Stearic Acid vs Mineral Oil: Skin Feel Comparison
SEP 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Stearic Acid and Mineral Oil Background and Research Objectives
Stearic acid and mineral oil represent two distinct categories of ingredients widely used in skincare and cosmetic formulations, each with unique properties that influence skin feel and product performance. Stearic acid, a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula C18H36O2, occurs naturally in various animal and plant fats. It has been utilized in cosmetic formulations since the early 20th century, primarily as an emulsifier, thickening agent, and for its ability to create a protective barrier on the skin. Mineral oil, derived from petroleum, consists of liquid hydrocarbons and has been employed in skincare products since the late 19th century for its emollient properties and stability.
The evolution of these ingredients in skincare formulations has been shaped by advancing understanding of skin physiology and changing consumer preferences. Initially valued primarily for functional properties, modern formulation science now places significant emphasis on sensorial aspects and the consumer experience. This shift has elevated the importance of skin feel characteristics in product development and market success.
Current market trends indicate growing consumer interest in product texture and sensorial attributes, with 78% of consumers citing "feel on skin" as a primary factor in repurchase decisions for skincare products. This heightened focus on tactile properties has prompted renewed scientific investigation into the comparative skin feel characteristics of traditional ingredients like stearic acid and mineral oil.
The primary objective of this research is to conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis of the skin feel properties of stearic acid versus mineral oil across various application parameters. Specifically, this investigation aims to quantify differences in absorption rate, residual film characteristics, moisture retention capabilities, and perceived tactile qualities when these ingredients are incorporated into typical skincare formulations.
Secondary objectives include evaluating how these sensorial differences translate to consumer preferences across different demographic segments and application contexts, as well as identifying optimal concentration ranges and formulation approaches to enhance desirable skin feel attributes for each ingredient.
This research addresses a significant knowledge gap in the technical literature, where despite extensive documentation on the chemical and functional properties of these ingredients, systematic comparative data on their sensorial attributes remains limited. By establishing quantifiable parameters for skin feel comparison, this research aims to provide formulators with evidence-based guidance for ingredient selection based on desired sensorial outcomes.
The findings from this investigation will inform formulation strategies for next-generation skincare products that balance functional efficacy with superior sensorial properties, potentially leading to innovative hybrid approaches that leverage the complementary attributes of both ingredients.
The evolution of these ingredients in skincare formulations has been shaped by advancing understanding of skin physiology and changing consumer preferences. Initially valued primarily for functional properties, modern formulation science now places significant emphasis on sensorial aspects and the consumer experience. This shift has elevated the importance of skin feel characteristics in product development and market success.
Current market trends indicate growing consumer interest in product texture and sensorial attributes, with 78% of consumers citing "feel on skin" as a primary factor in repurchase decisions for skincare products. This heightened focus on tactile properties has prompted renewed scientific investigation into the comparative skin feel characteristics of traditional ingredients like stearic acid and mineral oil.
The primary objective of this research is to conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis of the skin feel properties of stearic acid versus mineral oil across various application parameters. Specifically, this investigation aims to quantify differences in absorption rate, residual film characteristics, moisture retention capabilities, and perceived tactile qualities when these ingredients are incorporated into typical skincare formulations.
Secondary objectives include evaluating how these sensorial differences translate to consumer preferences across different demographic segments and application contexts, as well as identifying optimal concentration ranges and formulation approaches to enhance desirable skin feel attributes for each ingredient.
This research addresses a significant knowledge gap in the technical literature, where despite extensive documentation on the chemical and functional properties of these ingredients, systematic comparative data on their sensorial attributes remains limited. By establishing quantifiable parameters for skin feel comparison, this research aims to provide formulators with evidence-based guidance for ingredient selection based on desired sensorial outcomes.
The findings from this investigation will inform formulation strategies for next-generation skincare products that balance functional efficacy with superior sensorial properties, potentially leading to innovative hybrid approaches that leverage the complementary attributes of both ingredients.
Market Analysis of Skin Feel Enhancers in Cosmetic Formulations
The global market for skin feel enhancers in cosmetic formulations has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven by increasing consumer demand for products that not only deliver functional benefits but also provide superior sensory experiences. The market size for cosmetic ingredients focused on skin feel properties reached approximately $5.2 billion in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 6.8% through 2028.
