Evaluating Stearic Acid's Antioxidant Activity in Formulations
SEP 24, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Stearic Acid Antioxidant Properties Background and Objectives
Stearic acid, a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula C18H36O2, has been traditionally recognized for its role as an emulsifier and thickening agent in various formulations. However, recent scientific investigations have revealed its potential antioxidant properties, opening new avenues for its application in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries. The evolution of stearic acid research has transitioned from basic structural studies to more complex functional analyses, particularly focusing on its ability to neutralize free radicals and prevent oxidative damage.
The historical trajectory of stearic acid research began in the early 20th century with its identification and structural characterization. By the mid-20th century, its physical properties were well-documented, leading to widespread industrial applications. The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed a paradigm shift in research focus toward the biological and chemical activities of stearic acid, including its potential antioxidant capabilities.
Current technological trends indicate growing interest in natural antioxidants as alternatives to synthetic compounds, driven by consumer preference for "clean label" products. Stearic acid, being naturally occurring in various plant and animal sources, aligns perfectly with this trend. The scientific community has increasingly explored its antioxidant mechanisms, including hydrogen donation, metal chelation, and synergistic effects with other antioxidant compounds.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate stearic acid's antioxidant activity in various formulations, establishing standardized methodologies for assessment and quantification. This includes determining optimal concentration ranges for maximum antioxidant efficacy while maintaining formulation stability and functionality.
Secondary objectives encompass investigating the synergistic potential of stearic acid with other antioxidants, elucidating its mechanism of action at the molecular level, and developing predictive models for its performance in different matrix environments. Additionally, we aim to assess the impact of processing conditions on stearic acid's antioxidant stability and identify potential enhancement strategies.
The technological significance of this research extends beyond theoretical understanding to practical applications. As oxidative stability remains a critical challenge in product development across multiple industries, identifying effective and natural antioxidant solutions represents a substantial market opportunity. Stearic acid's dual functionality as both a structural component and potential antioxidant makes it particularly valuable for formulation scientists seeking multifunctional ingredients.
This research aligns with broader industry trends toward sustainable, multifunctional ingredients that can address multiple formulation challenges simultaneously. By establishing stearic acid's antioxidant credentials through rigorous scientific evaluation, we anticipate creating new value propositions for this widely available compound and potentially revolutionizing formulation approaches across multiple sectors.
The historical trajectory of stearic acid research began in the early 20th century with its identification and structural characterization. By the mid-20th century, its physical properties were well-documented, leading to widespread industrial applications. The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed a paradigm shift in research focus toward the biological and chemical activities of stearic acid, including its potential antioxidant capabilities.
Current technological trends indicate growing interest in natural antioxidants as alternatives to synthetic compounds, driven by consumer preference for "clean label" products. Stearic acid, being naturally occurring in various plant and animal sources, aligns perfectly with this trend. The scientific community has increasingly explored its antioxidant mechanisms, including hydrogen donation, metal chelation, and synergistic effects with other antioxidant compounds.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate stearic acid's antioxidant activity in various formulations, establishing standardized methodologies for assessment and quantification. This includes determining optimal concentration ranges for maximum antioxidant efficacy while maintaining formulation stability and functionality.
Secondary objectives encompass investigating the synergistic potential of stearic acid with other antioxidants, elucidating its mechanism of action at the molecular level, and developing predictive models for its performance in different matrix environments. Additionally, we aim to assess the impact of processing conditions on stearic acid's antioxidant stability and identify potential enhancement strategies.
The technological significance of this research extends beyond theoretical understanding to practical applications. As oxidative stability remains a critical challenge in product development across multiple industries, identifying effective and natural antioxidant solutions represents a substantial market opportunity. Stearic acid's dual functionality as both a structural component and potential antioxidant makes it particularly valuable for formulation scientists seeking multifunctional ingredients.
This research aligns with broader industry trends toward sustainable, multifunctional ingredients that can address multiple formulation challenges simultaneously. By establishing stearic acid's antioxidant credentials through rigorous scientific evaluation, we anticipate creating new value propositions for this widely available compound and potentially revolutionizing formulation approaches across multiple sectors.
Market Analysis for Antioxidant-Enhanced Formulations
The global market for antioxidant-enhanced formulations has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of oxidative stress and its effects on both product stability and human health. The antioxidant additives market was valued at approximately 3.25 billion USD in 2022 and is projected to reach 4.73 billion USD by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.5% during the forecast period.
Stearic acid-based antioxidant formulations represent an emerging segment within this market, particularly in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and food industries. Consumer demand for natural and sustainable antioxidant solutions has created a favorable environment for stearic acid applications, as it offers both functional benefits and aligns with clean label trends.
In the cosmetics sector, the market for antioxidant-enhanced skincare products has shown robust growth of 8.2% annually, with particular emphasis on anti-aging formulations where stearic acid serves dual purposes as an emollient and potential antioxidant. Major cosmetic brands have increased their R&D investments in multifunctional ingredients like stearic acid by 12% in the past two years.
The pharmaceutical industry presents another significant market opportunity, with antioxidant excipients in drug formulations growing at 5.7% annually. Stearic acid's potential to enhance drug stability while providing antioxidant properties positions it favorably in this sector, particularly for lipid-based drug delivery systems.
