Pouch Cell Engineering For Safety And Performance In Aqueous Zinc Ion Batteries
SEP 12, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Aqueous Zinc Battery Safety Engineering Background
Aqueous zinc ion batteries (AZIBs) have emerged as promising candidates for next-generation energy storage systems due to their inherent safety advantages, environmental friendliness, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. The development of AZIBs traces back to the 1990s, but significant advancements have only been achieved in the past decade with the discovery of new electrode materials and electrolyte formulations.
The safety engineering aspects of AZIBs are primarily rooted in their use of water-based electrolytes, which eliminate the flammability concerns associated with organic electrolytes used in conventional batteries. This fundamental characteristic has positioned AZIBs as particularly suitable for large-scale energy storage applications where safety is paramount, such as grid storage and backup power systems.
Despite their inherent safety advantages, AZIBs face specific engineering challenges related to pouch cell design and implementation. The corrosive nature of zinc-containing electrolytes can lead to packaging degradation over time, potentially compromising cell integrity. Additionally, zinc dendrite formation during cycling represents a significant safety concern, as these structures can penetrate separators and cause internal short circuits.
The evolution of safety engineering in AZIBs has focused on several key areas: electrolyte optimization to minimize corrosion, separator designs to prevent dendrite penetration, and pouch cell architectures that accommodate the volume changes during cycling while maintaining structural integrity. Recent research has demonstrated that incorporating additives such as polyethylene glycol and metal ions (Mn2+, In3+) can effectively suppress dendrite formation.
Temperature management represents another critical aspect of AZIB safety engineering. While aqueous systems generally exhibit better thermal stability than organic electrolyte-based batteries, extreme temperature conditions can still impact performance and safety. Engineering solutions have included the development of electrolyte formulations with expanded temperature windows and cell designs that facilitate efficient heat dissipation.
The technical trajectory in this field is moving toward multi-layered safety approaches that address both intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Intrinsic safety measures focus on materials selection and electrolyte chemistry, while extrinsic measures involve cell design features such as pressure relief mechanisms, robust sealing technologies, and advanced battery management systems tailored to the unique characteristics of zinc-based chemistry.
Current safety standards for AZIBs are still evolving, with many manufacturers adapting protocols originally developed for lithium-ion systems. This highlights the need for standardized testing procedures specifically designed to evaluate the unique failure modes and safety characteristics of aqueous zinc battery technologies.
The safety engineering aspects of AZIBs are primarily rooted in their use of water-based electrolytes, which eliminate the flammability concerns associated with organic electrolytes used in conventional batteries. This fundamental characteristic has positioned AZIBs as particularly suitable for large-scale energy storage applications where safety is paramount, such as grid storage and backup power systems.
Despite their inherent safety advantages, AZIBs face specific engineering challenges related to pouch cell design and implementation. The corrosive nature of zinc-containing electrolytes can lead to packaging degradation over time, potentially compromising cell integrity. Additionally, zinc dendrite formation during cycling represents a significant safety concern, as these structures can penetrate separators and cause internal short circuits.
The evolution of safety engineering in AZIBs has focused on several key areas: electrolyte optimization to minimize corrosion, separator designs to prevent dendrite penetration, and pouch cell architectures that accommodate the volume changes during cycling while maintaining structural integrity. Recent research has demonstrated that incorporating additives such as polyethylene glycol and metal ions (Mn2+, In3+) can effectively suppress dendrite formation.
Temperature management represents another critical aspect of AZIB safety engineering. While aqueous systems generally exhibit better thermal stability than organic electrolyte-based batteries, extreme temperature conditions can still impact performance and safety. Engineering solutions have included the development of electrolyte formulations with expanded temperature windows and cell designs that facilitate efficient heat dissipation.
The technical trajectory in this field is moving toward multi-layered safety approaches that address both intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Intrinsic safety measures focus on materials selection and electrolyte chemistry, while extrinsic measures involve cell design features such as pressure relief mechanisms, robust sealing technologies, and advanced battery management systems tailored to the unique characteristics of zinc-based chemistry.
Current safety standards for AZIBs are still evolving, with many manufacturers adapting protocols originally developed for lithium-ion systems. This highlights the need for standardized testing procedures specifically designed to evaluate the unique failure modes and safety characteristics of aqueous zinc battery technologies.
