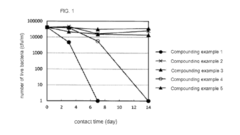
Enhancements in Carboxylic Acid-Derived Antimicrobial Agents
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Antimicrobial Evolution
The evolution of antimicrobial agents has been a critical journey in the fight against infectious diseases. From the serendipitous discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming in 1928 to the sophisticated synthetic compounds of today, the field has undergone remarkable transformations. The early 20th century saw the rise of sulfonamides, followed by the golden age of antibiotics in the 1940s and 1950s, which brought forth a plethora of natural and semi-synthetic compounds.
As bacterial resistance emerged, the focus shifted towards developing new classes of antimicrobials. The 1960s and 1970s witnessed the introduction of quinolones and cephalosporins, expanding the arsenal against resistant pathogens. The late 20th century marked a decline in new antibiotic discoveries, prompting researchers to explore alternative approaches, including the modification of existing compounds.
Carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents have played a significant role in this evolution. These compounds, characterized by their carboxyl group (-COOH), have shown promise due to their ability to disrupt bacterial cell membranes and inhibit essential enzymes. The development of these agents has progressed from simple fatty acids to more complex structures with enhanced antimicrobial properties.
Recent advancements in carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials have focused on improving their efficacy, reducing side effects, and overcoming resistance mechanisms. Researchers have explored various strategies, including the incorporation of additional functional groups, the development of prodrugs, and the creation of hybrid molecules combining carboxylic acid moieties with other antimicrobial structures.
The evolution of these agents has also been influenced by the growing understanding of bacterial resistance mechanisms. This knowledge has led to the design of compounds that can bypass or inhibit resistance pathways, such as efflux pumps or enzymatic degradation. Additionally, the concept of targeting multiple bacterial targets simultaneously has gained traction, resulting in the development of dual-action or even multi-target carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials.
The advent of nanotechnology has further propelled the field, enabling the creation of nanocarriers that can enhance the delivery and efficacy of carboxylic acid-based antimicrobials. These nanoformulations have shown promise in overcoming barriers such as poor solubility and limited bioavailability, which have historically hindered the development of many potential antimicrobial compounds.
As the threat of antimicrobial resistance continues to grow, the evolution of carboxylic acid-derived agents remains a critical area of research. The ongoing efforts to enhance these compounds reflect the broader trends in antimicrobial development, emphasizing the need for innovative approaches to combat emerging pathogens and preserve the efficacy of our antimicrobial arsenal.
As bacterial resistance emerged, the focus shifted towards developing new classes of antimicrobials. The 1960s and 1970s witnessed the introduction of quinolones and cephalosporins, expanding the arsenal against resistant pathogens. The late 20th century marked a decline in new antibiotic discoveries, prompting researchers to explore alternative approaches, including the modification of existing compounds.
Carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents have played a significant role in this evolution. These compounds, characterized by their carboxyl group (-COOH), have shown promise due to their ability to disrupt bacterial cell membranes and inhibit essential enzymes. The development of these agents has progressed from simple fatty acids to more complex structures with enhanced antimicrobial properties.
Recent advancements in carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials have focused on improving their efficacy, reducing side effects, and overcoming resistance mechanisms. Researchers have explored various strategies, including the incorporation of additional functional groups, the development of prodrugs, and the creation of hybrid molecules combining carboxylic acid moieties with other antimicrobial structures.
The evolution of these agents has also been influenced by the growing understanding of bacterial resistance mechanisms. This knowledge has led to the design of compounds that can bypass or inhibit resistance pathways, such as efflux pumps or enzymatic degradation. Additionally, the concept of targeting multiple bacterial targets simultaneously has gained traction, resulting in the development of dual-action or even multi-target carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials.
The advent of nanotechnology has further propelled the field, enabling the creation of nanocarriers that can enhance the delivery and efficacy of carboxylic acid-based antimicrobials. These nanoformulations have shown promise in overcoming barriers such as poor solubility and limited bioavailability, which have historically hindered the development of many potential antimicrobial compounds.
