Developing Sensor Materials with Sulphanilic Acid: A Comparative Study
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulphanilic Acid Sensors: Background and Objectives
Sulphanilic acid, a versatile aromatic compound, has emerged as a promising material for sensor development in recent years. The evolution of sensor technology has been driven by the increasing demand for rapid, sensitive, and selective detection methods across various industries. Sulphanilic acid-based sensors represent a significant advancement in this field, offering unique properties that make them suitable for a wide range of applications.
The history of sulphanilic acid in sensor technology can be traced back to its initial use in colorimetric assays. Over time, researchers recognized its potential for more sophisticated sensing applications due to its chemical structure and reactivity. The presence of both amino and sulfonic acid groups in sulphanilic acid provides excellent opportunities for functionalization and interaction with target analytes.
As sensor technology progressed, the focus shifted towards developing materials that could offer improved sensitivity, selectivity, and stability. Sulphanilic acid emerged as a promising candidate due to its ability to form stable diazonium salts, which can be further modified to create tailored sensing platforms. This characteristic has opened up new avenues for sensor design and optimization.
The current technological landscape sees sulphanilic acid being utilized in various sensor types, including electrochemical, optical, and colorimetric sensors. Each of these sensor categories leverages the unique properties of sulphanilic acid to achieve specific detection goals. For instance, electrochemical sensors exploit the redox properties of sulphanilic acid derivatives, while optical sensors take advantage of its chromophoric nature.
The primary objective of research in sulphanilic acid-based sensors is to develop highly sensitive and selective detection methods for a wide range of analytes. These include environmental pollutants, biomarkers, food contaminants, and industrial chemicals. Researchers aim to create sensors that can operate in complex matrices with minimal interference, providing reliable and accurate results in real-world applications.
Another crucial goal is to enhance the stability and longevity of sulphanilic acid sensors. This involves developing strategies to prevent degradation of the sensing material and maintain consistent performance over extended periods. Additionally, there is a strong focus on improving the response time and reversibility of these sensors, enabling rapid and repeated measurements.
As the field of sensor technology continues to evolve, the integration of sulphanilic acid-based sensors with advanced data processing and miniaturization techniques is becoming increasingly important. This convergence aims to create portable, user-friendly devices that can provide real-time analysis in various settings, from environmental monitoring to point-of-care diagnostics.
The history of sulphanilic acid in sensor technology can be traced back to its initial use in colorimetric assays. Over time, researchers recognized its potential for more sophisticated sensing applications due to its chemical structure and reactivity. The presence of both amino and sulfonic acid groups in sulphanilic acid provides excellent opportunities for functionalization and interaction with target analytes.
As sensor technology progressed, the focus shifted towards developing materials that could offer improved sensitivity, selectivity, and stability. Sulphanilic acid emerged as a promising candidate due to its ability to form stable diazonium salts, which can be further modified to create tailored sensing platforms. This characteristic has opened up new avenues for sensor design and optimization.
The current technological landscape sees sulphanilic acid being utilized in various sensor types, including electrochemical, optical, and colorimetric sensors. Each of these sensor categories leverages the unique properties of sulphanilic acid to achieve specific detection goals. For instance, electrochemical sensors exploit the redox properties of sulphanilic acid derivatives, while optical sensors take advantage of its chromophoric nature.
The primary objective of research in sulphanilic acid-based sensors is to develop highly sensitive and selective detection methods for a wide range of analytes. These include environmental pollutants, biomarkers, food contaminants, and industrial chemicals. Researchers aim to create sensors that can operate in complex matrices with minimal interference, providing reliable and accurate results in real-world applications.
Another crucial goal is to enhance the stability and longevity of sulphanilic acid sensors. This involves developing strategies to prevent degradation of the sensing material and maintain consistent performance over extended periods. Additionally, there is a strong focus on improving the response time and reversibility of these sensors, enabling rapid and repeated measurements.
As the field of sensor technology continues to evolve, the integration of sulphanilic acid-based sensors with advanced data processing and miniaturization techniques is becoming increasingly important. This convergence aims to create portable, user-friendly devices that can provide real-time analysis in various settings, from environmental monitoring to point-of-care diagnostics.
Market Analysis for Sulphanilic Acid-Based Sensors
The market for sulphanilic acid-based sensors is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries. These sensors offer unique advantages in detecting and monitoring specific chemical compounds, making them valuable in environmental monitoring, industrial processes, and healthcare applications.
