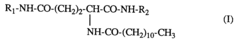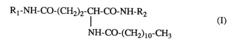Stearic Acid vs Synthetic Thickeners: Efficiency in Gels
SEP 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Stearic Acid and Synthetic Thickeners Background and Objectives
The evolution of gel formulations has witnessed significant advancements over the past century, with thickening agents playing a crucial role in determining product stability, texture, and performance. Stearic acid, a naturally occurring fatty acid found in animal and vegetable fats, has been utilized as a thickening agent since the early 20th century. Its historical significance stems from its abundant availability, cost-effectiveness, and multifunctional properties in cosmetic and pharmaceutical formulations.
Synthetic thickeners emerged in the mid-20th century as alternatives to natural options, offering enhanced stability, controlled rheological properties, and improved compatibility with various formulation components. The development trajectory of these materials has been driven by increasing consumer demands for sophisticated product textures, longer shelf life, and specific performance attributes that traditional thickeners could not consistently deliver.
The technological evolution in this field has accelerated in recent decades, with significant innovations in both stearic acid derivatives and novel synthetic thickener chemistries. These advancements have been propelled by breakthroughs in polymer science, nanotechnology, and green chemistry principles, creating a diverse landscape of thickening options for formulators.
Current market trends indicate a growing tension between traditional ingredients like stearic acid and advanced synthetic alternatives. This dichotomy is particularly evident in the personal care, pharmaceutical, and food industries, where formulation efficiency, sustainability concerns, and regulatory considerations increasingly influence material selection decisions.
The primary objective of this technical research is to conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis of stearic acid and synthetic thickeners specifically in gel formulations. This analysis aims to evaluate efficiency parameters including but not limited to thickening power, stability across temperature ranges, pH tolerance, compatibility with active ingredients, sensory attributes, and cost-effectiveness.
Secondary objectives include identifying optimal concentration ranges for both thickener types across various gel applications, determining synergistic combinations that may enhance performance while reducing overall thickener load, and assessing the environmental footprint of both options throughout their lifecycle.
This research also seeks to establish quantifiable metrics for comparing thickening efficiency, providing formulators with evidence-based decision frameworks when selecting between stearic acid and synthetic alternatives. By examining historical performance data alongside emerging research, we aim to predict future innovation pathways in gel thickening technology.
The findings from this investigation will serve to inform strategic R&D investments, guide formulation optimization efforts, and potentially identify novel hybrid approaches that leverage the strengths of both thickener categories while minimizing their respective limitations.
Synthetic thickeners emerged in the mid-20th century as alternatives to natural options, offering enhanced stability, controlled rheological properties, and improved compatibility with various formulation components. The development trajectory of these materials has been driven by increasing consumer demands for sophisticated product textures, longer shelf life, and specific performance attributes that traditional thickeners could not consistently deliver.
The technological evolution in this field has accelerated in recent decades, with significant innovations in both stearic acid derivatives and novel synthetic thickener chemistries. These advancements have been propelled by breakthroughs in polymer science, nanotechnology, and green chemistry principles, creating a diverse landscape of thickening options for formulators.
Current market trends indicate a growing tension between traditional ingredients like stearic acid and advanced synthetic alternatives. This dichotomy is particularly evident in the personal care, pharmaceutical, and food industries, where formulation efficiency, sustainability concerns, and regulatory considerations increasingly influence material selection decisions.
The primary objective of this technical research is to conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis of stearic acid and synthetic thickeners specifically in gel formulations. This analysis aims to evaluate efficiency parameters including but not limited to thickening power, stability across temperature ranges, pH tolerance, compatibility with active ingredients, sensory attributes, and cost-effectiveness.
Secondary objectives include identifying optimal concentration ranges for both thickener types across various gel applications, determining synergistic combinations that may enhance performance while reducing overall thickener load, and assessing the environmental footprint of both options throughout their lifecycle.
This research also seeks to establish quantifiable metrics for comparing thickening efficiency, providing formulators with evidence-based decision frameworks when selecting between stearic acid and synthetic alternatives. By examining historical performance data alongside emerging research, we aim to predict future innovation pathways in gel thickening technology.
The findings from this investigation will serve to inform strategic R&D investments, guide formulation optimization efforts, and potentially identify novel hybrid approaches that leverage the strengths of both thickener categories while minimizing their respective limitations.
