How to Improve Stearic Acid’s Utility in Powder Compression
SEP 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Stearic Acid in Powder Compression: Background and Objectives
Stearic acid has been a cornerstone in powder compression technology for decades, serving as a vital lubricant in pharmaceutical tablet manufacturing, metallurgical powder processing, and ceramic production. This long-chain fatty acid, characterized by its 18-carbon backbone and carboxylic acid functionality, first gained industrial recognition in the early 20th century when powder metallurgy techniques began to evolve beyond rudimentary applications.
The evolution of stearic acid usage in powder compression has followed a trajectory closely aligned with advancements in material science and manufacturing technology. Initially employed primarily as a die-wall lubricant, its application has expanded to include roles as a glidant, anti-adherent, and in some cases, a binding agent. This multifunctionality has cemented its position as an industry standard despite the emergence of synthetic alternatives.
Current technical challenges in powder compression revolve around achieving optimal particle distribution, reducing ejection forces, and maintaining consistent tablet quality across high-speed production environments. Stearic acid's performance in these areas, while generally acceptable, presents opportunities for significant enhancement through innovative formulation and application techniques.
The primary technical objective of this research is to identify and develop methodologies that maximize stearic acid's efficiency in powder compression processes. This includes optimizing concentration levels, particle size distribution, and mixing protocols to enhance lubrication effectiveness while minimizing negative impacts on tablet strength and dissolution characteristics.
Global trends indicate a growing demand for more efficient powder compression technologies, driven by the pharmaceutical industry's push toward continuous manufacturing and the metal powder industry's adoption of more complex geometries. These trends necessitate lubricants that can perform consistently under varied processing conditions and with diverse powder compositions.
Recent advancements in surface chemistry and computational modeling have opened new avenues for understanding stearic acid's behavior at molecular interfaces. These insights provide a foundation for developing enhanced formulations that address current limitations in coverage uniformity and sensitivity to processing parameters.
The technological trajectory suggests potential for significant improvements in stearic acid's utility through targeted modifications of its physical properties, novel delivery mechanisms, and synergistic combinations with complementary additives. These improvements align with industry demands for more robust, versatile lubricants capable of supporting increasingly sophisticated powder compression applications.
The evolution of stearic acid usage in powder compression has followed a trajectory closely aligned with advancements in material science and manufacturing technology. Initially employed primarily as a die-wall lubricant, its application has expanded to include roles as a glidant, anti-adherent, and in some cases, a binding agent. This multifunctionality has cemented its position as an industry standard despite the emergence of synthetic alternatives.
Current technical challenges in powder compression revolve around achieving optimal particle distribution, reducing ejection forces, and maintaining consistent tablet quality across high-speed production environments. Stearic acid's performance in these areas, while generally acceptable, presents opportunities for significant enhancement through innovative formulation and application techniques.
The primary technical objective of this research is to identify and develop methodologies that maximize stearic acid's efficiency in powder compression processes. This includes optimizing concentration levels, particle size distribution, and mixing protocols to enhance lubrication effectiveness while minimizing negative impacts on tablet strength and dissolution characteristics.
Global trends indicate a growing demand for more efficient powder compression technologies, driven by the pharmaceutical industry's push toward continuous manufacturing and the metal powder industry's adoption of more complex geometries. These trends necessitate lubricants that can perform consistently under varied processing conditions and with diverse powder compositions.
Recent advancements in surface chemistry and computational modeling have opened new avenues for understanding stearic acid's behavior at molecular interfaces. These insights provide a foundation for developing enhanced formulations that address current limitations in coverage uniformity and sensitivity to processing parameters.
The technological trajectory suggests potential for significant improvements in stearic acid's utility through targeted modifications of its physical properties, novel delivery mechanisms, and synergistic combinations with complementary additives. These improvements align with industry demands for more robust, versatile lubricants capable of supporting increasingly sophisticated powder compression applications.
