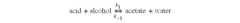Ethyl Propanoate: Mechanism in Esterification Process Optimization
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Esterification Background
Esterification is a fundamental chemical reaction in organic synthesis, playing a crucial role in various industrial processes. This reaction involves the condensation of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid to form an ester and water. The mechanism of esterification has been extensively studied and optimized over the years, with particular focus on improving yield, reaction rates, and selectivity.
The history of esterification dates back to the early 19th century when chemists first observed the formation of esters from alcohols and acids. However, it wasn't until the mid-20th century that the reaction mechanism was fully elucidated. The classical Fischer esterification, named after Emil Fischer, involves the use of a strong acid catalyst to facilitate the reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid.
In the context of ethyl propanoate synthesis, the esterification process involves the reaction between ethanol and propanoic acid. This particular ester is widely used in the food and fragrance industries due to its fruity aroma, resembling that of pineapple. The optimization of this process has been a subject of ongoing research, aiming to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
The traditional approach to esterification often involves the use of homogeneous acid catalysts, such as sulfuric acid or p-toluenesulfonic acid. These catalysts effectively promote the reaction but present challenges in terms of product separation and environmental concerns. As a result, recent research has focused on developing heterogeneous catalysts and alternative reaction conditions to address these issues.
One significant advancement in esterification technology has been the development of continuous flow processes. These systems offer advantages over batch reactions, including improved heat and mass transfer, enhanced safety, and the potential for process intensification. In the case of ethyl propanoate synthesis, continuous flow reactors have demonstrated increased productivity and reduced reaction times compared to conventional batch methods.
Another area of focus in esterification optimization has been the exploration of green chemistry principles. This includes the use of bio-based feedstocks, environmentally benign solvents, and recyclable catalysts. For ethyl propanoate production, researchers have investigated the use of biocatalysts, such as lipases, which can operate under milder conditions and offer high selectivity.
The mechanism of esterification in the context of ethyl propanoate synthesis involves several key steps. Initially, the acid catalyst protonates the carbonyl oxygen of propanoic acid, increasing the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon. The ethanol then acts as a nucleophile, attacking the carbonyl carbon to form a tetrahedral intermediate. Subsequent proton transfers and the elimination of water lead to the formation of the ester product.
Understanding and optimizing this mechanism is crucial for improving the overall efficiency of the esterification process. Factors such as reaction temperature, catalyst type and concentration, reactant ratios, and water removal techniques all play significant roles in determining the reaction kinetics and equilibrium.
The history of esterification dates back to the early 19th century when chemists first observed the formation of esters from alcohols and acids. However, it wasn't until the mid-20th century that the reaction mechanism was fully elucidated. The classical Fischer esterification, named after Emil Fischer, involves the use of a strong acid catalyst to facilitate the reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid.
In the context of ethyl propanoate synthesis, the esterification process involves the reaction between ethanol and propanoic acid. This particular ester is widely used in the food and fragrance industries due to its fruity aroma, resembling that of pineapple. The optimization of this process has been a subject of ongoing research, aiming to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
The traditional approach to esterification often involves the use of homogeneous acid catalysts, such as sulfuric acid or p-toluenesulfonic acid. These catalysts effectively promote the reaction but present challenges in terms of product separation and environmental concerns. As a result, recent research has focused on developing heterogeneous catalysts and alternative reaction conditions to address these issues.
One significant advancement in esterification technology has been the development of continuous flow processes. These systems offer advantages over batch reactions, including improved heat and mass transfer, enhanced safety, and the potential for process intensification. In the case of ethyl propanoate synthesis, continuous flow reactors have demonstrated increased productivity and reduced reaction times compared to conventional batch methods.
Another area of focus in esterification optimization has been the exploration of green chemistry principles. This includes the use of bio-based feedstocks, environmentally benign solvents, and recyclable catalysts. For ethyl propanoate production, researchers have investigated the use of biocatalysts, such as lipases, which can operate under milder conditions and offer high selectivity.