As the threat of antimicrobial resistance continues to grow, the evolution of carboxylic acid-derived agents remains a critical area of research. The ongoing efforts to enhance these compounds reflect the broader trends in antimicrobial development, emphasizing the need for innovative approaches to combat emerging pathogens and preserve the efficacy of our antimicrobial arsenal.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents has been steadily increasing due to the growing concern over antibiotic resistance and the need for more effective and safer antimicrobial solutions. This trend is particularly evident in healthcare, food and beverage, personal care, and agricultural sectors.
In the healthcare industry, there is a pressing need for novel antimicrobial agents to combat multidrug-resistant pathogens. Carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials offer a promising alternative to traditional antibiotics, as they often exhibit broad-spectrum activity and lower propensity for resistance development. Hospitals and healthcare facilities are increasingly adopting these agents for surface disinfection and medical device coatings to reduce healthcare-associated infections.
The food and beverage industry is another significant driver of market demand for carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials. With consumers becoming more health-conscious and demanding clean-label products, there is a growing preference for natural preservatives. Organic acids and their derivatives are viewed as safer alternatives to synthetic preservatives, leading to their increased use in food packaging, processing, and preservation applications.
In the personal care and cosmetics sector, the demand for carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials is rising due to the growing awareness of hygiene and the need for effective yet gentle preservatives. These compounds are being incorporated into a wide range of products, including soaps, shampoos, lotions, and oral care items, to extend shelf life and enhance product safety.
The agricultural industry is also contributing to the market growth of carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials. As concerns over food safety and crop protection intensify, farmers and agribusinesses are seeking more sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions. These antimicrobial agents are being used in crop protection formulations, post-harvest treatments, and animal feed additives to improve yield and reduce losses due to microbial contamination.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials, driven by stringent regulations on food safety and healthcare-associated infections. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of hygiene practices.
The market for these antimicrobial agents is projected to expand significantly in the next decade, with a compound annual growth rate estimated to be in the high single digits. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of these compounds across various end-use industries and the continuous research and development efforts to enhance their efficacy and safety profiles.
In the healthcare industry, there is a pressing need for novel antimicrobial agents to combat multidrug-resistant pathogens. Carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials offer a promising alternative to traditional antibiotics, as they often exhibit broad-spectrum activity and lower propensity for resistance development. Hospitals and healthcare facilities are increasingly adopting these agents for surface disinfection and medical device coatings to reduce healthcare-associated infections.
The food and beverage industry is another significant driver of market demand for carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials. With consumers becoming more health-conscious and demanding clean-label products, there is a growing preference for natural preservatives. Organic acids and their derivatives are viewed as safer alternatives to synthetic preservatives, leading to their increased use in food packaging, processing, and preservation applications.
In the personal care and cosmetics sector, the demand for carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials is rising due to the growing awareness of hygiene and the need for effective yet gentle preservatives. These compounds are being incorporated into a wide range of products, including soaps, shampoos, lotions, and oral care items, to extend shelf life and enhance product safety.
The agricultural industry is also contributing to the market growth of carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials. As concerns over food safety and crop protection intensify, farmers and agribusinesses are seeking more sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions. These antimicrobial agents are being used in crop protection formulations, post-harvest treatments, and animal feed additives to improve yield and reduce losses due to microbial contamination.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials, driven by stringent regulations on food safety and healthcare-associated infections. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of hygiene practices.
The market for these antimicrobial agents is projected to expand significantly in the next decade, with a compound annual growth rate estimated to be in the high single digits. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of these compounds across various end-use industries and the continuous research and development efforts to enhance their efficacy and safety profiles.
Technical Challenges
The development of carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents faces several significant technical challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and effectiveness. One of the primary obstacles is the limited spectrum of activity exhibited by many of these compounds. While some carboxylic acid derivatives show promising results against specific pathogens, they often lack broad-spectrum efficacy, which is crucial for addressing diverse microbial threats in various applications.