In the environmental sector, sulphanilic acid-based sensors are gaining traction for their ability to detect pollutants and contaminants in water and air. The growing emphasis on environmental protection and stringent regulations are fueling the adoption of these sensors for real-time monitoring of water quality and air pollution levels. This segment is expected to show robust growth as governments worldwide implement stricter environmental policies.
The industrial sector represents another key market for sulphanilic acid-based sensors. These sensors are increasingly used in process control and quality assurance applications, particularly in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries. Their ability to detect specific compounds with high sensitivity and selectivity makes them invaluable for ensuring product quality and safety. The trend towards automation and smart manufacturing is likely to further boost the demand for these sensors in industrial settings.
In healthcare, sulphanilic acid-based sensors are finding applications in diagnostic tools and medical devices. Their potential for rapid and accurate detection of certain biomarkers makes them promising for point-of-care testing and continuous health monitoring. As the healthcare industry moves towards personalized medicine and remote patient monitoring, the market for these sensors is expected to expand significantly.
The global market for chemical sensors, which includes sulphanilic acid-based sensors, is projected to grow steadily over the next few years. Factors such as technological advancements, miniaturization of sensors, and integration with IoT platforms are driving this growth. Additionally, the increasing focus on wearable technology and smart devices is opening new avenues for sensor applications, further expanding the market potential.
However, the market also faces challenges. The complexity of manufacturing high-quality sulphanilic acid-based sensors and the need for specialized expertise can limit market entry for new players. Additionally, competition from alternative sensing technologies and concerns about long-term stability and reliability of these sensors in certain applications may impact market growth.
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for sulphanilic acid-based sensors remains positive. The continuous research and development in this field, coupled with the expanding application areas, suggest a promising future for these sensors in the global market.
In the environmental sector, sulphanilic acid-based sensors are gaining traction for their ability to detect pollutants and contaminants in water and air. The growing emphasis on environmental protection and stringent regulations are fueling the adoption of these sensors for real-time monitoring of water quality and air pollution levels. This segment is expected to show robust growth as governments worldwide implement stricter environmental policies.
The industrial sector represents another key market for sulphanilic acid-based sensors. These sensors are increasingly used in process control and quality assurance applications, particularly in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries. Their ability to detect specific compounds with high sensitivity and selectivity makes them invaluable for ensuring product quality and safety. The trend towards automation and smart manufacturing is likely to further boost the demand for these sensors in industrial settings.
In healthcare, sulphanilic acid-based sensors are finding applications in diagnostic tools and medical devices. Their potential for rapid and accurate detection of certain biomarkers makes them promising for point-of-care testing and continuous health monitoring. As the healthcare industry moves towards personalized medicine and remote patient monitoring, the market for these sensors is expected to expand significantly.
The global market for chemical sensors, which includes sulphanilic acid-based sensors, is projected to grow steadily over the next few years. Factors such as technological advancements, miniaturization of sensors, and integration with IoT platforms are driving this growth. Additionally, the increasing focus on wearable technology and smart devices is opening new avenues for sensor applications, further expanding the market potential.
However, the market also faces challenges. The complexity of manufacturing high-quality sulphanilic acid-based sensors and the need for specialized expertise can limit market entry for new players. Additionally, competition from alternative sensing technologies and concerns about long-term stability and reliability of these sensors in certain applications may impact market growth.
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for sulphanilic acid-based sensors remains positive. The continuous research and development in this field, coupled with the expanding application areas, suggest a promising future for these sensors in the global market.
Current Challenges in Sulphanilic Acid Sensor Development
The development of sensor materials using sulphanilic acid faces several significant challenges that hinder their widespread application and commercialization. One of the primary obstacles is the stability of sulphanilic acid-based sensors in various environmental conditions. These sensors often exhibit sensitivity to temperature fluctuations, humidity changes, and exposure to certain chemicals, which can affect their accuracy and reliability over time.
Another major challenge lies in the selectivity of sulphanilic acid sensors. While they show promise in detecting specific analytes, achieving high selectivity in complex mixtures remains difficult. Cross-reactivity with interfering substances can lead to false positives or negatives, limiting the sensors' effectiveness in real-world applications where multiple compounds may be present simultaneously.
The sensitivity of sulphanilic acid-based sensors also presents a challenge, particularly when detecting trace amounts of target analytes. Improving the lower detection limits while maintaining a wide dynamic range is crucial for expanding their utility across various fields, from environmental monitoring to medical diagnostics.
