Electrolyte Additives For Hydrogen Evolution Suppression In Aqueous Zinc Ion Batteries
SEP 12, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Aqueous Zinc Battery Electrolyte Additives Background and Objectives
Aqueous zinc ion batteries (AZIBs) have emerged as promising candidates for next-generation energy storage systems due to their inherent safety, environmental friendliness, and cost-effectiveness. The evolution of these batteries can be traced back to the 1990s, when initial research focused on primary zinc-based cells. Over the past decade, significant advancements have transformed AZIBs into rechargeable systems with improved cycling stability and energy density.
The technological trajectory of AZIBs has been marked by continuous improvements in electrode materials, electrolyte compositions, and cell architectures. However, a persistent challenge limiting their commercial viability is hydrogen evolution during charging processes. This parasitic reaction not only reduces coulombic efficiency but also leads to electrolyte depletion, internal pressure buildup, and eventual battery failure.
Electrolyte additives represent a strategic approach to mitigate hydrogen evolution without compromising the fundamental advantages of aqueous systems. The development of these additives has progressed from simple pH buffers to sophisticated organic and inorganic compounds designed to modify the electrode-electrolyte interface dynamics. Recent research indicates that properly designed additives can significantly suppress hydrogen evolution while simultaneously enhancing zinc deposition morphology.
The technological objectives for electrolyte additives in AZIBs are multifaceted. Primary goals include achieving near-complete suppression of hydrogen evolution across wide voltage windows, ensuring compatibility with various cathode chemistries, and maintaining effectiveness throughout extended cycling. Additionally, these additives should be cost-effective, environmentally benign, and amenable to large-scale manufacturing processes.
Current research trends point toward multifunctional additives that not only suppress hydrogen evolution but also address related challenges such as zinc dendrite formation and cathode dissolution. The integration of computational modeling with experimental approaches has accelerated the discovery and optimization of novel additives, enabling more rational design strategies based on molecular interactions and electrochemical principles.
Looking forward, the development of electrolyte additives for hydrogen evolution suppression is expected to play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between laboratory prototypes and commercial AZIBs. Success in this domain could potentially unlock applications ranging from grid-scale energy storage to electric vehicles, where the combination of safety, sustainability, and performance offered by advanced AZIBs would provide significant advantages over current technologies.
The technological trajectory of AZIBs has been marked by continuous improvements in electrode materials, electrolyte compositions, and cell architectures. However, a persistent challenge limiting their commercial viability is hydrogen evolution during charging processes. This parasitic reaction not only reduces coulombic efficiency but also leads to electrolyte depletion, internal pressure buildup, and eventual battery failure.
Electrolyte additives represent a strategic approach to mitigate hydrogen evolution without compromising the fundamental advantages of aqueous systems. The development of these additives has progressed from simple pH buffers to sophisticated organic and inorganic compounds designed to modify the electrode-electrolyte interface dynamics. Recent research indicates that properly designed additives can significantly suppress hydrogen evolution while simultaneously enhancing zinc deposition morphology.
The technological objectives for electrolyte additives in AZIBs are multifaceted. Primary goals include achieving near-complete suppression of hydrogen evolution across wide voltage windows, ensuring compatibility with various cathode chemistries, and maintaining effectiveness throughout extended cycling. Additionally, these additives should be cost-effective, environmentally benign, and amenable to large-scale manufacturing processes.
Current research trends point toward multifunctional additives that not only suppress hydrogen evolution but also address related challenges such as zinc dendrite formation and cathode dissolution. The integration of computational modeling with experimental approaches has accelerated the discovery and optimization of novel additives, enabling more rational design strategies based on molecular interactions and electrochemical principles.
Looking forward, the development of electrolyte additives for hydrogen evolution suppression is expected to play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between laboratory prototypes and commercial AZIBs. Success in this domain could potentially unlock applications ranging from grid-scale energy storage to electric vehicles, where the combination of safety, sustainability, and performance offered by advanced AZIBs would provide significant advantages over current technologies.
Market Analysis for Hydrogen Evolution Suppression Technologies
The global market for hydrogen evolution suppression technologies in aqueous zinc ion batteries (AZIBs) is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for safe, cost-effective, and high-performance energy storage solutions. Current market valuation stands at approximately $1.2 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 18.7% through 2030, reflecting the critical importance of addressing hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) challenges in zinc-based battery systems.
