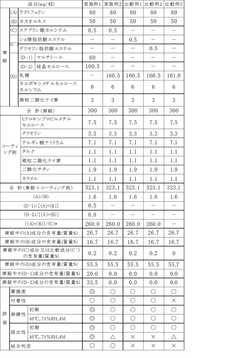
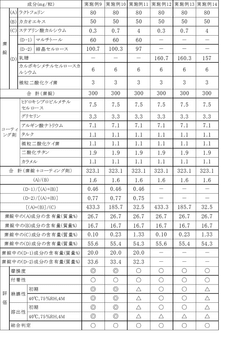
Optimizing Stearic Acid for High Compression Tablet Formulations
SEP 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Stearic Acid in Tablet Formulation: Background and Objectives
Stearic acid has emerged as a critical excipient in pharmaceutical tablet formulation, with its history dating back to the early 20th century when it was first recognized for its lubricating properties. Over the decades, this fatty acid has evolved from a simple lubricant to a multifunctional excipient that significantly influences tablet compression characteristics, dissolution profiles, and overall stability.
The pharmaceutical industry has witnessed a progressive shift toward direct compression as the preferred method for tablet manufacturing, driven by efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and reduced processing steps. This evolution has placed greater demands on excipients to perform optimally under high compression forces, making the optimization of stearic acid increasingly relevant in modern formulation science.
Recent technological advancements in particle engineering and surface modification have opened new avenues for enhancing stearic acid's functionality. The development of specialized grades with controlled particle size distribution, specific surface area, and modified crystal habits has expanded its application potential beyond traditional uses as a lubricant and glidant.
The primary objective of optimizing stearic acid for high compression tablet formulations is to achieve an ideal balance between its lubricating efficiency and potential negative impacts on tablet hardness and dissolution. This optimization aims to develop formulations that can withstand high compression forces while maintaining rapid disintegration and dissolution profiles, particularly crucial for immediate-release dosage forms.
Another key goal is to establish predictive models that can accurately forecast the behavior of stearic acid under varying compression conditions, enabling formulators to make informed decisions during the development process. This includes understanding the complex interplay between stearic acid concentration, mixing time, particle characteristics, and compression parameters.
Additionally, this technical exploration seeks to address the challenges associated with stearic acid's hydrophobic nature, which can potentially create water-repellent barriers around drug particles, affecting dissolution rates. Innovative approaches to mitigate these effects while preserving the beneficial properties of stearic acid represent a significant area of interest.
The global trend toward continuous manufacturing in pharmaceutical production further emphasizes the need for robust excipients that perform consistently across varying process conditions. Optimizing stearic acid to meet these demands requires a comprehensive understanding of its material properties and behavior under dynamic processing environments.
The pharmaceutical industry has witnessed a progressive shift toward direct compression as the preferred method for tablet manufacturing, driven by efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and reduced processing steps. This evolution has placed greater demands on excipients to perform optimally under high compression forces, making the optimization of stearic acid increasingly relevant in modern formulation science.
Recent technological advancements in particle engineering and surface modification have opened new avenues for enhancing stearic acid's functionality. The development of specialized grades with controlled particle size distribution, specific surface area, and modified crystal habits has expanded its application potential beyond traditional uses as a lubricant and glidant.
The primary objective of optimizing stearic acid for high compression tablet formulations is to achieve an ideal balance between its lubricating efficiency and potential negative impacts on tablet hardness and dissolution. This optimization aims to develop formulations that can withstand high compression forces while maintaining rapid disintegration and dissolution profiles, particularly crucial for immediate-release dosage forms.
Another key goal is to establish predictive models that can accurately forecast the behavior of stearic acid under varying compression conditions, enabling formulators to make informed decisions during the development process. This includes understanding the complex interplay between stearic acid concentration, mixing time, particle characteristics, and compression parameters.