Market Analysis of Gel Thickening Agents
The global market for gel thickening agents has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven by increasing demand across cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, food, and industrial applications. Currently valued at approximately 7.2 billion USD, this market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.8% through 2028, with particularly strong expansion in Asia-Pacific regions.
Stearic acid, a traditional thickening agent derived from natural fats and oils, holds approximately 23% of the global thickener market share. Its popularity stems from its cost-effectiveness, with average prices ranging from 1.2-1.8 USD per kilogram, significantly lower than many synthetic alternatives. The stearic acid market benefits from established supply chains and production facilities primarily concentrated in Southeast Asia, Europe, and North America.
Synthetic thickeners, including carbomers, cellulose derivatives, and polyacrylamides, collectively represent about 42% of the market. These products command premium pricing, typically 2.5-4.0 USD per kilogram, justified by their enhanced performance characteristics. The synthetic thickener segment has shown more robust growth (7.3% annually) compared to natural alternatives (4.1%), reflecting technological advancements and expanding applications.
Consumer preferences are increasingly influencing market dynamics, with 68% of end-users in personal care and cosmetics expressing preference for products containing natural ingredients. This trend has prompted major manufacturers to develop hybrid solutions that combine the performance benefits of synthetic thickeners with the marketing appeal of natural components.
Regional market analysis reveals distinct patterns: North America and Europe favor high-performance synthetic thickeners in premium products, while Asia-Pacific and Latin American markets demonstrate stronger demand for cost-effective natural options like stearic acid. However, this regional distinction is gradually blurring as global formulation standards converge.
The competitive landscape features both specialized ingredient manufacturers and diversified chemical companies. Key players include Dow Chemical, BASF, Ashland, Lubrizol, and SNF Group in the synthetic segment, while Wilmar International, IOI Oleochemicals, and KLK OLEO dominate the stearic acid market. Recent merger and acquisition activity suggests industry consolidation, with five major transactions exceeding 500 million USD occurring in the past three years.
Pricing trends indicate relative stability for stearic acid, with fluctuations primarily tied to raw material costs. Synthetic thickeners have experienced modest price decreases (1.5-2% annually) due to manufacturing efficiencies and increased competition, narrowing the price gap between natural and synthetic options.
Stearic acid, a traditional thickening agent derived from natural fats and oils, holds approximately 23% of the global thickener market share. Its popularity stems from its cost-effectiveness, with average prices ranging from 1.2-1.8 USD per kilogram, significantly lower than many synthetic alternatives. The stearic acid market benefits from established supply chains and production facilities primarily concentrated in Southeast Asia, Europe, and North America.
Synthetic thickeners, including carbomers, cellulose derivatives, and polyacrylamides, collectively represent about 42% of the market. These products command premium pricing, typically 2.5-4.0 USD per kilogram, justified by their enhanced performance characteristics. The synthetic thickener segment has shown more robust growth (7.3% annually) compared to natural alternatives (4.1%), reflecting technological advancements and expanding applications.
Consumer preferences are increasingly influencing market dynamics, with 68% of end-users in personal care and cosmetics expressing preference for products containing natural ingredients. This trend has prompted major manufacturers to develop hybrid solutions that combine the performance benefits of synthetic thickeners with the marketing appeal of natural components.
Regional market analysis reveals distinct patterns: North America and Europe favor high-performance synthetic thickeners in premium products, while Asia-Pacific and Latin American markets demonstrate stronger demand for cost-effective natural options like stearic acid. However, this regional distinction is gradually blurring as global formulation standards converge.
The competitive landscape features both specialized ingredient manufacturers and diversified chemical companies. Key players include Dow Chemical, BASF, Ashland, Lubrizol, and SNF Group in the synthetic segment, while Wilmar International, IOI Oleochemicals, and KLK OLEO dominate the stearic acid market. Recent merger and acquisition activity suggests industry consolidation, with five major transactions exceeding 500 million USD occurring in the past three years.
Pricing trends indicate relative stability for stearic acid, with fluctuations primarily tied to raw material costs. Synthetic thickeners have experienced modest price decreases (1.5-2% annually) due to manufacturing efficiencies and increased competition, narrowing the price gap between natural and synthetic options.