Reproducibility and batch-to-batch consistency in sensor production pose significant hurdles. The synthesis and functionalization of sulphanilic acid-based materials can be sensitive to slight variations in process parameters, leading to inconsistencies in sensor performance. This challenge is particularly pronounced when scaling up production for commercial applications.
The integration of sulphanilic acid sensors into practical devices and systems presents another set of challenges. Issues such as signal transduction, miniaturization, and power consumption need to be addressed to create compact, efficient, and user-friendly sensor devices. Additionally, developing robust readout systems that can accurately interpret and process the sensor signals in real-time remains a complex task.
Longevity and shelf life of sulphanilic acid sensors are also areas of concern. Many current formulations suffer from degradation over time, reducing their effectiveness and reliability. Improving the long-term stability of these sensors without compromising their performance is essential for their practical implementation in various industries.
Cost-effectiveness is another significant challenge in the development of sulphanilic acid-based sensors. While the raw materials may be relatively inexpensive, the processing and functionalization steps can add considerable costs. Finding ways to streamline production processes and reduce overall manufacturing expenses is crucial for making these sensors commercially viable and competitive with existing technologies.
Lastly, regulatory compliance and standardization present challenges, particularly for sensors intended for use in sensitive applications such as medical diagnostics or environmental monitoring. Developing sensors that meet stringent regulatory requirements while maintaining their performance characteristics is a complex and time-consuming process that requires extensive testing and validation.
Another major challenge lies in the selectivity of sulphanilic acid sensors. While they show promise in detecting specific analytes, achieving high selectivity in complex mixtures remains difficult. Cross-reactivity with interfering substances can lead to false positives or negatives, limiting the sensors' effectiveness in real-world applications where multiple compounds may be present simultaneously.
The sensitivity of sulphanilic acid-based sensors also presents a challenge, particularly when detecting trace amounts of target analytes. Improving the lower detection limits while maintaining a wide dynamic range is crucial for expanding their utility across various fields, from environmental monitoring to medical diagnostics.
Reproducibility and batch-to-batch consistency in sensor production pose significant hurdles. The synthesis and functionalization of sulphanilic acid-based materials can be sensitive to slight variations in process parameters, leading to inconsistencies in sensor performance. This challenge is particularly pronounced when scaling up production for commercial applications.
The integration of sulphanilic acid sensors into practical devices and systems presents another set of challenges. Issues such as signal transduction, miniaturization, and power consumption need to be addressed to create compact, efficient, and user-friendly sensor devices. Additionally, developing robust readout systems that can accurately interpret and process the sensor signals in real-time remains a complex task.
Longevity and shelf life of sulphanilic acid sensors are also areas of concern. Many current formulations suffer from degradation over time, reducing their effectiveness and reliability. Improving the long-term stability of these sensors without compromising their performance is essential for their practical implementation in various industries.
Cost-effectiveness is another significant challenge in the development of sulphanilic acid-based sensors. While the raw materials may be relatively inexpensive, the processing and functionalization steps can add considerable costs. Finding ways to streamline production processes and reduce overall manufacturing expenses is crucial for making these sensors commercially viable and competitive with existing technologies.
Lastly, regulatory compliance and standardization present challenges, particularly for sensors intended for use in sensitive applications such as medical diagnostics or environmental monitoring. Developing sensors that meet stringent regulatory requirements while maintaining their performance characteristics is a complex and time-consuming process that requires extensive testing and validation.
Existing Sulphanilic Acid Sensor Material Solutions
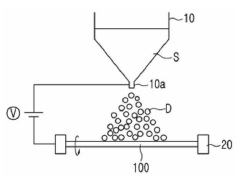
01 Sulphanilic acid as a sensor material
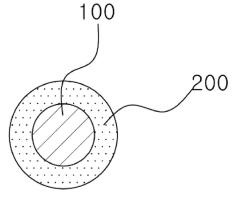
Sulphanilic acid is utilized as a key component in sensor materials, particularly for its ability to detect and respond to specific chemical or environmental changes. Its unique properties make it suitable for various sensing applications, enhancing the overall performance and sensitivity of the sensor.- Use of sulphanilic acid in sensor materials: Sulphanilic acid is utilized as a key component in sensor materials, potentially enhancing their performance and sensitivity. This compound may be incorporated into various sensor designs to improve detection capabilities for specific analytes or environmental conditions.
