Assessing Stearic Acid's Role in Thermoplastic Stability
SEP 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Stearic Acid in Thermoplastics: Background and Objectives
Stearic acid has emerged as a significant component in thermoplastic formulations over the past several decades, evolving from a simple lubricant to a multifunctional additive. The historical development of stearic acid applications in polymers can be traced back to the 1950s when researchers first recognized its potential as a processing aid. Since then, its role has expanded considerably, particularly in the last two decades with the growing demand for more stable and durable thermoplastic materials across various industries.
The technical evolution of stearic acid utilization shows a clear trajectory from basic applications to sophisticated formulation science. Initially employed primarily as an external lubricant, research has progressively revealed its capabilities as a heat stabilizer, acid scavenger, and nucleating agent. Recent advancements have focused on understanding the molecular interactions between stearic acid and various polymer matrices, leading to more targeted and efficient applications.
Current industry trends indicate a growing interest in optimizing stearic acid concentrations and modifications to enhance thermoplastic stability under increasingly demanding conditions. The push toward higher processing temperatures, longer service lifetimes, and more aggressive environmental exposures has intensified research efforts in this domain. Additionally, the sustainability movement has sparked investigations into bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived stearic acid, presenting both challenges and opportunities for innovation.
The global market for thermoplastic stabilizers, including stearic acid-based formulations, has shown consistent growth at approximately 4.5% annually, with projections suggesting accelerated expansion in emerging economies where manufacturing sectors are rapidly developing. This market trajectory underscores the continued relevance and importance of stearic acid research in polymer science.
The primary technical objectives of current research include: quantifying the precise mechanisms by which stearic acid enhances thermal stability across different polymer types; determining optimal concentration ranges for various application environments; investigating synergistic effects with other additives; developing predictive models for long-term performance; and exploring novel derivatives with enhanced functionality. These objectives align with broader industry goals of extending product lifespans, reducing material consumption, and minimizing environmental impact.
Regulatory considerations have also become increasingly important, with restrictions on certain traditional stabilizers creating new opportunities for stearic acid-based alternatives. The generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status of stearic acid in many jurisdictions provides a competitive advantage in applications where consumer safety is paramount, such as food packaging and medical devices.
The technical evolution of stearic acid utilization shows a clear trajectory from basic applications to sophisticated formulation science. Initially employed primarily as an external lubricant, research has progressively revealed its capabilities as a heat stabilizer, acid scavenger, and nucleating agent. Recent advancements have focused on understanding the molecular interactions between stearic acid and various polymer matrices, leading to more targeted and efficient applications.
Current industry trends indicate a growing interest in optimizing stearic acid concentrations and modifications to enhance thermoplastic stability under increasingly demanding conditions. The push toward higher processing temperatures, longer service lifetimes, and more aggressive environmental exposures has intensified research efforts in this domain. Additionally, the sustainability movement has sparked investigations into bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived stearic acid, presenting both challenges and opportunities for innovation.
The global market for thermoplastic stabilizers, including stearic acid-based formulations, has shown consistent growth at approximately 4.5% annually, with projections suggesting accelerated expansion in emerging economies where manufacturing sectors are rapidly developing. This market trajectory underscores the continued relevance and importance of stearic acid research in polymer science.
The primary technical objectives of current research include: quantifying the precise mechanisms by which stearic acid enhances thermal stability across different polymer types; determining optimal concentration ranges for various application environments; investigating synergistic effects with other additives; developing predictive models for long-term performance; and exploring novel derivatives with enhanced functionality. These objectives align with broader industry goals of extending product lifespans, reducing material consumption, and minimizing environmental impact.
Regulatory considerations have also become increasingly important, with restrictions on certain traditional stabilizers creating new opportunities for stearic acid-based alternatives. The generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status of stearic acid in many jurisdictions provides a competitive advantage in applications where consumer safety is paramount, such as food packaging and medical devices.