Another major challenge lies in the stability of these antimicrobial agents under different environmental conditions. Many carboxylic acid-derived compounds are susceptible to degradation or inactivation when exposed to extreme pH levels, high temperatures, or oxidizing agents. This instability can significantly reduce their effectiveness in real-world applications, particularly in industries such as food preservation or medical device coatings, where harsh conditions are common.
The development of resistance by microorganisms poses a continuous challenge in the field of antimicrobial agents. As with many other antimicrobial compounds, there is a risk that pathogens may develop resistance to carboxylic acid-derived agents over time. This necessitates ongoing research into novel molecular structures and mechanisms of action to stay ahead of evolving microbial defenses.
Biocompatibility and toxicity concerns present another significant hurdle. While carboxylic acids are generally considered safe, some derivatives may exhibit cytotoxicity or cause irritation when used in high concentrations or for prolonged periods. Balancing antimicrobial efficacy with safety for human and environmental health remains a critical challenge in the development of these agents.
The scalability of production processes for carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials is another technical challenge. Many promising compounds are difficult or expensive to synthesize at industrial scales, limiting their commercial viability. Developing cost-effective and efficient production methods is essential for the widespread adoption of these antimicrobial agents.
Formulation challenges also play a significant role in the development of effective products. Incorporating carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials into various matrices (such as polymers, coatings, or consumer products) while maintaining their activity and stability is a complex task. Issues such as solubility, compatibility with other ingredients, and controlled release mechanisms need to be addressed to create practical and effective antimicrobial solutions.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape presents a significant challenge for the commercialization of novel carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents. Navigating the complex approval processes for new antimicrobial compounds, especially for use in sensitive applications like food preservation or medical devices, requires extensive safety and efficacy data. This regulatory burden can significantly delay the introduction of innovative solutions to the market.
Another major challenge lies in the stability of these antimicrobial agents under different environmental conditions. Many carboxylic acid-derived compounds are susceptible to degradation or inactivation when exposed to extreme pH levels, high temperatures, or oxidizing agents. This instability can significantly reduce their effectiveness in real-world applications, particularly in industries such as food preservation or medical device coatings, where harsh conditions are common.
The development of resistance by microorganisms poses a continuous challenge in the field of antimicrobial agents. As with many other antimicrobial compounds, there is a risk that pathogens may develop resistance to carboxylic acid-derived agents over time. This necessitates ongoing research into novel molecular structures and mechanisms of action to stay ahead of evolving microbial defenses.
Biocompatibility and toxicity concerns present another significant hurdle. While carboxylic acids are generally considered safe, some derivatives may exhibit cytotoxicity or cause irritation when used in high concentrations or for prolonged periods. Balancing antimicrobial efficacy with safety for human and environmental health remains a critical challenge in the development of these agents.
The scalability of production processes for carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials is another technical challenge. Many promising compounds are difficult or expensive to synthesize at industrial scales, limiting their commercial viability. Developing cost-effective and efficient production methods is essential for the widespread adoption of these antimicrobial agents.
Formulation challenges also play a significant role in the development of effective products. Incorporating carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials into various matrices (such as polymers, coatings, or consumer products) while maintaining their activity and stability is a complex task. Issues such as solubility, compatibility with other ingredients, and controlled release mechanisms need to be addressed to create practical and effective antimicrobial solutions.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape presents a significant challenge for the commercialization of novel carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents. Navigating the complex approval processes for new antimicrobial compounds, especially for use in sensitive applications like food preservation or medical devices, requires extensive safety and efficacy data. This regulatory burden can significantly delay the introduction of innovative solutions to the market.
Current Solutions
01 Carboxylic acid derivatives as antimicrobial agents
Various carboxylic acid derivatives have been developed and utilized as effective antimicrobial agents. These compounds exhibit broad-spectrum activity against bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms. The antimicrobial properties of these derivatives can be enhanced through structural modifications and formulation improvements.- Synthesis of novel carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents: Development of new antimicrobial compounds derived from carboxylic acids, focusing on structural modifications to enhance their efficacy against various pathogens. These novel agents may include derivatives of existing antimicrobials or entirely new molecular structures designed to combat resistant microorganisms.