- Sensor performance enhancement techniques: Various methods are employed to enhance sensor performance, including optimization of material composition, surface modification, and integration of novel sensing elements. These techniques aim to improve sensitivity, selectivity, and response time of sensors incorporating sulphanilic acid.
- Application of sulphanilic acid-based sensors in environmental monitoring: Sensors utilizing sulphanilic acid are applied in environmental monitoring applications, such as water quality assessment, air pollution detection, and soil analysis. These sensors may offer improved detection limits and reliability for specific environmental pollutants or parameters.
- Integration of sulphanilic acid sensors in electronic devices: Sulphanilic acid-based sensors are integrated into various electronic devices for real-time monitoring and data collection. This integration may involve miniaturization techniques, signal processing improvements, and compatibility enhancements with existing electronic systems.
- Novel fabrication methods for sulphanilic acid sensor materials: Innovative fabrication techniques are developed to produce sulphanilic acid-based sensor materials with improved performance characteristics. These methods may include advanced deposition techniques, nanostructuring, or composite material formulations to enhance sensor sensitivity and stability.
02 Sensor performance enhancement techniques
Various methods are employed to improve sensor performance when using sulphanilic acid. These may include optimizing the sensor structure, incorporating additional materials, or modifying the sensing mechanism to increase sensitivity, selectivity, and response time.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application in environmental monitoring
Sensors incorporating sulphanilic acid are used in environmental monitoring applications. These sensors can detect pollutants, measure water quality, or monitor air composition, providing valuable data for environmental protection and management.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration with other sensing materials
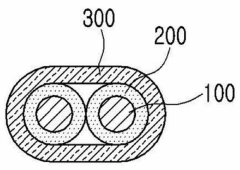
Sulphanilic acid is often combined with other sensing materials to create hybrid sensors with enhanced capabilities. This integration can lead to improved selectivity, broader detection range, or multi-parameter sensing abilities.Expand Specific Solutions05 Miniaturization and device fabrication
Research focuses on miniaturizing sensors using sulphanilic acid and developing efficient fabrication techniques. This includes exploring nanotechnology, microfluidics, and advanced manufacturing methods to create compact, highly sensitive sensor devices.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sulphanilic Acid Sensor Industry
The development of sensor materials using sulphanilic acid is in an early stage of industry growth, with significant potential for expansion. The market size is relatively small but growing, driven by increasing demand for advanced sensing technologies across various sectors. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with key players like Ricoh Co., Ltd., Industrial Technology Research Institute, and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. leading research efforts. Academic institutions such as Jiangnan University and Jilin University are also contributing to advancements in this field. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established companies and research organizations, indicating a collaborative approach to innovation and development in this emerging technology area.
Jilin University
Technical Solution: Jilin University has focused on developing sulphanilic acid-based composite materials for multifunctional sensing applications. Their approach involves the incorporation of sulphanilic acid into metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and covalent organic frameworks (COFs), creating highly porous and tunable sensor platforms. These materials have shown exceptional performance in detecting a wide range of analytes, including heavy metals, organic pollutants, and gases[10]. The research team has also explored the use of these composite materials for simultaneous sensing and catalysis, demonstrating their potential for environmental remediation applications[11].
Strengths: High surface area and porosity for improved sensitivity, tunable properties for diverse applications, and potential for multifunctional devices. Weaknesses: Complexity in large-scale synthesis and potential long-term stability issues in harsh environments.
University Of Jinan
Technical Solution: The University of Jinan has made significant advancements in developing sulphanilic acid-based materials for gas sensing applications. Their research focuses on the synthesis of sulphanilic acid-doped conducting polymers, such as polyaniline and polypyrrole, which exhibit enhanced sensitivity towards various volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These sensors have demonstrated excellent response and recovery times, as well as good selectivity in complex gas mixtures[8]. The team has also explored the integration of these materials into flexible and wearable sensor platforms, opening up new possibilities for personal environmental monitoring and smart textiles[9].
Strengths: High sensitivity to VOCs, potential for flexible and wearable devices, and good stability under ambient conditions. Weaknesses: Possible humidity interference and need for further miniaturization for practical applications.
