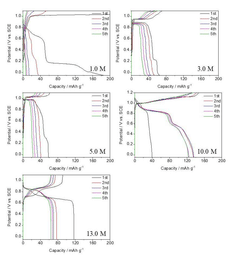
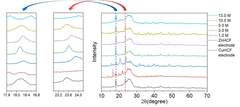
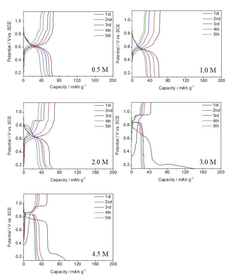
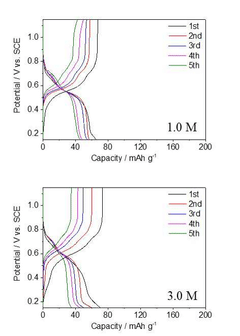
Scale-Up Considerations For Prussian Blue Analog Cathodes In Aqueous Zinc Ion Batteries
SEP 12, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PBA Cathode Development History and Objectives
Prussian Blue Analogs (PBAs) have emerged as promising cathode materials for aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) due to their open framework structure, abundant redox-active sites, and excellent ion transport properties. The development of PBA cathodes can be traced back to the early 2010s when researchers began exploring alternative battery chemistries beyond lithium-ion systems to address concerns related to cost, safety, and resource availability.
The initial research on PBAs focused primarily on their application in sodium and potassium-ion batteries. However, around 2015, scientists began investigating their potential in zinc-based systems, recognizing the advantages of zinc's high theoretical capacity (820 mAh/g), low redox potential (-0.76V vs. SHE), and abundance in the Earth's crust. Early PBA cathodes for zinc systems faced significant challenges including poor cycling stability, limited rate capability, and structural degradation during charge-discharge processes.
A pivotal advancement occurred in 2016-2017 when researchers successfully demonstrated the reversible intercalation of zinc ions into various PBA frameworks, particularly copper and nickel hexacyanoferrates. These early prototypes achieved modest capacities of 50-70 mAh/g with limited cycle life, establishing the proof-of-concept for zinc-PBA battery systems.
The period from 2018 to 2020 witnessed substantial improvements in PBA cathode performance through strategic modifications of the crystal structure, controlled defect engineering, and optimization of the electrolyte composition. These efforts resulted in enhanced capacity retention and improved rate capability, with some formulations achieving over 90% capacity retention after 1000 cycles.
Recent developments have focused on addressing the scalability challenges of PBA cathodes. Laboratory-scale synthesis methods, typically producing milligram quantities through co-precipitation or hydrothermal routes, face significant hurdles when translated to industrial production scales. The primary technical objectives now center on developing scalable synthesis protocols that maintain precise control over particle morphology, size distribution, and crystal structure while minimizing defects and impurities.
Current research aims to achieve several critical objectives: increasing the energy density beyond 100 Wh/kg at the cell level, extending cycle life to over 5000 cycles with minimal capacity fade, improving rate performance to support fast charging capabilities, and developing manufacturing processes compatible with existing battery production infrastructure. Additionally, there is growing emphasis on reducing the environmental footprint of PBA synthesis by employing green chemistry principles and minimizing the use of toxic precursors.
The ultimate goal is to position PBA-based AZIBs as a viable alternative to lithium-ion batteries for stationary energy storage applications, particularly in grid-scale implementations where cost, safety, and longevity are paramount considerations.
The initial research on PBAs focused primarily on their application in sodium and potassium-ion batteries. However, around 2015, scientists began investigating their potential in zinc-based systems, recognizing the advantages of zinc's high theoretical capacity (820 mAh/g), low redox potential (-0.76V vs. SHE), and abundance in the Earth's crust. Early PBA cathodes for zinc systems faced significant challenges including poor cycling stability, limited rate capability, and structural degradation during charge-discharge processes.
A pivotal advancement occurred in 2016-2017 when researchers successfully demonstrated the reversible intercalation of zinc ions into various PBA frameworks, particularly copper and nickel hexacyanoferrates. These early prototypes achieved modest capacities of 50-70 mAh/g with limited cycle life, establishing the proof-of-concept for zinc-PBA battery systems.