Food applications represent the largest market segment for antioxidant additives, accounting for 42% of the total market share. Stearic acid's GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) status makes it particularly attractive for food manufacturers seeking clean label solutions to extend shelf life and maintain product quality.
Regional analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently dominate the market for advanced antioxidant formulations, collectively accounting for 58% of global consumption. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 9.3% annually, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and growing awareness of preventive healthcare.
Market challenges include price sensitivity, particularly in developing economies, and regulatory hurdles related to claims substantiation. Additionally, competition from established synthetic antioxidants presents a barrier to market penetration for stearic acid-based solutions, necessitating robust efficacy data and clear value proposition demonstrations.
Consumer trends favoring the market include growing preference for multifunctional ingredients, increased demand for natural preservatives, and heightened awareness of oxidative stress in aging and disease processes. These trends collectively create a favorable environment for continued research and development of stearic acid's antioxidant properties in various formulations.
Stearic acid-based antioxidant formulations represent an emerging segment within this market, particularly in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and food industries. Consumer demand for natural and sustainable antioxidant solutions has created a favorable environment for stearic acid applications, as it offers both functional benefits and aligns with clean label trends.
In the cosmetics sector, the market for antioxidant-enhanced skincare products has shown robust growth of 8.2% annually, with particular emphasis on anti-aging formulations where stearic acid serves dual purposes as an emollient and potential antioxidant. Major cosmetic brands have increased their R&D investments in multifunctional ingredients like stearic acid by 12% in the past two years.
The pharmaceutical industry presents another significant market opportunity, with antioxidant excipients in drug formulations growing at 5.7% annually. Stearic acid's potential to enhance drug stability while providing antioxidant properties positions it favorably in this sector, particularly for lipid-based drug delivery systems.
Food applications represent the largest market segment for antioxidant additives, accounting for 42% of the total market share. Stearic acid's GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) status makes it particularly attractive for food manufacturers seeking clean label solutions to extend shelf life and maintain product quality.
Regional analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently dominate the market for advanced antioxidant formulations, collectively accounting for 58% of global consumption. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 9.3% annually, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and growing awareness of preventive healthcare.
Market challenges include price sensitivity, particularly in developing economies, and regulatory hurdles related to claims substantiation. Additionally, competition from established synthetic antioxidants presents a barrier to market penetration for stearic acid-based solutions, necessitating robust efficacy data and clear value proposition demonstrations.
Consumer trends favoring the market include growing preference for multifunctional ingredients, increased demand for natural preservatives, and heightened awareness of oxidative stress in aging and disease processes. These trends collectively create a favorable environment for continued research and development of stearic acid's antioxidant properties in various formulations.
Current Status and Challenges in Antioxidant Research
The field of antioxidant research has witnessed significant advancements globally, with particular focus on natural compounds like stearic acid. Current research indicates that stearic acid, traditionally known for its emollient properties, demonstrates promising antioxidant capabilities in various formulations. Studies across North America, Europe, and Asia have documented its efficacy in neutralizing free radicals and preventing oxidative damage, particularly in cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications.
Despite these promising findings, researchers face substantial challenges in fully characterizing stearic acid's antioxidant mechanisms. The primary technical hurdle involves quantifying its antioxidant activity across different pH levels and temperatures, as these factors significantly influence its performance. Additionally, stearic acid's limited solubility in aqueous systems restricts its application range, necessitating innovative delivery systems for optimal efficacy.
Another significant constraint is the variability in antioxidant potency depending on the source and purity of stearic acid. Research indicates that stearic acid derived from plant sources may exhibit different antioxidant profiles compared to synthetic variants, creating inconsistencies in experimental results and commercial applications. This variability complicates standardization efforts and regulatory approvals.
Geographically, antioxidant research involving stearic acid shows distinct patterns. European institutions lead in fundamental research on mechanism elucidation, while Asian research centers, particularly in Japan and South Korea, focus on application-specific formulations. North American research predominantly addresses regulatory aspects and clinical validation of stearic acid's antioxidant claims.
The integration of stearic acid with other antioxidants presents another technical challenge. Current research suggests both synergistic and antagonistic effects when combined with vitamins C and E or other fatty acids, but comprehensive compatibility studies remain limited. This knowledge gap impedes the development of optimized multi-component antioxidant systems.
Measurement standardization represents a persistent challenge in the field. Various methodologies—including DPPH assays, ORAC values, and lipid peroxidation inhibition tests—yield different results when evaluating stearic acid's antioxidant capacity. This methodological inconsistency hampers cross-study comparisons and slows consensus-building regarding its efficacy.
Recent technological limitations in real-time monitoring of stearic acid's antioxidant activity in complex formulations further complicate research efforts. While advanced analytical techniques like electron spin resonance spectroscopy show promise, their accessibility and standardization remain limited. Consequently, researchers struggle to accurately predict stearic acid's long-term antioxidant stability in final products, particularly under varying storage conditions.
Despite these promising findings, researchers face substantial challenges in fully characterizing stearic acid's antioxidant mechanisms. The primary technical hurdle involves quantifying its antioxidant activity across different pH levels and temperatures, as these factors significantly influence its performance. Additionally, stearic acid's limited solubility in aqueous systems restricts its application range, necessitating innovative delivery systems for optimal efficacy.