Market Analysis of Stearic Acid in Pharmaceutical Tableting
The global market for stearic acid in pharmaceutical tableting has been experiencing steady growth, driven by the increasing demand for solid oral dosage forms. As of 2023, the pharmaceutical excipient market is valued at approximately $7.9 billion, with lubricants constituting about 8% of this market. Stearic acid, as one of the primary lubricants, holds a significant share within this segment.
The pharmaceutical industry represents the third-largest application sector for stearic acid, following personal care and food applications. Within pharmaceutical tableting specifically, stearic acid commands roughly 15% of the tablet lubricant market, competing primarily with magnesium stearate, which holds about 60% market share.
Regional analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently dominate the consumption of pharmaceutical-grade stearic acid, accounting for approximately 35% and 30% of the global market respectively. However, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly India and China, is witnessing the fastest growth rate at 7.8% annually, attributed to the rapid expansion of generic drug manufacturing facilities in these countries.
Market dynamics are increasingly influenced by the growing preference for direct compression methods in tablet manufacturing, which has intensified the demand for efficient lubricants like stearic acid. The direct compression segment is growing at 6.5% annually, outpacing traditional wet granulation methods.
Price trends show moderate volatility, with pharmaceutical-grade stearic acid commanding premium pricing compared to industrial grades. The average price ranges between $2.50-$3.20 per kilogram, depending on purity levels and regional supply-demand balances. This represents a 15-20% premium over technical-grade stearic acid used in other industries.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for naturally derived excipients, creating a niche market for vegetable-sourced stearic acid over animal-derived alternatives. This segment is growing at nearly twice the rate of the overall stearic acid market in pharmaceuticals.
Market forecasts project the pharmaceutical stearic acid market to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% through 2028, driven by increasing tablet production volumes globally and the expansion of pharmaceutical manufacturing in emerging markets. The continuous development of modified release formulations and orally disintegrating tablets is expected to further boost demand for specialized grades of stearic acid with enhanced functionality in powder compression applications.
The pharmaceutical industry represents the third-largest application sector for stearic acid, following personal care and food applications. Within pharmaceutical tableting specifically, stearic acid commands roughly 15% of the tablet lubricant market, competing primarily with magnesium stearate, which holds about 60% market share.
Regional analysis indicates that North America and Europe currently dominate the consumption of pharmaceutical-grade stearic acid, accounting for approximately 35% and 30% of the global market respectively. However, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly India and China, is witnessing the fastest growth rate at 7.8% annually, attributed to the rapid expansion of generic drug manufacturing facilities in these countries.
Market dynamics are increasingly influenced by the growing preference for direct compression methods in tablet manufacturing, which has intensified the demand for efficient lubricants like stearic acid. The direct compression segment is growing at 6.5% annually, outpacing traditional wet granulation methods.
Price trends show moderate volatility, with pharmaceutical-grade stearic acid commanding premium pricing compared to industrial grades. The average price ranges between $2.50-$3.20 per kilogram, depending on purity levels and regional supply-demand balances. This represents a 15-20% premium over technical-grade stearic acid used in other industries.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for naturally derived excipients, creating a niche market for vegetable-sourced stearic acid over animal-derived alternatives. This segment is growing at nearly twice the rate of the overall stearic acid market in pharmaceuticals.
Market forecasts project the pharmaceutical stearic acid market to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% through 2028, driven by increasing tablet production volumes globally and the expansion of pharmaceutical manufacturing in emerging markets. The continuous development of modified release formulations and orally disintegrating tablets is expected to further boost demand for specialized grades of stearic acid with enhanced functionality in powder compression applications.
Technical Challenges in Stearic Acid Lubrication Performance
Despite stearic acid's widespread use as a lubricant in powder compression processes, several technical challenges limit its optimal performance. The primary issue stems from its inherent physicochemical properties, particularly its hydrophobicity and poor water solubility. These characteristics can lead to uneven distribution within powder mixtures, resulting in inconsistent lubrication across the compression matrix and potentially causing quality variations in the final compressed products.
