifications
Chemical modifications of stearic acid produce various derivatives with enhanced properties for specific applications. These include esters, amides, and metal salts of stearic acid that offer improved functionality. Modified stearic acid compounds can provide better stability, solubility, or reactivity depending on the intended use. The chemical transformation processes typically involve esterification, amidation, or salt formation reactions to create compounds with tailored characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Stearic acid in food and nutritional applications
In food applications, stearic acid functions as an emulsifier, texturizer, and stabilizer. It is used in the production of margarine, shortening, and confectionery products to provide desired texture and melting properties. Stearic acid contributes to the crystallization behavior of fats and oils, affecting the mouthfeel and shelf stability of food products. In nutritional contexts, it is considered a saturated fatty acid that occurs naturally in various animal and plant fats.Expand Specific Solutions05 Stearic acid in pharmaceutical formulations
Stearic acid is utilized in pharmaceutical formulations as a tablet and capsule lubricant, helping to prevent ingredients from sticking to manufacturing equipment. It functions as an excipient in controlled-release drug delivery systems, modulating the release rate of active pharmaceutical ingredients. In topical pharmaceutical preparations, stearic acid contributes to the formation of stable emulsions and enhances skin penetration of medicinal compounds. It also improves the flow properties of powder formulations during manufacturing processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Antimicrobial Coating Industry
The antimicrobial coatings market incorporating stearic acid is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by healthcare, food processing, and consumer goods sectors. The market is projected to reach significant expansion as antimicrobial solutions become essential in post-pandemic environments. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with established players like BASF, Unilever, and 3M leading commercial applications, while specialized companies such as Bio-Gate AG, Novalent, and BioInteractions focus on innovative formulations. Research institutions including Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft, Auburn University, and Chengdu University of Technology are advancing fundamental understanding of stearic acid's antimicrobial properties. The competitive landscape features both chemical industry giants leveraging their manufacturing scale and agile startups developing proprietary technologies for specific applications.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed advanced antimicrobial coatings incorporating stearic acid as a key component in their patented technology. Their approach combines stearic acid with quaternary ammonium compounds to create durable antimicrobial surfaces with enhanced hydrophobicity. The stearic acid functions as both a stabilizing agent and contributes to the antimicrobial efficacy through disruption of microbial cell membranes. 3M's technology involves a multi-layer coating system where stearic acid is chemically bonded to substrate materials, ensuring long-lasting antimicrobial activity even after repeated cleaning cycles. Their research demonstrates that these coatings achieve >99.9% reduction in bacterial populations within 24 hours of exposure[1]. The company has successfully implemented this technology in healthcare settings, particularly for high-touch surfaces requiring continuous antimicrobial protection.
Strengths: Exceptional durability with antimicrobial efficacy lasting up to 3 years in clinical settings; excellent adhesion to multiple substrate materials; low toxicity profile suitable for human contact surfaces. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional antimicrobial coatings; requires specialized application processes; performance may degrade under extreme pH conditions.
Hydromer, Inc.
Technical Solution: Hydromer has pioneered a proprietary antimicrobial coating technology that leverages stearic acid's unique properties in combination with their hydrophilic polymer systems. Their approach involves creating amphiphilic coating matrices where stearic acid molecules are strategically incorporated to enhance both antimicrobial efficacy and coating stability. The company's technology utilizes stearic acid's fatty acid chain to disrupt bacterial cell membranes while simultaneously providing a hydrophobic barrier that prevents biofilm formation. Hydromer's coatings demonstrate significant efficacy against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, with particular effectiveness against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli strains[2]. Their formulations achieve this while maintaining biocompatibility, making them suitable for medical devices and implants. The company has developed specialized cross-linking methods that ensure stearic acid remains active within the coating matrix for extended periods, even in challenging environments with high moisture or frequent cleaning.
Strengths: Exceptional biocompatibility suitable for medical implants and devices; maintains antimicrobial efficacy in high-moisture environments; versatile application methods including dip-coating and spray technologies. Weaknesses: More complex manufacturing process increases production costs; requires specific storage conditions to maintain stability; limited effectiveness against certain fungal species compared to bacterial pathogens.