- Formulation strategies for improved delivery of carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials: Innovative formulation approaches to enhance the delivery and effectiveness of carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents. This may include the use of nanoparticles, liposomes, or other carrier systems to improve stability, bioavailability, and targeted delivery of the active compounds.
- Combination therapies with carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials: Exploration of synergistic effects by combining carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents with other classes of antimicrobials or adjuvants. This approach aims to enhance overall antimicrobial efficacy, reduce the development of resistance, and potentially lower required dosages.
- Surface modification and coating technologies using carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials: Development of methods to incorporate carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents into surface coatings or materials. This can include techniques for creating antimicrobial textiles, medical devices, or other surfaces to prevent microbial colonization and biofilm formation.
- Environmental and industrial applications of enhanced carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials: Adaptation and optimization of carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents for use in environmental and industrial settings. This may involve developing formulations for water treatment, food preservation, or industrial cleaning that offer improved efficacy and sustainability compared to traditional antimicrobial solutions.
02 Synergistic combinations with other antimicrobial compounds
Combining carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents with other antimicrobial compounds can lead to synergistic effects, enhancing overall antimicrobial activity. These combinations may include other organic acids, essential oils, or conventional antibiotics, resulting in improved efficacy against a wider range of pathogens.Expand Specific Solutions03 Formulation techniques for improved stability and efficacy
Advanced formulation techniques have been developed to enhance the stability and efficacy of carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents. These may include encapsulation methods, controlled release systems, and the use of specific carriers or excipients to improve the delivery and performance of the active compounds.Expand Specific Solutions04 Novel carboxylic acid derivatives with enhanced properties
Research has led to the development of novel carboxylic acid derivatives with enhanced antimicrobial properties. These new compounds may exhibit improved potency, broader spectrum of activity, or reduced toxicity compared to existing agents. Structure-activity relationship studies have guided the design of these enhanced derivatives.Expand Specific Solutions05 Application-specific enhancements for carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials
Carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents have been tailored for specific applications, such as personal care products, food preservation, and medical devices. These enhancements may involve modifications to improve compatibility with other ingredients, enhance skin penetration, or provide sustained antimicrobial activity in specific environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for effective and sustainable antimicrobial solutions across various industries. The global market size is expanding, with key players like Ecolab, Bayer, and BASF leading innovation efforts. Technological advancements are focused on enhancing efficacy, reducing environmental impact, and addressing antimicrobial resistance. Companies such as Melinta Therapeutics and Actelion Pharmaceuticals are actively developing novel compounds, while established players like Henkel and L'Oréal are incorporating these agents into consumer products. The technology is maturing, with ongoing research at institutions like East China University of Science & Technology and Sichuan University contributing to its evolution.
Ecolab USA, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ecolab has focused on developing carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents for use in industrial and institutional settings. Their research has led to the creation of novel sanitizers and disinfectants based on organic acids and their derivatives[13]. One of their key innovations is the development of peroxycarboxylic acid-based sanitizers that offer rapid and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity while being environmentally friendly[14]. Ecolab has also explored the use of carboxylic acid-based antimicrobials in food safety applications, focusing on solutions that are effective against foodborne pathogens while meeting strict regulatory requirements[15].
Strengths: Expertise in industrial-scale antimicrobial solutions, focus on environmentally friendly formulations. Weaknesses: Limited to specific application areas, potential corrosion issues with some formulations.
Bayer AG
Technical Solution: Bayer AG has made significant advancements in carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents, particularly in the field of agricultural applications. Their research focuses on developing novel fungicides with carboxylic acid moieties that exhibit enhanced efficacy against plant pathogens[4]. One of their key innovations is the development of Fluopyram, a succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor (SDHI) fungicide containing a pyridine-carboxamide group[5]. Bayer has also explored the use of carboxylic acid derivatives in combination with other active ingredients to create synergistic effects and broaden the spectrum of antimicrobial activity[6].
Strengths: Strong research capabilities in agricultural antimicrobials, innovative combinations for enhanced efficacy. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns, development of resistance in target organisms.