The period from 2018 to 2020 witnessed substantial improvements in PBA cathode performance through strategic modifications of the crystal structure, controlled defect engineering, and optimization of the electrolyte composition. These efforts resulted in enhanced capacity retention and improved rate capability, with some formulations achieving over 90% capacity retention after 1000 cycles.
Recent developments have focused on addressing the scalability challenges of PBA cathodes. Laboratory-scale synthesis methods, typically producing milligram quantities through co-precipitation or hydrothermal routes, face significant hurdles when translated to industrial production scales. The primary technical objectives now center on developing scalable synthesis protocols that maintain precise control over particle morphology, size distribution, and crystal structure while minimizing defects and impurities.
Current research aims to achieve several critical objectives: increasing the energy density beyond 100 Wh/kg at the cell level, extending cycle life to over 5000 cycles with minimal capacity fade, improving rate performance to support fast charging capabilities, and developing manufacturing processes compatible with existing battery production infrastructure. Additionally, there is growing emphasis on reducing the environmental footprint of PBA synthesis by employing green chemistry principles and minimizing the use of toxic precursors.
The ultimate goal is to position PBA-based AZIBs as a viable alternative to lithium-ion batteries for stationary energy storage applications, particularly in grid-scale implementations where cost, safety, and longevity are paramount considerations.
Market Analysis for Aqueous Zinc Ion Battery Technologies
The global market for aqueous zinc ion batteries (AZIBs) is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable energy storage solutions. The market size for AZIBs was valued at approximately $450 million in 2022 and is projected to reach $1.2 billion by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of 17.8%. This growth trajectory is particularly notable in regions with strong renewable energy initiatives, including Europe, North America, and parts of Asia.
The demand for AZIBs is primarily fueled by their inherent advantages over conventional lithium-ion batteries, including enhanced safety profiles, lower production costs, and reduced environmental impact. These benefits position AZIBs as an attractive alternative for grid-scale energy storage, backup power systems, and certain consumer electronics applications where safety and cost considerations outweigh energy density requirements.
Market segmentation reveals that grid-scale energy storage represents the largest application segment for AZIBs, accounting for roughly 45% of the total market share. This is followed by industrial applications (30%), consumer electronics (15%), and emerging applications such as electric vehicles and portable power solutions (10%). The growing integration of renewable energy sources into power grids is expected to further accelerate demand for grid-scale AZIB solutions.
Regional analysis indicates that Asia-Pacific currently dominates the AZIB market with approximately 40% market share, led by China, Japan, and South Korea. North America follows with 30% market share, while Europe accounts for 25%. The remaining 5% is distributed across other regions. China, in particular, has emerged as both the largest producer and consumer of AZIB technologies, supported by government initiatives promoting clean energy solutions.
Prussian Blue Analog (PBA) cathodes represent a significant segment within the AZIB market, valued at approximately $180 million in 2022. This segment is projected to grow at a faster rate than the overall AZIB market, with an estimated CAGR of 20.5% through 2028. The superior performance characteristics of PBA cathodes, including high stability and excellent cycle life, are driving their adoption across various AZIB applications.
Key market drivers include increasing renewable energy integration, growing demand for safe and sustainable energy storage solutions, and supportive government policies promoting clean energy technologies. Conversely, market restraints include competition from established battery technologies, technical challenges related to scale-up manufacturing, and limited awareness among potential end-users regarding AZIB benefits.
The competitive landscape features both established battery manufacturers expanding into AZIB technologies and specialized startups focused exclusively on zinc-based energy storage solutions. Strategic partnerships between material suppliers, battery manufacturers, and end-users are becoming increasingly common as the industry works to overcome scale-up challenges and accelerate commercial adoption.
The demand for AZIBs is primarily fueled by their inherent advantages over conventional lithium-ion batteries, including enhanced safety profiles, lower production costs, and reduced environmental impact. These benefits position AZIBs as an attractive alternative for grid-scale energy storage, backup power systems, and certain consumer electronics applications where safety and cost considerations outweigh energy density requirements.
Market segmentation reveals that grid-scale energy storage represents the largest application segment for AZIBs, accounting for roughly 45% of the total market share. This is followed by industrial applications (30%), consumer electronics (15%), and emerging applications such as electric vehicles and portable power solutions (10%). The growing integration of renewable energy sources into power grids is expected to further accelerate demand for grid-scale AZIB solutions.
