Enhancing Stearic Acid Use in Green Cleaning Formulations
SEP 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Stearic Acid in Green Cleaning: Background and Objectives
Stearic acid, a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula C18H36O2, has emerged as a significant component in the evolution of green cleaning formulations. Historically, cleaning products have relied heavily on petrochemical-based ingredients that pose environmental and health concerns. The shift towards sustainable alternatives has positioned bio-based fatty acids, particularly stearic acid, as valuable ingredients in environmentally responsible cleaning solutions.
The development trajectory of stearic acid in cleaning applications has seen significant advancement over the past two decades. Initially utilized primarily in soap manufacturing, its application has expanded to include a diverse range of cleaning products, including laundry detergents, dishwashing liquids, and multi-surface cleaners. This evolution reflects broader industry trends toward sustainability and reduced environmental impact.
Current technical objectives for enhancing stearic acid use in green cleaning formulations center on several key areas. Foremost is improving the solubility and dispersion characteristics of stearic acid in water-based formulations, as its hydrophobic nature presents challenges in aqueous systems. Additionally, research aims to optimize the synergistic effects between stearic acid and other bio-based ingredients to enhance cleaning efficacy without compromising environmental credentials.
Another critical objective involves developing processing techniques that maintain the functional properties of stearic acid while reducing energy consumption during manufacturing. This includes exploration of low-temperature emulsification methods and novel stabilization approaches that preserve the structural integrity of stearic acid molecules in diverse formulation environments.
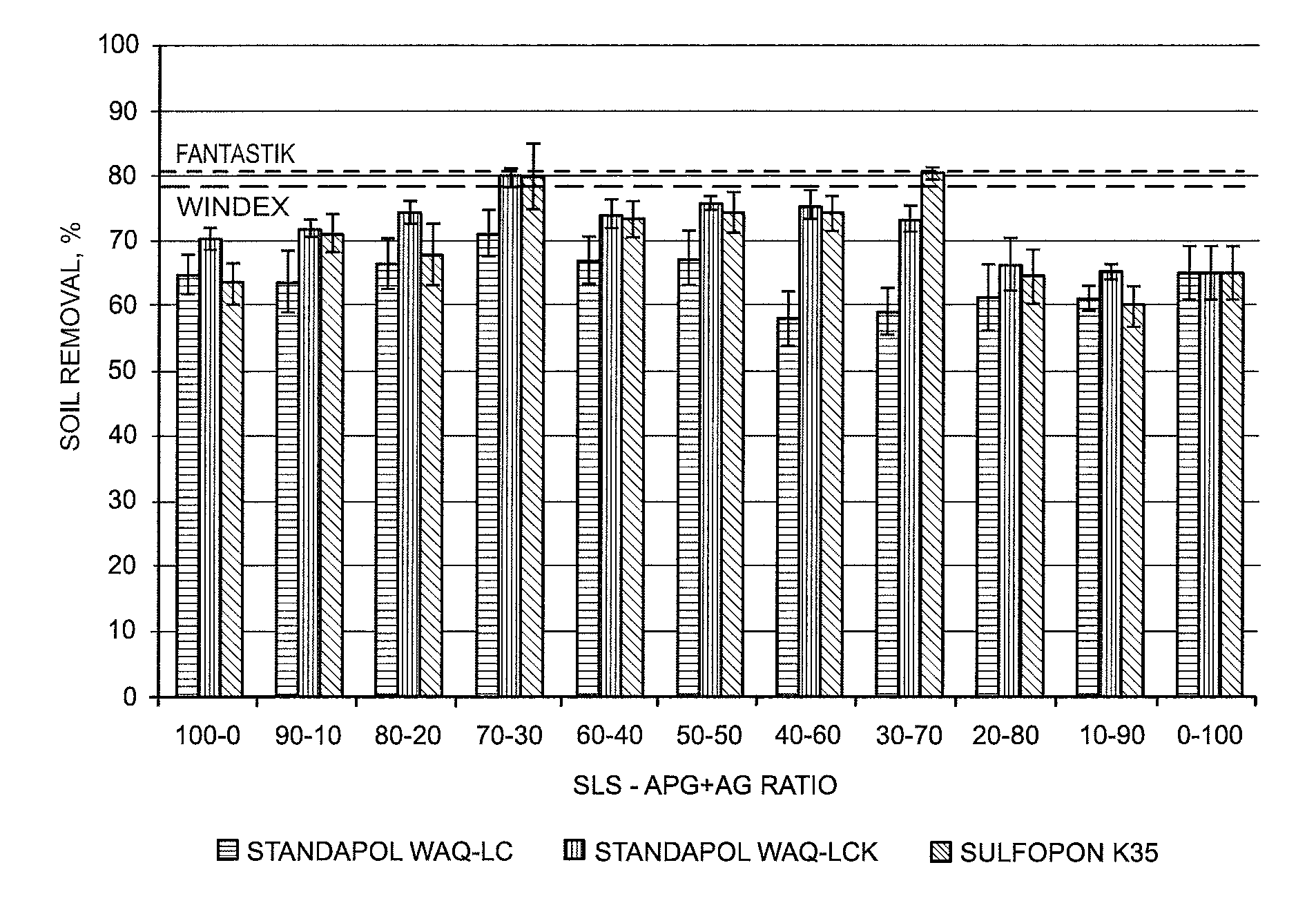
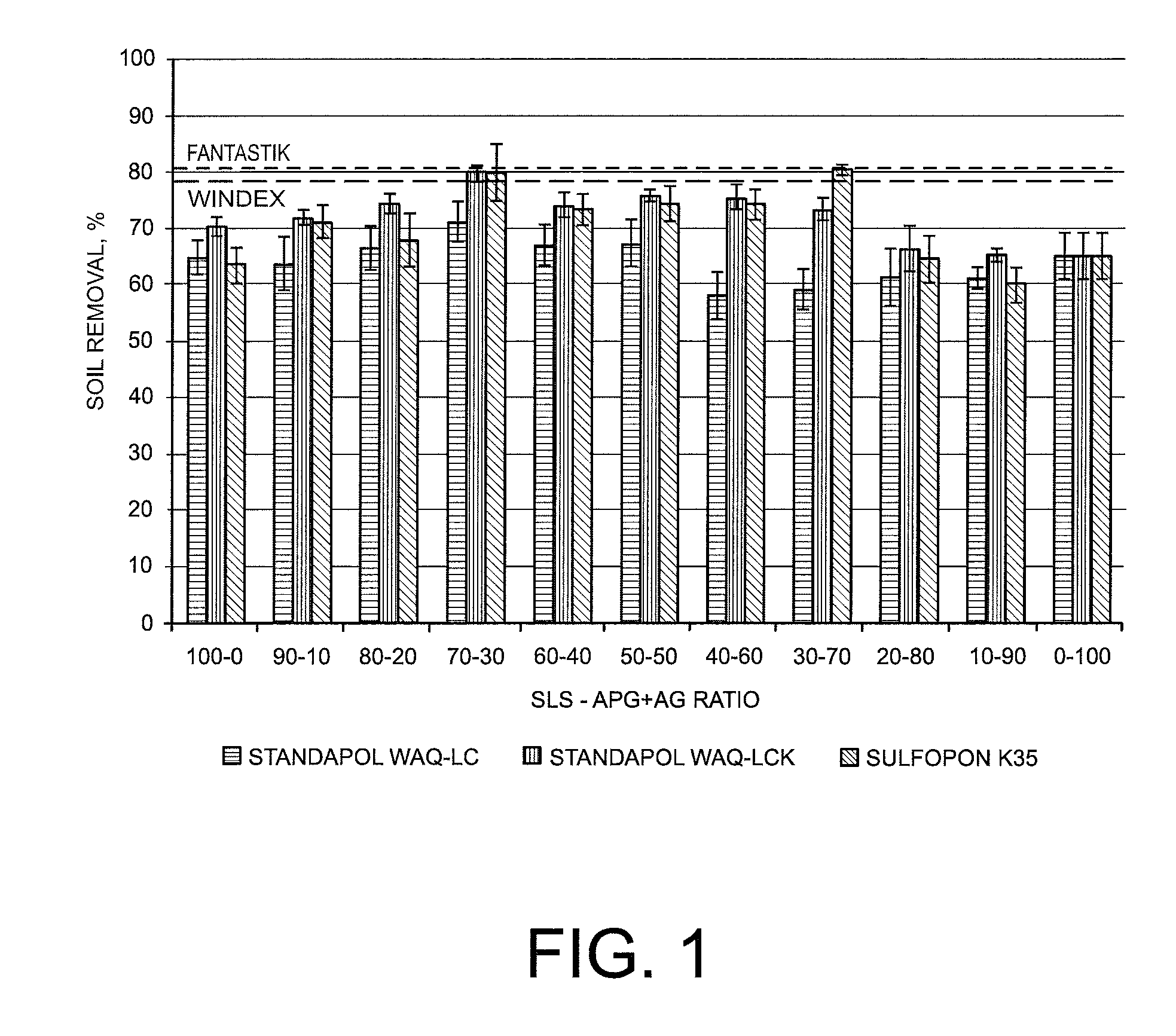
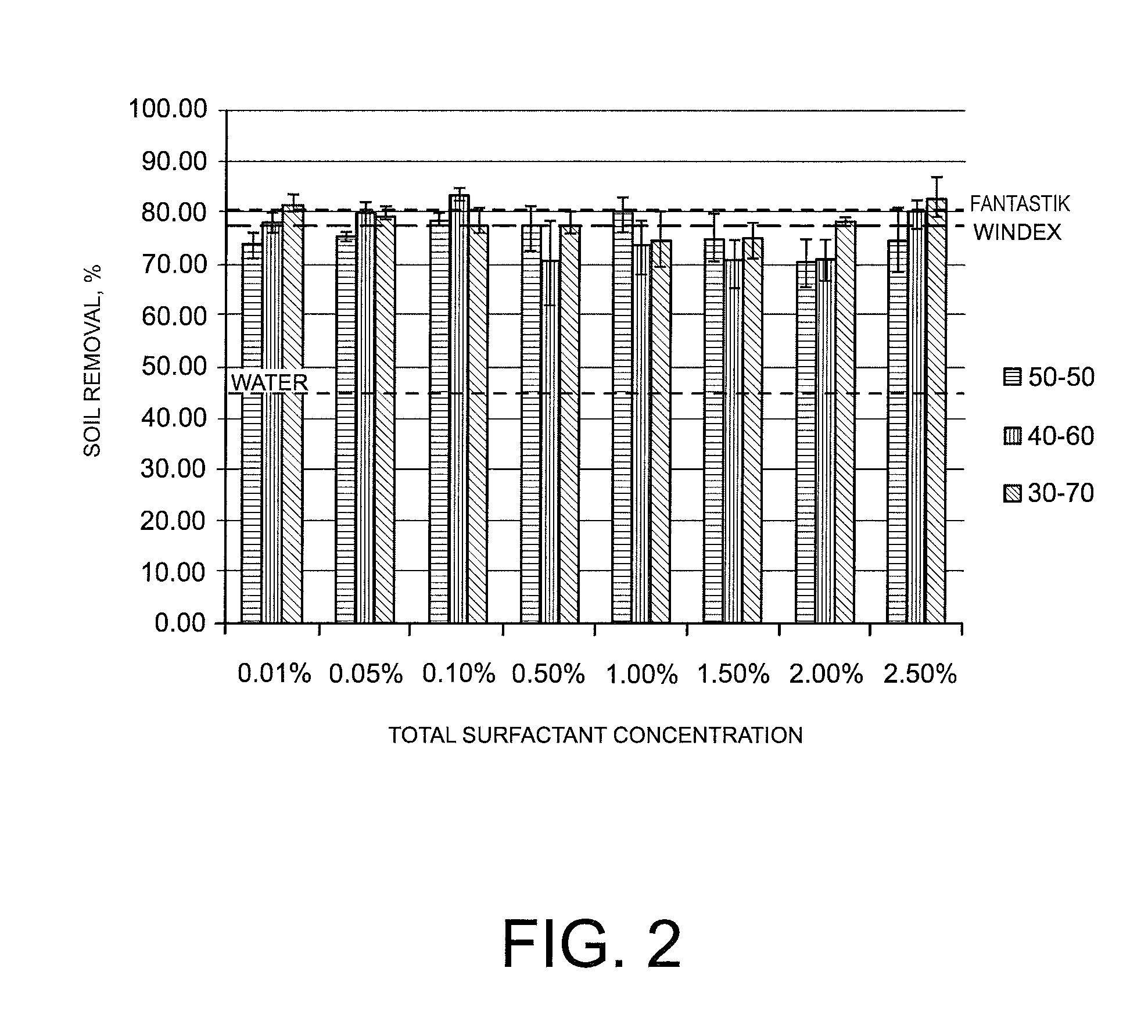
The technical landscape also reveals growing interest in modifying stearic acid derivatives to enhance specific performance attributes, such as foam stability, soil removal capabilities, and biodegradability profiles. These modifications seek to address performance gaps that have historically limited the adoption of bio-based alternatives in commercial cleaning applications.
Regulatory developments globally have further accelerated interest in stearic acid applications, with increasingly stringent restrictions on conventional petrochemical surfactants creating market opportunities for bio-based alternatives. The European Union's chemical strategy for sustainability and similar initiatives in North America and Asia have established favorable conditions for innovation in this space.
The ultimate technical goal remains developing cost-effective, high-performance green cleaning formulations that leverage stearic acid's unique properties while meeting or exceeding the performance standards established by conventional products. This requires interdisciplinary approaches combining surfactant chemistry, formulation science, and sustainability metrics to create next-generation cleaning solutions that balance efficacy, environmental impact, and economic viability.
The development trajectory of stearic acid in cleaning applications has seen significant advancement over the past two decades. Initially utilized primarily in soap manufacturing, its application has expanded to include a diverse range of cleaning products, including laundry detergents, dishwashing liquids, and multi-surface cleaners. This evolution reflects broader industry trends toward sustainability and reduced environmental impact.
Current technical objectives for enhancing stearic acid use in green cleaning formulations center on several key areas. Foremost is improving the solubility and dispersion characteristics of stearic acid in water-based formulations, as its hydrophobic nature presents challenges in aqueous systems. Additionally, research aims to optimize the synergistic effects between stearic acid and other bio-based ingredients to enhance cleaning efficacy without compromising environmental credentials.