Core Innovations
Compositions with antimicrobial properties
PatentPendingUS20240122891A1
Innovation
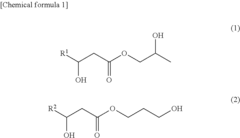
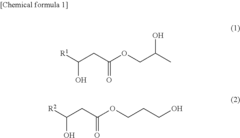
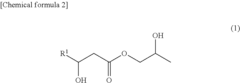
- A cosmetic or pharmaceutical composition comprising alkanediol esters of carboxylic acids with 6 to 12 C atoms, emulsifiers, and antimicrobial agents, where the alkanediol esters enhance the antimicrobial efficacy of commercially available agents, allowing for lower dosages and improved skin tolerance and stability.
Antimicrobial agent
PatentActiveUS20150005378A1
Innovation
- Development of a propanediol mono-β-hydroxycarboxylic acid ester with specific alkyl groups, produced through enzyme reactions or chemical synthesis, exhibiting excellent antimicrobial activity against fungi like molds and yeasts, which can be compounded into various products to enhance antiseptic effects.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental bodies and international organizations. These regulations are crucial in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and responsible use of these agents in different applications.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in regulating antimicrobial agents, including those derived from carboxylic acids. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for evaluating new drug applications and ensuring compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). For antimicrobial agents used in food products, the FDA's Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition (CFSAN) oversees their regulation.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also has jurisdiction over certain antimicrobial agents, particularly those used as pesticides or disinfectants. The EPA's Office of Pesticide Programs regulates these substances under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA).
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is the primary regulatory body for antimicrobial agents used in human and veterinary medicine. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) assesses the safety of antimicrobials used in food production. The EU's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation also applies to many carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines and recommendations for the use of antimicrobial agents, particularly in the context of combating antimicrobial resistance. The Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the WHO and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), sets international food standards that include regulations on antimicrobial agents in food products.
Recent regulatory trends have focused on addressing the growing concern of antimicrobial resistance. Many jurisdictions have implemented stricter controls on the use of antimicrobial agents, particularly in agriculture and animal husbandry. For instance, the EU has banned the use of antibiotics for growth promotion in animal feed since 2006.
Regulatory bodies are also increasingly emphasizing the importance of developing new antimicrobial agents to combat resistant pathogens. The FDA's Generating Antibiotic Incentives Now (GAIN) Act provides incentives for the development of novel antibacterial and antifungal drugs. Similarly, the EU has implemented the New Drugs for Bad Bugs (ND4BB) program to stimulate antibiotic discovery and development.
As research in carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Future regulations may focus on promoting the development of targeted, narrow-spectrum antimicrobials to minimize the risk of resistance development. Additionally, there may be increased emphasis on the environmental impact of these agents, leading to more stringent regulations on their production, use, and disposal.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in regulating antimicrobial agents, including those derived from carboxylic acids. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for evaluating new drug applications and ensuring compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). For antimicrobial agents used in food products, the FDA's Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition (CFSAN) oversees their regulation.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also has jurisdiction over certain antimicrobial agents, particularly those used as pesticides or disinfectants. The EPA's Office of Pesticide Programs regulates these substances under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA).
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is the primary regulatory body for antimicrobial agents used in human and veterinary medicine. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) assesses the safety of antimicrobials used in food production. The EU's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation also applies to many carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines and recommendations for the use of antimicrobial agents, particularly in the context of combating antimicrobial resistance. The Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the WHO and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), sets international food standards that include regulations on antimicrobial agents in food products.
Recent regulatory trends have focused on addressing the growing concern of antimicrobial resistance. Many jurisdictions have implemented stricter controls on the use of antimicrobial agents, particularly in agriculture and animal husbandry. For instance, the EU has banned the use of antibiotics for growth promotion in animal feed since 2006.
Regulatory bodies are also increasingly emphasizing the importance of developing new antimicrobial agents to combat resistant pathogens. The FDA's Generating Antibiotic Incentives Now (GAIN) Act provides incentives for the development of novel antibacterial and antifungal drugs. Similarly, the EU has implemented the New Drugs for Bad Bugs (ND4BB) program to stimulate antibiotic discovery and development.