Regional analysis indicates that Asia-Pacific currently dominates the AZIB market with approximately 40% market share, led by China, Japan, and South Korea. North America follows with 30% market share, while Europe accounts for 25%. The remaining 5% is distributed across other regions. China, in particular, has emerged as both the largest producer and consumer of AZIB technologies, supported by government initiatives promoting clean energy solutions.
Prussian Blue Analog (PBA) cathodes represent a significant segment within the AZIB market, valued at approximately $180 million in 2022. This segment is projected to grow at a faster rate than the overall AZIB market, with an estimated CAGR of 20.5% through 2028. The superior performance characteristics of PBA cathodes, including high stability and excellent cycle life, are driving their adoption across various AZIB applications.
Key market drivers include increasing renewable energy integration, growing demand for safe and sustainable energy storage solutions, and supportive government policies promoting clean energy technologies. Conversely, market restraints include competition from established battery technologies, technical challenges related to scale-up manufacturing, and limited awareness among potential end-users regarding AZIB benefits.
The competitive landscape features both established battery manufacturers expanding into AZIB technologies and specialized startups focused exclusively on zinc-based energy storage solutions. Strategic partnerships between material suppliers, battery manufacturers, and end-users are becoming increasingly common as the industry works to overcome scale-up challenges and accelerate commercial adoption.
Technical Barriers in PBA Cathode Scale-Up
The scale-up of Prussian Blue Analog (PBA) cathodes for aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) faces several significant technical barriers that must be addressed before commercial viability can be achieved. One of the primary challenges is the inconsistent synthesis of high-quality PBA materials at large scales. Laboratory-scale synthesis methods often rely on precise control of reaction conditions, including temperature, concentration, and reaction time, which becomes increasingly difficult to maintain uniformly in larger reaction vessels. This leads to batch-to-batch variations in crystal structure, particle size distribution, and electrochemical performance.
Material stability presents another critical barrier. PBAs are known to suffer from structural degradation during cycling, particularly in aqueous environments. The Zn2+ insertion/extraction process can cause lattice distortion and collapse over extended cycling, leading to capacity fading. This issue becomes more pronounced when scaling up, as larger electrode areas may experience non-uniform current distribution and localized stress points that accelerate degradation.
The manufacturing processes for PBA cathodes also pose significant challenges. Current slurry preparation methods developed for small-scale electrodes may not translate effectively to industrial-scale production. Issues such as poor dispersion of active materials, binder compatibility, and electrode thickness uniformity become more problematic at larger scales. Additionally, the drying process for aqueous-based slurries requires careful control to prevent cracking and delamination in larger electrode sheets.
Interfacial engineering between the PBA cathode and the electrolyte represents another barrier. The solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation in AZIBs is not well understood at scale, and controlling this interface becomes more challenging with increased electrode dimensions. Zinc dendrite formation and side reactions at the cathode surface can lead to performance deterioration and safety concerns in larger battery formats.
Cost considerations also present significant hurdles. While PBAs utilize relatively earth-abundant elements compared to lithium-ion battery cathodes, the synthesis processes often involve multiple steps and require precise control, making them expensive to scale. The use of transition metals like copper, iron, and nickel, while less costly than cobalt or lithium, still contributes significantly to the overall material cost when considering industrial production volumes.
Environmental and safety concerns emerge more prominently at scale. The synthesis of PBAs often involves cyanide-containing precursors, which pose handling and waste management challenges. Developing greener synthesis routes that maintain material performance while eliminating toxic precursors remains a significant technical barrier to overcome for industrial-scale production.
Material stability presents another critical barrier. PBAs are known to suffer from structural degradation during cycling, particularly in aqueous environments. The Zn2+ insertion/extraction process can cause lattice distortion and collapse over extended cycling, leading to capacity fading. This issue becomes more pronounced when scaling up, as larger electrode areas may experience non-uniform current distribution and localized stress points that accelerate degradation.
The manufacturing processes for PBA cathodes also pose significant challenges. Current slurry preparation methods developed for small-scale electrodes may not translate effectively to industrial-scale production. Issues such as poor dispersion of active materials, binder compatibility, and electrode thickness uniformity become more problematic at larger scales. Additionally, the drying process for aqueous-based slurries requires careful control to prevent cracking and delamination in larger electrode sheets.