Another significant challenge is stearic acid's sensitivity to processing conditions. Temperature fluctuations during manufacturing can dramatically affect its performance, as stearic acid has a relatively low melting point (69-70°C). When exposed to elevated temperatures during high-speed compression processes, it may partially melt, leading to over-lubrication in certain areas and potential adherence to punch surfaces, which compromises the integrity of the compressed product.
The particle size distribution of stearic acid presents another technical hurdle. Conventional grades often exhibit wide particle size distributions, which can lead to segregation during mixing and non-uniform lubrication. This heterogeneity becomes particularly problematic in pharmaceutical applications where content uniformity is critical for therapeutic efficacy and regulatory compliance.
Compatibility issues with other formulation components also pose significant challenges. Stearic acid may interact unfavorably with certain active pharmaceutical ingredients or excipients, potentially affecting drug stability, dissolution profiles, or bioavailability. These interactions are often difficult to predict and may only become apparent during stability testing or clinical studies.
The lubricant concentration paradox represents another technical challenge. While higher concentrations of stearic acid generally improve lubrication efficiency and reduce ejection forces, they simultaneously tend to decrease the mechanical strength of the compressed product and may retard dissolution rates. Finding the optimal concentration that balances these competing factors remains a persistent challenge for formulators.
Environmental and processing variables further complicate stearic acid's performance. Humidity levels during manufacturing can affect its functionality, as can the mixing time and intensity. Overmixing can lead to excessive coating of particles, potentially compromising binding properties, while undermixing results in inadequate lubrication and increased friction during compression.
Lastly, there are increasing regulatory and sustainability concerns regarding traditional stearic acid sources. Many commercial grades are derived from animal fats, raising issues for vegetarian/vegan products and religious considerations. Plant-derived alternatives may have different performance characteristics, creating additional technical challenges when substituting traditional sources.
Another significant challenge is stearic acid's sensitivity to processing conditions. Temperature fluctuations during manufacturing can dramatically affect its performance, as stearic acid has a relatively low melting point (69-70°C). When exposed to elevated temperatures during high-speed compression processes, it may partially melt, leading to over-lubrication in certain areas and potential adherence to punch surfaces, which compromises the integrity of the compressed product.
The particle size distribution of stearic acid presents another technical hurdle. Conventional grades often exhibit wide particle size distributions, which can lead to segregation during mixing and non-uniform lubrication. This heterogeneity becomes particularly problematic in pharmaceutical applications where content uniformity is critical for therapeutic efficacy and regulatory compliance.
Compatibility issues with other formulation components also pose significant challenges. Stearic acid may interact unfavorably with certain active pharmaceutical ingredients or excipients, potentially affecting drug stability, dissolution profiles, or bioavailability. These interactions are often difficult to predict and may only become apparent during stability testing or clinical studies.
The lubricant concentration paradox represents another technical challenge. While higher concentrations of stearic acid generally improve lubrication efficiency and reduce ejection forces, they simultaneously tend to decrease the mechanical strength of the compressed product and may retard dissolution rates. Finding the optimal concentration that balances these competing factors remains a persistent challenge for formulators.
Environmental and processing variables further complicate stearic acid's performance. Humidity levels during manufacturing can affect its functionality, as can the mixing time and intensity. Overmixing can lead to excessive coating of particles, potentially compromising binding properties, while undermixing results in inadequate lubrication and increased friction during compression.
Lastly, there are increasing regulatory and sustainability concerns regarding traditional stearic acid sources. Many commercial grades are derived from animal fats, raising issues for vegetarian/vegan products and religious considerations. Plant-derived alternatives may have different performance characteristics, creating additional technical challenges when substituting traditional sources.