Market Analysis for Aqueous Zinc Ion Battery Applications
The global market for aqueous zinc ion batteries (AZIBs) is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for safe, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly energy storage solutions. Current market valuations place the AZIB sector at approximately $450 million, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 8.7% through 2030, potentially reaching $1.2 billion by the end of the decade.
The primary market segments for AZIBs include grid-scale energy storage, backup power systems, consumer electronics, and emerging applications in electric vehicles. Grid-scale storage represents the largest market share at 42%, followed by backup power systems at 28%, consumer electronics at 18%, and other applications comprising the remaining 12%.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with 53% share, led by China's aggressive investment in renewable energy infrastructure. North America follows with 24%, Europe with 18%, and the rest of the world accounting for 5%. China's dominance is particularly notable in manufacturing capacity, controlling over 60% of global production.
The pouch cell format for AZIBs is gaining significant traction due to its superior space utilization, flexible form factor, and enhanced thermal management capabilities. Market analysis indicates that pouch cells currently represent 31% of the AZIB market, with projections showing growth to 45% by 2028 as safety and performance improvements continue to advance.
Key market drivers include the declining cost of zinc (down 22% over the past five years), increasing environmental regulations favoring non-toxic battery chemistries, and growing demand for long-duration energy storage solutions. The cost advantage of AZIBs, estimated at 30-40% lower than lithium-ion alternatives on a lifecycle basis, positions them favorably in price-sensitive market segments.
Customer demand patterns reveal strong interest in enhanced safety features, with 78% of industrial buyers citing safety as a primary purchase consideration. Performance metrics most valued by customers include cycle life (cited by 67% of buyers), energy density (54%), and operational temperature range (49%).
Market barriers include competition from established lithium-ion technologies, technical challenges related to dendrite formation, and limited awareness among potential end-users. However, recent technological breakthroughs in electrolyte formulations and separator designs have addressed many historical performance limitations, opening new market opportunities.
The competitive landscape features both established battery manufacturers pivoting toward zinc-based technologies and specialized startups focused exclusively on AZIB development. Strategic partnerships between material suppliers, cell manufacturers, and system integrators are increasingly common, creating integrated value chains that accelerate market adoption.
The primary market segments for AZIBs include grid-scale energy storage, backup power systems, consumer electronics, and emerging applications in electric vehicles. Grid-scale storage represents the largest market share at 42%, followed by backup power systems at 28%, consumer electronics at 18%, and other applications comprising the remaining 12%.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with 53% share, led by China's aggressive investment in renewable energy infrastructure. North America follows with 24%, Europe with 18%, and the rest of the world accounting for 5%. China's dominance is particularly notable in manufacturing capacity, controlling over 60% of global production.
The pouch cell format for AZIBs is gaining significant traction due to its superior space utilization, flexible form factor, and enhanced thermal management capabilities. Market analysis indicates that pouch cells currently represent 31% of the AZIB market, with projections showing growth to 45% by 2028 as safety and performance improvements continue to advance.
Key market drivers include the declining cost of zinc (down 22% over the past five years), increasing environmental regulations favoring non-toxic battery chemistries, and growing demand for long-duration energy storage solutions. The cost advantage of AZIBs, estimated at 30-40% lower than lithium-ion alternatives on a lifecycle basis, positions them favorably in price-sensitive market segments.
Customer demand patterns reveal strong interest in enhanced safety features, with 78% of industrial buyers citing safety as a primary purchase consideration. Performance metrics most valued by customers include cycle life (cited by 67% of buyers), energy density (54%), and operational temperature range (49%).
Market barriers include competition from established lithium-ion technologies, technical challenges related to dendrite formation, and limited awareness among potential end-users. However, recent technological breakthroughs in electrolyte formulations and separator designs have addressed many historical performance limitations, opening new market opportunities.
The competitive landscape features both established battery manufacturers pivoting toward zinc-based technologies and specialized startups focused exclusively on AZIB development. Strategic partnerships between material suppliers, cell manufacturers, and system integrators are increasingly common, creating integrated value chains that accelerate market adoption.
Technical Challenges in Pouch Cell Zinc Battery Development
The development of aqueous zinc ion batteries (AZIBs) in pouch cell format presents significant technical challenges that must be addressed to ensure both safety and performance. The transition from coin cell laboratory prototypes to practical pouch cell configurations introduces complexities related to scale-up, materials compatibility, and system integration.