Interfacial engineering between the PBA cathode and the electrolyte represents another barrier. The solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation in AZIBs is not well understood at scale, and controlling this interface becomes more challenging with increased electrode dimensions. Zinc dendrite formation and side reactions at the cathode surface can lead to performance deterioration and safety concerns in larger battery formats.
Cost considerations also present significant hurdles. While PBAs utilize relatively earth-abundant elements compared to lithium-ion battery cathodes, the synthesis processes often involve multiple steps and require precise control, making them expensive to scale. The use of transition metals like copper, iron, and nickel, while less costly than cobalt or lithium, still contributes significantly to the overall material cost when considering industrial production volumes.
Environmental and safety concerns emerge more prominently at scale. The synthesis of PBAs often involves cyanide-containing precursors, which pose handling and waste management challenges. Developing greener synthesis routes that maintain material performance while eliminating toxic precursors remains a significant technical barrier to overcome for industrial-scale production.
Current Scale-Up Methodologies for PBA Cathodes
01 Synthesis and composition optimization of Prussian Blue Analogs
Various methods for synthesizing Prussian Blue Analogs (PBAs) with optimized compositions for use as cathodes in aqueous zinc ion batteries. These methods focus on controlling crystal structure, particle size, and elemental composition to enhance electrochemical performance. Techniques include precipitation methods, hydrothermal synthesis, and post-synthesis treatments to improve stability and ion diffusion properties, which are critical for large-scale applications.- Composition and structure optimization of Prussian Blue Analogs: Optimizing the composition and crystal structure of Prussian Blue Analogs (PBAs) is crucial for enhancing their performance as cathodes in aqueous zinc-ion batteries. This includes controlling the metal ion substitution, vacancy concentration, and crystallinity to improve the electrochemical stability and ion diffusion kinetics. Structural modifications can significantly impact the capacity, cycling stability, and rate capability of PBA cathodes during scale-up production.
- Electrolyte formulation for PBA-based zinc-ion batteries: The composition of aqueous electrolytes plays a critical role in the performance of Prussian Blue Analog cathodes in zinc-ion batteries. Optimized electrolyte formulations can mitigate zinc dendrite formation, reduce side reactions, and enhance zinc ion transport. Additives and pH adjustments in the electrolyte can significantly improve the cycling stability and capacity retention of PBA cathodes during large-scale battery operation.
- Manufacturing techniques for scalable PBA cathode production: Scalable manufacturing processes for Prussian Blue Analog cathodes require careful consideration of synthesis methods, coating techniques, and quality control measures. Continuous flow synthesis, spray drying, and roll-to-roll electrode fabrication are promising approaches for mass production. Controlling particle size distribution, electrode thickness uniformity, and adhesion to current collectors are essential factors for maintaining consistent performance in large-format zinc-ion batteries.
- Interface engineering and protective coatings for PBA cathodes: Interface engineering and protective coatings can significantly enhance the stability and performance of Prussian Blue Analog cathodes in aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Surface modifications using carbon materials, polymers, or metal oxides can protect PBA particles from dissolution and structural degradation during cycling. These protective strategies are particularly important for maintaining electrode integrity during scale-up, where increased electrode dimensions can exacerbate degradation mechanisms.
- Performance evaluation and testing protocols for scaled-up PBA batteries: Standardized testing protocols and performance evaluation metrics are essential for assessing the scalability of Prussian Blue Analog cathodes in zinc-ion batteries. Long-term cycling tests, rate capability assessments, and temperature performance evaluations provide critical data for scale-up considerations. Advanced characterization techniques such as in-situ XRD, operando spectroscopy, and post-mortem analysis help identify failure mechanisms and optimize battery design for commercial applications.