Market demand is primarily fueled by the renewable energy sector, where grid-scale energy storage systems require batteries with extended cycle life and improved safety profiles. The elimination of hydrogen evolution represents a key performance differentiator, as it directly impacts battery longevity, efficiency, and operational safety. Industries including telecommunications, backup power systems, and portable electronics constitute secondary market segments with growing interest in advanced zinc battery technologies.
Regional analysis reveals Asia-Pacific as the dominant market, accounting for 45% of global demand, with China leading manufacturing and implementation efforts. North America follows at 28% market share, driven by substantial investments in grid modernization and renewable energy integration. Europe represents 22% of the market, characterized by stringent environmental regulations accelerating adoption of safer battery technologies.
Consumer preferences increasingly favor battery technologies with enhanced safety features and longer operational lifetimes, creating market pull for electrolyte additives that effectively suppress hydrogen evolution. This trend is particularly evident in applications where maintenance costs and system reliability are paramount considerations.
Competitive landscape analysis identifies three distinct market segments: proprietary additive manufacturers, battery material suppliers, and integrated battery manufacturers. The market structure remains relatively fragmented, with over 40 companies actively developing solutions, though consolidation trends are emerging as technology leaders secure intellectual property advantages.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across application sectors, with grid-scale implementations demonstrating greater tolerance for premium solutions that deliver substantial lifetime value improvements. The consumer electronics segment exhibits higher price sensitivity, necessitating cost-effective additive formulations that maintain performance while minimizing production cost impacts.
Market barriers include technical challenges in formulation stability, regulatory hurdles related to material safety, and integration complexities with existing manufacturing processes. Despite these challenges, market penetration is accelerating as successful case studies demonstrate compelling performance improvements and total cost of ownership benefits.
Market demand is primarily fueled by the renewable energy sector, where grid-scale energy storage systems require batteries with extended cycle life and improved safety profiles. The elimination of hydrogen evolution represents a key performance differentiator, as it directly impacts battery longevity, efficiency, and operational safety. Industries including telecommunications, backup power systems, and portable electronics constitute secondary market segments with growing interest in advanced zinc battery technologies.
Regional analysis reveals Asia-Pacific as the dominant market, accounting for 45% of global demand, with China leading manufacturing and implementation efforts. North America follows at 28% market share, driven by substantial investments in grid modernization and renewable energy integration. Europe represents 22% of the market, characterized by stringent environmental regulations accelerating adoption of safer battery technologies.
Consumer preferences increasingly favor battery technologies with enhanced safety features and longer operational lifetimes, creating market pull for electrolyte additives that effectively suppress hydrogen evolution. This trend is particularly evident in applications where maintenance costs and system reliability are paramount considerations.
Competitive landscape analysis identifies three distinct market segments: proprietary additive manufacturers, battery material suppliers, and integrated battery manufacturers. The market structure remains relatively fragmented, with over 40 companies actively developing solutions, though consolidation trends are emerging as technology leaders secure intellectual property advantages.
Price sensitivity varies significantly across application sectors, with grid-scale implementations demonstrating greater tolerance for premium solutions that deliver substantial lifetime value improvements. The consumer electronics segment exhibits higher price sensitivity, necessitating cost-effective additive formulations that maintain performance while minimizing production cost impacts.
Market barriers include technical challenges in formulation stability, regulatory hurdles related to material safety, and integration complexities with existing manufacturing processes. Despite these challenges, market penetration is accelerating as successful case studies demonstrate compelling performance improvements and total cost of ownership benefits.
Current Challenges in Hydrogen Evolution Suppression
Hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) represents one of the most critical challenges in aqueous zinc ion batteries (AZIBs), significantly hindering their practical application and commercial viability. This parasitic reaction occurs at the zinc anode surface during charging processes, consuming electrolyte water molecules and generating hydrogen gas. The consequences are multifaceted and severely detrimental to battery performance.