Current Methodologies for Stearic Acid Implementation
01 Cosmetic and personal care applications
Stearic acid is widely used in cosmetic and personal care products as an emulsifier, thickening agent, and stabilizer. It helps create creamy textures in lotions, creams, and soaps while providing moisturizing properties. In sunscreen formulations, it contributes to water resistance and smooth application. Stearic acid also serves as a cleansing agent in soaps and can improve the feel and consistency of various personal care products.- Cosmetic and personal care applications: Stearic acid is widely used in cosmetic and personal care products as an emulsifier, thickening agent, and stabilizer. It helps create creamy textures in lotions, creams, and soaps while providing moisturizing properties. In sunscreen formulations, it contributes to water resistance and smooth application. Stearic acid also serves as a cleansing agent in soaps and can improve the feel and consistency of various personal care products.
- Industrial lubricants and coatings: Stearic acid functions as an important component in industrial lubricants, providing friction reduction and improved performance in various mechanical applications. It is incorporated into coatings and surface treatments to enhance water repellency and durability. In metal processing, stearic acid acts as a release agent and lubricant. It is also used in the production of specialized industrial coatings that require specific physical properties.
- Food industry applications: In the food industry, stearic acid serves as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and texture modifier. It is used in the production of confectionery products, baked goods, and processed foods to improve consistency and extend shelf life. Stearic acid helps control crystallization in fat-based products like chocolate and margarine. It also functions as a food-grade lubricant in food processing equipment and contributes to the glossy appearance of certain food products.
- Pharmaceutical formulations: Stearic acid is utilized in pharmaceutical formulations as a tablet and capsule lubricant, helping to prevent ingredients from sticking to manufacturing equipment. It serves as an excipient in controlled-release drug delivery systems, modifying the release rate of active ingredients. In topical pharmaceutical preparations, stearic acid contributes to stability and improves skin adhesion. It also functions as a hardening agent in suppositories and as a base in various medicinal ointments.
- Chemical synthesis and manufacturing: Stearic acid serves as a key raw material in the synthesis of various chemical compounds including esters, amides, and metallic stearates. It is used in the production of rubber compounds to improve processing characteristics and final product properties. In plastic manufacturing, stearic acid functions as a release agent and processing aid. It also plays a role in the production of candles, providing hardness and improving burning characteristics.
02 Food industry applications
In the food industry, stearic acid functions as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and texture modifier. It is used in the production of margarine, shortening, and confectionery products to improve consistency and prevent separation. Stearic acid helps control crystallization in chocolate manufacturing, enhancing texture and shelf stability. It also serves as a processing aid in various food applications and can be used as a lubricant in food processing equipment.Expand Specific Solutions03 Industrial and manufacturing uses
Stearic acid has numerous industrial applications including as a lubricant, release agent, and processing aid in rubber, plastic, and metal manufacturing. It serves as a key ingredient in candle making, providing hardness and opacity. In the textile industry, it functions as a softening agent and water repellent. Stearic acid is also used in the production of various chemicals, including metallic stearates that have applications as stabilizers and lubricants in polymers and construction materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Pharmaceutical and medical applications
Stearic acid is utilized in pharmaceutical formulations as a tablet and capsule lubricant, helping to prevent ingredients from sticking to manufacturing equipment. It functions as an excipient in controlled-release drug delivery systems, modulating the release rate of active ingredients. In topical medical preparations, it serves as a base for ointments and creams, providing consistency and enhancing skin penetration of active ingredients. Stearic acid derivatives are also being explored for their potential therapeutic properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and sustainable applications
Stearic acid is increasingly being used in environmentally friendly applications such as biodegradable plastics and biofuels. It serves as a component in the production of biodiesel and other renewable energy sources. In green chemistry, stearic acid derived from plant sources provides a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based chemicals. It is also utilized in eco-friendly lubricants and as a processing aid in the manufacturing of various sustainable materials and products.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Powder Compression
The stearic acid powder compression technology landscape is currently in a growth phase, with increasing applications across pharmaceutical, chemical, and materials industries. The market is expanding steadily, driven by demand for improved tablet formulations and advanced powder metallurgy applications. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across different sectors. Leading players like Vectura Ltd. and Glaxo Group demonstrate advanced capabilities in pharmaceutical applications, while Diamet Corp. and JFE Steel show expertise in powder metallurgy implementations. Companies such as LG Chem and Arkema are advancing chemical applications, while Otsuka Pharmaceutical and Baxter International focus on specialized drug delivery systems. The competitive landscape features both established corporations with extensive R&D capabilities and specialized firms developing niche applications, indicating a dynamic market with significant innovation potential.