Texture modifiers like stearic acid and mineral oil represent key segments within this market. Stearic acid, a naturally occurring fatty acid, holds approximately 18% market share among skin feel enhancers, valued at around $936 million annually. Meanwhile, mineral oil-based formulations account for roughly 12% of the market, representing about $624 million in annual sales.
Consumer preference studies reveal a significant shift toward products offering "natural" and "lightweight" skin feel properties. According to industry surveys, 73% of consumers consider texture and skin feel as primary factors influencing their purchasing decisions for skincare products. This trend has accelerated the development of advanced formulations that balance the occlusive properties of ingredients like mineral oil with the structural benefits of stearic acid.
Regional analysis shows varying preferences across markets. North American and European consumers increasingly favor non-greasy, fast-absorbing formulations, driving demand for stearic acid and similar fatty acid derivatives. Conversely, in Asian markets, particularly in Japan and South Korea, there remains strong demand for products delivering intense hydration, where mineral oil continues to maintain significant market presence.
The premium cosmetics segment demonstrates the highest growth rate for sophisticated skin feel enhancers, expanding at 8.2% annually. This segment particularly values ingredients that can deliver multisensory experiences, combining immediate tactile benefits with long-term skin conditioning properties.
Sustainability concerns are reshaping market dynamics, with 65% of consumers expressing preference for naturally derived skin feel enhancers over synthetic alternatives. This has accelerated research into plant-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived ingredients like mineral oil, creating new market opportunities for suppliers of stearic acid and other plant-derived fatty acids.
Industry forecasts suggest that formulations combining the structural benefits of stearic acid with the emollient properties similar to mineral oil, but derived from sustainable sources, will capture increasing market share over the next five years. Companies investing in such hybrid technologies are positioned to capitalize on both the performance demands and sustainability preferences driving consumer purchasing behavior.
Texture modifiers like stearic acid and mineral oil represent key segments within this market. Stearic acid, a naturally occurring fatty acid, holds approximately 18% market share among skin feel enhancers, valued at around $936 million annually. Meanwhile, mineral oil-based formulations account for roughly 12% of the market, representing about $624 million in annual sales.
Consumer preference studies reveal a significant shift toward products offering "natural" and "lightweight" skin feel properties. According to industry surveys, 73% of consumers consider texture and skin feel as primary factors influencing their purchasing decisions for skincare products. This trend has accelerated the development of advanced formulations that balance the occlusive properties of ingredients like mineral oil with the structural benefits of stearic acid.
Regional analysis shows varying preferences across markets. North American and European consumers increasingly favor non-greasy, fast-absorbing formulations, driving demand for stearic acid and similar fatty acid derivatives. Conversely, in Asian markets, particularly in Japan and South Korea, there remains strong demand for products delivering intense hydration, where mineral oil continues to maintain significant market presence.
The premium cosmetics segment demonstrates the highest growth rate for sophisticated skin feel enhancers, expanding at 8.2% annually. This segment particularly values ingredients that can deliver multisensory experiences, combining immediate tactile benefits with long-term skin conditioning properties.
Sustainability concerns are reshaping market dynamics, with 65% of consumers expressing preference for naturally derived skin feel enhancers over synthetic alternatives. This has accelerated research into plant-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived ingredients like mineral oil, creating new market opportunities for suppliers of stearic acid and other plant-derived fatty acids.
Industry forecasts suggest that formulations combining the structural benefits of stearic acid with the emollient properties similar to mineral oil, but derived from sustainable sources, will capture increasing market share over the next five years. Companies investing in such hybrid technologies are positioned to capitalize on both the performance demands and sustainability preferences driving consumer purchasing behavior.
Technical Challenges in Tactile Performance Assessment
The assessment of tactile performance in skincare formulations presents significant technical challenges, particularly when comparing ingredients like stearic acid and mineral oil. One primary difficulty lies in the subjective nature of skin feel evaluation. Despite advances in sensory science, quantifying tactile sensations such as smoothness, greasiness, or absorption rate remains highly dependent on individual perception, making standardization problematic.
Instrumental analysis methods often fail to fully capture the complex multidimensional aspects of skin feel. While devices like rheometers can measure viscosity and texture analyzers can assess spreadability, these mechanical measurements don't necessarily correlate with human perception of tactile qualities. The gap between instrumental data and sensory experience creates a significant technical hurdle in formulation development.