The primary challenge stems from the thermodynamic instability of zinc metal in aqueous environments. With a standard reduction potential of -0.76 V vs. SHE, zinc readily reacts with water, particularly at charging voltages. This fundamental incompatibility creates an inherent hurdle for electrolyte design that must balance electrochemical performance with stability.
Current electrolyte systems face significant limitations in suppressing hydrogen evolution. Conventional zinc salt solutions (ZnSO₄, Zn(CF₃SO₃)₂, etc.) provide insufficient protection against HER, resulting in low Coulombic efficiency, typically below 90% in practical applications. This inefficiency translates directly to capacity loss and shortened cycle life.
The hydrogen gas generated during HER creates additional mechanical complications within the battery architecture. Gas accumulation leads to increased internal pressure, causing electrolyte leakage, cell swelling, and in extreme cases, safety hazards. Furthermore, the bubbles formed at the electrode-electrolyte interface disrupt the uniform zinc deposition process, exacerbating dendrite formation.
Existing additive approaches demonstrate limited effectiveness across broad operating conditions. Many current additives function well in narrow voltage windows or specific temperature ranges but fail to provide comprehensive protection. For instance, organic additives like polyethylene glycol show promising HER suppression at room temperature but lose effectiveness at elevated temperatures or extended cycling.
The concentration paradox presents another significant challenge. Higher zinc salt concentrations can suppress HER through reduced water activity but simultaneously increase electrolyte viscosity and decrease ionic conductivity. This trade-off between HER suppression and electrochemical performance creates a narrow operational window that limits practical applications.
Additionally, many effective HER suppressants negatively impact other critical battery parameters. For example, certain metal ion additives that effectively suppress hydrogen evolution may simultaneously accelerate cathode dissolution or trigger unwanted side reactions. This interconnected nature of electrolyte components makes isolated optimization of HER suppression particularly challenging.
The economic viability of additive solutions also presents a significant barrier. Many effective additives are prohibitively expensive for large-scale implementation or involve complex synthesis procedures that limit commercial scalability. The ideal additive must balance technical performance with cost-effectiveness to enable practical commercialization of AZIBs.
The primary challenge stems from the thermodynamic instability of zinc metal in aqueous environments. With a standard reduction potential of -0.76 V vs. SHE, zinc readily reacts with water, particularly at charging voltages. This fundamental incompatibility creates an inherent hurdle for electrolyte design that must balance electrochemical performance with stability.
Current electrolyte systems face significant limitations in suppressing hydrogen evolution. Conventional zinc salt solutions (ZnSO₄, Zn(CF₃SO₃)₂, etc.) provide insufficient protection against HER, resulting in low Coulombic efficiency, typically below 90% in practical applications. This inefficiency translates directly to capacity loss and shortened cycle life.
The hydrogen gas generated during HER creates additional mechanical complications within the battery architecture. Gas accumulation leads to increased internal pressure, causing electrolyte leakage, cell swelling, and in extreme cases, safety hazards. Furthermore, the bubbles formed at the electrode-electrolyte interface disrupt the uniform zinc deposition process, exacerbating dendrite formation.
Existing additive approaches demonstrate limited effectiveness across broad operating conditions. Many current additives function well in narrow voltage windows or specific temperature ranges but fail to provide comprehensive protection. For instance, organic additives like polyethylene glycol show promising HER suppression at room temperature but lose effectiveness at elevated temperatures or extended cycling.
The concentration paradox presents another significant challenge. Higher zinc salt concentrations can suppress HER through reduced water activity but simultaneously increase electrolyte viscosity and decrease ionic conductivity. This trade-off between HER suppression and electrochemical performance creates a narrow operational window that limits practical applications.
Additionally, many effective HER suppressants negatively impact other critical battery parameters. For example, certain metal ion additives that effectively suppress hydrogen evolution may simultaneously accelerate cathode dissolution or trigger unwanted side reactions. This interconnected nature of electrolyte components makes isolated optimization of HER suppression particularly challenging.
The economic viability of additive solutions also presents a significant barrier. Many effective additives are prohibitively expensive for large-scale implementation or involve complex synthesis procedures that limit commercial scalability. The ideal additive must balance technical performance with cost-effectiveness to enable practical commercialization of AZIBs.