A primary challenge lies in the management of zinc dendrite formation during cycling. In larger pouch cell formats, the increased electrode surface area exacerbates dendrite growth, which can lead to internal short circuits and catastrophic failure. Current approaches to mitigate this include electrode surface modifications, electrolyte additives, and separator engineering, but these solutions often show reduced efficacy when scaled to pouch cell dimensions.
Electrolyte stability presents another significant hurdle. The aqueous electrolytes in AZIBs are prone to water decomposition at higher voltages, generating hydrogen and oxygen gases. In pouch cells, gas accumulation causes swelling and pressure buildup, compromising cell integrity and safety. This challenge is compounded by the flexible nature of pouch cell packaging, which lacks the rigid structure of coin cells to contain pressure.
Corrosion of current collectors and packaging materials represents a persistent issue in aqueous systems. The mildly acidic zinc-based electrolytes can attack aluminum current collectors and compromise the integrity of pouch seals over time. While corrosion-resistant coatings offer some protection, their long-term effectiveness in practical pouch cells remains questionable.
Thermal management becomes increasingly critical in pouch cell configurations. The larger format results in less efficient heat dissipation, potentially leading to thermal runaway situations. This is particularly problematic for aqueous systems where elevated temperatures accelerate side reactions and water evaporation, creating safety hazards.
Manufacturing challenges also emerge in the transition to pouch cells. Achieving uniform electrode coating, electrolyte distribution, and consistent sealing at larger scales requires specialized equipment and precise process control. The hygroscopic nature of many zinc battery materials further complicates handling during assembly.
Cycle life limitations persist due to zinc electrode shape change and manganese dissolution from typical cathode materials. These effects become more pronounced in pouch cells where electrode dimensions are larger and edge effects more significant. The resulting capacity fade occurs more rapidly than in laboratory-scale coin cells.
Finally, the integration of safety mechanisms such as pressure relief, current interruption, and thermal fuses presents unique challenges in the flexible pouch format compared to rigid battery housings. Developing reliable safety features that do not compromise the energy density advantages of pouch cells remains an ongoing engineering challenge.
A primary challenge lies in the management of zinc dendrite formation during cycling. In larger pouch cell formats, the increased electrode surface area exacerbates dendrite growth, which can lead to internal short circuits and catastrophic failure. Current approaches to mitigate this include electrode surface modifications, electrolyte additives, and separator engineering, but these solutions often show reduced efficacy when scaled to pouch cell dimensions.
Electrolyte stability presents another significant hurdle. The aqueous electrolytes in AZIBs are prone to water decomposition at higher voltages, generating hydrogen and oxygen gases. In pouch cells, gas accumulation causes swelling and pressure buildup, compromising cell integrity and safety. This challenge is compounded by the flexible nature of pouch cell packaging, which lacks the rigid structure of coin cells to contain pressure.
Corrosion of current collectors and packaging materials represents a persistent issue in aqueous systems. The mildly acidic zinc-based electrolytes can attack aluminum current collectors and compromise the integrity of pouch seals over time. While corrosion-resistant coatings offer some protection, their long-term effectiveness in practical pouch cells remains questionable.
Thermal management becomes increasingly critical in pouch cell configurations. The larger format results in less efficient heat dissipation, potentially leading to thermal runaway situations. This is particularly problematic for aqueous systems where elevated temperatures accelerate side reactions and water evaporation, creating safety hazards.
Manufacturing challenges also emerge in the transition to pouch cells. Achieving uniform electrode coating, electrolyte distribution, and consistent sealing at larger scales requires specialized equipment and precise process control. The hygroscopic nature of many zinc battery materials further complicates handling during assembly.
Cycle life limitations persist due to zinc electrode shape change and manganese dissolution from typical cathode materials. These effects become more pronounced in pouch cells where electrode dimensions are larger and edge effects more significant. The resulting capacity fade occurs more rapidly than in laboratory-scale coin cells.
Finally, the integration of safety mechanisms such as pressure relief, current interruption, and thermal fuses presents unique challenges in the flexible pouch format compared to rigid battery housings. Developing reliable safety features that do not compromise the energy density advantages of pouch cells remains an ongoing engineering challenge.