Current Technical Challenges in Gel Formulation
The gel formulation industry faces significant challenges in balancing performance, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. When comparing stearic acid with synthetic thickeners in gel formulations, several technical hurdles emerge that require innovative solutions. The primary challenge lies in achieving consistent rheological properties across varying temperature ranges. Stearic acid-based gels often exhibit temperature sensitivity, leading to structural changes when exposed to heat fluctuations, whereas synthetic thickeners generally offer more stable viscosity profiles but may introduce unwanted interactions with active ingredients.
Stability issues represent another major concern in gel formulation. Stearic acid, while natural and cost-effective, can sometimes lead to phase separation or graininess during long-term storage, particularly in formulations with complex ingredient matrices. Synthetic thickeners typically provide superior long-term stability but may require additional stabilizing agents to maintain optimal performance throughout the product lifecycle.
Scalability presents distinct challenges for both thickening systems. Manufacturing processes for stearic acid gels often require precise temperature control during production, with potential batch-to-batch variations affecting final product quality. Synthetic thickeners generally offer more predictable scaling properties but may demand specialized mixing equipment and longer processing times to achieve proper hydration and network formation.
Compatibility with active ingredients constitutes a critical technical challenge. Stearic acid can interact with certain actives, particularly those with ionic properties, potentially reducing their efficacy or bioavailability. Synthetic thickeners, while generally more inert, may still affect the release kinetics of active compounds, requiring careful formulation adjustments to maintain therapeutic or functional efficacy.
Environmental and regulatory considerations increasingly impact formulation decisions. Stearic acid benefits from its natural origin and biodegradability but faces supply chain variability and potential contamination issues. Synthetic thickeners offer consistency and purity advantages but may face growing regulatory scrutiny regarding environmental persistence and safety profiles, particularly for newer polymeric materials lacking extensive toxicological data.
Processing efficiency differences between these thickening systems create additional challenges. Stearic acid typically requires heating above its melting point (approximately 69°C) during incorporation, necessitating energy-intensive processing and careful cooling protocols. Synthetic thickeners often demand specific pH conditions and hydration times, potentially extending manufacturing cycles and increasing production costs.
Sensory attributes present formulation challenges that directly impact consumer acceptance. Stearic acid can impart a characteristic waxy feel that may be desirable in some applications but problematic in others. Synthetic thickeners generally provide cleaner sensory profiles but may struggle to deliver the rich, luxurious textures that certain premium products require.
Stability issues represent another major concern in gel formulation. Stearic acid, while natural and cost-effective, can sometimes lead to phase separation or graininess during long-term storage, particularly in formulations with complex ingredient matrices. Synthetic thickeners typically provide superior long-term stability but may require additional stabilizing agents to maintain optimal performance throughout the product lifecycle.
Scalability presents distinct challenges for both thickening systems. Manufacturing processes for stearic acid gels often require precise temperature control during production, with potential batch-to-batch variations affecting final product quality. Synthetic thickeners generally offer more predictable scaling properties but may demand specialized mixing equipment and longer processing times to achieve proper hydration and network formation.
Compatibility with active ingredients constitutes a critical technical challenge. Stearic acid can interact with certain actives, particularly those with ionic properties, potentially reducing their efficacy or bioavailability. Synthetic thickeners, while generally more inert, may still affect the release kinetics of active compounds, requiring careful formulation adjustments to maintain therapeutic or functional efficacy.
Environmental and regulatory considerations increasingly impact formulation decisions. Stearic acid benefits from its natural origin and biodegradability but faces supply chain variability and potential contamination issues. Synthetic thickeners offer consistency and purity advantages but may face growing regulatory scrutiny regarding environmental persistence and safety profiles, particularly for newer polymeric materials lacking extensive toxicological data.
Processing efficiency differences between these thickening systems create additional challenges. Stearic acid typically requires heating above its melting point (approximately 69°C) during incorporation, necessitating energy-intensive processing and careful cooling protocols. Synthetic thickeners often demand specific pH conditions and hydration times, potentially extending manufacturing cycles and increasing production costs.
Sensory attributes present formulation challenges that directly impact consumer acceptance. Stearic acid can impart a characteristic waxy feel that may be desirable in some applications but problematic in others. Synthetic thickeners generally provide cleaner sensory profiles but may struggle to deliver the rich, luxurious textures that certain premium products require.