Market Analysis of Stabilized Thermoplastic Products
The global market for stabilized thermoplastic products has experienced substantial growth over the past decade, driven primarily by increasing demand across automotive, packaging, construction, and consumer goods industries. The market value reached approximately $168 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% through 2028, potentially reaching $235 billion by the end of the forecast period.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the stabilized thermoplastic market, accounting for nearly 45% of global consumption, with China being the largest contributor. North America and Europe follow with market shares of 25% and 22% respectively, while Latin America and the Middle East & Africa collectively represent the remaining 8%.
The automotive sector remains the largest end-user of stabilized thermoplastic products, consuming roughly 32% of global production. The industry's shift toward lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions has significantly boosted demand for thermally stable polymers. Packaging applications follow closely at 28%, driven by requirements for heat-resistant food containers and durable consumer packaging.
Consumer preference for sustainable and environmentally friendly products has created a distinct market segment for bio-based stabilized thermoplastics, currently valued at $12 billion and growing at 9.3% annually—significantly outpacing the overall market growth rate. This trend reflects increasing regulatory pressure and corporate sustainability commitments worldwide.
Price sensitivity varies considerably across application segments. High-performance applications in aerospace and medical devices demonstrate low price elasticity, with customers willing to pay premium prices for guaranteed thermal stability. Conversely, mass-market applications in packaging and consumer goods exhibit higher price sensitivity, creating competitive pressure on manufacturers to optimize formulations while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
The competitive landscape features both specialized additive manufacturers and integrated polymer producers. Major players include Clariant, BASF, Songwon Industrial, and Addivant, collectively controlling approximately 65% of the thermal stabilizer market. Recent merger and acquisition activity suggests industry consolidation, with larger chemical conglomerates acquiring specialized stabilizer technology firms to expand their product portfolios.
Market research indicates that products incorporating stearic acid-based stabilizers command a price premium of 7-12% compared to conventional alternatives, reflecting their superior performance characteristics and longer service life. This premium positioning has attracted new market entrants, particularly from emerging economies, intensifying competition and driving innovation in formulation technologies.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the stabilized thermoplastic market, accounting for nearly 45% of global consumption, with China being the largest contributor. North America and Europe follow with market shares of 25% and 22% respectively, while Latin America and the Middle East & Africa collectively represent the remaining 8%.
The automotive sector remains the largest end-user of stabilized thermoplastic products, consuming roughly 32% of global production. The industry's shift toward lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions has significantly boosted demand for thermally stable polymers. Packaging applications follow closely at 28%, driven by requirements for heat-resistant food containers and durable consumer packaging.
Consumer preference for sustainable and environmentally friendly products has created a distinct market segment for bio-based stabilized thermoplastics, currently valued at $12 billion and growing at 9.3% annually—significantly outpacing the overall market growth rate. This trend reflects increasing regulatory pressure and corporate sustainability commitments worldwide.
Price sensitivity varies considerably across application segments. High-performance applications in aerospace and medical devices demonstrate low price elasticity, with customers willing to pay premium prices for guaranteed thermal stability. Conversely, mass-market applications in packaging and consumer goods exhibit higher price sensitivity, creating competitive pressure on manufacturers to optimize formulations while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
The competitive landscape features both specialized additive manufacturers and integrated polymer producers. Major players include Clariant, BASF, Songwon Industrial, and Addivant, collectively controlling approximately 65% of the thermal stabilizer market. Recent merger and acquisition activity suggests industry consolidation, with larger chemical conglomerates acquiring specialized stabilizer technology firms to expand their product portfolios.
Market research indicates that products incorporating stearic acid-based stabilizers command a price premium of 7-12% compared to conventional alternatives, reflecting their superior performance characteristics and longer service life. This premium positioning has attracted new market entrants, particularly from emerging economies, intensifying competition and driving innovation in formulation technologies.