Another significant constraint is the variability in antioxidant potency depending on the source and purity of stearic acid. Research indicates that stearic acid derived from plant sources may exhibit different antioxidant profiles compared to synthetic variants, creating inconsistencies in experimental results and commercial applications. This variability complicates standardization efforts and regulatory approvals.
Geographically, antioxidant research involving stearic acid shows distinct patterns. European institutions lead in fundamental research on mechanism elucidation, while Asian research centers, particularly in Japan and South Korea, focus on application-specific formulations. North American research predominantly addresses regulatory aspects and clinical validation of stearic acid's antioxidant claims.
The integration of stearic acid with other antioxidants presents another technical challenge. Current research suggests both synergistic and antagonistic effects when combined with vitamins C and E or other fatty acids, but comprehensive compatibility studies remain limited. This knowledge gap impedes the development of optimized multi-component antioxidant systems.
Measurement standardization represents a persistent challenge in the field. Various methodologies—including DPPH assays, ORAC values, and lipid peroxidation inhibition tests—yield different results when evaluating stearic acid's antioxidant capacity. This methodological inconsistency hampers cross-study comparisons and slows consensus-building regarding its efficacy.
Recent technological limitations in real-time monitoring of stearic acid's antioxidant activity in complex formulations further complicate research efforts. While advanced analytical techniques like electron spin resonance spectroscopy show promise, their accessibility and standardization remain limited. Consequently, researchers struggle to accurately predict stearic acid's long-term antioxidant stability in final products, particularly under varying storage conditions.
Existing Methodologies for Evaluating Antioxidant Activity
01 Antioxidant properties of stearic acid in food applications
Stearic acid exhibits antioxidant activity in food products by inhibiting lipid oxidation and extending shelf life. When incorporated into food formulations, it can protect against oxidative degradation of oils and fats. The antioxidant mechanism involves the fatty acid's ability to scavenge free radicals and prevent the propagation of oxidation reactions, particularly in high-fat food systems. This property makes stearic acid valuable in food preservation and stability enhancement.- Stearic acid as a natural antioxidant in food preservation: Stearic acid exhibits antioxidant properties that can be utilized in food preservation systems. When incorporated into food formulations, it helps prevent oxidation of fats and oils, extending shelf life and maintaining product quality. The antioxidant activity is particularly effective when combined with other natural preservatives, creating synergistic effects that enhance overall stability of food products.
- Stearic acid derivatives with enhanced antioxidant properties: Chemical modifications of stearic acid can significantly enhance its antioxidant capabilities. These derivatives, including esters and amides of stearic acid, demonstrate improved free radical scavenging activity compared to the parent compound. The structural modifications typically involve introducing additional functional groups that contribute to electron donation or hydrogen atom transfer mechanisms, which are essential for antioxidant activity.
- Stearic acid in cosmetic formulations as an antioxidant: In cosmetic applications, stearic acid serves dual functions as both an emulsifier and antioxidant. It helps protect cosmetic formulations from oxidative degradation while also providing skin benefits. When incorporated into skincare products, it contributes to the stability of other active ingredients and helps prevent rancidity. The antioxidant effect is particularly valuable in formulations containing polyunsaturated oils and other oxidation-prone components.
- Synergistic antioxidant effects of stearic acid with other compounds: Stearic acid demonstrates enhanced antioxidant activity when combined with other antioxidant compounds such as tocopherols, ascorbic acid, and plant extracts. These combinations create synergistic effects that provide superior protection against oxidative stress compared to individual components. The mechanisms involve complementary pathways of free radical neutralization and regeneration of oxidized antioxidants, creating more effective protective systems for various applications.
- Industrial applications of stearic acid's antioxidant properties: Beyond food and cosmetics, stearic acid's antioxidant properties find applications in industrial settings such as polymer stabilization, lubricant formulations, and fuel additives. In these contexts, stearic acid helps prevent oxidative degradation of materials, extending their useful life and maintaining performance characteristics. The compound's thermal stability makes it particularly valuable in high-temperature applications where oxidation reactions are accelerated.