Another critical objective involves developing processing techniques that maintain the functional properties of stearic acid while reducing energy consumption during manufacturing. This includes exploration of low-temperature emulsification methods and novel stabilization approaches that preserve the structural integrity of stearic acid molecules in diverse formulation environments.
The technical landscape also reveals growing interest in modifying stearic acid derivatives to enhance specific performance attributes, such as foam stability, soil removal capabilities, and biodegradability profiles. These modifications seek to address performance gaps that have historically limited the adoption of bio-based alternatives in commercial cleaning applications.
Regulatory developments globally have further accelerated interest in stearic acid applications, with increasingly stringent restrictions on conventional petrochemical surfactants creating market opportunities for bio-based alternatives. The European Union's chemical strategy for sustainability and similar initiatives in North America and Asia have established favorable conditions for innovation in this space.
The ultimate technical goal remains developing cost-effective, high-performance green cleaning formulations that leverage stearic acid's unique properties while meeting or exceeding the performance standards established by conventional products. This requires interdisciplinary approaches combining surfactant chemistry, formulation science, and sustainability metrics to create next-generation cleaning solutions that balance efficacy, environmental impact, and economic viability.
Market Analysis of Eco-Friendly Cleaning Products
The global market for eco-friendly cleaning products has experienced substantial growth over the past decade, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and health concerns related to traditional cleaning chemicals. This segment has evolved from a niche market to a mainstream consumer category, with annual growth rates consistently outpacing the broader cleaning products industry.
Consumer demand for green cleaning formulations has been particularly strong in North America, Western Europe, and developed Asian markets such as Japan and South Korea. Recent market research indicates that approximately 65% of consumers across these regions consider environmental impact when purchasing household cleaning products, representing a significant shift in consumer priorities compared to just five years ago.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated this trend, with heightened awareness of cleaning efficacy combined with increased concern about chemical exposure in home environments. This has created a unique market opportunity for products that can deliver both effective cleaning performance and environmental credentials.
Stearic acid, a naturally occurring fatty acid found in various animal and vegetable fats, presents significant potential in this evolving market landscape. Traditional applications of stearic acid in cleaning products have been limited, but recent innovations in formulation technology have expanded its utility in eco-friendly cleaning solutions.
Market segmentation analysis reveals particularly strong growth potential in household surface cleaners, laundry detergents, and dishwashing products. The premium segment of these categories shows the highest adoption rates for green formulations, though price sensitivity remains a barrier to broader market penetration in middle and lower-income consumer segments.
Regulatory trends globally are increasingly favorable for green cleaning formulations. The European Union's chemical regulation framework REACH, California's Cleaning Product Right to Know Act, and similar initiatives in other jurisdictions are creating market conditions that favor products with improved environmental and toxicological profiles. These regulatory developments are expected to continue driving market growth for eco-friendly cleaning products incorporating natural ingredients like stearic acid.
Distribution channels for eco-friendly cleaning products have diversified significantly, with direct-to-consumer models and specialty retailers gaining market share alongside traditional retail channels. This multi-channel approach has improved accessibility and visibility for green cleaning brands, contributing to market expansion beyond the early-adopter consumer segment.
Consumer demand for green cleaning formulations has been particularly strong in North America, Western Europe, and developed Asian markets such as Japan and South Korea. Recent market research indicates that approximately 65% of consumers across these regions consider environmental impact when purchasing household cleaning products, representing a significant shift in consumer priorities compared to just five years ago.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated this trend, with heightened awareness of cleaning efficacy combined with increased concern about chemical exposure in home environments. This has created a unique market opportunity for products that can deliver both effective cleaning performance and environmental credentials.
Stearic acid, a naturally occurring fatty acid found in various animal and vegetable fats, presents significant potential in this evolving market landscape. Traditional applications of stearic acid in cleaning products have been limited, but recent innovations in formulation technology have expanded its utility in eco-friendly cleaning solutions.
Market segmentation analysis reveals particularly strong growth potential in household surface cleaners, laundry detergents, and dishwashing products. The premium segment of these categories shows the highest adoption rates for green formulations, though price sensitivity remains a barrier to broader market penetration in middle and lower-income consumer segments.
Regulatory trends globally are increasingly favorable for green cleaning formulations. The European Union's chemical regulation framework REACH, California's Cleaning Product Right to Know Act, and similar initiatives in other jurisdictions are creating market conditions that favor products with improved environmental and toxicological profiles. These regulatory developments are expected to continue driving market growth for eco-friendly cleaning products incorporating natural ingredients like stearic acid.