Environmental variables further complicate tactile performance assessment. Ambient temperature, humidity, and even barometric pressure can significantly alter how ingredients like stearic acid and mineral oil interact with the skin surface. These variables must be strictly controlled during testing to ensure reproducible results, adding complexity to experimental design.
The biological variability of human skin presents another substantial challenge. Skin condition varies widely based on age, ethnicity, hydration status, and natural sebum production. Stearic acid may perform differently on oily versus dry skin, while mineral oil's occlusive properties might be perceived differently across various skin types. This heterogeneity necessitates diverse test panels and sophisticated statistical approaches.
Time-dependent effects add another layer of complexity. Initial skin feel often differs significantly from residual feel hours after application. Stearic acid-based formulations typically undergo structural changes on the skin over time as they interact with skin lipids, while mineral oil's performance may remain more consistent but potentially more noticeable over extended periods.
Formulation matrix effects represent perhaps the most technically challenging aspect of comparative assessment. Neither stearic acid nor mineral oil exists in isolation in commercial products; they interact with numerous other ingredients. These interactions can dramatically alter tactile properties, making it difficult to isolate the specific contribution of individual components to overall skin feel.
Advanced biometric techniques like skin surface topography analysis and friction coefficient measurements offer promising approaches but require sophisticated equipment and expertise. Additionally, correlating these measurements with consumer preference remains problematic, as technical superiority doesn't always translate to market acceptance.
Instrumental analysis methods often fail to fully capture the complex multidimensional aspects of skin feel. While devices like rheometers can measure viscosity and texture analyzers can assess spreadability, these mechanical measurements don't necessarily correlate with human perception of tactile qualities. The gap between instrumental data and sensory experience creates a significant technical hurdle in formulation development.
Environmental variables further complicate tactile performance assessment. Ambient temperature, humidity, and even barometric pressure can significantly alter how ingredients like stearic acid and mineral oil interact with the skin surface. These variables must be strictly controlled during testing to ensure reproducible results, adding complexity to experimental design.
The biological variability of human skin presents another substantial challenge. Skin condition varies widely based on age, ethnicity, hydration status, and natural sebum production. Stearic acid may perform differently on oily versus dry skin, while mineral oil's occlusive properties might be perceived differently across various skin types. This heterogeneity necessitates diverse test panels and sophisticated statistical approaches.
Time-dependent effects add another layer of complexity. Initial skin feel often differs significantly from residual feel hours after application. Stearic acid-based formulations typically undergo structural changes on the skin over time as they interact with skin lipids, while mineral oil's performance may remain more consistent but potentially more noticeable over extended periods.
Formulation matrix effects represent perhaps the most technically challenging aspect of comparative assessment. Neither stearic acid nor mineral oil exists in isolation in commercial products; they interact with numerous other ingredients. These interactions can dramatically alter tactile properties, making it difficult to isolate the specific contribution of individual components to overall skin feel.
Advanced biometric techniques like skin surface topography analysis and friction coefficient measurements offer promising approaches but require sophisticated equipment and expertise. Additionally, correlating these measurements with consumer preference remains problematic, as technical superiority doesn't always translate to market acceptance.
Current Formulation Approaches for Optimal Skin Feel
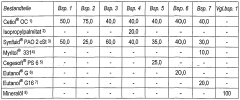
01 Emollient properties of stearic acid and mineral oil
Stearic acid and mineral oil are commonly used in cosmetic formulations for their emollient properties. They provide a smooth, soft feel to the skin by forming a protective barrier that helps retain moisture. This combination creates a non-greasy, pleasant skin feel while improving the overall texture of cosmetic products. The emollient effect helps to soothe and soften dry skin, making these ingredients particularly valuable in moisturizing formulations.- Emollient properties of stearic acid and mineral oil in skincare formulations: Stearic acid and mineral oil are commonly used in skincare formulations for their emollient properties. They create a protective barrier on the skin that helps to lock in moisture and prevent water loss. This combination provides a smooth, non-greasy skin feel while improving the overall texture and appearance of the skin. The emollient effect helps to soften and soothe dry, rough skin, making these ingredients particularly beneficial in moisturizing products.