02 Stearic acid in cosmetic formulations as an antioxidant stabilizer
In cosmetic and personal care products, stearic acid functions as both an emulsifier and antioxidant stabilizer. It helps protect cosmetic formulations from oxidation and rancidity, thereby extending product shelf life. When combined with other antioxidants, stearic acid can enhance the overall stability of the formulation and protect active ingredients from degradation. Its antioxidant activity contributes to maintaining the efficacy and sensory properties of cosmetic products over time.Expand Specific Solutions03 Synergistic effects of stearic acid with other antioxidants
Stearic acid demonstrates synergistic antioxidant effects when combined with other antioxidant compounds such as tocopherols, ascorbic acid, and plant extracts. These combinations can significantly enhance the overall antioxidant capacity of formulations beyond what individual components provide alone. The synergistic mechanisms involve complementary radical scavenging pathways and regeneration of primary antioxidants. This approach is particularly effective in complex systems where multiple oxidation mechanisms may be present.Expand Specific Solutions04 Stearic acid derivatives with enhanced antioxidant activity
Chemical modifications of stearic acid can produce derivatives with enhanced antioxidant properties. These derivatives include stearic acid esters, amides, and metal complexes that demonstrate improved free radical scavenging ability compared to the parent compound. The structural modifications typically target the carboxylic acid group to create compounds with greater stability and bioavailability. These derivatives find applications in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and industrial products where superior antioxidant performance is required.Expand Specific Solutions05 Stearic acid in polymer stabilization and industrial applications
Stearic acid functions as an antioxidant in polymer systems and industrial applications by preventing oxidative degradation of materials. It can be incorporated into plastics, rubbers, and other polymers to extend their service life and maintain physical properties. The antioxidant mechanism involves neutralizing free radicals generated during processing and exposure to environmental stressors. Additionally, stearic acid can act as a processing aid while simultaneously providing antioxidant protection in industrial formulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Antioxidant Formulation Development
The stearic acid antioxidant activity market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing applications in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and food industries. The global market size for antioxidant additives is projected to reach approximately $6 billion by 2025, with stearic acid derivatives representing a significant segment. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with established players like L'Oréal and Beiersdorf leading cosmetic applications, while companies such as Lubrizol and DSM IP Assets focus on industrial formulations. Emerging research from Polnox Corp. and academic institutions like Brigham Young University is advancing the understanding of stearic acid's antioxidant mechanisms. Chinese manufacturers including PetroChina and Sinopec are expanding production capacity, while specialized firms like Unigen and Azura Ophthalmics are developing novel applications in targeted formulations.
L'Oréal SA
Technical Solution: L'Oréal has developed comprehensive evaluation methodologies for stearic acid's antioxidant activity in cosmetic formulations. Their approach combines in vitro and ex vivo testing protocols to quantify free radical scavenging capacity. The company utilizes DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) and ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) assays to measure direct antioxidant effects, while also employing lipid peroxidation inhibition tests to assess protection against oxidative stress in emulsion systems. L'Oréal has pioneered the integration of stearic acid derivatives with enhanced antioxidant properties, particularly through esterification with phenolic compounds to create synergistic antioxidant effects. Their research demonstrates that stearic acid at 0.5-2% concentration provides optimal stability in water-in-oil emulsions while contributing to the overall antioxidant defense system of formulations. The company has also developed proprietary accelerated aging protocols specifically designed to evaluate the long-term efficacy of stearic acid as an antioxidant in various cosmetic matrices.
Strengths: Extensive research infrastructure allows for comprehensive evaluation across multiple formulation types. Their methods effectively distinguish between stearic acid's direct antioxidant activity and its indirect stabilizing effects on other antioxidants. Weaknesses: Their evaluation protocols may be overly specialized for cosmetic applications, potentially limiting transferability to other industries like food or pharmaceuticals.
Beiersdorf AG
Technical Solution: Beiersdorf has developed a multi-tiered approach to evaluate stearic acid's antioxidant activity in skincare formulations. Their methodology incorporates both chemical and biological assessment systems. At the chemical level, they employ electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy to directly measure free radical scavenging activity of stearic acid in various formulation environments. This is complemented by a lipid peroxidation inhibition assay using a liposome model system that mimics skin lipid structures. For biological relevance, Beiersdorf utilizes reconstructed human epidermis models to evaluate the protective effects of stearic acid-containing formulations against UV and pollution-induced oxidative stress. Their research has demonstrated that stearic acid at concentrations of 1-3% exhibits moderate direct antioxidant activity but significantly enhances the stability and efficacy of other antioxidants in formulations. Beiersdorf has also pioneered the development of a "Cellular Antioxidant Protection Factor" (CAP) assay that quantifies the overall antioxidant protection provided by complex formulations containing stearic acid and other ingredients under conditions that simulate real-world usage.
Strengths: Their evaluation approach bridges the gap between in vitro chemical assays and biological relevance through the use of advanced skin models. The CAP assay provides a holistic measurement of antioxidant activity in complex formulations. Weaknesses: The specialized equipment and expertise required for their evaluation methods may limit accessibility for smaller companies or research institutions.