Vectura Ltd.
Technical Solution: Vectura has developed a proprietary DPI (Dry Powder Inhaler) technology that incorporates stearic acid as a flow aid and compression modifier. Their approach involves treating stearic acid particles with surface modification techniques to improve particle-particle interactions during compression. The company utilizes a controlled micronization process that creates stearic acid particles with specific surface area characteristics (typically 5-10 m²/g), optimizing its lubricant properties while minimizing negative effects on tablet strength. Vectura's formulation technology includes co-processing stearic acid with other excipients through spray drying, creating composite particles that distribute the stearic acid more uniformly throughout the powder blend, resulting in more consistent compression properties and reduced sensitivity to mixing time variations.
Strengths: Improved powder flow properties and reduced sticking to die walls during compression; enables lower compression forces while maintaining tablet integrity. Weaknesses: The surface modification process adds manufacturing complexity and cost; performance may vary with different active ingredients.
Glaxo Group Ltd.
Technical Solution: Glaxo Group has pioneered an innovative approach to stearic acid utilization in pharmaceutical tablet manufacturing through their "Controlled Release Matrix Technology." This system employs specially processed stearic acid with precise particle size distribution (predominantly in the 10-50 μm range) and modified crystal habits. Their technique involves co-processing stearic acid with hydrophilic polymers under controlled temperature conditions (typically 65-75°C) to create semi-crystalline matrices that improve compressibility while maintaining controlled release properties. The company has developed a proprietary hot-melt granulation process where stearic acid serves dual functions as both a binder and release-modifying agent, allowing for direct compression of otherwise problematic formulations. This approach has demonstrated a 30-40% improvement in tablet hardness compared to conventional stearic acid usage while maintaining dissolution profiles within desired specifications.
Strengths: Dual functionality as both lubricant and release modifier; enables direct compression of difficult formulations; improves tablet hardness without compromising dissolution. Weaknesses: Requires precise temperature control during processing; may not be suitable for heat-sensitive active ingredients; performance can be affected by storage conditions.
Key Patents and Research on Enhanced Stearic Acid Functionality
Powder formulation for ingredient dispersion
PatentInactiveUS20230218517A1
Innovation
- A powder formulation comprising effervescent aids, diluents, emulsifiers, and hydration aids that facilitate the complete dispersion of insoluble, oil-based, or poorly dispersible ingredients in liquids, improving uniformity, texture, and hydration, and utilizing a floating delivery system for enhanced absorption and bioavailability.
A process for the production of a powdered composition, the powdered composition obtained thereby and uses thereof
PatentWO2012130260A1
Innovation
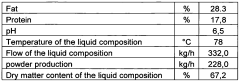
- A spray-drying process using a combination of air and steam to atomize a highly concentrated liquid composition, with a first atomization step followed by a second step and subsequent drying, allowing for increased production capacity while maintaining desirable powder characteristics like bulk density and reducing heat damage.
Regulatory Considerations for Excipient Modifications
Regulatory frameworks governing pharmaceutical excipients play a critical role in the development and implementation of modified stearic acid formulations for powder compression. The FDA, EMA, and other global regulatory bodies have established specific guidelines for excipient modifications that must be carefully navigated when enhancing stearic acid's functionality. These regulations typically require comprehensive documentation of any chemical modifications, processing changes, or novel applications of existing excipients.