The mechanism of esterification in the context of ethyl propanoate synthesis involves several key steps. Initially, the acid catalyst protonates the carbonyl oxygen of propanoic acid, increasing the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon. The ethanol then acts as a nucleophile, attacking the carbonyl carbon to form a tetrahedral intermediate. Subsequent proton transfers and the elimination of water lead to the formation of the ester product.
Understanding and optimizing this mechanism is crucial for improving the overall efficiency of the esterification process. Factors such as reaction temperature, catalyst type and concentration, reactant ratios, and water removal techniques all play significant roles in determining the reaction kinetics and equilibrium.
Market Analysis
The market for ethyl propanoate, a key ester in the flavor and fragrance industry, has been experiencing steady growth due to its versatile applications. This compound is widely used as a fruity flavoring agent in food products, beverages, and cosmetics, contributing to its increasing demand. The global ester market, which includes ethyl propanoate, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, driven by the rising consumer preference for natural and organic products.
In the food and beverage sector, ethyl propanoate finds extensive use as a flavoring agent, particularly in fruit-flavored products. The compound's ability to impart a pineapple-like aroma makes it a popular choice among manufacturers seeking to enhance their product offerings. As consumers continue to demand more diverse and exotic flavors, the market for ethyl propanoate is expected to grow further.
The cosmetics and personal care industry also represents a significant market for ethyl propanoate. Its pleasant fruity scent makes it an attractive ingredient in perfumes, lotions, and other personal care products. With the global cosmetics market expanding rapidly, the demand for ethyl propanoate in this sector is likely to increase correspondingly.
The pharmaceutical industry is another potential growth area for ethyl propanoate. While its use in this sector is currently limited, ongoing research into its potential applications as a solvent or intermediate in drug synthesis could open up new market opportunities in the future.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key market for ethyl propanoate, driven by the rapid growth of the food and beverage industry in countries like China and India. North America and Europe continue to be significant consumers of ethyl propanoate, particularly in the flavor and fragrance sectors.
The market for ethyl propanoate is characterized by a high degree of fragmentation, with numerous small and medium-sized players competing alongside larger chemical companies. This competitive landscape has led to increased focus on process optimization and cost reduction strategies among manufacturers.
Environmental regulations and sustainability concerns are increasingly influencing the market dynamics for ethyl propanoate. As a result, there is growing interest in developing more environmentally friendly production methods, such as biocatalytic processes, which could potentially reshape the market in the coming years.
In conclusion, the market for ethyl propanoate shows promising growth potential, driven by its diverse applications and the expanding end-user industries. However, manufacturers will need to focus on process optimization and sustainable production methods to maintain their competitive edge in this evolving market landscape.
In the food and beverage sector, ethyl propanoate finds extensive use as a flavoring agent, particularly in fruit-flavored products. The compound's ability to impart a pineapple-like aroma makes it a popular choice among manufacturers seeking to enhance their product offerings. As consumers continue to demand more diverse and exotic flavors, the market for ethyl propanoate is expected to grow further.
The cosmetics and personal care industry also represents a significant market for ethyl propanoate. Its pleasant fruity scent makes it an attractive ingredient in perfumes, lotions, and other personal care products. With the global cosmetics market expanding rapidly, the demand for ethyl propanoate in this sector is likely to increase correspondingly.
The pharmaceutical industry is another potential growth area for ethyl propanoate. While its use in this sector is currently limited, ongoing research into its potential applications as a solvent or intermediate in drug synthesis could open up new market opportunities in the future.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key market for ethyl propanoate, driven by the rapid growth of the food and beverage industry in countries like China and India. North America and Europe continue to be significant consumers of ethyl propanoate, particularly in the flavor and fragrance sectors.
The market for ethyl propanoate is characterized by a high degree of fragmentation, with numerous small and medium-sized players competing alongside larger chemical companies. This competitive landscape has led to increased focus on process optimization and cost reduction strategies among manufacturers.