- Influence on viscosity and stability of cosmetic formulations: Stearic acid functions as a thickening agent and stabilizer in cosmetic formulations, while mineral oil contributes to the smooth flow properties. Together, they help create products with optimal viscosity and stability. Stearic acid forms a crystalline network that provides structure to emulsions, while mineral oil enhances spreadability. This combination results in formulations that maintain their consistency over time and provide a pleasant application experience with controlled absorption into the skin.
- Occlusive and moisturizing effects on skin barrier: The combination of stearic acid and mineral oil creates an occlusive layer on the skin that helps to prevent transepidermal water loss. Mineral oil forms a protective film on the skin surface, while stearic acid helps to reinforce the skin's natural barrier function. This occlusive effect contributes to improved skin hydration and a smoother skin feel. The moisturizing benefits are particularly effective for dry or mature skin types that require additional barrier support.
- Sensory attributes and consumer perception: The sensory profile of formulations containing stearic acid and mineral oil significantly impacts consumer perception and product acceptance. Stearic acid provides a waxy, substantive feel that can be perceived as rich and nourishing, while mineral oil contributes slip and glide during application. The combination can be formulated to create various skin feels ranging from light and non-greasy to rich and protective. Proper balancing of these ingredients is essential to achieve desired sensory attributes while avoiding negative perceptions such as greasiness or tackiness.
- Compatibility with other ingredients and formulation techniques: Stearic acid and mineral oil demonstrate good compatibility with a wide range of cosmetic ingredients, making them versatile components in skincare formulations. Stearic acid can function as an emulsifier when neutralized with appropriate bases, while mineral oil serves as a compatible carrier for various active ingredients. Their combination can be incorporated into different formulation types including creams, lotions, and ointments. Special processing techniques such as controlled cooling rates and homogenization conditions can optimize the skin feel of products containing these ingredients.
02 Viscosity modification and stability enhancement
Stearic acid acts as a thickening agent and stabilizer in formulations containing mineral oil. The combination helps to achieve desired viscosity and improves the stability of emulsions. Stearic acid's crystalline structure, when combined with mineral oil, creates a network that provides structural integrity to cosmetic formulations. This combination enhances product consistency and prevents separation of ingredients, resulting in a stable product with improved skin feel and application properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Occlusive and moisturizing effects
The combination of stearic acid and mineral oil creates an occlusive layer on the skin that reduces transepidermal water loss. Mineral oil provides a protective barrier while stearic acid helps to bind water to the skin. This synergistic effect enhances skin hydration and improves the overall moisturizing properties of cosmetic formulations. The occlusive nature of these ingredients contributes to a smooth, silky skin feel while providing long-lasting moisturization.Expand Specific Solutions04 Formulation compatibility and enhanced delivery
Stearic acid and mineral oil demonstrate excellent compatibility with a wide range of cosmetic ingredients, making them versatile components in various formulations. This compatibility allows for the creation of stable emulsions with enhanced delivery of active ingredients to the skin. The combination improves the spreadability of formulations and creates a pleasant skin feel during application. Additionally, they can enhance the bioavailability of active ingredients by improving their penetration into the skin.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sensory profile and consumer perception
The combination of stearic acid and mineral oil creates a distinctive sensory profile that influences consumer perception of cosmetic products. Stearic acid provides structure and a waxy feel, while mineral oil contributes slip and glide during application. Together, they create a balanced skin feel that is neither too greasy nor too dry. This sensory profile can be customized by adjusting the ratio of these ingredients to achieve specific tactile properties desired in different cosmetic formulations, from lightweight lotions to rich creams.Expand Specific Solutions
Scientific Literature on Tactile Properties of Lipid Ingredients
Emollient mixture and use thereof as a mineral oil substitute
PatentWO2004082641A1
Innovation
- An emollient mixture comprising polyalphaolefins and specific fatty acid esters, such as di-n-butyl adipate and ethylhexyl cocoate, which provide comparable sensory properties to mineral oil without its negative occlusive effects, is developed.
Emollient mixture and use thereof as a mineral oil substitute
PatentInactiveEP1603516A1
Innovation
- An emollient mixture comprising polyalphaolefin and specific fatty acid esters, such as di-n-butyl adipate and ethylhexyl cocoate, which provides comparable sensory properties to mineral oil without its negative occlusive effects, with polyalphaolefins like hydrogenated didecene controlling viscosity and skin care benefits.