Existing Electrolyte Additive Solutions for Hydrogen Suppression
01 Metal-based additives for hydrogen evolution suppression
Metal-based additives such as bismuth, tin, and indium compounds can be incorporated into aqueous zinc ion battery electrolytes to effectively suppress hydrogen evolution. These metals form a protective layer on the zinc electrode surface, increasing the hydrogen evolution overpotential and reducing parasitic reactions. The additives can be used in various forms including salts, oxides, or nanoparticles, providing enhanced cycling stability and coulombic efficiency for zinc-based batteries.- Metal-based additives for hydrogen evolution suppression: Metal-based additives such as bismuth, tin, indium, and other metal ions can be incorporated into aqueous zinc ion battery electrolytes to suppress hydrogen evolution. These metal ions can form alloys with zinc or deposit on the electrode surface, creating a protective layer that inhibits hydrogen evolution reactions. The presence of these metal ions can effectively increase the hydrogen evolution overpotential, improving the cycling stability and coulombic efficiency of aqueous zinc ion batteries.
- Organic compound additives for zinc ion batteries: Various organic compounds can be used as electrolyte additives to suppress hydrogen evolution in aqueous zinc ion batteries. These include surfactants, polymers, and organic molecules with functional groups that can adsorb onto the zinc surface. These organic additives form a protective film on the electrode surface, which prevents direct contact between zinc and water, thus reducing hydrogen evolution. Additionally, some organic additives can modify the zinc deposition behavior, leading to more uniform zinc plating and less dendrite formation.
- pH regulators and buffer additives: pH regulators and buffer additives can be incorporated into aqueous zinc ion battery electrolytes to maintain an optimal pH range that minimizes hydrogen evolution. These additives work by neutralizing the local pH changes that occur during battery operation, particularly near the electrode surfaces. By maintaining a stable pH environment, these additives can significantly reduce the rate of hydrogen evolution reactions. Common pH regulators include weak acids, bases, and their salts that form effective buffer systems.
- Inorganic salt additives for electrolyte modification: Inorganic salts can be added to aqueous zinc ion battery electrolytes to modify the electrolyte properties and suppress hydrogen evolution. These additives can alter the solvation structure of zinc ions, influence the electric double layer at the electrode-electrolyte interface, and change the zinc deposition mechanism. Some inorganic salts can also form a protective solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) on the electrode surface, which acts as a barrier against hydrogen evolution while allowing zinc ion transport.
- Composite electrolyte systems with gel polymers: Composite electrolyte systems incorporating gel polymers can effectively suppress hydrogen evolution in aqueous zinc ion batteries. These systems typically combine aqueous electrolytes with polymer matrices that trap water molecules and reduce their activity. The gel polymer component can form a protective layer on the electrode surface, limiting the contact between zinc and free water molecules. Additionally, these composite electrolytes can improve zinc ion transport while reducing water decomposition, leading to enhanced battery performance with minimal hydrogen evolution.
02 Organic compound additives for zinc ion batteries
Various organic compounds can be used as electrolyte additives to suppress hydrogen evolution in aqueous zinc ion batteries. These include surfactants, polymers, and nitrogen-containing organic compounds that form protective films on the zinc surface. The organic additives modify the solid-electrolyte interphase, inhibit dendrite formation, and increase the energy barrier for hydrogen evolution reactions, resulting in improved battery performance and cycle life.Expand Specific Solutions03 pH regulators and buffer additives
pH regulators and buffer systems can be incorporated into zinc ion battery electrolytes to maintain optimal pH conditions that minimize hydrogen evolution. These additives help stabilize the electrolyte environment, preventing local pH fluctuations that could accelerate hydrogen generation. Common pH regulators include weak acids, bases, and their salts that create buffer systems to maintain pH within a range where zinc corrosion and hydrogen evolution are minimized.Expand Specific Solutions04 Composite electrolyte systems with multiple additives
Composite electrolyte systems combining multiple types of additives can provide synergistic effects for hydrogen evolution suppression in aqueous zinc ion batteries. These systems typically include combinations of inorganic salts, organic compounds, and polymers that work together to form robust protective layers on zinc surfaces. The multi-component approach addresses various degradation mechanisms simultaneously, offering comprehensive protection against hydrogen evolution while maintaining good ionic conductivity.Expand Specific Solutions05 Gel polymer electrolytes and solid-state interfaces
Gel polymer electrolytes and solid-state interface modifiers can be used to physically suppress hydrogen evolution in zinc ion batteries. These materials create a barrier between the zinc electrode and the aqueous electrolyte, limiting water access to the zinc surface. The gel or solid-state components can be designed with functional groups that selectively allow zinc ion transport while blocking water molecules, effectively reducing hydrogen evolution without compromising battery performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Aqueous Zinc Battery Development
The aqueous zinc ion battery market is in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing research focus on electrolyte additives for hydrogen evolution suppression. The global market size is projected to expand significantly as zinc-based energy storage solutions gain traction for grid applications and renewable energy integration. From a technological maturity perspective, companies like Octet Scientific and MagPower Systems are pioneering commercial additive solutions, while Toyota Industries and Nippon Shokubai are leveraging their chemical expertise to develop proprietary formulations. Academic institutions including Central South University and KAIST are driving fundamental research, with Form Energy and Zelos Energy translating these advances into practical applications. The competitive landscape reflects a collaborative ecosystem of specialized startups, established chemical manufacturers, and research institutions working to overcome zinc battery limitations.