Current Challenges in Thermoplastic Stabilization
The thermoplastic industry currently faces significant challenges in maintaining product stability across diverse applications and environmental conditions. Thermal degradation remains a primary concern, as exposure to elevated temperatures during processing and end-use applications can trigger chain scission, cross-linking, and oxidation reactions that compromise material integrity. These degradation mechanisms not only affect mechanical properties but also impact color stability and surface appearance.
Processing inconsistencies present another major challenge, with variations in temperature profiles, shear rates, and residence times leading to unpredictable stabilizer performance. The industry struggles to develop universal stabilization packages that perform consistently across different processing methods including injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding.
Environmental factors have emerged as increasingly critical considerations. UV radiation exposure accelerates degradation in outdoor applications, while moisture absorption can catalyze hydrolytic degradation in certain polymer systems. These environmental stressors often work synergistically, complicating stabilization efforts and requiring multi-functional additive systems.
The migration of stabilizers represents a persistent technical hurdle. Low molecular weight additives tend to bloom to the surface or leach out over time, particularly at elevated temperatures or in contact with solvents. This phenomenon reduces long-term protection and may introduce regulatory concerns in sensitive applications such as food packaging or medical devices.
Regulatory pressures continue to intensify, with increasing restrictions on traditional stabilizers containing heavy metals, halogenated compounds, or substances of very high concern (SVHCs). This regulatory landscape has created an urgent need for environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain performance standards while meeting compliance requirements.
Compatibility issues between stabilizers and other additives in complex formulations frequently lead to antagonistic interactions that diminish overall effectiveness. These interactions can reduce stabilizer efficiency or create unexpected side reactions that negatively impact physical properties or processing characteristics.
Cost considerations remain paramount, as manufacturers seek economically viable stabilization solutions that do not significantly increase production costs. The balance between performance, regulatory compliance, and economic feasibility presents a continuous challenge for formulators and material scientists.
The integration of stearic acid into stabilization systems introduces additional complexities related to its dual functionality as both a processing aid and potential stabilizer. Understanding its precise mechanisms of action, optimal concentration levels, and interactions with primary antioxidants and other stabilizers requires sophisticated analytical approaches and accelerated aging methodologies that accurately predict long-term performance.
Processing inconsistencies present another major challenge, with variations in temperature profiles, shear rates, and residence times leading to unpredictable stabilizer performance. The industry struggles to develop universal stabilization packages that perform consistently across different processing methods including injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding.
Environmental factors have emerged as increasingly critical considerations. UV radiation exposure accelerates degradation in outdoor applications, while moisture absorption can catalyze hydrolytic degradation in certain polymer systems. These environmental stressors often work synergistically, complicating stabilization efforts and requiring multi-functional additive systems.
The migration of stabilizers represents a persistent technical hurdle. Low molecular weight additives tend to bloom to the surface or leach out over time, particularly at elevated temperatures or in contact with solvents. This phenomenon reduces long-term protection and may introduce regulatory concerns in sensitive applications such as food packaging or medical devices.
Regulatory pressures continue to intensify, with increasing restrictions on traditional stabilizers containing heavy metals, halogenated compounds, or substances of very high concern (SVHCs). This regulatory landscape has created an urgent need for environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain performance standards while meeting compliance requirements.
Compatibility issues between stabilizers and other additives in complex formulations frequently lead to antagonistic interactions that diminish overall effectiveness. These interactions can reduce stabilizer efficiency or create unexpected side reactions that negatively impact physical properties or processing characteristics.
Cost considerations remain paramount, as manufacturers seek economically viable stabilization solutions that do not significantly increase production costs. The balance between performance, regulatory compliance, and economic feasibility presents a continuous challenge for formulators and material scientists.
The integration of stearic acid into stabilization systems introduces additional complexities related to its dual functionality as both a processing aid and potential stabilizer. Understanding its precise mechanisms of action, optimal concentration levels, and interactions with primary antioxidants and other stabilizers requires sophisticated analytical approaches and accelerated aging methodologies that accurately predict long-term performance.