Critical Analysis of Stearic Acid Antioxidant Mechanisms
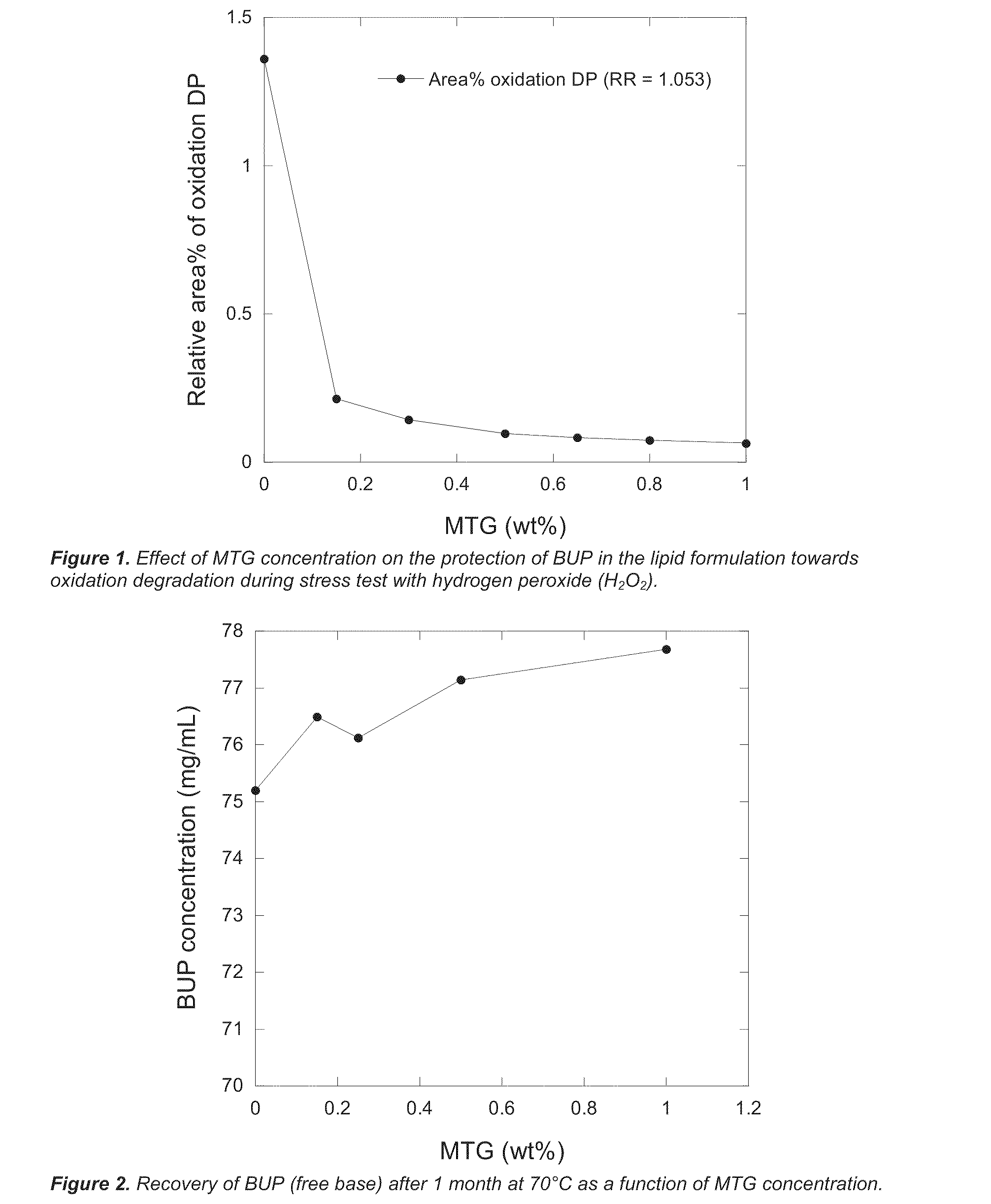
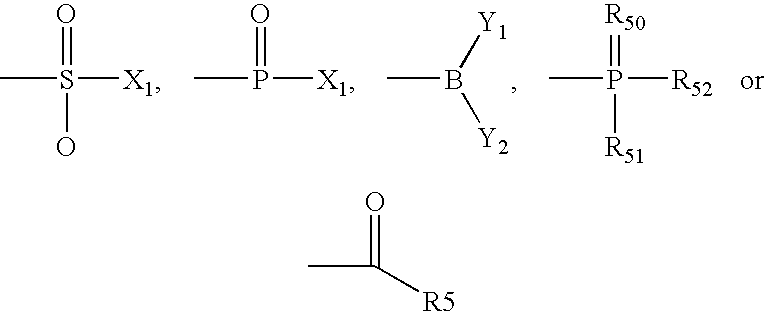
Lipid formulations comprising a thiolated antioxidant
PatentActiveUS20110230569A1
Innovation
- Incorporating thiolated antioxidants, such as mono-thioglycerol (MTG) and cysteine analogues, into lipid matrices to reduce oxidative degradation, combined with chelating agents like EDTA, to stabilize both the bioactive agents and lipid components.