Additionally, this technical exploration seeks to address the challenges associated with stearic acid's hydrophobic nature, which can potentially create water-repellent barriers around drug particles, affecting dissolution rates. Innovative approaches to mitigate these effects while preserving the beneficial properties of stearic acid represent a significant area of interest.
The global trend toward continuous manufacturing in pharmaceutical production further emphasizes the need for robust excipients that perform consistently across varying process conditions. Optimizing stearic acid to meet these demands requires a comprehensive understanding of its material properties and behavior under dynamic processing environments.
Market Analysis of High Compression Tablet Technologies
The high compression tablet technology market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by pharmaceutical industry demands for more efficient drug delivery systems. The global market for tablet compression technologies reached approximately $2.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.7% through 2028, according to industry reports. This growth is particularly pronounced in regions with established pharmaceutical manufacturing bases such as North America, Europe, and increasingly in Asia-Pacific markets.
The demand for high compression tablet technologies is primarily fueled by several key factors. First, the pharmaceutical industry's continuous pursuit of improved bioavailability and controlled release formulations has necessitated advanced compression technologies. Second, the growing prevalence of chronic diseases requiring long-term medication has increased the need for stable, consistent tablet formulations. Third, regulatory pressures for quality consistency and reduced variability in pharmaceutical products have pushed manufacturers toward more sophisticated compression technologies.
Market segmentation reveals distinct categories within high compression tablet technologies. Direct compression technologies hold the largest market share at approximately 45%, followed by wet granulation (30%) and dry granulation (20%) technologies. The remaining market comprises specialized technologies including hot-melt extrusion and others. This distribution reflects the industry's preference for cost-effective and scalable manufacturing processes.
Excipient technologies, particularly those involving stearic acid and its derivatives, represent a rapidly growing segment within this market. The global pharmaceutical excipient market related to tablet binding and compression was valued at $1.1 billion in 2022, with stearic acid-based products accounting for approximately 12% of this value. This segment is expected to grow at 6.3% annually, outpacing the overall market.
Regional analysis shows North America leading with 38% market share, followed by Europe (32%), Asia-Pacific (24%), and rest of the world (6%). However, the fastest growth is occurring in emerging markets, particularly India and China, where pharmaceutical manufacturing capacity is expanding rapidly. These regions are showing annual growth rates of 8-10% in high compression tablet technology adoption.
Customer segmentation indicates that large pharmaceutical manufacturers account for 65% of market demand, while generic drug manufacturers represent 25%, and contract manufacturing organizations the remaining 10%. This distribution highlights the technology's importance across various pharmaceutical business models and production scales.
The competitive landscape features both established equipment manufacturers and specialized excipient suppliers. Key market challenges include the need for formulations that maintain stability under high compression forces, reducing ejection forces during manufacturing, and ensuring consistent dissolution profiles across production batches.
The demand for high compression tablet technologies is primarily fueled by several key factors. First, the pharmaceutical industry's continuous pursuit of improved bioavailability and controlled release formulations has necessitated advanced compression technologies. Second, the growing prevalence of chronic diseases requiring long-term medication has increased the need for stable, consistent tablet formulations. Third, regulatory pressures for quality consistency and reduced variability in pharmaceutical products have pushed manufacturers toward more sophisticated compression technologies.
Market segmentation reveals distinct categories within high compression tablet technologies. Direct compression technologies hold the largest market share at approximately 45%, followed by wet granulation (30%) and dry granulation (20%) technologies. The remaining market comprises specialized technologies including hot-melt extrusion and others. This distribution reflects the industry's preference for cost-effective and scalable manufacturing processes.
Excipient technologies, particularly those involving stearic acid and its derivatives, represent a rapidly growing segment within this market. The global pharmaceutical excipient market related to tablet binding and compression was valued at $1.1 billion in 2022, with stearic acid-based products accounting for approximately 12% of this value. This segment is expected to grow at 6.3% annually, outpacing the overall market.