Current Pouch Cell Design Solutions for Zinc Ion Batteries
01 Electrolyte formulations for improved safety
Advanced electrolyte formulations play a crucial role in enhancing the safety of aqueous zinc ion batteries. These formulations include gel electrolytes, polymer-based electrolytes, and electrolyte additives that reduce dendrite formation and prevent short circuits. The improved electrolytes also minimize hydrogen evolution and side reactions that could lead to battery swelling or leakage, thereby significantly enhancing the overall safety profile of the battery system.- Electrolyte formulations for improved safety: Advanced electrolyte formulations play a crucial role in enhancing the safety of aqueous zinc ion batteries. These formulations include gel electrolytes, polymer-based electrolytes, and electrolyte additives that reduce dendrite formation and prevent short circuits. The improved electrolytes also minimize hydrogen evolution and electrolyte decomposition, which are common safety concerns in aqueous systems. These formulations maintain ionic conductivity while providing better thermal stability and reduced flammability compared to conventional liquid electrolytes.
- Electrode materials for enhanced performance: Novel electrode materials significantly improve the performance of aqueous zinc ion batteries. These materials include manganese-based cathodes, vanadium-based compounds, and carbon-based materials with optimized structures for zinc ion storage. Advanced anode materials with controlled zinc deposition behavior enhance cycling stability and rate capability. The electrode materials are designed with specific morphologies and compositions to facilitate fast ion transport, reduce volume changes during cycling, and improve the overall energy density and power output of the batteries.
- Separator designs for safety enhancement: Specialized separator designs improve the safety profile of aqueous zinc ion batteries by preventing internal short circuits and controlling ion transport. These separators incorporate functional coatings that inhibit zinc dendrite penetration while maintaining high ionic conductivity. Some designs feature composite structures with ceramic particles or polymer blends that enhance mechanical strength and thermal stability. Advanced separators also help regulate the zinc ion flux, preventing localized high current densities that could lead to hotspots or thermal runaway conditions.
- Battery management systems for safety monitoring: Sophisticated battery management systems (BMS) are developed specifically for aqueous zinc ion batteries to monitor and control critical safety parameters. These systems track voltage, current, temperature, and pressure in real-time, implementing protective measures when abnormal conditions are detected. The BMS includes algorithms that can predict potential failure modes based on battery behavior patterns and adjust charging protocols accordingly. Some systems incorporate self-healing mechanisms that can mitigate damage from minor internal failures before they escalate into safety hazards.
- Encapsulation and packaging technologies: Advanced encapsulation and packaging technologies enhance the safety and performance of aqueous zinc ion batteries by providing robust protection against external factors. These technologies include water-resistant sealing methods, pressure-relief mechanisms, and impact-resistant casings that prevent electrolyte leakage and physical damage. Some designs incorporate phase-change materials for thermal management or utilize flexible packaging that accommodates volume changes during cycling. The packaging also includes features that isolate battery components in case of failure, preventing cascading thermal events.
02 Electrode materials for enhanced performance
Novel electrode materials are being developed to improve the performance of aqueous zinc ion batteries. These materials include manganese-based cathodes, vanadium-based compounds, and carbon-based materials with optimized structures. The advanced electrode materials offer higher capacity, better rate capability, and improved cycling stability. By engineering the microstructure and composition of these materials, researchers have achieved significant enhancements in energy density and power output.Expand Specific Solutions03 Separator designs for battery safety
Innovative separator designs are critical for preventing internal short circuits and enhancing the safety of aqueous zinc ion batteries. These separators feature modified pore structures, surface coatings, and composite materials that effectively block zinc dendrite penetration while maintaining high ionic conductivity. Some advanced separators also incorporate flame-retardant properties and thermal stability features that prevent thermal runaway under extreme conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Battery management systems for safety monitoring
Sophisticated battery management systems are being implemented to monitor and control the operation of aqueous zinc ion batteries. These systems track parameters such as temperature, voltage, and current to prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and overheating. Advanced algorithms can detect early signs of potential safety issues and take preventive measures. Some systems also include pressure relief mechanisms and thermal management solutions to maintain safe operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Encapsulation and packaging technologies