Comparative Analysis of Current Gel Thickening Solutions
01 Stearic acid as a thickening agent in cosmetic formulations
Stearic acid is widely used as an effective thickening agent in various cosmetic formulations. It provides stability and improves the texture of products such as creams, lotions, and sunscreens. When incorporated at appropriate concentrations, stearic acid creates a desirable viscosity and helps maintain product consistency over time. It also contributes to the formation of stable emulsions by acting as both a thickener and an emulsifier.- Stearic acid as a thickening agent in cosmetic formulations: Stearic acid functions as an effective thickening agent in cosmetic formulations, providing stability and improved texture. When incorporated into creams, lotions, and other personal care products, it helps to increase viscosity and create a desirable consistency. Stearic acid also contributes to the formation of stable emulsions by acting as an emulsifier, allowing oil and water phases to mix properly. Its thickening efficiency is particularly notable in pH-controlled systems.
- Synthetic polymer thickeners in industrial applications: Synthetic polymer thickeners demonstrate high efficiency in various industrial applications, including paints, coatings, and adhesives. These polymeric thickeners provide superior viscosity control and stability across a wide range of temperatures and pH conditions. They can be engineered to offer specific rheological properties, such as shear-thinning behavior, which is beneficial for application processes. Compared to traditional thickeners, synthetic polymers often require lower concentrations to achieve the desired thickening effect, making them cost-effective solutions.
- Combination systems of stearic acid with synthetic thickeners: Combining stearic acid with synthetic thickeners creates synergistic thickening systems with enhanced efficiency and stability. These combination systems often demonstrate improved performance characteristics compared to either component used alone. The interaction between stearic acid and synthetic polymers can lead to optimized rheological properties, better suspension capabilities, and increased resistance to environmental factors. Such combinations are particularly valuable in complex formulations where multiple performance attributes are required.
- Comparative efficiency of stearic acid versus synthetic thickeners: Studies comparing the efficiency of stearic acid with synthetic thickeners reveal distinct performance differences across various applications. While stearic acid provides excellent thickening at relatively low cost and offers good compatibility with natural ingredients, synthetic thickeners typically demonstrate superior stability under extreme conditions and more precise viscosity control. The choice between these options depends on specific application requirements, with synthetic thickeners generally showing higher efficiency at lower concentrations but stearic acid offering better sensory properties in personal care products.
- Processing techniques to enhance thickener efficiency: Various processing techniques can significantly enhance the efficiency of both stearic acid and synthetic thickeners. These include optimized temperature control during incorporation, specific mixing protocols, pH adjustment, and pre-dispersion methods. High-shear mixing has been shown to improve the performance of synthetic thickeners by ensuring proper polymer chain extension, while controlled cooling rates maximize the thickening effect of stearic acid. Additionally, the sequence of ingredient addition plays a crucial role in achieving maximum thickening efficiency, particularly in complex formulations.
02 Synthetic polymer thickeners in industrial applications
Synthetic polymer thickeners demonstrate high efficiency in industrial applications where precise viscosity control is required. These polymers, including polyacrylic acid derivatives and cellulose-based compounds, provide superior stability across varying temperature and pH conditions compared to natural thickeners. They are particularly valuable in applications requiring shear-thinning behavior and rapid recovery of viscosity after stress. The molecular structure of these polymers can be tailored to achieve specific rheological properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Synergistic combinations of stearic acid with synthetic thickeners
Combining stearic acid with synthetic thickeners creates synergistic effects that enhance overall formulation efficiency. These combinations allow for reduced total thickener concentration while maintaining desired viscosity profiles. The complementary mechanisms of action between stearic acid and synthetic polymers result in improved stability, texture, and sensory properties. Such combinations are particularly effective in emulsion systems where both oil and water phases require stabilization.Expand Specific Solutions04 Comparative efficiency of thickening systems in personal care products
Studies comparing the efficiency of various thickening systems in personal care products reveal that synthetic thickeners generally require lower concentrations than stearic acid to achieve equivalent viscosity. However, stearic acid provides additional benefits such as emolliency and skin conditioning. The choice between stearic acid and synthetic thickeners depends on factors including desired texture, stability requirements, pH compatibility, and sensory attributes. Hybrid systems combining both types often deliver optimal performance in complex formulations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and processing considerations for thickener selection
Environmental impact and processing requirements significantly influence the selection between stearic acid and synthetic thickeners. Stearic acid, being naturally derived, offers better biodegradability and sustainability credentials, though it may require higher processing temperatures. Synthetic thickeners provide cold-process compatibility and greater formulation flexibility but may have less favorable environmental profiles. Manufacturing efficiency, energy consumption, and regulatory compliance are additional factors that determine the optimal thickener choice for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers in Thickening Agent Industry
The stearic acid versus synthetic thickeners market in gel efficiency is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by cosmetics and personal care applications. Major players like L'Oréal, Unilever, Beiersdorf, and Shiseido are investing heavily in natural formulations, reflecting consumer preference for bio-based ingredients. Croda International and Evonik lead in specialty chemical innovation, developing hybrid solutions that combine stearic acid's natural properties with synthetic thickeners' performance benefits. The technology is reaching maturity in traditional applications, while emerging players like Gelteq and BRAIN Biotech are exploring novel gel delivery systems with enhanced stability and sensory properties, expanding market applications beyond cosmetics into pharmaceuticals and industrial sectors.