02 Structural modifications for improved ion storage capacity
Structural engineering approaches to enhance the zinc ion storage capacity of Prussian Blue Analog cathodes. These modifications include creating defect-rich structures, controlling vacancy concentrations, and developing hierarchical architectures. By optimizing the crystal lattice and pore structure, these innovations improve ion diffusion pathways and accommodation sites, leading to higher capacity retention during scale-up and extended cycling.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrolyte formulations for enhanced battery performance
Development of specialized electrolyte formulations that work synergistically with Prussian Blue Analog cathodes in aqueous zinc ion batteries. These electrolytes incorporate additives to suppress hydrogen evolution, prevent zinc dendrite formation, and stabilize the cathode-electrolyte interface. Optimized electrolyte compositions are crucial for maintaining performance consistency during scale-up, particularly in preventing capacity fading and extending cycle life.Expand Specific Solutions04 Manufacturing techniques for large-scale production
Industrial manufacturing processes and techniques specifically designed for scaling up the production of Prussian Blue Analog cathodes. These include continuous flow synthesis methods, spray drying, roll-to-roll coating processes, and quality control protocols. The innovations address challenges in maintaining consistent material properties, electrode thickness uniformity, and adhesion to current collectors when transitioning from laboratory to commercial-scale production.Expand Specific Solutions05 Interface engineering and composite materials
Development of composite materials and interface engineering strategies to enhance the performance of Prussian Blue Analog cathodes. These approaches include carbon coating, conductive polymer integration, and creation of hybrid structures with other active materials. The composite structures improve electrical conductivity, mechanical stability, and ion transport properties, which are essential factors for maintaining performance during scale-up to larger battery formats.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Zinc-Ion Battery Development
The aqueous zinc-ion battery market with Prussian Blue Analog (PBA) cathodes is in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing research intensity and commercial interest. The global market for these sustainable energy storage solutions is projected to expand significantly as demand for safer, cost-effective alternatives to lithium-ion batteries grows. Technologically, PBA cathode scale-up faces varying maturity levels across key players. CATL and Altris AB lead commercial development, with Altris achieving small-scale industrial production of Fennac cathodes and planning GWh facilities. Academic institutions like Huazhong University of Science & Technology and Northwestern University are advancing fundamental research, while Toyota, Sharp, and AIST contribute significant industrial R&D. Bangpu Recycling companies are positioning for the circular economy aspects, addressing end-of-life considerations essential for large-scale deployment.
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd. (CATL) has developed an advanced scale-up methodology for Prussian Blue Analog (PBA) cathodes in aqueous zinc ion batteries. Their approach focuses on optimizing the synthesis process through a controlled co-precipitation method that maintains precise stoichiometry during large-scale production. CATL employs a proprietary flow reactor system that ensures uniform particle size distribution and crystal structure consistency across batches. Their process incorporates real-time monitoring of reaction parameters including pH, temperature, and concentration gradients to maintain quality during scale-up. Additionally, CATL has implemented innovative post-synthesis treatments including controlled thermal annealing and surface modification techniques to enhance the structural stability and cycling performance of PBA cathodes. Their manufacturing process addresses common challenges in PBA production such as controlling vacancies and water content in the crystal structure, which significantly impacts electrochemical performance.
Strengths: CATL's extensive manufacturing infrastructure allows for rapid scale-up from laboratory to industrial production. Their established quality control systems ensure consistent performance across large production volumes. Weaknesses: Their approach may require specialized equipment and precise process control that increases production costs compared to conventional cathode materials.
Shenzhen Enyou New Energy Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Shenzhen Enyou New Energy Technology has developed a comprehensive scale-up strategy for Prussian Blue Analog cathodes focused on addressing key industrial manufacturing challenges. Their approach employs a modified room-temperature co-precipitation method that significantly reduces energy consumption during synthesis while maintaining precise control over crystal structure. The company has engineered specialized mixing equipment that ensures homogeneous reaction conditions even in large-volume reactors, preventing localized concentration gradients that can lead to structural defects. Their technology incorporates innovative stabilization techniques including controlled ion exchange processes that enhance the structural integrity of PBA frameworks during cycling. Shenzhen Enyou has also developed advanced electrode formulation methods that optimize the ratio of active material, conductive additives, and binders specifically for aqueous zinc ion battery applications. Their manufacturing process includes specialized calendering techniques that achieve optimal electrode density while preserving the porous structure necessary for efficient ion transport.
Strengths: Their room-temperature synthesis approach significantly reduces energy costs during manufacturing. Their electrode formulation technology achieves excellent adhesion and electrical contact between components. Weaknesses: Their PBA materials may exhibit slower reaction kinetics compared to some competitors, potentially limiting high-rate performance in fast-charging applications.
Critical Patents in PBA Synthesis and Manufacturing
Zinc-ion secondary battery comprising Prussian Blue Analogous(PBAs) cathode
PatentActiveKR1020210060910A
Innovation
- A zinc ion secondary battery utilizing a Prussian Blue Analog (PBA) positive electrode and an aqueous electrolyte containing zinc ions, with materials like CuHCF, FeHCF, and MnHCMn, enabling high conductivity and rapid zinc ion diffusion.