Regional analysis shows North America leading with 38% market share, followed by Europe (32%), Asia-Pacific (24%), and rest of the world (6%). However, the fastest growth is occurring in emerging markets, particularly India and China, where pharmaceutical manufacturing capacity is expanding rapidly. These regions are showing annual growth rates of 8-10% in high compression tablet technology adoption.
Customer segmentation indicates that large pharmaceutical manufacturers account for 65% of market demand, while generic drug manufacturers represent 25%, and contract manufacturing organizations the remaining 10%. This distribution highlights the technology's importance across various pharmaceutical business models and production scales.
The competitive landscape features both established equipment manufacturers and specialized excipient suppliers. Key market challenges include the need for formulations that maintain stability under high compression forces, reducing ejection forces during manufacturing, and ensuring consistent dissolution profiles across production batches.
Current Challenges in Stearic Acid Optimization
Despite the widespread use of stearic acid as a lubricant in tablet formulations, pharmaceutical manufacturers face significant challenges when optimizing this excipient for high compression tablet production. The primary issue stems from stearic acid's sensitivity to processing parameters, particularly temperature and pressure variations during manufacturing. When exposed to elevated temperatures, stearic acid can undergo polymorphic transformations, shifting between its C, B, and E forms, which exhibit different melting points and lubricating properties.
The inconsistent particle size distribution of commercial stearic acid presents another major challenge. Variations in particle morphology and size significantly impact flow properties and compression characteristics, leading to unpredictable tablet hardness and disintegration profiles. This variability is particularly problematic for high-dose formulations where even minor changes in lubricant performance can dramatically affect final product quality.
Hydrophobicity management represents a critical optimization challenge. While stearic acid's hydrophobic nature provides excellent lubrication, excessive concentrations can create a water-repellent film around drug particles, impeding tablet disintegration and dissolution. This effect becomes more pronounced in high-compression environments where the lubricant can be more thoroughly distributed throughout the tablet matrix.
Compatibility issues with active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) further complicate optimization efforts. Stearic acid may interact with certain drugs, particularly those containing amine groups, potentially forming stearate salts that alter drug solubility and bioavailability. These interactions are difficult to predict and can vary based on compression force and manufacturing conditions.
Scale-up challenges present significant hurdles when transitioning from laboratory to commercial production. The behavior of stearic acid often changes with equipment size and processing speeds, requiring extensive reformulation efforts. Manufacturers frequently observe that optimal concentrations determined in small-scale studies prove inadequate during commercial production, necessitating time-consuming adjustments.
Regulatory considerations add another layer of complexity. Different grades of stearic acid (vegetable vs. animal-derived) must meet specific purity requirements, and manufacturers must demonstrate consistent performance across batches. The increasing regulatory scrutiny on excipient variability has made it essential to develop robust formulation strategies that can accommodate the inherent variability of stearic acid.
Environmental factors, including humidity and storage conditions, can alter stearic acid's performance over time. This instability creates challenges for maintaining consistent tablet quality throughout the product's shelf life, particularly for medications distributed globally across various climatic zones.
The inconsistent particle size distribution of commercial stearic acid presents another major challenge. Variations in particle morphology and size significantly impact flow properties and compression characteristics, leading to unpredictable tablet hardness and disintegration profiles. This variability is particularly problematic for high-dose formulations where even minor changes in lubricant performance can dramatically affect final product quality.
Hydrophobicity management represents a critical optimization challenge. While stearic acid's hydrophobic nature provides excellent lubrication, excessive concentrations can create a water-repellent film around drug particles, impeding tablet disintegration and dissolution. This effect becomes more pronounced in high-compression environments where the lubricant can be more thoroughly distributed throughout the tablet matrix.
Compatibility issues with active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) further complicate optimization efforts. Stearic acid may interact with certain drugs, particularly those containing amine groups, potentially forming stearate salts that alter drug solubility and bioavailability. These interactions are difficult to predict and can vary based on compression force and manufacturing conditions.