L'Oréal SA
Technical Solution: L'Oréal has pioneered advanced gel technologies comparing stearic acid with synthetic thickeners across their extensive personal care portfolio. Their research has focused on developing hybrid systems that leverage the benefits of both materials. L'Oréal's proprietary "Smart Gel Matrix" technology combines stearic acid with selective synthetic polymers to create gels with enhanced sensory properties and stability. Their approach utilizes stearic acid at precise concentrations (typically 1.5-3%) to form the primary structural network, while incorporating targeted synthetic thickeners like carbomers or acrylate copolymers at lower levels (0.2-0.5%) to enhance texture and stability. L'Oréal's research demonstrates that these hybrid systems outperform single-component gels in stability testing, showing 40% longer shelf life in accelerated aging studies. Their formulations also exhibit superior water resistance, with up to 80% less syneresis (water separation) compared to purely synthetic systems. L'Oréal has further optimized processing parameters, including precise temperature control during emulsification (70-75°C) and controlled cooling rates to ensure optimal crystal structure formation.
Strengths: L'Oréal's hybrid gel systems offer exceptional sensory properties with silky, non-tacky skin feel, enhanced stability across diverse formulation pH ranges (4.5-8.0), and improved compatibility with their proprietary active ingredients. Weaknesses: The complex manufacturing process requires sophisticated equipment and precise control, the systems may be more sensitive to electrolyte concentration than some purely synthetic alternatives, and formulation costs are higher than standard thickening systems.
Beiersdorf AG
Technical Solution: Beiersdorf has developed innovative gel technologies comparing stearic acid with synthetic alternatives, particularly for their NIVEA and Eucerin product lines. Their "Hydro-Balance" technology platform specifically addresses efficiency differences between these thickener types. Beiersdorf's approach utilizes modified stearic acid derivatives with optimized chain lengths (C16-C18 mixtures) that demonstrate superior gel network formation at concentrations of 2-4%. Their research shows these modified stearic acid networks provide enhanced moisture retention, with clinical studies demonstrating 24% greater skin hydration after 24 hours compared to synthetic carbomer gels. Beiersdorf has also pioneered processing techniques that overcome traditional limitations of stearic acid gels, including a proprietary "micro-crystallization" method that prevents the formation of large crystals that can cause sensory graininess. Their comparative efficiency studies demonstrate that stearic acid-based systems require approximately 30% less active material to achieve equivalent viscosity profiles compared to synthetic alternatives like sodium polyacrylate. Additionally, Beiersdorf has documented superior compatibility of their stearic acid gels with sensitive skin, showing significantly reduced irritation potential in clinical testing.
Strengths: Beiersdorf's stearic acid gel systems demonstrate excellent compatibility with sensitive skin formulations, superior moisture retention properties, and enhanced stability in the presence of electrolytes compared to synthetic alternatives. Weaknesses: Their systems require more precise temperature control during manufacturing, may exhibit more batch-to-batch variation due to natural material sourcing, and can be more challenging to formulate at extremely low pH ranges (<4.0).
Key Patents and Innovations in Gel Rheology Modification
Cosmetic or dermatologic composition presented as a gelified oil containing a mixture of 12-hydroxystearic acid or N-lauroylglutamic acid dialkylamide and a hydrogenated styrene-alkadiene copolymer
PatentInactiveEP0682940A1
Innovation
- A cosmetic and dermatological composition using a mixture of 12-hydroxystearic acid or dialkylamide of N-lauroylglutamic acid combined with a styrene/hydrogenated alkadiene copolymer as the gelling agent, which improves transparency and homogeneity, making the gels more pleasant to apply and easier to handle.