Distribution channels for eco-friendly cleaning products have diversified significantly, with direct-to-consumer models and specialty retailers gaining market share alongside traditional retail channels. This multi-channel approach has improved accessibility and visibility for green cleaning brands, contributing to market expansion beyond the early-adopter consumer segment.
Technical Challenges in Stearic Acid Formulations
Despite the numerous benefits of stearic acid in green cleaning formulations, several significant technical challenges impede its widespread adoption and optimal performance. The primary obstacle lies in stearic acid's poor solubility in water at ambient temperatures, as it is a long-chain fatty acid with pronounced hydrophobic properties. This characteristic necessitates the use of additional solubilizers or higher processing temperatures, which can compromise the "green" credentials of the final formulation and increase production costs.
The pH sensitivity of stearic acid presents another formidable challenge. In alkaline environments, stearic acid forms soap-like compounds (metal stearates) which, while useful for cleaning, can leave residues on surfaces and potentially interact negatively with hard water minerals. Conversely, in acidic conditions, stearic acid remains largely undissociated, limiting its effectiveness as a cleaning agent and potentially causing precipitation issues in the formulation.
Temperature stability poses significant hurdles for stearic acid incorporation. With a melting point of approximately 69°C, stearic acid solidifies at room temperature, potentially causing crystallization in finished products during storage or transportation in colder environments. This can lead to inconsistent product performance and undesirable aesthetic qualities such as cloudiness or separation in liquid formulations.
Compatibility with other green ingredients represents another technical challenge. Many eco-friendly formulations contain plant-based surfactants, enzymes, or natural fragrances that may interact unpredictably with stearic acid. These interactions can result in reduced efficacy, stability issues, or unintended chemical reactions that compromise product performance or shelf life.
The oxidative stability of stearic acid in formulations exposed to air, light, and varying temperatures remains problematic. Over time, oxidation can lead to rancidity, color changes, and the development of off-odors, significantly reducing consumer acceptance of the product despite its environmental benefits.
Manufacturing challenges also exist, particularly in achieving consistent dispersion of stearic acid throughout water-based formulations. The need for high-temperature processing followed by controlled cooling adds complexity to production processes and increases energy consumption, potentially offsetting some environmental benefits of the green formulation.
Biodegradability optimization presents a paradox: while stearic acid is inherently biodegradable, formulations must balance rapid environmental breakdown with adequate shelf stability. Achieving this balance without resorting to synthetic preservatives or stabilizers that might compromise the product's green credentials requires sophisticated formulation expertise.
The pH sensitivity of stearic acid presents another formidable challenge. In alkaline environments, stearic acid forms soap-like compounds (metal stearates) which, while useful for cleaning, can leave residues on surfaces and potentially interact negatively with hard water minerals. Conversely, in acidic conditions, stearic acid remains largely undissociated, limiting its effectiveness as a cleaning agent and potentially causing precipitation issues in the formulation.
Temperature stability poses significant hurdles for stearic acid incorporation. With a melting point of approximately 69°C, stearic acid solidifies at room temperature, potentially causing crystallization in finished products during storage or transportation in colder environments. This can lead to inconsistent product performance and undesirable aesthetic qualities such as cloudiness or separation in liquid formulations.
Compatibility with other green ingredients represents another technical challenge. Many eco-friendly formulations contain plant-based surfactants, enzymes, or natural fragrances that may interact unpredictably with stearic acid. These interactions can result in reduced efficacy, stability issues, or unintended chemical reactions that compromise product performance or shelf life.
The oxidative stability of stearic acid in formulations exposed to air, light, and varying temperatures remains problematic. Over time, oxidation can lead to rancidity, color changes, and the development of off-odors, significantly reducing consumer acceptance of the product despite its environmental benefits.
Manufacturing challenges also exist, particularly in achieving consistent dispersion of stearic acid throughout water-based formulations. The need for high-temperature processing followed by controlled cooling adds complexity to production processes and increases energy consumption, potentially offsetting some environmental benefits of the green formulation.
Biodegradability optimization presents a paradox: while stearic acid is inherently biodegradable, formulations must balance rapid environmental breakdown with adequate shelf stability. Achieving this balance without resorting to synthetic preservatives or stabilizers that might compromise the product's green credentials requires sophisticated formulation expertise.
Current Green Formulation Techniques Using Stearic Acid
01 Stearic acid in cosmetic and personal care formulations
Stearic acid is widely used in cosmetic and personal care products as an emulsifier, thickening agent, and stabilizer. It helps create creamy textures in lotions, creams, and sunscreens while providing a protective barrier on the skin. In these formulations, stearic acid contributes to product consistency, improves spreadability, and enhances the skin feel of the final product.- Stearic acid in cosmetic and personal care formulations: Stearic acid is widely used in cosmetic and personal care products as an emulsifier, thickening agent, and stabilizer. It helps create creamy textures in lotions, creams, and sunscreens while providing a protective barrier on the skin. In these formulations, stearic acid contributes to product consistency, improves spreadability, and enhances the skin feel of the final product.