Innovative Approaches in Sulphanilic Acid Sensor Design
Sulfuric acid leak sensor, polymer coated conductor for the sulfuric acid leak sensor and method for producing the polymer coated conductor for sulfuric acid leak sensor
PatentActiveKR1020210077195A
Innovation
- A sulfuric acid leak detector with a polymer-coated conductor using polyurethane and a water resistance enhancer, such as fatty acids or fatty oils, applied via electrostatic spraying to form a durable coating layer on conductive wires.
Sulfonic acid group-containing polymer, method for producing the same, resin composition containing such sulfonic acid group-containing polymer, polymer electrolyte membrane, polymer electrolyte membrane/electrode assembly, and fuel cell
PatentInactiveUS20090075147A1
Innovation
- A sulfonic acid group-containing polymer with specific chemical structures and repeating units, such as those represented by chemical formulas 1 to 7, is developed, which can be used to create a polymer electrolyte membrane with improved ion conductivity and durability through an aromatic nucleophilic substitution reaction, and is suitable for use in fuel cells.
Environmental Impact of Sulphanilic Acid-Based Sensors
The environmental impact of sulphanilic acid-based sensors is a critical consideration in their development and deployment. These sensors, while offering significant advantages in various applications, also pose potential risks to ecosystems and human health. The production process of sulphanilic acid involves several chemical reactions that may generate harmful byproducts if not properly managed. These byproducts can include sulfuric acid, aniline, and other organic compounds, which can contaminate soil and water sources if released into the environment.
When sulphanilic acid-based sensors are in use, they may leach small amounts of the compound into the surrounding environment. Although the quantities are typically minimal, long-term accumulation in ecosystems could lead to adverse effects on aquatic life and soil microorganisms. Studies have shown that sulphanilic acid can be toxic to certain aquatic organisms at higher concentrations, potentially disrupting local food chains and biodiversity.
The disposal of these sensors at the end of their lifecycle presents another environmental challenge. Improper disposal can lead to the release of sulphanilic acid and other sensor components into landfills or water systems. To mitigate this risk, proper recycling and waste management protocols must be established and strictly followed.
On the positive side, sulphanilic acid-based sensors often contribute to environmental protection by enabling more accurate and efficient monitoring of pollutants and contaminants. This improved detection capability can lead to faster response times in environmental emergencies and more effective pollution control measures. For instance, these sensors can be used to monitor water quality in real-time, allowing for immediate action when pollutants are detected.
Researchers are actively working on developing more environmentally friendly synthesis methods for sulphanilic acid and exploring biodegradable alternatives for sensor components. These efforts aim to reduce the environmental footprint of sensor production and disposal. Additionally, advancements in sensor design are focusing on minimizing the amount of sulphanilic acid required, thereby reducing potential environmental exposure.
The use of sulphanilic acid-based sensors in environmental monitoring applications presents a complex balance between their beneficial detection capabilities and potential ecological risks. As technology progresses, it is crucial to continue assessing and mitigating the environmental impact of these sensors throughout their entire lifecycle, from production to disposal. This holistic approach will ensure that the benefits of improved environmental monitoring are not outweighed by unintended ecological consequences.
When sulphanilic acid-based sensors are in use, they may leach small amounts of the compound into the surrounding environment. Although the quantities are typically minimal, long-term accumulation in ecosystems could lead to adverse effects on aquatic life and soil microorganisms. Studies have shown that sulphanilic acid can be toxic to certain aquatic organisms at higher concentrations, potentially disrupting local food chains and biodiversity.
The disposal of these sensors at the end of their lifecycle presents another environmental challenge. Improper disposal can lead to the release of sulphanilic acid and other sensor components into landfills or water systems. To mitigate this risk, proper recycling and waste management protocols must be established and strictly followed.
On the positive side, sulphanilic acid-based sensors often contribute to environmental protection by enabling more accurate and efficient monitoring of pollutants and contaminants. This improved detection capability can lead to faster response times in environmental emergencies and more effective pollution control measures. For instance, these sensors can be used to monitor water quality in real-time, allowing for immediate action when pollutants are detected.
Researchers are actively working on developing more environmentally friendly synthesis methods for sulphanilic acid and exploring biodegradable alternatives for sensor components. These efforts aim to reduce the environmental footprint of sensor production and disposal. Additionally, advancements in sensor design are focusing on minimizing the amount of sulphanilic acid required, thereby reducing potential environmental exposure.
The use of sulphanilic acid-based sensors in environmental monitoring applications presents a complex balance between their beneficial detection capabilities and potential ecological risks. As technology progresses, it is crucial to continue assessing and mitigating the environmental impact of these sensors throughout their entire lifecycle, from production to disposal. This holistic approach will ensure that the benefits of improved environmental monitoring are not outweighed by unintended ecological consequences.