When modifying stearic acid for improved powder compression properties, manufacturers must consider the regulatory classification of their changes. Minor physical modifications may fall under existing monographs, while significant chemical alterations could require new safety assessments and regulatory approvals. The ICH Q3C guidelines on residual solvents become particularly relevant when solvent-based modification processes are employed to alter stearic acid's properties.
Stability testing requirements represent another crucial regulatory consideration. Modified stearic acid formulations must demonstrate consistent performance throughout the product's shelf life under various environmental conditions. Regulatory bodies typically require accelerated and long-term stability data to ensure that the excipient modifications do not negatively impact product integrity over time.
Impurity profiles and specifications constitute a significant regulatory focus area. Any modification to stearic acid must be accompanied by thorough characterization of potential impurities introduced during the modification process. Regulatory thresholds for reporting, identification, and qualification of impurities must be strictly adhered to, particularly when novel processing methods are employed.
The regulatory pathway also differs based on the intended application. Modifications aimed at pharmaceutical applications face more stringent requirements compared to those for food or cosmetic uses. Cross-industry applications of modified stearic acid may require navigating multiple regulatory frameworks simultaneously, adding complexity to the development process.
Documentation requirements for excipient modifications include detailed manufacturing process descriptions, analytical method validations, and comprehensive characterization data. Regulatory bodies increasingly expect Quality by Design (QbD) approaches that demonstrate thorough understanding of how processing parameters affect critical quality attributes of the modified stearic acid.
International harmonization efforts, such as those by the International Pharmaceutical Excipients Council (IPEC), have established guidelines for excipient modifications that can streamline regulatory approvals across multiple jurisdictions. Leveraging these harmonized approaches can significantly reduce the regulatory burden when developing globally marketed products containing modified stearic acid formulations.
When modifying stearic acid for improved powder compression properties, manufacturers must consider the regulatory classification of their changes. Minor physical modifications may fall under existing monographs, while significant chemical alterations could require new safety assessments and regulatory approvals. The ICH Q3C guidelines on residual solvents become particularly relevant when solvent-based modification processes are employed to alter stearic acid's properties.
Stability testing requirements represent another crucial regulatory consideration. Modified stearic acid formulations must demonstrate consistent performance throughout the product's shelf life under various environmental conditions. Regulatory bodies typically require accelerated and long-term stability data to ensure that the excipient modifications do not negatively impact product integrity over time.
Impurity profiles and specifications constitute a significant regulatory focus area. Any modification to stearic acid must be accompanied by thorough characterization of potential impurities introduced during the modification process. Regulatory thresholds for reporting, identification, and qualification of impurities must be strictly adhered to, particularly when novel processing methods are employed.
The regulatory pathway also differs based on the intended application. Modifications aimed at pharmaceutical applications face more stringent requirements compared to those for food or cosmetic uses. Cross-industry applications of modified stearic acid may require navigating multiple regulatory frameworks simultaneously, adding complexity to the development process.
Documentation requirements for excipient modifications include detailed manufacturing process descriptions, analytical method validations, and comprehensive characterization data. Regulatory bodies increasingly expect Quality by Design (QbD) approaches that demonstrate thorough understanding of how processing parameters affect critical quality attributes of the modified stearic acid.
International harmonization efforts, such as those by the International Pharmaceutical Excipients Council (IPEC), have established guidelines for excipient modifications that can streamline regulatory approvals across multiple jurisdictions. Leveraging these harmonized approaches can significantly reduce the regulatory burden when developing globally marketed products containing modified stearic acid formulations.
Sustainability and Green Chemistry Aspects of Stearic Acid Production
The sustainability aspects of stearic acid production have become increasingly important as industries seek to improve its utility in powder compression applications. Traditional production methods of stearic acid primarily rely on animal fats and vegetable oils, with palm oil being a dominant source. However, concerns regarding deforestation and habitat destruction associated with palm plantations have prompted research into alternative, more sustainable feedstocks.