- Stearic acid in industrial applications and manufacturing: Stearic acid serves as an important raw material in various industrial processes including rubber manufacturing, plastic production, and textile processing. It functions as a release agent, lubricant, and processing aid that improves material properties and manufacturing efficiency. The compound's physical characteristics make it valuable for controlling viscosity, preventing material adhesion to equipment, and enhancing the performance of finished industrial products.
- Stearic acid derivatives and chemical modifications: Chemical modifications of stearic acid produce various derivatives with enhanced properties for specific applications. These include metal stearates, stearic esters, and amides that offer improved functionality compared to the parent compound. The modification processes involve reactions with alcohols, amines, or metal salts to create compounds with altered solubility, melting points, and chemical reactivity tailored for particular industrial or consumer product needs.
- Stearic acid in food applications: In food applications, stearic acid functions as an emulsifier, texturizer, and anti-sticking agent. It is used in the production of confectionery, baked goods, and processed foods to improve texture, extend shelf life, and prevent ingredients from sticking together. The compound's ability to form stable emulsions and its high melting point make it particularly valuable in food manufacturing processes requiring specific textural properties.
- Sustainable production and environmental aspects of stearic acid: Recent innovations focus on developing sustainable methods for stearic acid production from renewable resources such as plant oils and agricultural waste. These environmentally friendly approaches aim to reduce the carbon footprint associated with traditional petroleum-based production methods. Research includes enzymatic processes, green chemistry techniques, and biorefinery concepts that enable more efficient conversion of natural feedstocks into high-purity stearic acid while minimizing waste and environmental impact.
02 Stearic acid in industrial manufacturing processes
Stearic acid serves as an important raw material in various industrial manufacturing processes. It is used in the production of rubber, plastics, and textiles as a softening agent and lubricant. Additionally, it functions as a release agent in molding processes and as a component in metal working fluids. Its properties make it valuable for improving processing characteristics and final product quality in industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stearic acid derivatives and chemical modifications
Various derivatives and chemical modifications of stearic acid have been developed to enhance its properties for specific applications. These include esterification to produce stearates, hydrogenation processes, and formation of metal salts. Modified stearic acid compounds offer improved stability, solubility, or reactivity compared to the parent compound, expanding their utility across different industries and applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Stearic acid in pharmaceutical formulations
In pharmaceutical applications, stearic acid is utilized as an excipient in tablet and capsule formulations. It functions as a lubricant during the manufacturing process, preventing ingredients from sticking to equipment surfaces. Additionally, it can be incorporated into controlled-release drug delivery systems to modify drug release profiles. Its biocompatibility and stability make it suitable for various pharmaceutical dosage forms.Expand Specific Solutions05 Stearic acid in sustainable and bio-based applications
Stearic acid derived from renewable resources is increasingly being utilized in sustainable and bio-based applications. As a naturally occurring fatty acid, it can be sourced from plant oils and animal fats, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to petroleum-based chemicals. It is incorporated into biodegradable plastics, eco-friendly lubricants, and green surfactants, contributing to more sustainable product formulations across various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Competitors in Green Cleaning
The green cleaning formulation market is experiencing rapid growth, currently in the expansion phase with increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products. The global market size is projected to reach significant volumes as sustainability becomes a priority across consumer and industrial sectors. In terms of technical maturity, stearic acid integration in green cleaning formulations shows varying levels of advancement among key players. Industry leaders like Unilever, Ecolab, and S.C. Johnson have established robust R&D capabilities, while companies such as Blueland (One Home Brands) and Climeworks represent innovative disruptors focusing on sustainable chemistry. Traditional chemical manufacturers including BASF, Rhodia Operations, and Stepan Co. provide essential technical expertise in surfactant technology, creating a competitive landscape where established players and green-focused innovators are driving technical evolution through different approaches to stearic acid utilization.
Ecolab USA, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ecolab has developed advanced green cleaning formulations that optimize stearic acid as a key ingredient in their sustainable product line. Their approach involves using stearic acid as both a surfactant enhancer and foam stabilizer in concentrated cleaning solutions. The company has engineered proprietary blending techniques that allow stearic acid to work synergistically with plant-derived surfactants, creating highly effective cleaning products with reduced environmental impact. Ecolab's research has shown that their stearic acid formulations can reduce the overall chemical load by up to 30% while maintaining equivalent cleaning performance compared to conventional products. Their technology includes a specialized emulsification process that improves the solubility of stearic acid in water-based cleaning systems, overcoming one of the traditional limitations of this fatty acid in cleaning applications.
Strengths: Superior integration of stearic acid with other bio-based ingredients, resulting in highly effective cleaning performance with reduced environmental impact. Their formulations demonstrate excellent stability across varying water hardness conditions. Weaknesses: The specialized emulsification process requires precise manufacturing controls, potentially increasing production costs compared to conventional formulations.