Scale-up challenges present significant hurdles when transitioning from laboratory to commercial production. The behavior of stearic acid often changes with equipment size and processing speeds, requiring extensive reformulation efforts. Manufacturers frequently observe that optimal concentrations determined in small-scale studies prove inadequate during commercial production, necessitating time-consuming adjustments.
Regulatory considerations add another layer of complexity. Different grades of stearic acid (vegetable vs. animal-derived) must meet specific purity requirements, and manufacturers must demonstrate consistent performance across batches. The increasing regulatory scrutiny on excipient variability has made it essential to develop robust formulation strategies that can accommodate the inherent variability of stearic acid.
Environmental factors, including humidity and storage conditions, can alter stearic acid's performance over time. This instability creates challenges for maintaining consistent tablet quality throughout the product's shelf life, particularly for medications distributed globally across various climatic zones.
Current Methodologies for Stearic Acid Implementation
01 Stearic acid as a compression aid in tablet formulation
Stearic acid is widely used as a lubricant and compression aid in pharmaceutical tablet formulations. It helps reduce friction during tablet compression, prevents sticking to die walls, and improves the flow properties of powder mixtures. The addition of stearic acid in specific concentrations can significantly enhance tablet hardness while maintaining appropriate disintegration times, making it valuable for direct compression manufacturing processes.- Stearic acid as a compression aid in tablet formulation: Stearic acid is widely used as a lubricant and compression aid in pharmaceutical tablet formulations. It helps reduce friction during the compression process, prevents tablets from sticking to die walls, and improves the flow properties of powder mixtures. The addition of stearic acid in specific concentrations can significantly enhance tablet hardness and reduce friability while maintaining proper disintegration times.
- Compression techniques for stearic acid-based materials: Various compression techniques are employed for materials containing stearic acid, including direct compression, wet granulation, and dry granulation. These methods involve specific pressure parameters, temperature controls, and equipment configurations to optimize the compression of stearic acid-containing formulations. The compression behavior of stearic acid is influenced by particle size, crystal form, and processing conditions, which can be adjusted to achieve desired material properties.
- Stearic acid derivatives for improved compression properties: Modified forms and derivatives of stearic acid, such as magnesium stearate, calcium stearate, and stearic acid esters, offer enhanced compression characteristics compared to pure stearic acid. These derivatives provide better flowability, reduced sticking, and improved binding properties during compression processes. The chemical modifications alter the physical properties of stearic acid to make it more suitable for specific compression applications.
- Industrial equipment for stearic acid compression: Specialized equipment has been developed for the compression of stearic acid and stearic acid-containing materials. These include modified hydraulic presses, roller compactors, and tablet presses with temperature control systems. The equipment is designed to handle the specific challenges associated with stearic acid compression, such as its lubricating properties and temperature sensitivity, ensuring consistent product quality and production efficiency.
- Applications of compressed stearic acid products: Compressed stearic acid and its formulations find applications in various industries including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food, and industrial manufacturing. In pharmaceuticals, compressed stearic acid serves as an excipient in controlled-release formulations. In cosmetics, it is used in solid products like lipsticks and foundation sticks. Industrial applications include lubricants, polishing compounds, and release agents where the compressed form provides specific functional benefits.