Plant-based alternatives such as coconut oil, soybean oil, and algae-derived oils are emerging as promising sustainable sources. These alternatives can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of stearic acid production while maintaining the necessary physicochemical properties for powder compression applications. Life cycle assessments indicate that switching to these alternative sources could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 35% compared to conventional methods.
Green chemistry principles are being increasingly integrated into stearic acid production processes. Catalytic hydrogenation using heterogeneous catalysts has replaced traditional high-pressure hydrogenation methods, reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste generation. Additionally, solvent-free processes and the use of supercritical CO2 as a reaction medium represent significant advancements in environmentally friendly production techniques.
Water consumption remains a critical sustainability challenge in stearic acid manufacturing. Recent innovations include closed-loop water systems that can reduce freshwater requirements by up to 80%. Furthermore, wastewater treatment technologies specifically designed for fatty acid production facilities have improved the quality of discharged water, minimizing environmental impact on aquatic ecosystems.
Biodegradability is another key consideration for stearic acid's sustainability profile. As a naturally occurring fatty acid, stearic acid is inherently biodegradable, but its production byproducts may not share this characteristic. Research efforts are focused on ensuring that all components of the production process result in environmentally benign substances, particularly when considering end-of-life scenarios for products containing stearic acid as a compression aid.
Energy efficiency improvements in stearic acid production include the implementation of heat recovery systems and process intensification techniques. These advancements have reduced energy requirements by approximately 25% over the past decade. Additionally, renewable energy integration into production facilities is becoming more common, with several major producers committing to carbon-neutral operations by 2030.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly emphasizing sustainable production practices. The European Union's REACH regulations and similar initiatives globally are driving manufacturers to adopt greener production methods and transparent supply chains. This regulatory landscape is accelerating the transition toward more sustainable stearic acid production methodologies that maintain or enhance its utility in powder compression applications.
Plant-based alternatives such as coconut oil, soybean oil, and algae-derived oils are emerging as promising sustainable sources. These alternatives can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of stearic acid production while maintaining the necessary physicochemical properties for powder compression applications. Life cycle assessments indicate that switching to these alternative sources could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 35% compared to conventional methods.
Green chemistry principles are being increasingly integrated into stearic acid production processes. Catalytic hydrogenation using heterogeneous catalysts has replaced traditional high-pressure hydrogenation methods, reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste generation. Additionally, solvent-free processes and the use of supercritical CO2 as a reaction medium represent significant advancements in environmentally friendly production techniques.
Water consumption remains a critical sustainability challenge in stearic acid manufacturing. Recent innovations include closed-loop water systems that can reduce freshwater requirements by up to 80%. Furthermore, wastewater treatment technologies specifically designed for fatty acid production facilities have improved the quality of discharged water, minimizing environmental impact on aquatic ecosystems.
Biodegradability is another key consideration for stearic acid's sustainability profile. As a naturally occurring fatty acid, stearic acid is inherently biodegradable, but its production byproducts may not share this characteristic. Research efforts are focused on ensuring that all components of the production process result in environmentally benign substances, particularly when considering end-of-life scenarios for products containing stearic acid as a compression aid.
Energy efficiency improvements in stearic acid production include the implementation of heat recovery systems and process intensification techniques. These advancements have reduced energy requirements by approximately 25% over the past decade. Additionally, renewable energy integration into production facilities is becoming more common, with several major producers committing to carbon-neutral operations by 2030.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly emphasizing sustainable production practices. The European Union's REACH regulations and similar initiatives globally are driving manufacturers to adopt greener production methods and transparent supply chains. This regulatory landscape is accelerating the transition toward more sustainable stearic acid production methodologies that maintain or enhance its utility in powder compression applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!