Existing Stearic Acid-Based Stabilization Methods
01 Thermal stability enhancement methods for stearic acid
Various methods can be employed to enhance the thermal stability of stearic acid, which is crucial for its applications in high-temperature processes. These methods include the addition of antioxidants, metal chelating agents, and specific stabilizers that prevent oxidative degradation. The thermal stability can also be improved by controlling processing conditions such as temperature, pressure, and exposure to oxygen. These enhancements allow stearic acid to maintain its properties even when subjected to elevated temperatures during manufacturing or application processes.- Thermal stability enhancement of stearic acid: Various methods can be employed to enhance the thermal stability of stearic acid, which is crucial for applications involving high-temperature processing. These methods include the addition of antioxidants, metal chelators, and specific stabilizing compounds that prevent degradation when exposed to heat. Enhanced thermal stability ensures that stearic acid maintains its functional properties in formulations subjected to elevated temperatures during manufacturing or use.
- Oxidation resistance in stearic acid formulations: Improving the oxidation resistance of stearic acid is essential for maintaining its efficacy and extending shelf life. This can be achieved through the incorporation of antioxidants such as tocopherols, ascorbic acid derivatives, or synthetic compounds that inhibit free radical formation. Proper packaging and storage conditions also play a significant role in preventing oxidative degradation of stearic acid-containing products.
- pH stabilization of stearic acid systems: The stability of stearic acid is significantly influenced by pH conditions. Buffering agents and pH adjusters can be incorporated into formulations to maintain optimal pH ranges that prevent degradation or unwanted reactions. Controlling pH helps preserve the functional properties of stearic acid in various applications, particularly in cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and food products where stability across different environments is required.
- Emulsion stability with stearic acid: Stearic acid plays a crucial role in emulsion stability as an emulsifier or co-emulsifier. Its stability can be enhanced through proper formulation techniques, including the selection of compatible co-emulsifiers, optimizing the phase ratio, and controlling processing parameters. Stable emulsions containing stearic acid require careful consideration of factors such as temperature during preparation, homogenization conditions, and the presence of electrolytes.
- Chemical modification for improved stearic acid stability: Chemical modifications of stearic acid, such as esterification, hydrogenation, or the formation of metal salts, can significantly improve its stability profile. These modifications alter the chemical properties of stearic acid, making it less susceptible to degradation under various conditions. Modified forms often exhibit enhanced resistance to oxidation, hydrolysis, and thermal decomposition, expanding the range of applications where stearic acid can be effectively utilized.
02 Chemical stabilization of stearic acid in formulations
Chemical stabilization techniques are essential for maintaining the integrity of stearic acid in various formulations. These include pH adjustment to optimal levels, incorporation of synergistic stabilizer compounds, and the use of buffer systems. Certain additives like tocopherols, ascorbic acid derivatives, and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) can significantly improve the chemical stability of stearic acid by preventing oxidation and hydrolysis reactions. These stabilization methods are particularly important in cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and food applications where product shelf-life and efficacy depend on the stability of stearic acid.Expand Specific Solutions03 Storage and handling conditions for preserving stearic acid stability
Proper storage and handling conditions are critical for maintaining the stability of stearic acid. These include storage in cool, dry environments away from direct sunlight, use of airtight containers to prevent moisture absorption and oxidation, and implementation of appropriate packaging materials that do not react with the acid. Temperature control during storage is particularly important, as elevated temperatures can accelerate degradation processes. Additionally, minimizing exposure to air during handling and processing helps preserve the acid's chemical properties and extends its useful life in industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Stabilization of stearic acid in emulsion systems
In emulsion systems, stearic acid stability presents unique challenges that require specific stabilization approaches. The incorporation of emulsion stabilizers, surfactants, and co-emulsifiers can help maintain the structural integrity of stearic acid within these systems. Techniques such as homogenization optimization, particle size control, and the use of protective colloids enhance the stability of stearic acid in emulsions. These methods prevent phase separation, coalescence, and degradation of stearic acid, ensuring consistent performance in cosmetic formulations, food products, and pharmaceutical preparations where emulsion stability is critical.Expand Specific Solutions05 Compatibility enhancement of stearic acid with other ingredients