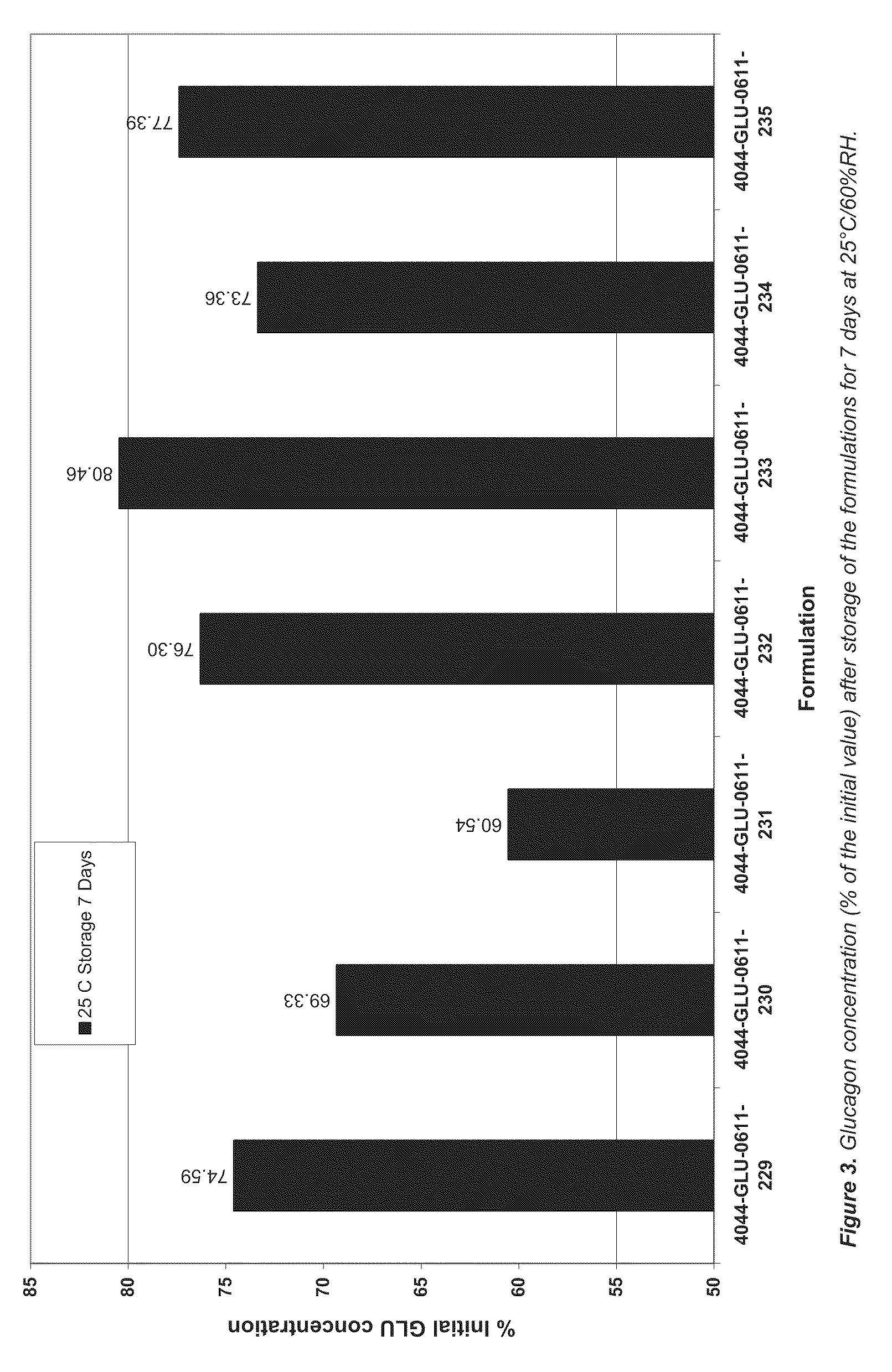
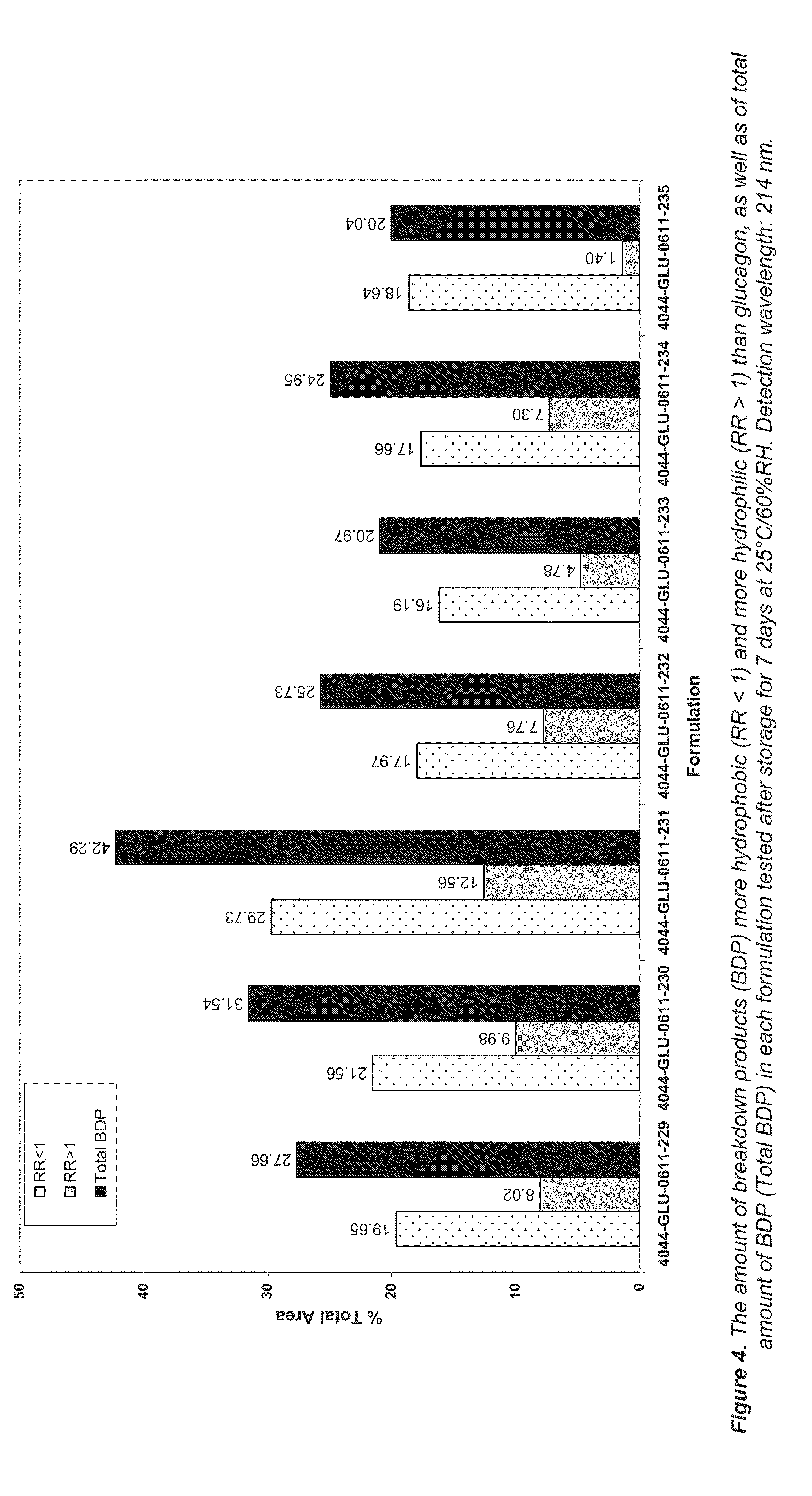
Method of regulating glucose metabolism, and reagents related thereto
PatentInactiveUS20040176307A1
Innovation
- Administration of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPIV) inhibitors to prolong the half-life of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and other proglucagon-derived peptides, enhancing insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, thereby reducing insulin resistance and improving glycemic control.
Stability and Shelf-life Enhancement Strategies
Stability and shelf-life enhancement strategies for formulations containing stearic acid require a multifaceted approach that leverages both the inherent properties of stearic acid and complementary stabilization techniques. The antioxidant activity of stearic acid can be optimized through strategic formulation design that considers environmental factors, packaging solutions, and synergistic ingredient combinations.
Temperature control represents a critical factor in maintaining stearic acid's stability and antioxidant efficacy. Research indicates that storing formulations at temperatures below 25°C significantly reduces oxidation rates and extends shelf-life by up to 40% compared to ambient storage conditions. Implementing cold chain management for sensitive formulations can further enhance stability profiles, particularly for cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications.
Light protection strategies must be incorporated as UV exposure catalyzes oxidation reactions that compromise stearic acid's functional properties. Amber or opaque packaging materials that block wavelengths between 290-400nm have demonstrated effectiveness in preserving antioxidant activity for extended periods. Studies show that proper light protection can maintain over 85% of initial antioxidant capacity after 12 months of storage.
Oxygen exclusion techniques represent another crucial stability enhancement approach. Modified atmosphere packaging with nitrogen or argon flushing has proven effective in minimizing oxidative degradation. Additionally, incorporating oxygen scavengers into packaging systems can reduce headspace oxygen levels below 0.01%, significantly extending product stability.