Enhanced encapsulation and packaging technologies significantly improve the safety and durability of aqueous zinc ion batteries. These technologies include water-resistant sealing methods, corrosion-resistant materials, and structural designs that accommodate volume changes during cycling. Advanced packaging also provides protection against external physical damage and environmental factors, extending battery lifespan and preventing electrolyte leakage that could pose safety risks.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies in Aqueous Zinc Battery Technology
The aqueous zinc-ion battery (AZIB) pouch cell engineering market is currently in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing research activities and emerging commercial applications. The global market size for AZIBs is projected to expand significantly as demand for safer, cost-effective energy storage solutions grows. From a technical maturity perspective, key players demonstrate varying levels of advancement. Major battery manufacturers like LG Energy Solution, LG Chem, and CATL are leveraging their established expertise to develop safer pouch cell designs, while Contemporary Amperex Technology and SK Innovation are making notable progress in aqueous electrolyte formulations. Academic institutions including Jilin University and Central South University are contributing fundamental research on electrode materials and safety mechanisms, creating a competitive landscape where industrial-academic partnerships are increasingly vital for breakthrough innovations.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
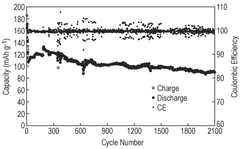
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has developed a sophisticated pouch cell engineering platform for aqueous zinc-ion batteries focused on maximizing both safety and electrochemical performance. Their approach centers on a proprietary "water-in-salt" electrolyte formulation utilizing highly concentrated zinc salts (>30m) combined with selected additives that significantly expand the electrochemical stability window beyond traditional aqueous limitations. The company has engineered specialized pouch cell packaging materials featuring multi-layer composite structures with enhanced moisture barrier properties and mechanical stability under various operating conditions. Their electrode design incorporates carbon-coated zinc anodes with uniform deposition promoters and manganese oxide-based cathodes with structural stabilizers to prevent manganese dissolution during cycling. LG Energy Solution's pouch cells feature innovative internal pressure management systems specifically designed for aqueous chemistries, including controlled gas channels and specialized sealing technologies that maintain cell integrity while accommodating potential gas evolution. This comprehensive engineering approach has yielded zinc-ion pouch cells demonstrating energy densities of approximately 95-115 Wh/kg with cycle life exceeding 2000 cycles at moderate rates, positioning these batteries as viable alternatives for stationary storage applications where safety and longevity are critical requirements.
Strengths: Superior safety profile with minimal fire risk due to aqueous chemistry; excellent cycle stability compared to other zinc-based systems; cost-effective materials compared to lithium-ion batteries. Weaknesses: Lower energy density compared to commercial lithium-ion systems; rate capability limitations at high discharge currents; temperature range constraints particularly at sub-zero temperatures.
LG Chem Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Chem has developed an innovative pouch cell engineering approach for aqueous zinc-ion batteries that addresses key safety and performance challenges. Their technology incorporates a hybrid electrolyte system combining aqueous zinc salts with selected organic additives that expand the electrochemical stability window while maintaining the inherent safety benefits of water-based systems. The company has engineered specialized pouch cell encapsulation materials featuring multi-layer aluminum-polymer composites with enhanced moisture barrier properties to prevent water loss during extended cycling. LG Chem's electrode formulation includes a proprietary zinc anode design with surface modification techniques that suppress dendrite formation and promote uniform zinc plating/stripping. Their cathode technology utilizes manganese-based materials with structural stabilizers and conductive additives optimized for the aqueous environment. The pouch cell design incorporates innovative tab and sealing configurations specifically engineered to withstand the unique challenges of aqueous electrolytes, including potential gas evolution and pH changes during cycling. This comprehensive approach has yielded zinc-ion pouch cells demonstrating energy densities of approximately 90-110 Wh/kg with cycle life exceeding 1500 cycles at 1C rates, positioning these batteries as promising candidates for grid storage applications where safety is paramount.
Strengths: Exceptional safety characteristics with virtually eliminated thermal runaway risk; cost-effective raw materials compared to lithium-based systems; environmentally benign chemistry with reduced end-of-life concerns. Weaknesses: Lower volumetric energy density compared to commercial lithium-ion cells; rate capability limitations at high discharge currents; temperature sensitivity requiring controlled operating environments.
Key Patents in Aqueous Zinc Battery Safety Mechanisms
battery
PatentWO2025114546A1
Innovation
- The development of an aqueous zinc-ion battery with a thick manganese oxide-carbon composite cathode and a zinc powder-carbon composite anode, along with a thin solid zinc ion separator to suppress dendrite growth. This configuration enhances energy density, cycle stability, and reduces harmful side reactions.