The Clorox Co.
Technical Solution: Clorox has developed a strategic approach to incorporating stearic acid in their green cleaning portfolio through their "IGNITE" sustainability platform. Their technical innovation focuses on using stearic acid as both a cleaning enhancer and as a natural thickening agent in their plant-based cleaning formulations. Clorox's research has demonstrated that properly formulated stearic acid can improve product stability and extend shelf life while reducing the need for synthetic stabilizers. Their formulation approach includes a proprietary saponification process that converts stearic acid into partially neutralized salts that offer enhanced water solubility while maintaining cleaning efficacy. Clorox has also pioneered the use of stearic acid in combination with plant-derived solvents to create highly effective degreasers that can replace traditional petroleum-based products. Their technical data shows that these formulations can achieve up to 95% biodegradability while matching or exceeding the performance of conventional alternatives.
Strengths: Excellent integration of stearic acid as both a functional cleaning ingredient and formulation stabilizer, reducing the need for additional synthetic additives. Their products demonstrate strong consumer acceptance due to effective performance. Weaknesses: Their formulation approach requires precise pH control during manufacturing, which can increase production complexity and quality control requirements.
Key Patents and Innovations in Stearic Acid Technology
Advanced novel ECO-friendly compositions
PatentInactiveUS20200148975A1
Innovation
- Development of non-toxic, eco-friendly compositions that can be used for a wide range of applications including crop treatment, cleaning, and sanitization, utilizing ingredients like sodium carbonate, potassium hydroxide, and alkyl polyglycosides, which are biodegradable and safe for surfaces and the environment.
Green compositions containing synergistic blends of surfactants and linkers
PatentActiveUS8283304B2
Innovation
- The development of nano- or micro-emulsions containing 'green' surfactants, linkers, natural fragrances, and insecticides derived from renewable sources, which synergistically enhance cleaning performance and allow for stable emulsion formation at room temperature.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Stearic Acid Products
The environmental impact of stearic acid-based cleaning products requires comprehensive assessment across their entire lifecycle. When properly formulated for green cleaning applications, stearic acid products demonstrate several positive environmental attributes compared to conventional cleaning agents containing synthetic surfactants and petrochemical derivatives.
Stearic acid, derived from natural sources such as vegetable oils and animal fats, presents a significantly lower environmental footprint during raw material acquisition. Life cycle assessments indicate that plant-derived stearic acid production generates approximately 65% less greenhouse gas emissions compared to petroleum-based surfactants. Additionally, the biodegradability profile of stearic acid is exceptional, with studies demonstrating complete degradation within 28 days under standard environmental conditions.
Water system impacts reveal that stearic acid-based formulations exhibit reduced aquatic toxicity. Research conducted by the Environmental Protection Agency shows that when properly formulated, these products demonstrate LC50 values (lethal concentration affecting 50% of test organisms) significantly higher than conventional cleaning agents, indicating lower toxicity to aquatic organisms. This is particularly important as cleaning products inevitably enter waterways through disposal systems.
Energy consumption analysis throughout the product lifecycle demonstrates that green cleaning formulations incorporating stearic acid typically require 30-40% less energy during manufacturing compared to conventional alternatives. This efficiency stems from simpler processing requirements and lower temperature thresholds during production phases.
Waste generation metrics are equally favorable, with stearic acid formulations producing approximately 25% less packaging waste due to higher concentration possibilities and reduced chemical residue concerns. The absence of persistent chemical compounds in wastewater treatment processes further enhances their environmental profile.
Carbon footprint calculations reveal that stearic acid-based green cleaning products can reduce overall carbon emissions by 40-50% compared to conventional cleaning agents when considering the entire product lifecycle from raw material extraction through disposal. This significant reduction stems primarily from renewable sourcing and efficient manufacturing processes.
However, challenges remain regarding agricultural land use for plant-derived stearic acid sources and potential competition with food production. Sustainable sourcing certification programs have emerged to address these concerns, with RSPO (Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil) certification becoming increasingly important for manufacturers utilizing palm-derived stearic acid in their formulations.
Future environmental impact improvements will likely focus on closed-loop systems for stearic acid recovery from waste streams and development of even more concentrated formulations to reduce transportation emissions and packaging requirements.
Stearic acid, derived from natural sources such as vegetable oils and animal fats, presents a significantly lower environmental footprint during raw material acquisition. Life cycle assessments indicate that plant-derived stearic acid production generates approximately 65% less greenhouse gas emissions compared to petroleum-based surfactants. Additionally, the biodegradability profile of stearic acid is exceptional, with studies demonstrating complete degradation within 28 days under standard environmental conditions.