Synergistic antioxidant combinations offer substantial benefits when formulating with stearic acid. Incorporating complementary antioxidants such as tocopherols, ascorbyl palmitate, or butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) at carefully calibrated ratios can create protective networks that enhance overall stability. Research demonstrates that these combinations often exhibit superadditive effects, providing protection greater than the sum of individual components.
pH optimization represents another critical stability parameter. Maintaining formulations within the pH range of 4.5-6.5 has been shown to minimize hydrolytic degradation of stearic acid while preserving its antioxidant functionality. Buffer systems incorporating citrate or phosphate can help maintain this optimal pH range throughout the product lifecycle.
Chelating agents such as EDTA or citric acid effectively sequester metal ions that would otherwise catalyze oxidation reactions. At concentrations of 0.05-0.1%, these agents significantly reduce metal-induced oxidation pathways that would compromise stearic acid's stability and functional properties.
Implementation of accelerated stability testing protocols enables rapid assessment of formulation stability under stressed conditions. This approach facilitates efficient optimization of stabilization strategies before full-scale production, reducing development timelines and ensuring robust commercial formulations.
Temperature control represents a critical factor in maintaining stearic acid's stability and antioxidant efficacy. Research indicates that storing formulations at temperatures below 25°C significantly reduces oxidation rates and extends shelf-life by up to 40% compared to ambient storage conditions. Implementing cold chain management for sensitive formulations can further enhance stability profiles, particularly for cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications.
Light protection strategies must be incorporated as UV exposure catalyzes oxidation reactions that compromise stearic acid's functional properties. Amber or opaque packaging materials that block wavelengths between 290-400nm have demonstrated effectiveness in preserving antioxidant activity for extended periods. Studies show that proper light protection can maintain over 85% of initial antioxidant capacity after 12 months of storage.
Oxygen exclusion techniques represent another crucial stability enhancement approach. Modified atmosphere packaging with nitrogen or argon flushing has proven effective in minimizing oxidative degradation. Additionally, incorporating oxygen scavengers into packaging systems can reduce headspace oxygen levels below 0.01%, significantly extending product stability.