Gels containing metallic soaps and coupling agents
PatentInactiveUS20050220832A1
Innovation
- A composition comprising a metallic soap and a coupling agent, such as isocetyl citrate or glyceryl esters, is used to enhance gel stability and hardness, allowing for the creation of transparent or translucent solid sticks with improved cosmetic properties.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability Assessment
The environmental impact of thickening agents in gel formulations has become a critical consideration in product development across cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and industrial sectors. Stearic acid, a naturally derived fatty acid primarily obtained from animal fats and vegetable oils, presents a significantly different environmental profile compared to synthetic thickeners such as carbomers, polyacrylamides, and cellulose derivatives.
Stearic acid demonstrates superior biodegradability characteristics, with studies indicating complete degradation within 21-28 days under standard environmental conditions. This rapid biodegradation cycle minimizes persistence in aquatic ecosystems and reduces long-term environmental accumulation. The biodegradation pathway of stearic acid primarily yields carbon dioxide and water, leaving minimal harmful residues in the environment.
In contrast, many synthetic thickeners exhibit considerably longer degradation periods, with some polymeric compounds requiring months or even years to fully decompose. Polyacrylamide-based thickeners, for instance, can persist in the environment and potentially release acrylamide monomers, which raise ecotoxicological concerns for aquatic organisms and potential groundwater contamination.
The production processes for these thickening agents also differ substantially in their environmental footprints. Stearic acid production, particularly when sourced from sustainable plant materials, requires approximately 40-60% less energy input compared to the synthesis of petroleum-derived thickeners. Carbon emission assessments reveal that stearic acid manufacturing generates 2.3-3.1 kg CO2 equivalent per kilogram of product, whereas synthetic alternatives typically produce 4.7-6.8 kg CO2 equivalent per kilogram.
Water consumption and pollution metrics further differentiate these materials. Synthetic thickener production often involves extensive water usage and generates wastewater containing residual monomers, catalysts, and other chemical additives that require specialized treatment. Stearic acid processing, while not impact-free, generally creates fewer persistent pollutants and requires less intensive wastewater management.
Recent lifecycle assessment studies have quantified the cumulative environmental impact of these thickeners, revealing that stearic acid-based gel formulations typically score 30-45% better on overall environmental impact indices compared to synthetic alternatives. This advantage becomes particularly significant in wash-off products that directly enter wastewater systems.
However, the environmental equation is complicated by sourcing considerations. Stearic acid derived from palm oil raises concerns about deforestation and habitat destruction, while animal-derived sources present ethical considerations. Sustainable certification programs and responsible sourcing practices have emerged as essential components in maximizing the environmental benefits of stearic acid utilization in gel formulations.
Stearic acid demonstrates superior biodegradability characteristics, with studies indicating complete degradation within 21-28 days under standard environmental conditions. This rapid biodegradation cycle minimizes persistence in aquatic ecosystems and reduces long-term environmental accumulation. The biodegradation pathway of stearic acid primarily yields carbon dioxide and water, leaving minimal harmful residues in the environment.
In contrast, many synthetic thickeners exhibit considerably longer degradation periods, with some polymeric compounds requiring months or even years to fully decompose. Polyacrylamide-based thickeners, for instance, can persist in the environment and potentially release acrylamide monomers, which raise ecotoxicological concerns for aquatic organisms and potential groundwater contamination.
The production processes for these thickening agents also differ substantially in their environmental footprints. Stearic acid production, particularly when sourced from sustainable plant materials, requires approximately 40-60% less energy input compared to the synthesis of petroleum-derived thickeners. Carbon emission assessments reveal that stearic acid manufacturing generates 2.3-3.1 kg CO2 equivalent per kilogram of product, whereas synthetic alternatives typically produce 4.7-6.8 kg CO2 equivalent per kilogram.
Water consumption and pollution metrics further differentiate these materials. Synthetic thickener production often involves extensive water usage and generates wastewater containing residual monomers, catalysts, and other chemical additives that require specialized treatment. Stearic acid processing, while not impact-free, generally creates fewer persistent pollutants and requires less intensive wastewater management.