Enhancing the compatibility of stearic acid with other ingredients is essential for formulation stability. This can be achieved through the use of solubilizers, co-solvents, and compatibility agents that improve miscibility and prevent precipitation or separation. Modification techniques such as esterification or salt formation can alter the physicochemical properties of stearic acid to improve its compatibility with polar or non-polar components. Additionally, processing methods like controlled heating, proper mixing sequences, and appropriate dispersion techniques can significantly improve the integration of stearic acid with other ingredients in complex formulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
The stearic acid market for thermoplastic stability is in a mature growth phase with an estimated global market value exceeding $1.5 billion. Technical maturity is high, with established players like BASF Corp. and Arkema France SA offering advanced formulations for industrial applications. Innovation is focused on sustainable solutions, with companies like Plantic Technologies and NOR-X Industry developing bio-based alternatives. Research institutions including Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft and University of Leeds are advancing fundamental understanding of stearic acid's stabilizing mechanisms. Asian manufacturers such as Lotte Advanced Materials and Zhejiang Transfar Whyyon Chemical are rapidly expanding market share through cost-effective production and application-specific formulations, particularly in automotive and electronics sectors where thermal stability requirements are increasingly stringent.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a comprehensive approach to stearic acid utilization in thermoplastic stabilization through their Irganox® and Irgastab® product lines. Their technology involves using stearic acid as both a processing aid and stabilizer in polymer formulations. BASF's research has shown that controlled amounts of stearic acid (typically 0.1-0.5% by weight) can significantly improve melt flow characteristics while simultaneously acting as an acid scavenger to neutralize catalyst residues in polyolefins[1]. Their proprietary formulations combine stearic acid with hindered phenolic antioxidants and phosphite co-stabilizers to create synergistic stabilization systems that address multiple degradation pathways simultaneously. BASF has also pioneered metal stearate combinations (particularly calcium and zinc stearates) that provide enhanced long-term thermal stability during both processing and end-use applications[3].
Strengths: Superior synergistic formulations combining stearic acid with other stabilizers for comprehensive protection; extensive polymer compatibility across multiple resin types; excellent processing improvement characteristics. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to basic stearic acid additives; potential for antagonistic interactions with certain flame retardants; limited effectiveness in very high-temperature engineering plastics.
Arkema France SA
Technical Solution: Arkema has developed an innovative approach to thermoplastic stabilization utilizing modified stearic acid derivatives in their Plastistrength® and Biostrength® product lines. Their technology focuses on stearic acid's role as both a processing aid and long-term thermal stabilizer. Arkema's research has demonstrated that functionalized stearic acid compounds can significantly improve the thermal oxidative stability of polymers during processing and throughout the product lifecycle. Their proprietary process involves grafting specific functional groups onto stearic acid molecules to enhance compatibility with different polymer matrices and improve stabilization efficiency[2]. For PVC applications, Arkema has developed calcium-zinc stearate complexes that serve as effective heat stabilizers while meeting stringent environmental regulations. In polyolefins, their technology incorporates stearic acid derivatives that act as acid scavengers to neutralize catalyst residues and prevent corrosion of processing equipment[4].
Strengths: Highly effective functionalized stearic acid derivatives with enhanced polymer compatibility; environmentally friendly formulations meeting global regulatory standards; excellent long-term thermal protection. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional stearic acid additives; potential for migration in certain polymer systems; limited effectiveness in extremely high-temperature processing conditions.
Key Patents and Research on Stearic Acid Mechanisms
Reinforcing compositions for thermoplastic polymers comprising a synergistic combination of micronised silica and calcium salt having improved anti-caking and flowing properties
PatentInactiveEP0705881A1
Innovation
- A reinforcing composition comprising a synergistic combination of micronized silica and calcium carbonate, with calcium carbonate coated in stearic acid, is introduced to enhance anti-caking and flowability properties, allowing for improved handling and storage of impact additives.