Water system impacts reveal that stearic acid-based formulations exhibit reduced aquatic toxicity. Research conducted by the Environmental Protection Agency shows that when properly formulated, these products demonstrate LC50 values (lethal concentration affecting 50% of test organisms) significantly higher than conventional cleaning agents, indicating lower toxicity to aquatic organisms. This is particularly important as cleaning products inevitably enter waterways through disposal systems.
Energy consumption analysis throughout the product lifecycle demonstrates that green cleaning formulations incorporating stearic acid typically require 30-40% less energy during manufacturing compared to conventional alternatives. This efficiency stems from simpler processing requirements and lower temperature thresholds during production phases.
Waste generation metrics are equally favorable, with stearic acid formulations producing approximately 25% less packaging waste due to higher concentration possibilities and reduced chemical residue concerns. The absence of persistent chemical compounds in wastewater treatment processes further enhances their environmental profile.
Carbon footprint calculations reveal that stearic acid-based green cleaning products can reduce overall carbon emissions by 40-50% compared to conventional cleaning agents when considering the entire product lifecycle from raw material extraction through disposal. This significant reduction stems primarily from renewable sourcing and efficient manufacturing processes.
However, challenges remain regarding agricultural land use for plant-derived stearic acid sources and potential competition with food production. Sustainable sourcing certification programs have emerged to address these concerns, with RSPO (Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil) certification becoming increasingly important for manufacturers utilizing palm-derived stearic acid in their formulations.
Future environmental impact improvements will likely focus on closed-loop systems for stearic acid recovery from waste streams and development of even more concentrated formulations to reduce transportation emissions and packaging requirements.
Regulatory Compliance for Green Cleaning Formulations
The regulatory landscape for green cleaning formulations incorporating stearic acid is increasingly complex, with multiple layers of compliance requirements across different jurisdictions. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates cleaning products primarily through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). For stearic acid formulations to qualify as "green," they must meet the EPA's Safer Choice Program criteria, which evaluates both the environmental and human health impacts of ingredients.
The European Union imposes more stringent regulations through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) and the Classification, Labeling and Packaging (CLP) Regulation. Stearic acid itself is generally recognized as safe, but formulations containing this ingredient must still undergo comprehensive safety assessments and biodegradability testing to comply with the EU Ecolabel criteria for cleaning products.
Voluntary certification programs have become increasingly important market differentiators. These include Green Seal (GS-37 for industrial and institutional cleaners), UL ECOLOGO, and USDA BioPreferred Program. Each program has specific requirements regarding biodegradability, aquatic toxicity, VOC content, and packaging sustainability that stearic acid formulations must meet to obtain certification.
Labeling requirements present another compliance challenge. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) in the US and similar bodies internationally mandate specific hazard communications on product labels. For green cleaning products containing stearic acid, transparent ingredient disclosure is becoming standard practice, with many jurisdictions requiring detailed ingredient lists and potential allergen warnings.
Recent regulatory trends indicate a move toward stricter VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) limits in cleaning products. While stearic acid itself is non-volatile, other components in the formulation must be carefully selected to meet increasingly stringent VOC thresholds, particularly in regions like California where the California Air Resources Board (CARB) sets more restrictive standards than federal regulations.
Emerging regulations on microplastics and persistent chemicals are also relevant to stearic acid formulations. The EU's proposed restrictions on intentionally added microplastics and similar initiatives in other regions may impact certain delivery systems for stearic acid in cleaning products, necessitating reformulation or alternative approaches to maintain compliance while preserving efficacy.
The European Union imposes more stringent regulations through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) and the Classification, Labeling and Packaging (CLP) Regulation. Stearic acid itself is generally recognized as safe, but formulations containing this ingredient must still undergo comprehensive safety assessments and biodegradability testing to comply with the EU Ecolabel criteria for cleaning products.
Voluntary certification programs have become increasingly important market differentiators. These include Green Seal (GS-37 for industrial and institutional cleaners), UL ECOLOGO, and USDA BioPreferred Program. Each program has specific requirements regarding biodegradability, aquatic toxicity, VOC content, and packaging sustainability that stearic acid formulations must meet to obtain certification.
Labeling requirements present another compliance challenge. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) in the US and similar bodies internationally mandate specific hazard communications on product labels. For green cleaning products containing stearic acid, transparent ingredient disclosure is becoming standard practice, with many jurisdictions requiring detailed ingredient lists and potential allergen warnings.
Recent regulatory trends indicate a move toward stricter VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) limits in cleaning products. While stearic acid itself is non-volatile, other components in the formulation must be carefully selected to meet increasingly stringent VOC thresholds, particularly in regions like California where the California Air Resources Board (CARB) sets more restrictive standards than federal regulations.
Emerging regulations on microplastics and persistent chemicals are also relevant to stearic acid formulations. The EU's proposed restrictions on intentionally added microplastics and similar initiatives in other regions may impact certain delivery systems for stearic acid in cleaning products, necessitating reformulation or alternative approaches to maintain compliance while preserving efficacy.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!