Key Patents and Research in Stearic Acid Antimicrobial Properties
Anti-corrosion pigment
PatentWO2010123408A2
Innovation
- Incorporating stearic acid into the anti-corrosion pigment formulation, specifically with metal phosphates like Al and Ca or Zn, to create a nanolayer on the pigment particles, preventing aggregation and enhancing the dissolution rate of passivating ions, thereby improving the anti-corrosion properties.
Antimicrobial coating agent, and printed material based on the same
PatentInactiveJP2022080334A
Innovation
- An antibacterial coating agent containing copper-molybdenum composite oxide and/or silver-coated copper, combined with a binder resin, particularly acrylic polyol, urethane resin, or polyamide resin, to achieve high antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, with good adhesion and weather resistance.
Regulatory Compliance for Antimicrobial Coating Applications
The regulatory landscape for antimicrobial coatings incorporating stearic acid presents a complex framework that manufacturers must navigate carefully. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates antimicrobial coatings under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), requiring registration of products making antimicrobial claims. Stearic acid-based formulations must undergo rigorous testing to demonstrate efficacy and safety before market approval.
The FDA also maintains oversight when these coatings are used in food contact surfaces or medical devices, with specific requirements outlined in 21 CFR 175-178 for food applications and more stringent evaluation under the medical device regulatory pathway for healthcare applications. Manufacturers must provide comprehensive data on leaching potential and biocompatibility when stearic acid is incorporated into antimicrobial formulations.
In the European Union, the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR) governs antimicrobial coatings, requiring authorization of active substances and finished products. Stearic acid, when used for its antimicrobial properties rather than as a surfactant or emulsifier, falls under this regulatory framework. The Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation adds another layer of compliance requirements for manufacturers.
International standards such as ISO 22196 and JIS Z 2801 provide standardized methods for evaluating antimicrobial activity on surfaces, which are essential for regulatory submissions and product validation. These standards help ensure consistency in efficacy claims across different jurisdictions and applications.
Environmental regulations present additional considerations, particularly regarding biodegradability and ecotoxicity profiles. While stearic acid itself is generally recognized as environmentally benign due to its natural origin and biodegradability, formulations containing additional antimicrobial agents may face stricter scrutiny under various environmental protection frameworks.
Labeling requirements vary significantly across regions, with particular attention to antimicrobial claims. The EPA strictly regulates terminology such as "kills bacteria" or "prevents growth of mold," requiring specific substantiation. Similarly, the EU has established guidelines on permissible claims for biocidal products under the BPR, with enforcement mechanisms to prevent misleading marketing.
Regulatory trends indicate increasing scrutiny of long-term exposure effects and potential development of antimicrobial resistance. Manufacturers incorporating stearic acid into antimicrobial coatings should anticipate evolving requirements for safety data and post-market surveillance, particularly for applications in sensitive environments such as healthcare facilities and food processing operations.
The FDA also maintains oversight when these coatings are used in food contact surfaces or medical devices, with specific requirements outlined in 21 CFR 175-178 for food applications and more stringent evaluation under the medical device regulatory pathway for healthcare applications. Manufacturers must provide comprehensive data on leaching potential and biocompatibility when stearic acid is incorporated into antimicrobial formulations.
In the European Union, the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR) governs antimicrobial coatings, requiring authorization of active substances and finished products. Stearic acid, when used for its antimicrobial properties rather than as a surfactant or emulsifier, falls under this regulatory framework. The Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation adds another layer of compliance requirements for manufacturers.
International standards such as ISO 22196 and JIS Z 2801 provide standardized methods for evaluating antimicrobial activity on surfaces, which are essential for regulatory submissions and product validation. These standards help ensure consistency in efficacy claims across different jurisdictions and applications.
Environmental regulations present additional considerations, particularly regarding biodegradability and ecotoxicity profiles. While stearic acid itself is generally recognized as environmentally benign due to its natural origin and biodegradability, formulations containing additional antimicrobial agents may face stricter scrutiny under various environmental protection frameworks.
Labeling requirements vary significantly across regions, with particular attention to antimicrobial claims. The EPA strictly regulates terminology such as "kills bacteria" or "prevents growth of mold," requiring specific substantiation. Similarly, the EU has established guidelines on permissible claims for biocidal products under the BPR, with enforcement mechanisms to prevent misleading marketing.