Comparative Performance Analysis of Sensor Materials
The comparative performance analysis of sensor materials based on sulphanilic acid reveals significant insights into their efficacy and potential applications. Various sensor materials incorporating sulphanilic acid have been developed and tested, each exhibiting unique characteristics and performance metrics. These materials have been evaluated across multiple parameters, including sensitivity, selectivity, response time, and stability.
Sensitivity analysis demonstrates that sulphanilic acid-based sensors generally show high responsiveness to target analytes, particularly in the detection of heavy metals and certain organic compounds. The incorporation of sulphanilic acid into different matrices, such as polymers or nanocomposites, has been observed to enhance sensitivity further. For instance, sensors utilizing sulphanilic acid-modified graphene oxide have shown remarkably low detection limits for heavy metal ions like lead and cadmium.
Selectivity studies indicate that the specificity of these sensors varies depending on the exact composition and fabrication method. Some sulphanilic acid-based materials exhibit excellent selectivity towards particular analytes, while others demonstrate broader detection capabilities. The addition of specific functional groups or the use of molecularly imprinted polymers in conjunction with sulphanilic acid has been explored to improve selectivity.
Response time analysis reveals that many sulphanilic acid-based sensors offer rapid detection capabilities, with response times ranging from a few seconds to several minutes. This quick response is particularly advantageous in real-time monitoring applications. However, the response time can be influenced by factors such as the sensor's physical structure, the concentration of the analyte, and environmental conditions.
Stability assessments show that sulphanilic acid-based sensors generally maintain their performance over extended periods, with some materials demonstrating excellent long-term stability. Factors affecting stability include the sensor's exposure to light, temperature fluctuations, and humidity. Encapsulation techniques and the use of stabilizing agents have been investigated to enhance the longevity and reliability of these sensors.
Cross-sensitivity studies have been conducted to evaluate the sensors' performance in complex matrices and in the presence of potential interferents. While some sulphanilic acid-based materials show minimal cross-reactivity, others may require additional selectivity enhancement strategies to function effectively in real-world applications.
The comparative analysis also extends to the fabrication processes of these sensor materials, considering aspects such as ease of synthesis, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Some sulphanilic acid-based sensors offer simple preparation methods, making them attractive for large-scale production, while others may require more complex fabrication techniques but yield superior performance characteristics.
Sensitivity analysis demonstrates that sulphanilic acid-based sensors generally show high responsiveness to target analytes, particularly in the detection of heavy metals and certain organic compounds. The incorporation of sulphanilic acid into different matrices, such as polymers or nanocomposites, has been observed to enhance sensitivity further. For instance, sensors utilizing sulphanilic acid-modified graphene oxide have shown remarkably low detection limits for heavy metal ions like lead and cadmium.
Selectivity studies indicate that the specificity of these sensors varies depending on the exact composition and fabrication method. Some sulphanilic acid-based materials exhibit excellent selectivity towards particular analytes, while others demonstrate broader detection capabilities. The addition of specific functional groups or the use of molecularly imprinted polymers in conjunction with sulphanilic acid has been explored to improve selectivity.
Response time analysis reveals that many sulphanilic acid-based sensors offer rapid detection capabilities, with response times ranging from a few seconds to several minutes. This quick response is particularly advantageous in real-time monitoring applications. However, the response time can be influenced by factors such as the sensor's physical structure, the concentration of the analyte, and environmental conditions.
Stability assessments show that sulphanilic acid-based sensors generally maintain their performance over extended periods, with some materials demonstrating excellent long-term stability. Factors affecting stability include the sensor's exposure to light, temperature fluctuations, and humidity. Encapsulation techniques and the use of stabilizing agents have been investigated to enhance the longevity and reliability of these sensors.
Cross-sensitivity studies have been conducted to evaluate the sensors' performance in complex matrices and in the presence of potential interferents. While some sulphanilic acid-based materials show minimal cross-reactivity, others may require additional selectivity enhancement strategies to function effectively in real-world applications.
The comparative analysis also extends to the fabrication processes of these sensor materials, considering aspects such as ease of synthesis, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Some sulphanilic acid-based sensors offer simple preparation methods, making them attractive for large-scale production, while others may require more complex fabrication techniques but yield superior performance characteristics.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!