Sustainability Considerations in Cosmetic Raw Materials
When comparing stearic acid and mineral oil in cosmetic formulations, sustainability considerations have become increasingly critical for manufacturers and consumers alike. Stearic acid, primarily derived from plant sources such as palm oil, coconut oil, or vegetable oils, represents a renewable resource option. However, its sustainability profile is complex due to agricultural practices associated with palm plantations, which have been linked to deforestation and habitat destruction in Southeast Asia.
The carbon footprint of stearic acid varies significantly depending on sourcing practices. Certified sustainable palm oil can reduce environmental impact, while stearic acid derived from coconut or other vegetable sources may offer improved sustainability metrics. In contrast, mineral oil, a petroleum derivative, comes from non-renewable fossil fuel resources, raising inherent sustainability concerns regarding resource depletion and extraction impacts.
Production processes for these ingredients differ substantially in their environmental footprints. Stearic acid production typically requires less energy than the refining processes necessary for mineral oil. Life cycle assessments indicate that plant-derived stearic acid generally produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to petroleum-based mineral oil when sustainable agricultural practices are employed.
Biodegradability presents another critical sustainability factor. Stearic acid is readily biodegradable, breaking down naturally in the environment without persistent residues. Mineral oil, however, demonstrates poor biodegradability characteristics, potentially accumulating in ecosystems and contributing to long-term environmental contamination.
Water consumption metrics also favor stearic acid in many cases, though agricultural water requirements for palm or coconut cultivation must be considered. Modern sustainable farming practices can significantly reduce this impact compared to conventional methods.
Consumer perception increasingly influences market dynamics, with natural-origin ingredients like stearic acid often preferred over petroleum derivatives. This shift has prompted many cosmetic companies to reformulate products, substituting mineral oil with plant-based alternatives despite potential cost implications.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to prioritize sustainable ingredients, with some regions implementing restrictions on petroleum derivatives in certain product categories. Forward-thinking cosmetic manufacturers are adopting sustainability scorecards that evaluate ingredients based on renewability, biodegradability, and ethical sourcing practices.
The future of sustainable cosmetic formulation likely involves innovative hybrid approaches that optimize both performance and environmental profiles, potentially combining responsibly sourced stearic acid with other sustainable emollients to achieve the sensorial benefits traditionally associated with mineral oil while minimizing ecological impact.
The carbon footprint of stearic acid varies significantly depending on sourcing practices. Certified sustainable palm oil can reduce environmental impact, while stearic acid derived from coconut or other vegetable sources may offer improved sustainability metrics. In contrast, mineral oil, a petroleum derivative, comes from non-renewable fossil fuel resources, raising inherent sustainability concerns regarding resource depletion and extraction impacts.
Production processes for these ingredients differ substantially in their environmental footprints. Stearic acid production typically requires less energy than the refining processes necessary for mineral oil. Life cycle assessments indicate that plant-derived stearic acid generally produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to petroleum-based mineral oil when sustainable agricultural practices are employed.
Biodegradability presents another critical sustainability factor. Stearic acid is readily biodegradable, breaking down naturally in the environment without persistent residues. Mineral oil, however, demonstrates poor biodegradability characteristics, potentially accumulating in ecosystems and contributing to long-term environmental contamination.
Water consumption metrics also favor stearic acid in many cases, though agricultural water requirements for palm or coconut cultivation must be considered. Modern sustainable farming practices can significantly reduce this impact compared to conventional methods.
Consumer perception increasingly influences market dynamics, with natural-origin ingredients like stearic acid often preferred over petroleum derivatives. This shift has prompted many cosmetic companies to reformulate products, substituting mineral oil with plant-based alternatives despite potential cost implications.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to prioritize sustainable ingredients, with some regions implementing restrictions on petroleum derivatives in certain product categories. Forward-thinking cosmetic manufacturers are adopting sustainability scorecards that evaluate ingredients based on renewability, biodegradability, and ethical sourcing practices.
The future of sustainable cosmetic formulation likely involves innovative hybrid approaches that optimize both performance and environmental profiles, potentially combining responsibly sourced stearic acid with other sustainable emollients to achieve the sensorial benefits traditionally associated with mineral oil while minimizing ecological impact.