Synergistic antioxidant combinations offer substantial benefits when formulating with stearic acid. Incorporating complementary antioxidants such as tocopherols, ascorbyl palmitate, or butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) at carefully calibrated ratios can create protective networks that enhance overall stability. Research demonstrates that these combinations often exhibit superadditive effects, providing protection greater than the sum of individual components.
pH optimization represents another critical stability parameter. Maintaining formulations within the pH range of 4.5-6.5 has been shown to minimize hydrolytic degradation of stearic acid while preserving its antioxidant functionality. Buffer systems incorporating citrate or phosphate can help maintain this optimal pH range throughout the product lifecycle.
Chelating agents such as EDTA or citric acid effectively sequester metal ions that would otherwise catalyze oxidation reactions. At concentrations of 0.05-0.1%, these agents significantly reduce metal-induced oxidation pathways that would compromise stearic acid's stability and functional properties.
Implementation of accelerated stability testing protocols enables rapid assessment of formulation stability under stressed conditions. This approach facilitates efficient optimization of stabilization strategies before full-scale production, reducing development timelines and ensuring robust commercial formulations.
Regulatory Considerations for Antioxidant Claims
The regulatory landscape for antioxidant claims in formulations containing stearic acid requires careful navigation across multiple jurisdictional frameworks. In the United States, the FDA regulates antioxidant claims under both cosmetic and food additive regulations, with different standards applying depending on the intended use. For cosmetic applications, manufacturers must ensure that any antioxidant activity claims are substantiated by adequate scientific evidence, typically requiring in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrating measurable protective effects against oxidative stress.
The European Union, under Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 for cosmetic products, imposes stricter requirements for antioxidant claims. The European Commission's guidelines on cosmetic claims require that antioxidant properties must be demonstrated through standardized methodologies, with particular emphasis on the final formulation rather than individual ingredients. This presents a significant challenge for stearic acid-based formulations, as the antioxidant activity must be proven in the complete product matrix.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established several standards relevant to antioxidant testing, including ISO 16128 for natural and organic cosmetic ingredients and products. Compliance with these standards can provide a competitive advantage in global markets and strengthen regulatory submissions.
The classification of stearic acid varies significantly between regulatory bodies. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA for food applications, its status as an antioxidant specifically requires additional substantiation. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) maintains similar requirements for food applications, necessitating scientific evidence of antioxidant efficacy at specified concentrations.
Labeling requirements present another regulatory consideration. In most jurisdictions, antioxidant claims must be qualified based on the level of supporting evidence. Terms such as "helps protect against free radicals" versus "powerful antioxidant" carry different evidentiary burdens. The substantiation threshold increases with the strength of the claim, requiring manufacturers to carefully calibrate marketing language against available scientific support.
Recent regulatory trends indicate increasing scrutiny of antioxidant claims globally. The Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration and Health Canada have both issued guidance documents specifically addressing antioxidant claims in the past five years, suggesting a global movement toward more standardized evaluation criteria. Companies developing stearic acid formulations with antioxidant properties should anticipate this regulatory convergence and design testing protocols accordingly.
Regulatory compliance strategies should include comprehensive testing protocols that address both the antioxidant mechanism of action and quantifiable protective outcomes. Documentation should include stability studies demonstrating the persistence of antioxidant activity throughout the product's shelf life, particularly important for stearic acid formulations where oxidative stability may vary with formulation parameters.
The European Union, under Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 for cosmetic products, imposes stricter requirements for antioxidant claims. The European Commission's guidelines on cosmetic claims require that antioxidant properties must be demonstrated through standardized methodologies, with particular emphasis on the final formulation rather than individual ingredients. This presents a significant challenge for stearic acid-based formulations, as the antioxidant activity must be proven in the complete product matrix.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established several standards relevant to antioxidant testing, including ISO 16128 for natural and organic cosmetic ingredients and products. Compliance with these standards can provide a competitive advantage in global markets and strengthen regulatory submissions.
The classification of stearic acid varies significantly between regulatory bodies. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA for food applications, its status as an antioxidant specifically requires additional substantiation. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) maintains similar requirements for food applications, necessitating scientific evidence of antioxidant efficacy at specified concentrations.
Labeling requirements present another regulatory consideration. In most jurisdictions, antioxidant claims must be qualified based on the level of supporting evidence. Terms such as "helps protect against free radicals" versus "powerful antioxidant" carry different evidentiary burdens. The substantiation threshold increases with the strength of the claim, requiring manufacturers to carefully calibrate marketing language against available scientific support.
Recent regulatory trends indicate increasing scrutiny of antioxidant claims globally. The Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration and Health Canada have both issued guidance documents specifically addressing antioxidant claims in the past five years, suggesting a global movement toward more standardized evaluation criteria. Companies developing stearic acid formulations with antioxidant properties should anticipate this regulatory convergence and design testing protocols accordingly.
Regulatory compliance strategies should include comprehensive testing protocols that address both the antioxidant mechanism of action and quantifiable protective outcomes. Documentation should include stability studies demonstrating the persistence of antioxidant activity throughout the product's shelf life, particularly important for stearic acid formulations where oxidative stability may vary with formulation parameters.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!