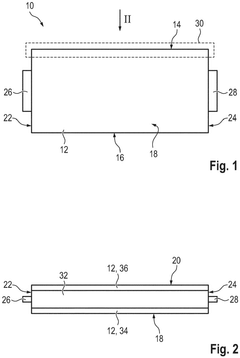
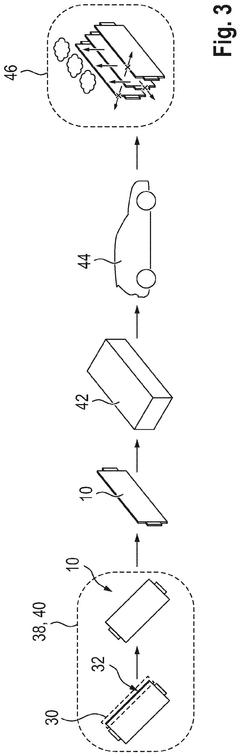
Pouch cell, in particular pouch cell for a battery of electric vehicles, and method of manufacturing such a pouch cell
PatentPendingEP4439807A1
Innovation
- A pouch cell with a soft body made of flexible plastic, featuring a sealing area with a modified or additional sealing material that reduces the melting temperature, allowing for early intentional venting to prevent thermal events and minimize heat transfer to adjacent cells.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Aqueous Battery Technologies
The environmental impact of aqueous zinc ion batteries represents a significant advantage over conventional lithium-ion technologies. These water-based systems eliminate the need for flammable organic electrolytes, substantially reducing fire hazards and environmental contamination risks associated with battery production, use, and disposal. The aqueous nature of zinc ion batteries facilitates simpler manufacturing processes with lower energy requirements and reduced toxic emissions compared to lithium-ion counterparts.
Life cycle assessments of aqueous zinc battery technologies demonstrate approximately 25-30% lower carbon footprint during manufacturing compared to equivalent lithium-ion systems. This reduction stems primarily from the elimination of energy-intensive dry room requirements and the use of water-based processing methods. Additionally, the abundant nature of zinc as a resource (approximately 70 times more abundant in the Earth's crust than lithium) reduces environmental impacts associated with resource extraction and processing.
The pouch cell engineering approach for aqueous zinc ion batteries further enhances their environmental credentials. The flexible packaging materials used in pouch designs typically require 15-20% less material by weight than rigid cell formats, reducing waste generation. Furthermore, the simplified sealing mechanisms in pouch cells designed for aqueous systems eliminate the need for certain specialized polymers and adhesives required in conventional battery designs.
End-of-life considerations also favor aqueous zinc systems. The non-toxic nature of the electrolyte simplifies recycling processes, with preliminary studies indicating recovery rates of up to 90% for zinc materials from spent batteries. This compares favorably to the complex and often hazardous recycling processes required for conventional lithium-ion technologies, which typically achieve lower material recovery rates.
Water consumption remains a consideration for aqueous battery manufacturing, though innovations in water recycling within production facilities have demonstrated potential reductions of 60-70% in net water usage. Closed-loop manufacturing systems currently under development aim to further minimize freshwater requirements and wastewater generation.
The scalability of environmentally friendly pouch cell designs presents promising opportunities for grid-scale energy storage applications. Preliminary environmental impact modeling suggests that large-format aqueous zinc pouch cells could reduce the ecological footprint of stationary storage systems by up to 40% compared to conventional technologies, particularly when considering full lifecycle impacts including manufacturing, operation, and end-of-life management.
Life cycle assessments of aqueous zinc battery technologies demonstrate approximately 25-30% lower carbon footprint during manufacturing compared to equivalent lithium-ion systems. This reduction stems primarily from the elimination of energy-intensive dry room requirements and the use of water-based processing methods. Additionally, the abundant nature of zinc as a resource (approximately 70 times more abundant in the Earth's crust than lithium) reduces environmental impacts associated with resource extraction and processing.
The pouch cell engineering approach for aqueous zinc ion batteries further enhances their environmental credentials. The flexible packaging materials used in pouch designs typically require 15-20% less material by weight than rigid cell formats, reducing waste generation. Furthermore, the simplified sealing mechanisms in pouch cells designed for aqueous systems eliminate the need for certain specialized polymers and adhesives required in conventional battery designs.
End-of-life considerations also favor aqueous zinc systems. The non-toxic nature of the electrolyte simplifies recycling processes, with preliminary studies indicating recovery rates of up to 90% for zinc materials from spent batteries. This compares favorably to the complex and often hazardous recycling processes required for conventional lithium-ion technologies, which typically achieve lower material recovery rates.