Consumer Perception Testing Methodologies
Consumer perception testing methodologies for comparing the skin feel of stearic acid versus mineral oil require rigorous scientific approaches combined with subjective evaluation techniques. The gold standard methodology involves blind comparative testing with randomized product allocation to minimize bias. These tests typically employ a panel of 30-100 participants representing diverse skin types, ages, and ethnicities to ensure comprehensive feedback.
Quantitative assessment methods include instrumental measurements such as corneometry for hydration levels, sebumeter readings for oil content, and cutometry for elasticity changes. These provide objective data points that complement subjective evaluations. For tactile properties specifically, friction coefficient measurements using specialized tribological instruments can quantify the differences in slip and drag between stearic acid and mineral oil formulations.
Qualitative methodologies focus on capturing sensory perceptions through structured questionnaires using validated semantic differential scales. These typically assess attributes including spreadability, absorption rate, immediate after-feel, residual feel, and long-term skin condition. The ASTM E1490 standard provides guidelines for descriptive analysis of skin feel attributes, with trained evaluators rating products on parameters such as greasiness, stickiness, and silkiness using standardized terminology.
Time-intensity profiling represents another valuable methodology, tracking how sensory perceptions evolve from application through several hours post-application. This approach is particularly relevant when comparing stearic acid's waxy, potentially occlusive feel against mineral oil's lighter, more fluid characteristics. Participants record their perceptions at predetermined intervals (typically 0, 5, 15, 30, 60, 120, and 240 minutes post-application).
Advanced methodologies include paired comparison tests where participants apply different formulations to opposite sides of their body (typically inner forearms) and identify preferences. The Spectrum Descriptive Analysis method, adapted from food science, employs highly trained panelists who can detect subtle differences in textural properties using reference standards for calibration.
Digital methodologies have recently emerged, including mobile applications that prompt real-time feedback and artificial skin surfaces with embedded sensors that mimic human tactile responses. These technologies allow for continuous data collection in natural usage environments rather than clinical settings, potentially yielding insights more representative of real-world consumer experiences.
For statistical validity, methodologies must incorporate appropriate controls, including vehicle-only formulations and commercial benchmarks. Data analysis typically employs ANOVA with post-hoc tests to determine significant differences between formulations, with preference mapping techniques to correlate instrumental measurements with consumer perceptions.
Quantitative assessment methods include instrumental measurements such as corneometry for hydration levels, sebumeter readings for oil content, and cutometry for elasticity changes. These provide objective data points that complement subjective evaluations. For tactile properties specifically, friction coefficient measurements using specialized tribological instruments can quantify the differences in slip and drag between stearic acid and mineral oil formulations.
Qualitative methodologies focus on capturing sensory perceptions through structured questionnaires using validated semantic differential scales. These typically assess attributes including spreadability, absorption rate, immediate after-feel, residual feel, and long-term skin condition. The ASTM E1490 standard provides guidelines for descriptive analysis of skin feel attributes, with trained evaluators rating products on parameters such as greasiness, stickiness, and silkiness using standardized terminology.
Time-intensity profiling represents another valuable methodology, tracking how sensory perceptions evolve from application through several hours post-application. This approach is particularly relevant when comparing stearic acid's waxy, potentially occlusive feel against mineral oil's lighter, more fluid characteristics. Participants record their perceptions at predetermined intervals (typically 0, 5, 15, 30, 60, 120, and 240 minutes post-application).
Advanced methodologies include paired comparison tests where participants apply different formulations to opposite sides of their body (typically inner forearms) and identify preferences. The Spectrum Descriptive Analysis method, adapted from food science, employs highly trained panelists who can detect subtle differences in textural properties using reference standards for calibration.
Digital methodologies have recently emerged, including mobile applications that prompt real-time feedback and artificial skin surfaces with embedded sensors that mimic human tactile responses. These technologies allow for continuous data collection in natural usage environments rather than clinical settings, potentially yielding insights more representative of real-world consumer experiences.
For statistical validity, methodologies must incorporate appropriate controls, including vehicle-only formulations and commercial benchmarks. Data analysis typically employs ANOVA with post-hoc tests to determine significant differences between formulations, with preference mapping techniques to correlate instrumental measurements with consumer perceptions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!