Use of at least one sulfur-containing amino acid for stabilizing recycled thermoplastics, stabilized recycled thermoplastic, stabilizer composition, masterbatch, and molding compound or molded part
PatentWO2022243354A1
Innovation
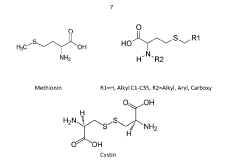
- The use of sulfur-containing amino acids like methionine and cystine, in combination with primary and secondary antioxidants, as stabilizers to protect thermoplastic recyclates from oxidative, thermal, and actinic degradation, offering a high-efficiency, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective stabilization solution.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of stearic acid in thermoplastic applications represents a critical consideration as industries increasingly prioritize sustainability. Stearic acid, derived primarily from animal fats and vegetable oils, offers a relatively lower environmental footprint compared to many synthetic stabilizers. Its biodegradable nature allows for reduced persistence in the environment when thermoplastic products reach end-of-life, potentially mitigating long-term ecological damage.
Production methods for stearic acid vary significantly in their environmental implications. Plant-based sources such as palm oil, while renewable, raise concerns regarding deforestation and habitat destruction when not sourced responsibly. Animal-derived stearic acid presents ethical considerations and potentially higher carbon footprints associated with livestock production. Recent innovations in fermentation-based production methods offer promising alternatives with reduced land use requirements and greenhouse gas emissions.
The incorporation of stearic acid as a thermal stabilizer contributes to extended product lifespans, indirectly reducing waste generation and resource consumption associated with premature product failure. This longevity effect represents a significant sustainability advantage when properly quantified in lifecycle assessments. Furthermore, the effective stabilization provided by stearic acid enables the use of recycled thermoplastic materials in more demanding applications, supporting circular economy initiatives.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly emphasize the importance of non-toxic additives in plastic formulations. Stearic acid's generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status positions it favorably against alternative stabilizers that may contain heavy metals or persistent organic pollutants. This advantage becomes particularly relevant as regulations like REACH in Europe and similar frameworks globally continue to restrict hazardous substances in consumer and industrial products.
End-of-life considerations reveal both advantages and challenges. While stearic acid itself biodegrades readily, its presence in thermoplastics does not necessarily enhance the biodegradability of the overall composite material. However, research indicates that stearic acid does not significantly interfere with mechanical recycling processes, allowing for multiple material lifecycles without degradation of properties when appropriate recycling infrastructure exists.
Carbon footprint analyses of stearic acid production and application demonstrate variable results depending on sourcing and manufacturing methods. Life cycle assessments indicate potential for carbon reduction when replacing synthetic stabilizers, particularly when bio-based feedstocks are utilized. Emerging technologies in green chemistry are exploring catalytic processes that could further reduce the environmental impact of stearic acid production through reduced energy requirements and solvent elimination.
Production methods for stearic acid vary significantly in their environmental implications. Plant-based sources such as palm oil, while renewable, raise concerns regarding deforestation and habitat destruction when not sourced responsibly. Animal-derived stearic acid presents ethical considerations and potentially higher carbon footprints associated with livestock production. Recent innovations in fermentation-based production methods offer promising alternatives with reduced land use requirements and greenhouse gas emissions.
The incorporation of stearic acid as a thermal stabilizer contributes to extended product lifespans, indirectly reducing waste generation and resource consumption associated with premature product failure. This longevity effect represents a significant sustainability advantage when properly quantified in lifecycle assessments. Furthermore, the effective stabilization provided by stearic acid enables the use of recycled thermoplastic materials in more demanding applications, supporting circular economy initiatives.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly emphasize the importance of non-toxic additives in plastic formulations. Stearic acid's generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status positions it favorably against alternative stabilizers that may contain heavy metals or persistent organic pollutants. This advantage becomes particularly relevant as regulations like REACH in Europe and similar frameworks globally continue to restrict hazardous substances in consumer and industrial products.