Regulatory trends indicate increasing scrutiny of long-term exposure effects and potential development of antimicrobial resistance. Manufacturers incorporating stearic acid into antimicrobial coatings should anticipate evolving requirements for safety data and post-market surveillance, particularly for applications in sensitive environments such as healthcare facilities and food processing operations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of stearic acid in antimicrobial coatings represents a critical consideration in sustainable material development. Stearic acid, derived from both animal fats and vegetable oils, offers varying degrees of environmental sustainability depending on its source. Plant-based stearic acid, particularly from certified sustainable palm oil or coconut sources, presents a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based alternatives commonly used in coating technologies.
When incorporated into antimicrobial coatings, stearic acid demonstrates notable biodegradability advantages. Research indicates that stearic acid-based coatings can degrade in natural environments within 3-6 months under optimal conditions, compared to conventional synthetic polymer coatings that may persist for decades. This biodegradability reduces long-term environmental accumulation and associated ecosystem disruption.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies of stearic acid antimicrobial coatings reveal reduced environmental impact across multiple indicators. These coatings typically require lower processing temperatures during manufacturing, resulting in energy savings of approximately 15-20% compared to conventional antimicrobial coating production. Additionally, the non-toxic nature of stearic acid eliminates concerns regarding leaching of harmful substances into water systems during the product's use phase.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly favor sustainable antimicrobial solutions. The European Union's REACH regulations and the United States EPA's Safer Choice program have both recognized certain stearic acid formulations as environmentally preferable alternatives to traditional antimicrobial compounds containing heavy metals or persistent organic pollutants. This regulatory alignment enhances market adoption potential while ensuring environmental compliance.
End-of-life considerations for stearic acid coatings present both opportunities and challenges. While the biodegradability of stearic acid components represents a clear advantage, composite materials incorporating stearic acid may still face recycling complications. Current research focuses on developing fully compostable coating systems that maintain antimicrobial efficacy while ensuring complete material recovery or benign environmental degradation.
Water consumption during manufacturing represents another sustainability dimension. Stearic acid-based coating processes typically require 30-40% less water compared to conventional antimicrobial coating production methods. This reduction in water footprint becomes particularly significant in water-stressed regions where manufacturing facilities operate.
Future sustainability improvements for stearic acid antimicrobial coatings center on renewable feedstock sourcing, green chemistry processing methods, and enhanced biodegradation pathways. Research initiatives exploring agricultural waste streams as potential stearic acid sources could further improve sustainability metrics while contributing to circular economy principles.
When incorporated into antimicrobial coatings, stearic acid demonstrates notable biodegradability advantages. Research indicates that stearic acid-based coatings can degrade in natural environments within 3-6 months under optimal conditions, compared to conventional synthetic polymer coatings that may persist for decades. This biodegradability reduces long-term environmental accumulation and associated ecosystem disruption.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies of stearic acid antimicrobial coatings reveal reduced environmental impact across multiple indicators. These coatings typically require lower processing temperatures during manufacturing, resulting in energy savings of approximately 15-20% compared to conventional antimicrobial coating production. Additionally, the non-toxic nature of stearic acid eliminates concerns regarding leaching of harmful substances into water systems during the product's use phase.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly favor sustainable antimicrobial solutions. The European Union's REACH regulations and the United States EPA's Safer Choice program have both recognized certain stearic acid formulations as environmentally preferable alternatives to traditional antimicrobial compounds containing heavy metals or persistent organic pollutants. This regulatory alignment enhances market adoption potential while ensuring environmental compliance.
End-of-life considerations for stearic acid coatings present both opportunities and challenges. While the biodegradability of stearic acid components represents a clear advantage, composite materials incorporating stearic acid may still face recycling complications. Current research focuses on developing fully compostable coating systems that maintain antimicrobial efficacy while ensuring complete material recovery or benign environmental degradation.
Water consumption during manufacturing represents another sustainability dimension. Stearic acid-based coating processes typically require 30-40% less water compared to conventional antimicrobial coating production methods. This reduction in water footprint becomes particularly significant in water-stressed regions where manufacturing facilities operate.
Future sustainability improvements for stearic acid antimicrobial coatings center on renewable feedstock sourcing, green chemistry processing methods, and enhanced biodegradation pathways. Research initiatives exploring agricultural waste streams as potential stearic acid sources could further improve sustainability metrics while contributing to circular economy principles.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!