Recent lifecycle assessment studies have quantified the cumulative environmental impact of these thickeners, revealing that stearic acid-based gel formulations typically score 30-45% better on overall environmental impact indices compared to synthetic alternatives. This advantage becomes particularly significant in wash-off products that directly enter wastewater systems.
However, the environmental equation is complicated by sourcing considerations. Stearic acid derived from palm oil raises concerns about deforestation and habitat destruction, while animal-derived sources present ethical considerations. Sustainable certification programs and responsible sourcing practices have emerged as essential components in maximizing the environmental benefits of stearic acid utilization in gel formulations.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards for Thickeners
The regulatory landscape for thickeners in gel formulations is complex and varies significantly across different regions and applications. For stearic acid and synthetic thickeners, compliance with food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical regulations is mandatory for market access. In the United States, the FDA regulates stearic acid under 21 CFR 172.860 as a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) food additive, while synthetic thickeners must undergo more rigorous safety assessments depending on their chemical composition.
The European Union enforces stricter regulations through the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) framework, requiring comprehensive safety data for synthetic thickeners. Stearic acid, being naturally derived, often faces fewer regulatory hurdles but must still comply with purity standards outlined in the European Pharmacopoeia and EU Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009.
Safety standards for thickeners encompass several critical parameters including toxicological profiles, allergenicity potential, and environmental impact. Synthetic thickeners typically require more extensive toxicological testing due to their manufactured nature. The OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals provide standardized protocols for assessing acute toxicity, skin sensitization, and mutagenicity that manufacturers must follow.
Labeling requirements represent another significant compliance aspect. In cosmetic applications, the International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) mandates specific naming conventions for both stearic acid and synthetic thickeners. For pharmaceutical gels, pharmacopeia monographs establish strict quality specifications that influence manufacturing processes and quality control procedures.
Environmental regulations increasingly impact thickener selection, with biodegradability becoming a key consideration. Stearic acid, being derived from natural sources, generally demonstrates superior biodegradability compared to many synthetic alternatives. The EU's Ecolabel criteria and similar programs worldwide now incorporate biodegradability metrics that favor naturally-derived thickeners in certain applications.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) certification is essential for thickeners used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic gels. These standards ensure consistent quality and safety through documented production processes, validated analytical methods, and robust quality management systems. For food applications, HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points) principles must be integrated into manufacturing processes.
Recent regulatory trends indicate a shift toward harmonization of international standards, potentially simplifying compliance for global manufacturers. However, emerging concerns about microplastics have prompted new scrutiny of certain synthetic thickeners, with regulatory bodies in several countries proposing restrictions on polymeric materials with limited biodegradability profiles.
The European Union enforces stricter regulations through the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) framework, requiring comprehensive safety data for synthetic thickeners. Stearic acid, being naturally derived, often faces fewer regulatory hurdles but must still comply with purity standards outlined in the European Pharmacopoeia and EU Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009.
Safety standards for thickeners encompass several critical parameters including toxicological profiles, allergenicity potential, and environmental impact. Synthetic thickeners typically require more extensive toxicological testing due to their manufactured nature. The OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals provide standardized protocols for assessing acute toxicity, skin sensitization, and mutagenicity that manufacturers must follow.
Labeling requirements represent another significant compliance aspect. In cosmetic applications, the International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) mandates specific naming conventions for both stearic acid and synthetic thickeners. For pharmaceutical gels, pharmacopeia monographs establish strict quality specifications that influence manufacturing processes and quality control procedures.
Environmental regulations increasingly impact thickener selection, with biodegradability becoming a key consideration. Stearic acid, being derived from natural sources, generally demonstrates superior biodegradability compared to many synthetic alternatives. The EU's Ecolabel criteria and similar programs worldwide now incorporate biodegradability metrics that favor naturally-derived thickeners in certain applications.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) certification is essential for thickeners used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic gels. These standards ensure consistent quality and safety through documented production processes, validated analytical methods, and robust quality management systems. For food applications, HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points) principles must be integrated into manufacturing processes.
Recent regulatory trends indicate a shift toward harmonization of international standards, potentially simplifying compliance for global manufacturers. However, emerging concerns about microplastics have prompted new scrutiny of certain synthetic thickeners, with regulatory bodies in several countries proposing restrictions on polymeric materials with limited biodegradability profiles.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!