End-of-life considerations reveal both advantages and challenges. While stearic acid itself biodegrades readily, its presence in thermoplastics does not necessarily enhance the biodegradability of the overall composite material. However, research indicates that stearic acid does not significantly interfere with mechanical recycling processes, allowing for multiple material lifecycles without degradation of properties when appropriate recycling infrastructure exists.
Carbon footprint analyses of stearic acid production and application demonstrate variable results depending on sourcing and manufacturing methods. Life cycle assessments indicate potential for carbon reduction when replacing synthetic stabilizers, particularly when bio-based feedstocks are utilized. Emerging technologies in green chemistry are exploring catalytic processes that could further reduce the environmental impact of stearic acid production through reduced energy requirements and solvent elimination.
Regulatory Framework for Polymer Additives
The regulatory landscape governing polymer additives, particularly stearic acid used for thermoplastic stability, has evolved significantly in response to growing environmental and health concerns. The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation represents one of the most comprehensive frameworks, requiring manufacturers and importers to register substances produced or imported in quantities over one ton annually, with specific documentation on safety profiles and risk management measures for stearic acid as a stabilizer.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates stearic acid under 21 CFR 178.3910 when used in food-contact polymers, establishing specific migration limits and usage conditions. The EPA also oversees stearic acid under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), particularly focusing on environmental impact assessments when used in high-volume thermoplastic applications.
Asian markets demonstrate varying regulatory approaches, with Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) implementing stringent requirements for polymer additives, while China has recently strengthened its regulatory framework through the Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances, affecting stearic acid importation and usage in thermoplastic manufacturing.
Industry-specific regulations further complicate compliance requirements. The automotive sector, through standards like GADSL (Global Automotive Declarable Substance List), restricts certain additives in vehicle components. Similarly, electronics manufacturers must adhere to RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives, which, while not directly restricting stearic acid, impact overall formulation strategies for thermoplastic stability.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a shift toward circular economy principles, with the EU's Circular Economy Action Plan potentially affecting how stearic acid is incorporated into thermoplastics to ensure recyclability. Several jurisdictions are developing extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes that may influence additive selection based on end-of-life considerations for thermoplastic products.
Compliance strategies for manufacturers utilizing stearic acid in thermoplastic formulations typically involve comprehensive substance inventories, regular regulatory monitoring systems, and reformulation capabilities to adapt to evolving restrictions. Many leading companies have established dedicated regulatory affairs departments specifically focused on polymer additives compliance, recognizing the complexity and regional variations in regulatory requirements.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates stearic acid under 21 CFR 178.3910 when used in food-contact polymers, establishing specific migration limits and usage conditions. The EPA also oversees stearic acid under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), particularly focusing on environmental impact assessments when used in high-volume thermoplastic applications.
Asian markets demonstrate varying regulatory approaches, with Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) implementing stringent requirements for polymer additives, while China has recently strengthened its regulatory framework through the Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances, affecting stearic acid importation and usage in thermoplastic manufacturing.
Industry-specific regulations further complicate compliance requirements. The automotive sector, through standards like GADSL (Global Automotive Declarable Substance List), restricts certain additives in vehicle components. Similarly, electronics manufacturers must adhere to RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives, which, while not directly restricting stearic acid, impact overall formulation strategies for thermoplastic stability.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a shift toward circular economy principles, with the EU's Circular Economy Action Plan potentially affecting how stearic acid is incorporated into thermoplastics to ensure recyclability. Several jurisdictions are developing extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes that may influence additive selection based on end-of-life considerations for thermoplastic products.
Compliance strategies for manufacturers utilizing stearic acid in thermoplastic formulations typically involve comprehensive substance inventories, regular regulatory monitoring systems, and reformulation capabilities to adapt to evolving restrictions. Many leading companies have established dedicated regulatory affairs departments specifically focused on polymer additives compliance, recognizing the complexity and regional variations in regulatory requirements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!