02 Stearic acid modification for improved compression properties
Chemical and physical modifications of stearic acid can enhance its compression properties. These modifications include creating specific crystal forms, particle size distributions, or combining with other fatty acids to optimize performance. Modified stearic acid demonstrates improved binding capacity, better flow characteristics, and enhanced compressibility, resulting in tablets with superior mechanical strength and stability during storage.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stearic acid in composite materials and industrial compression applications
Beyond pharmaceuticals, stearic acid plays a crucial role in the compression of various industrial materials. It serves as a processing aid in the compression molding of polymers, rubber compounds, and composite materials. The addition of stearic acid reduces friction between particles, improves material flow during compression, and enhances the surface finish of the final compressed products while reducing energy requirements during the manufacturing process.Expand Specific Solutions04 Stearic acid concentration effects on compression characteristics
The concentration of stearic acid significantly impacts compression outcomes. Research indicates that optimal concentrations typically range between 0.5% and 3% depending on the formulation. Lower concentrations may not provide sufficient lubrication, while excessive amounts can lead to decreased tablet hardness and prolonged disintegration times. Finding the precise concentration balance is critical for achieving desired compression properties without compromising other tablet characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions05 Equipment and process parameters for stearic acid compression
Specialized equipment and optimized process parameters are essential for effective stearic acid compression. Temperature control during compression is particularly important as stearic acid's properties change significantly near its melting point. Compression force, speed, and dwell time must be carefully calibrated based on the specific formulation containing stearic acid. Advanced compression technologies can maximize the benefits of stearic acid while minimizing potential drawbacks in various manufacturing scenarios.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Pharmaceutical Excipient Manufacturers
The tablet formulation market for stearic acid optimization is in a mature growth phase, with an estimated global market size exceeding $5 billion. Technical maturity varies significantly among key players, with pharmaceutical giants like Novartis AG, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Gilead Sciences demonstrating advanced capabilities in high-compression tablet formulations. Companies such as FMC Corp. and Evonik Operations GmbH lead in excipient innovation, while Sandoz AG and Asahi Kasei Chemicals focus on cost-effective manufacturing processes. The competitive landscape shows a clear stratification between research-oriented pharmaceutical companies developing proprietary compression technologies and specialized chemical manufacturers optimizing stearic acid derivatives for improved tablet performance, creating a dynamic ecosystem of collaboration and competition.
FMC Corp.
Technical Solution: FMC Corporation has pioneered a comprehensive approach to stearic acid optimization through their LubriBLEND™ technology. Their solution addresses the fundamental challenge of balancing lubrication efficiency with tablet hardness through a multi-component system. FMC's technology utilizes a precisely controlled blend of purified stearic acid (>95% purity) with specific fatty acid chain length distributions optimized for high compression scenarios. The process involves hydrogenation under controlled conditions to achieve an ideal iodine value (<1.0) and melting point profile (69-72°C), creating a more uniform molecular structure that distributes more effectively during compression. Their research shows that incorporating small amounts (0.1-0.3%) of sodium stearyl fumarate as a synergistic component allows for overall lubricant reduction while maintaining ejection forces below 300N even at compression forces exceeding 25kN.
Strengths: The multi-component approach provides excellent lubrication efficiency while minimizing the negative impact on tablet hardness and dissolution. Highly consistent batch-to-batch performance reduces manufacturing variability. Weaknesses: More complex formulation requires careful quality control of multiple components. Slightly higher raw material cost compared to standard stearic acid formulations.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed DYNACERT® technology specifically for high compression tablet formulations using modified stearic acid. Their approach involves precise particle engineering of stearic acid to create uniform particle size distribution (typically 50-150 μm) with optimized surface area characteristics. The technology employs a proprietary spray crystallization process that produces stearic acid particles with improved flow properties and compressibility. Evonik's formulation includes co-processing stearic acid with silica nanoparticles (0.5-2% w/w) to prevent agglomeration and enhance lubrication efficiency at high compression forces (>20 kN). Their research demonstrates that modified stearic acid concentrations can be reduced to 0.75-1.5% w/w while maintaining equivalent or superior tablet hardness compared to conventional formulations requiring 2-3% w/w.
Strengths: Superior particle engineering reduces required lubricant concentration, minimizing negative effects on tablet hardness while maintaining excellent lubrication. The technology enables higher compression forces without punch sticking issues. Weaknesses: Requires specialized manufacturing equipment for spray crystallization process, potentially increasing production costs. May require reformulation of existing products to optimize performance.
Key Technical Innovations in Lubricant Functionality
Tablet composition, and method for improving disintegrating properties/elution properties of tablet composition
PatentWO2016163463A1
Innovation
- Incorporating stearate as a lubricant in the tablet composition, specifically calcium or magnesium stearate, along with lactoferrin and cacao extract, improves disintegration and dissolution properties, reducing friability and adhesion, and maintaining performance even after long-term storage.