Rechargable zinc ion battery
PatentActiveIN202321012312A
Innovation
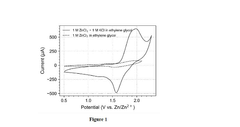
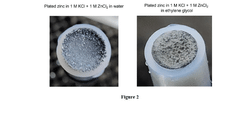
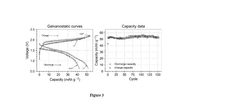
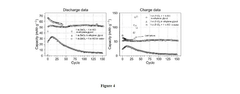
- A high-voltage rechargeable zinc ion battery using a dual ion electrolyte with zinc chloride and potassium chloride in ethylene glycol, featuring a copper hexacyanoferrate cathode that preferentially intercalates potassium ions, reducing wear and tear, and a zinc foil anode to address these limitations.
Environmental Impact Assessment of PBA Manufacturing
The manufacturing scale-up of Prussian Blue Analog (PBA) cathodes for aqueous zinc ion batteries necessitates a comprehensive environmental impact assessment to ensure sustainable industrial implementation. Current laboratory-scale synthesis methods typically involve chemical precipitation reactions using metal salts and hexacyanoferrate precursors, which generate various waste streams containing potentially harmful chemicals.
When scaled to industrial production levels, these processes would significantly increase chemical consumption and waste generation. The primary environmental concerns include the release of cyanide-containing compounds, heavy metal contamination, and the substantial water usage required for synthesis and purification steps. Particularly concerning is the potential for hexacyanoferrate complexes to decompose under certain conditions, releasing cyanide ions that pose serious environmental and health risks.
Energy consumption represents another critical environmental factor in PBA manufacturing. The synthesis often requires controlled temperature conditions and extended reaction times, which translate to considerable energy demands at industrial scale. Post-synthesis treatments such as filtration, washing, and drying further contribute to the energy footprint. Life cycle assessment studies indicate that the energy-intensive nature of these processes could potentially offset some of the environmental benefits gained from the batteries themselves.
Water usage and contamination present additional challenges. The aqueous synthesis routes commonly employed for PBAs require substantial volumes of water, both as reaction medium and for purification steps. Scaling up would exponentially increase water consumption, while the resulting wastewater would contain dissolved metal ions and other chemical residues requiring specialized treatment before discharge.
Chemical waste management constitutes a significant concern for industrial-scale PBA production. The synthesis generates various byproducts and unreacted precursors that must be properly handled. Current laboratory practices often involve simple neutralization and dilution approaches that would be inadequate at industrial scale, necessitating more sophisticated waste treatment systems to prevent environmental contamination.
Opportunities for environmental impact mitigation do exist through process optimization. Research indicates that greener synthesis routes using reduced-toxicity precursors, solvent recycling systems, and energy-efficient reaction conditions could substantially lower the environmental footprint. Additionally, implementing closed-loop manufacturing systems that recover and reuse chemical precursors would significantly reduce waste generation while improving economic viability.
When scaled to industrial production levels, these processes would significantly increase chemical consumption and waste generation. The primary environmental concerns include the release of cyanide-containing compounds, heavy metal contamination, and the substantial water usage required for synthesis and purification steps. Particularly concerning is the potential for hexacyanoferrate complexes to decompose under certain conditions, releasing cyanide ions that pose serious environmental and health risks.
Energy consumption represents another critical environmental factor in PBA manufacturing. The synthesis often requires controlled temperature conditions and extended reaction times, which translate to considerable energy demands at industrial scale. Post-synthesis treatments such as filtration, washing, and drying further contribute to the energy footprint. Life cycle assessment studies indicate that the energy-intensive nature of these processes could potentially offset some of the environmental benefits gained from the batteries themselves.
Water usage and contamination present additional challenges. The aqueous synthesis routes commonly employed for PBAs require substantial volumes of water, both as reaction medium and for purification steps. Scaling up would exponentially increase water consumption, while the resulting wastewater would contain dissolved metal ions and other chemical residues requiring specialized treatment before discharge.
Chemical waste management constitutes a significant concern for industrial-scale PBA production. The synthesis generates various byproducts and unreacted precursors that must be properly handled. Current laboratory practices often involve simple neutralization and dilution approaches that would be inadequate at industrial scale, necessitating more sophisticated waste treatment systems to prevent environmental contamination.