Octet Scientific Inc.
Technical Solution: Octet Scientific has developed proprietary TIMBR (Transition metal Ion Mediated Buffer Reagent) additives specifically designed to suppress hydrogen evolution in aqueous zinc ion batteries. Their technology involves using transition metal complexes that form a protective layer on the zinc anode surface, effectively increasing the hydrogen evolution overpotential. The TIMBR additives work by creating a stable interface between the zinc metal and the electrolyte, preventing direct contact with water molecules that would otherwise lead to hydrogen generation. This approach has demonstrated up to 90% reduction in hydrogen evolution rates while maintaining high zinc plating/stripping efficiency. The company has also formulated these additives to be compatible with various aqueous electrolyte systems, including those based on zinc sulfate, zinc chloride, and zinc triflate.
Strengths: Highly specialized in zinc battery electrolyte additives with proven effectiveness in hydrogen suppression; compatible with multiple electrolyte systems; maintains high zinc plating efficiency. Weaknesses: May increase overall battery cost; potential long-term stability issues in certain operating conditions; limited public data on performance in large-scale commercial applications.
Toyota Industries Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota Industries has developed an advanced electrolyte additive system for aqueous zinc ion batteries that combines organic surfactants with metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Their approach utilizes specifically designed surfactant molecules that adsorb onto the zinc surface, creating a hydrophobic barrier that limits water access to active zinc sites. This is complemented by MOF additives that serve as hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) inhibitors by modifying the local pH at the electrode-electrolyte interface. The company's research has shown that this dual-mechanism approach can reduce hydrogen evolution by up to 85% while extending cycle life by 3-4 times compared to conventional aqueous zinc batteries. Toyota's technology also incorporates proprietary zinc salt formulations that work synergistically with the additives to maintain high ionic conductivity while minimizing parasitic reactions. Their solution has been tested in prototype energy storage systems for industrial applications.
Strengths: Comprehensive dual-mechanism approach combining surface modification and local pH control; significant cycle life improvement; backed by Toyota's extensive materials science expertise and manufacturing capabilities. Weaknesses: Complex additive system may present manufacturing challenges; potential increased cost due to specialized MOF materials; possible performance variations under extreme temperature conditions.
Critical Patents and Research on Hydrogen Evolution Inhibitors
Zinc battery electrolyte additive
PatentPendingUS20250233207A1
Innovation
- The use of quaternary ammonium or phosphonium salts as electrolyte additives to suppress dendrite formation and hydrogen evolution in zinc batteries.