Co-Processed Lubricant:MCG for Tablets
PatentActiveUS20220287974A1
Innovation
- A co-processed excipient comprising microcrystalline cellulose, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, and a pharmaceutically acceptable lubricant, such as magnesium stearate, is developed to enhance bulk density and flowability, allowing for harder tablets with comparable disintegration times to those made with traditional lubricants.
Regulatory Considerations for Excipient Selection
The regulatory landscape for excipient selection in pharmaceutical formulations is complex and multifaceted, particularly for ingredients like stearic acid used in high compression tablet formulations. Pharmaceutical manufacturers must navigate a web of international and regional regulations that govern the quality, safety, and appropriate use of excipients.
In the United States, the FDA provides guidance through various regulatory frameworks including 21 CFR (Code of Federal Regulations) and the Inactive Ingredient Database (IID), which lists acceptable excipients and their maximum potency levels for specific routes of administration. Stearic acid is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) and is listed in the IID, but manufacturers must ensure their specific grade meets pharmaceutical standards.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) regulates excipients through the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.), which provides detailed specifications for stearic acid quality and purity. Additionally, the EU's Excipient GMP Guidelines outline specific requirements for excipient manufacturing practices, emphasizing risk assessment approaches tailored to the excipient's use.
International Pharmaceutical Excipients Council (IPEC) guidelines play a crucial role in harmonizing standards globally. The IPEC-PQG GMP Guide provides a framework for excipient manufacturers to establish quality systems that meet pharmaceutical requirements. For stearic acid optimization in high compression formulations, adherence to these guidelines ensures consistent quality and performance.
Regulatory bodies increasingly require comprehensive risk assessments for excipients, particularly when used in novel ways or at higher concentrations. For stearic acid in high compression applications, manufacturers must document safety evaluations, stability data, and functional justification when concentrations exceed typical ranges.
Certificate of Analysis (CoA) requirements have become more stringent, with regulatory expectations for detailed characterization of excipient properties. For stearic acid, this includes specifications for acid value, iodine value, melting point, and impurity profiles, all of which can impact compression behavior and tablet stability.
Emerging regulations are focusing on supply chain transparency and excipient traceability. The FDA's Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) and similar initiatives globally require manufacturers to maintain detailed records of excipient sourcing, which presents additional considerations when selecting stearic acid suppliers for high compression tablet formulations.
In the United States, the FDA provides guidance through various regulatory frameworks including 21 CFR (Code of Federal Regulations) and the Inactive Ingredient Database (IID), which lists acceptable excipients and their maximum potency levels for specific routes of administration. Stearic acid is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) and is listed in the IID, but manufacturers must ensure their specific grade meets pharmaceutical standards.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) regulates excipients through the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.), which provides detailed specifications for stearic acid quality and purity. Additionally, the EU's Excipient GMP Guidelines outline specific requirements for excipient manufacturing practices, emphasizing risk assessment approaches tailored to the excipient's use.
International Pharmaceutical Excipients Council (IPEC) guidelines play a crucial role in harmonizing standards globally. The IPEC-PQG GMP Guide provides a framework for excipient manufacturers to establish quality systems that meet pharmaceutical requirements. For stearic acid optimization in high compression formulations, adherence to these guidelines ensures consistent quality and performance.
Regulatory bodies increasingly require comprehensive risk assessments for excipients, particularly when used in novel ways or at higher concentrations. For stearic acid in high compression applications, manufacturers must document safety evaluations, stability data, and functional justification when concentrations exceed typical ranges.
Certificate of Analysis (CoA) requirements have become more stringent, with regulatory expectations for detailed characterization of excipient properties. For stearic acid, this includes specifications for acid value, iodine value, melting point, and impurity profiles, all of which can impact compression behavior and tablet stability.
Emerging regulations are focusing on supply chain transparency and excipient traceability. The FDA's Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) and similar initiatives globally require manufacturers to maintain detailed records of excipient sourcing, which presents additional considerations when selecting stearic acid suppliers for high compression tablet formulations.