Opportunities for environmental impact mitigation do exist through process optimization. Research indicates that greener synthesis routes using reduced-toxicity precursors, solvent recycling systems, and energy-efficient reaction conditions could substantially lower the environmental footprint. Additionally, implementing closed-loop manufacturing systems that recover and reuse chemical precursors would significantly reduce waste generation while improving economic viability.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
The economic viability of scaling up Prussian Blue Analog (PBA) cathodes for aqueous zinc ion batteries represents a critical factor in their commercial adoption. Current cost analysis indicates that raw material expenses for PBA synthesis are relatively favorable compared to conventional lithium-ion battery cathodes. The primary components—iron or other transition metal salts, hexacyanoferrate precursors, and basic reagents—benefit from established supply chains in the chemical industry, resulting in moderate procurement costs.
Manufacturing processes for PBA cathodes demonstrate promising economic potential when scaled. The ambient-temperature synthesis methods require significantly less energy input than high-temperature calcination processes used for oxide-based cathodes. This translates to lower capital expenditure for production facilities and reduced operational costs. Preliminary calculations suggest that large-scale production could achieve manufacturing costs below $80 per kWh, positioning these batteries competitively in the stationary storage market segment.
Investment requirements for scaling up present a balanced profile. The equipment needed for precipitation reactions, filtration, and drying processes leverages existing chemical manufacturing infrastructure, minimizing specialized capital investments. However, quality control systems for ensuring consistent crystal structure and composition represent additional cost factors that must be incorporated into economic models.
Life-cycle cost analysis reveals particular advantages for PBA-based zinc ion batteries. Their projected longer cycle life compared to lead-acid alternatives and the absence of expensive thermal management systems required by lithium-ion batteries contribute to favorable total cost of ownership metrics. Economic modeling suggests a potential levelized cost of storage (LCOS) between $0.15-0.25 per kWh-cycle, depending on application parameters and scale.
Market entry strategies must consider production volume thresholds for economic viability. Initial analysis indicates that medium-scale production (100-500 MWh annual capacity) represents the minimum economically sustainable operation, with significant cost improvements at gigawatt-hour scales. Strategic partnerships with existing battery manufacturers could reduce capital requirements through shared infrastructure utilization.
Sensitivity analysis highlights that precursor purity requirements significantly impact overall economics. Research into utilizing lower-purity starting materials while maintaining electrochemical performance could substantially improve cost structures. Additionally, recovery and recycling processes for zinc and PBA materials present opportunities to further enhance economic sustainability through circular economy approaches.
Manufacturing processes for PBA cathodes demonstrate promising economic potential when scaled. The ambient-temperature synthesis methods require significantly less energy input than high-temperature calcination processes used for oxide-based cathodes. This translates to lower capital expenditure for production facilities and reduced operational costs. Preliminary calculations suggest that large-scale production could achieve manufacturing costs below $80 per kWh, positioning these batteries competitively in the stationary storage market segment.
Investment requirements for scaling up present a balanced profile. The equipment needed for precipitation reactions, filtration, and drying processes leverages existing chemical manufacturing infrastructure, minimizing specialized capital investments. However, quality control systems for ensuring consistent crystal structure and composition represent additional cost factors that must be incorporated into economic models.
Life-cycle cost analysis reveals particular advantages for PBA-based zinc ion batteries. Their projected longer cycle life compared to lead-acid alternatives and the absence of expensive thermal management systems required by lithium-ion batteries contribute to favorable total cost of ownership metrics. Economic modeling suggests a potential levelized cost of storage (LCOS) between $0.15-0.25 per kWh-cycle, depending on application parameters and scale.
Market entry strategies must consider production volume thresholds for economic viability. Initial analysis indicates that medium-scale production (100-500 MWh annual capacity) represents the minimum economically sustainable operation, with significant cost improvements at gigawatt-hour scales. Strategic partnerships with existing battery manufacturers could reduce capital requirements through shared infrastructure utilization.
Sensitivity analysis highlights that precursor purity requirements significantly impact overall economics. Research into utilizing lower-purity starting materials while maintaining electrochemical performance could substantially improve cost structures. Additionally, recovery and recycling processes for zinc and PBA materials present opportunities to further enhance economic sustainability through circular economy approaches.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!