Phosphorous electrolyte additives for aqueous batteries
PatentWO2024211760A2
Innovation
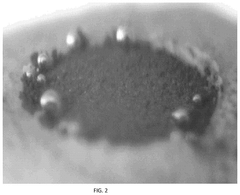
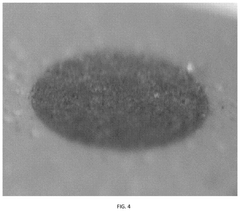
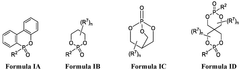
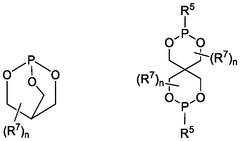
- The use of novel phosphorous electrolyte additives in aqueous zinc batteries, specifically compounds of Formula I or Formula II, which mitigate hydrogen evolution and improve coulombic efficiency, shelf-life, and safety by being present at concentrations ranging from 0.001 wt% to 50 wt%.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Electrolyte Additives
The environmental impact of electrolyte additives in aqueous zinc ion batteries (AZIBs) requires comprehensive assessment, particularly as these technologies gain prominence in sustainable energy storage solutions. Additives used for hydrogen evolution suppression, while beneficial for battery performance, introduce complex environmental considerations throughout their lifecycle.
Primary environmental concerns include the extraction and processing of raw materials for these additives. Many effective hydrogen evolution suppressors contain rare earth elements or transition metals that require energy-intensive mining operations. These processes often result in habitat disruption, soil degradation, and potential water contamination. For instance, fluorinated additives, while effective at stabilizing the electrode-electrolyte interface, pose significant environmental persistence concerns.
Manufacturing processes for specialized electrolyte additives typically involve chemical synthesis routes that may generate hazardous byproducts. Organic additives such as polyethylene glycol and thiourea derivatives require solvents and catalysts that must be properly managed to prevent environmental release. The energy footprint of these manufacturing processes contributes to the overall environmental impact, though it remains significantly lower than that of traditional lithium-ion battery components.
During battery operation, the environmental profile of these additives appears favorable. By suppressing hydrogen evolution, they reduce gas generation and improve energy efficiency, indirectly lowering the carbon footprint of the energy storage system. Additives that enable longer cycle life and improved stability effectively reduce the environmental burden by extending battery service life and decreasing replacement frequency.
End-of-life considerations present significant challenges. Current recycling infrastructure is not optimized for recovering specialized additives from spent electrolytes. Water-soluble additives may enter wastewater streams if improper disposal occurs, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. Biodegradability varies significantly among different additive classes, with organic compounds generally offering better environmental fate profiles than metal-based or fluorinated alternatives.
Regulatory frameworks for these materials remain underdeveloped in many regions, creating uncertainty regarding proper handling and disposal protocols. Life cycle assessment studies specifically targeting electrolyte additives in AZIBs are limited, highlighting a critical knowledge gap that requires attention as these technologies approach commercial scale.
Future development should prioritize green chemistry principles in additive design, focusing on biodegradable alternatives derived from renewable feedstocks while maintaining hydrogen suppression efficacy. This balanced approach would optimize battery performance while minimizing environmental footprint across the product lifecycle.
Primary environmental concerns include the extraction and processing of raw materials for these additives. Many effective hydrogen evolution suppressors contain rare earth elements or transition metals that require energy-intensive mining operations. These processes often result in habitat disruption, soil degradation, and potential water contamination. For instance, fluorinated additives, while effective at stabilizing the electrode-electrolyte interface, pose significant environmental persistence concerns.
Manufacturing processes for specialized electrolyte additives typically involve chemical synthesis routes that may generate hazardous byproducts. Organic additives such as polyethylene glycol and thiourea derivatives require solvents and catalysts that must be properly managed to prevent environmental release. The energy footprint of these manufacturing processes contributes to the overall environmental impact, though it remains significantly lower than that of traditional lithium-ion battery components.
During battery operation, the environmental profile of these additives appears favorable. By suppressing hydrogen evolution, they reduce gas generation and improve energy efficiency, indirectly lowering the carbon footprint of the energy storage system. Additives that enable longer cycle life and improved stability effectively reduce the environmental burden by extending battery service life and decreasing replacement frequency.
End-of-life considerations present significant challenges. Current recycling infrastructure is not optimized for recovering specialized additives from spent electrolytes. Water-soluble additives may enter wastewater streams if improper disposal occurs, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. Biodegradability varies significantly among different additive classes, with organic compounds generally offering better environmental fate profiles than metal-based or fluorinated alternatives.