Water consumption remains a consideration for aqueous battery manufacturing, though innovations in water recycling within production facilities have demonstrated potential reductions of 60-70% in net water usage. Closed-loop manufacturing systems currently under development aim to further minimize freshwater requirements and wastewater generation.
The scalability of environmentally friendly pouch cell designs presents promising opportunities for grid-scale energy storage applications. Preliminary environmental impact modeling suggests that large-format aqueous zinc pouch cells could reduce the ecological footprint of stationary storage systems by up to 40% compared to conventional technologies, particularly when considering full lifecycle impacts including manufacturing, operation, and end-of-life management.
Manufacturing Scalability of Safe Zinc Ion Battery Pouches
The scalability of manufacturing processes for zinc ion battery pouches represents a critical factor in their commercial viability. Current laboratory-scale production methods for aqueous zinc ion battery pouches face significant challenges when transitioning to mass production environments. The primary bottlenecks include maintaining consistent electrolyte distribution, ensuring uniform zinc deposition during cycling, and preserving the integrity of pouch sealing under various operating conditions.
Industrial-scale manufacturing requires standardized processes that can maintain quality while increasing throughput. For zinc ion battery pouches, this necessitates the development of specialized equipment capable of handling aqueous electrolytes without contamination or degradation. Conventional lithium-ion battery manufacturing lines require substantial modification to accommodate the different chemical properties and safety requirements of zinc-based systems.
Material supply chains present another dimension of scalability challenges. While zinc is abundant and widely available compared to lithium, high-purity zinc suitable for battery applications requires additional processing steps. Similarly, specialized separators and current collectors optimized for aqueous environments must be produced at scale with consistent quality to ensure battery performance and safety.
Cost considerations significantly impact manufacturing scalability. The economic advantage of zinc ion batteries lies in their potentially lower material costs compared to lithium-ion alternatives. However, this advantage may be offset by higher initial capital investments for specialized manufacturing equipment. A detailed cost analysis indicates that economies of scale could be achieved at production volumes exceeding 500 MWh annually, with material costs representing approximately 60% of the total manufacturing expense.
Safety protocols for mass production present unique requirements compared to laboratory settings. The aqueous nature of zinc ion batteries reduces fire risks but introduces different safety considerations related to hydrogen evolution and electrolyte leakage. Manufacturing facilities must implement appropriate ventilation systems, leak detection mechanisms, and quality control procedures specifically designed for aqueous battery systems.
Automation and quality control systems represent critical enablers for scalable manufacturing. In-line monitoring of electrolyte composition, electrode alignment, and pouch sealing integrity can significantly reduce defect rates. Advanced manufacturing execution systems (MES) tailored to zinc ion battery production can optimize process parameters in real-time, ensuring consistent product quality while maximizing throughput and minimizing waste.
Industrial-scale manufacturing requires standardized processes that can maintain quality while increasing throughput. For zinc ion battery pouches, this necessitates the development of specialized equipment capable of handling aqueous electrolytes without contamination or degradation. Conventional lithium-ion battery manufacturing lines require substantial modification to accommodate the different chemical properties and safety requirements of zinc-based systems.
Material supply chains present another dimension of scalability challenges. While zinc is abundant and widely available compared to lithium, high-purity zinc suitable for battery applications requires additional processing steps. Similarly, specialized separators and current collectors optimized for aqueous environments must be produced at scale with consistent quality to ensure battery performance and safety.
Cost considerations significantly impact manufacturing scalability. The economic advantage of zinc ion batteries lies in their potentially lower material costs compared to lithium-ion alternatives. However, this advantage may be offset by higher initial capital investments for specialized manufacturing equipment. A detailed cost analysis indicates that economies of scale could be achieved at production volumes exceeding 500 MWh annually, with material costs representing approximately 60% of the total manufacturing expense.
Safety protocols for mass production present unique requirements compared to laboratory settings. The aqueous nature of zinc ion batteries reduces fire risks but introduces different safety considerations related to hydrogen evolution and electrolyte leakage. Manufacturing facilities must implement appropriate ventilation systems, leak detection mechanisms, and quality control procedures specifically designed for aqueous battery systems.
Automation and quality control systems represent critical enablers for scalable manufacturing. In-line monitoring of electrolyte composition, electrode alignment, and pouch sealing integrity can significantly reduce defect rates. Advanced manufacturing execution systems (MES) tailored to zinc ion battery production can optimize process parameters in real-time, ensuring consistent product quality while maximizing throughput and minimizing waste.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!