As research in carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Future regulations may focus on promoting the development of targeted, narrow-spectrum antimicrobials to minimize the risk of resistance development. Additionally, there may be increased emphasis on the environmental impact of these agents, leading to more stringent regulations on their production, use, and disposal.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobial agents is a critical consideration in their development and application. These compounds, while effective against various microorganisms, can have both positive and negative effects on the environment. One of the primary benefits is their potential to reduce the use of traditional antibiotics, which have contributed to the growing problem of antibiotic resistance. By providing alternative antimicrobial solutions, carboxylic acid derivatives can help mitigate this global health threat and reduce the environmental burden of antibiotic residues.
However, the production and use of these agents also raise environmental concerns. The synthesis of carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials often involves chemical processes that may generate waste products and consume energy resources. Manufacturers must implement sustainable practices to minimize the environmental footprint of production, such as adopting green chemistry principles and optimizing reaction conditions to reduce solvent use and improve atom economy.
The fate of these antimicrobial agents in the environment after use is another crucial aspect to consider. Some carboxylic acid derivatives may persist in water systems or soil, potentially affecting non-target organisms and ecosystems. Research into the biodegradability and ecotoxicology of these compounds is essential to ensure their environmental safety. Studies have shown that certain carboxylic acid-based antimicrobials can be readily biodegraded by environmental microorganisms, which is a favorable characteristic compared to more persistent conventional antibiotics.
The impact on aquatic ecosystems is of particular concern, as these agents may enter water bodies through various pathways, including wastewater discharge. Monitoring programs and advanced water treatment technologies are necessary to detect and remove these compounds from effluents. Additionally, the potential for bioaccumulation in aquatic organisms and subsequent effects on the food chain must be thoroughly investigated to prevent unintended ecological consequences.
In agricultural applications, carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials used as feed additives or crop protection agents may have direct interactions with soil microbiota. While they can help control plant pathogens, there is a need to assess their long-term effects on beneficial soil microorganisms and overall soil health. Sustainable agricultural practices should be developed to optimize the use of these agents while maintaining ecological balance.
The environmental impact assessment of carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials should also consider their potential to induce resistance in environmental microorganisms. Although these agents may offer advantages over traditional antibiotics, the possibility of cross-resistance or co-resistance with other antimicrobials must be evaluated to ensure their long-term efficacy and minimize environmental risks.
However, the production and use of these agents also raise environmental concerns. The synthesis of carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials often involves chemical processes that may generate waste products and consume energy resources. Manufacturers must implement sustainable practices to minimize the environmental footprint of production, such as adopting green chemistry principles and optimizing reaction conditions to reduce solvent use and improve atom economy.
The fate of these antimicrobial agents in the environment after use is another crucial aspect to consider. Some carboxylic acid derivatives may persist in water systems or soil, potentially affecting non-target organisms and ecosystems. Research into the biodegradability and ecotoxicology of these compounds is essential to ensure their environmental safety. Studies have shown that certain carboxylic acid-based antimicrobials can be readily biodegraded by environmental microorganisms, which is a favorable characteristic compared to more persistent conventional antibiotics.
The impact on aquatic ecosystems is of particular concern, as these agents may enter water bodies through various pathways, including wastewater discharge. Monitoring programs and advanced water treatment technologies are necessary to detect and remove these compounds from effluents. Additionally, the potential for bioaccumulation in aquatic organisms and subsequent effects on the food chain must be thoroughly investigated to prevent unintended ecological consequences.
In agricultural applications, carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials used as feed additives or crop protection agents may have direct interactions with soil microbiota. While they can help control plant pathogens, there is a need to assess their long-term effects on beneficial soil microorganisms and overall soil health. Sustainable agricultural practices should be developed to optimize the use of these agents while maintaining ecological balance.
The environmental impact assessment of carboxylic acid-derived antimicrobials should also consider their potential to induce resistance in environmental microorganisms. Although these agents may offer advantages over traditional antibiotics, the possibility of cross-resistance or co-resistance with other antimicrobials must be evaluated to ensure their long-term efficacy and minimize environmental risks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!