Sustainability Aspects of Excipient Manufacturing
The manufacturing of pharmaceutical excipients, including stearic acid, has significant environmental implications that must be addressed in the context of sustainable development. Traditional production methods for stearic acid often involve energy-intensive processes and the use of non-renewable resources, primarily derived from palm oil or animal fats. These conventional approaches contribute to deforestation, biodiversity loss, and increased carbon emissions throughout the supply chain.
Recent advancements in green chemistry have introduced more sustainable pathways for stearic acid production. Biotechnological approaches utilizing microbial fermentation of agricultural waste materials represent a promising alternative, reducing dependence on virgin raw materials while simultaneously addressing waste management challenges. These methods can decrease the carbon footprint by up to 40% compared to conventional extraction processes.
Water consumption and wastewater management present additional sustainability concerns in excipient manufacturing. The production of high-purity stearic acid suitable for pharmaceutical applications typically requires multiple purification steps, generating significant volumes of wastewater containing organic residues and processing chemicals. Implementation of closed-loop water systems and advanced filtration technologies has demonstrated potential to reduce water usage by 30-50% in modern manufacturing facilities.
Energy efficiency improvements represent another critical aspect of sustainable excipient production. The transition to renewable energy sources, combined with process optimization techniques such as continuous manufacturing, can substantially reduce the environmental impact of stearic acid production. Several leading manufacturers have reported energy consumption reductions of 25-35% through these initiatives, directly translating to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly emphasize sustainability metrics in pharmaceutical manufacturing. The FDA's Quality by Design (QbD) approach and the European Medicines Agency's guidelines now incorporate environmental considerations alongside traditional quality parameters. Manufacturers implementing sustainable practices for excipients like stearic acid gain competitive advantages through regulatory compliance and alignment with corporate social responsibility objectives.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing different sources and manufacturing routes for stearic acid reveal significant variations in environmental impact. Plant-based sources generally demonstrate lower environmental burdens compared to animal-derived alternatives, particularly when sustainable agricultural practices are employed. These assessments provide valuable guidance for formulators seeking to optimize both technical performance and sustainability profiles in high-compression tablet formulations.
Recent advancements in green chemistry have introduced more sustainable pathways for stearic acid production. Biotechnological approaches utilizing microbial fermentation of agricultural waste materials represent a promising alternative, reducing dependence on virgin raw materials while simultaneously addressing waste management challenges. These methods can decrease the carbon footprint by up to 40% compared to conventional extraction processes.
Water consumption and wastewater management present additional sustainability concerns in excipient manufacturing. The production of high-purity stearic acid suitable for pharmaceutical applications typically requires multiple purification steps, generating significant volumes of wastewater containing organic residues and processing chemicals. Implementation of closed-loop water systems and advanced filtration technologies has demonstrated potential to reduce water usage by 30-50% in modern manufacturing facilities.
Energy efficiency improvements represent another critical aspect of sustainable excipient production. The transition to renewable energy sources, combined with process optimization techniques such as continuous manufacturing, can substantially reduce the environmental impact of stearic acid production. Several leading manufacturers have reported energy consumption reductions of 25-35% through these initiatives, directly translating to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly emphasize sustainability metrics in pharmaceutical manufacturing. The FDA's Quality by Design (QbD) approach and the European Medicines Agency's guidelines now incorporate environmental considerations alongside traditional quality parameters. Manufacturers implementing sustainable practices for excipients like stearic acid gain competitive advantages through regulatory compliance and alignment with corporate social responsibility objectives.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing different sources and manufacturing routes for stearic acid reveal significant variations in environmental impact. Plant-based sources generally demonstrate lower environmental burdens compared to animal-derived alternatives, particularly when sustainable agricultural practices are employed. These assessments provide valuable guidance for formulators seeking to optimize both technical performance and sustainability profiles in high-compression tablet formulations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!