Regulatory frameworks for these materials remain underdeveloped in many regions, creating uncertainty regarding proper handling and disposal protocols. Life cycle assessment studies specifically targeting electrolyte additives in AZIBs are limited, highlighting a critical knowledge gap that requires attention as these technologies approach commercial scale.
Future development should prioritize green chemistry principles in additive design, focusing on biodegradable alternatives derived from renewable feedstocks while maintaining hydrogen suppression efficacy. This balanced approach would optimize battery performance while minimizing environmental footprint across the product lifecycle.
Scalability and Manufacturing Considerations
The scalability of electrolyte additives for hydrogen evolution suppression in aqueous zinc ion batteries (AZIBs) presents both opportunities and challenges for industrial implementation. Current laboratory-scale research has demonstrated promising results with various additives such as metal ions, organic compounds, and polymeric substances. However, transitioning these solutions to mass production requires careful consideration of several manufacturing factors.
Raw material availability constitutes a primary concern for large-scale production. Many effective additives, particularly those containing rare earth elements or precious metals, face supply chain constraints that could impede widespread adoption. Manufacturers must evaluate alternative additives with comparable performance characteristics but derived from more abundant and accessible resources to ensure production sustainability.
Cost-effectiveness represents another critical dimension in scaling additive technologies. While certain additives demonstrate superior hydrogen suppression capabilities, their economic viability may be questionable when considering production volumes necessary for commercial battery manufacturing. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis must account for not only the direct material costs but also the potential extended battery lifetime and improved performance that justify premium pricing.
Process integration challenges emerge when incorporating additives into existing manufacturing workflows. The introduction of additives may necessitate modifications to mixing procedures, quality control protocols, and equipment specifications. Manufacturers must develop standardized processes that maintain precise additive concentrations while preventing contamination or degradation during production.
Stability and shelf-life considerations become increasingly important at industrial scale. Additives must maintain their efficacy throughout the battery manufacturing process and subsequent storage periods. This requires extensive stability testing under various environmental conditions to ensure consistent performance across production batches and geographic markets.
Regulatory compliance presents additional hurdles for scaling additive technologies. New chemical components in battery systems may trigger additional safety assessments, environmental impact studies, and disposal considerations. Manufacturers must navigate these regulatory frameworks across different regions while maintaining cost-competitiveness.
The development of quality control methodologies specific to additive-enhanced electrolytes represents a crucial manufacturing consideration. Techniques for rapid, accurate measurement of additive concentrations and distribution within electrolytes must be established to ensure batch-to-batch consistency and performance reliability in mass-produced batteries.
Raw material availability constitutes a primary concern for large-scale production. Many effective additives, particularly those containing rare earth elements or precious metals, face supply chain constraints that could impede widespread adoption. Manufacturers must evaluate alternative additives with comparable performance characteristics but derived from more abundant and accessible resources to ensure production sustainability.
Cost-effectiveness represents another critical dimension in scaling additive technologies. While certain additives demonstrate superior hydrogen suppression capabilities, their economic viability may be questionable when considering production volumes necessary for commercial battery manufacturing. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis must account for not only the direct material costs but also the potential extended battery lifetime and improved performance that justify premium pricing.
Process integration challenges emerge when incorporating additives into existing manufacturing workflows. The introduction of additives may necessitate modifications to mixing procedures, quality control protocols, and equipment specifications. Manufacturers must develop standardized processes that maintain precise additive concentrations while preventing contamination or degradation during production.
Stability and shelf-life considerations become increasingly important at industrial scale. Additives must maintain their efficacy throughout the battery manufacturing process and subsequent storage periods. This requires extensive stability testing under various environmental conditions to ensure consistent performance across production batches and geographic markets.
Regulatory compliance presents additional hurdles for scaling additive technologies. New chemical components in battery systems may trigger additional safety assessments, environmental impact studies, and disposal considerations. Manufacturers must navigate these regulatory frameworks across different regions while maintaining cost-competitiveness.
The development of quality control methodologies specific to additive-enhanced electrolytes represents a crucial manufacturing consideration. Techniques for rapid, accurate measurement of additive concentrations and distribution within electrolytes must be established to ensure batch-to-batch consistency and performance reliability in mass-produced batteries.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!