Environmental regulations and sustainability concerns are increasingly influencing the market dynamics for ethyl propanoate. As a result, there is growing interest in developing more environmentally friendly production methods, such as biocatalytic processes, which could potentially reshape the market in the coming years.
In conclusion, the market for ethyl propanoate shows promising growth potential, driven by its diverse applications and the expanding end-user industries. However, manufacturers will need to focus on process optimization and sustainable production methods to maintain their competitive edge in this evolving market landscape.
Technical Challenges
The optimization of the esterification process for ethyl propanoate production faces several technical challenges that require careful consideration and innovative solutions. One of the primary obstacles is achieving and maintaining the optimal reaction conditions. The esterification reaction between propionic acid and ethanol is reversible and equilibrium-limited, necessitating precise control over temperature, pressure, and reactant ratios to maximize yield and selectivity.
Catalyst selection and performance pose another significant challenge. While traditional acid catalysts like sulfuric acid are effective, they present corrosion issues and environmental concerns. The development of heterogeneous catalysts with high activity, selectivity, and stability remains an ongoing research focus. These catalysts must withstand the reaction conditions and maintain their efficacy over extended periods to be economically viable for industrial applications.
Water removal during the esterification process is crucial for driving the reaction towards completion, as water is a byproduct that can hinder the forward reaction. Implementing efficient water removal techniques, such as reactive distillation or membrane separation, without compromising the overall process efficiency is a complex engineering challenge. Balancing the energy requirements for water removal with the overall process economics adds another layer of complexity to this issue.
The presence of side reactions and the formation of unwanted byproducts represent additional technical hurdles. Minimizing the production of diethyl ether, a common side product in acid-catalyzed esterification, requires careful control of reaction parameters and catalyst properties. Developing selective catalysts or process conditions that suppress these side reactions while maintaining high conversion rates for the desired ester is an ongoing area of research.
Scale-up and process intensification present challenges in translating laboratory-scale optimizations to industrial production. Ensuring uniform mixing, heat transfer, and mass transfer in larger reactors while maintaining the optimal reaction conditions achieved at smaller scales requires sophisticated engineering solutions. Additionally, integrating process intensification techniques, such as microreactor technology or continuous flow processes, into existing production frameworks poses both technical and economic challenges.
Lastly, meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations and sustainability goals adds another dimension to the technical challenges. Developing greener processes that reduce energy consumption, minimize waste generation, and utilize renewable feedstocks is becoming increasingly important. This includes exploring bio-based catalysts, implementing solvent-free reactions, and designing more efficient separation and purification methods to reduce the environmental footprint of ethyl propanoate production.
Catalyst selection and performance pose another significant challenge. While traditional acid catalysts like sulfuric acid are effective, they present corrosion issues and environmental concerns. The development of heterogeneous catalysts with high activity, selectivity, and stability remains an ongoing research focus. These catalysts must withstand the reaction conditions and maintain their efficacy over extended periods to be economically viable for industrial applications.
Water removal during the esterification process is crucial for driving the reaction towards completion, as water is a byproduct that can hinder the forward reaction. Implementing efficient water removal techniques, such as reactive distillation or membrane separation, without compromising the overall process efficiency is a complex engineering challenge. Balancing the energy requirements for water removal with the overall process economics adds another layer of complexity to this issue.
The presence of side reactions and the formation of unwanted byproducts represent additional technical hurdles. Minimizing the production of diethyl ether, a common side product in acid-catalyzed esterification, requires careful control of reaction parameters and catalyst properties. Developing selective catalysts or process conditions that suppress these side reactions while maintaining high conversion rates for the desired ester is an ongoing area of research.
Scale-up and process intensification present challenges in translating laboratory-scale optimizations to industrial production. Ensuring uniform mixing, heat transfer, and mass transfer in larger reactors while maintaining the optimal reaction conditions achieved at smaller scales requires sophisticated engineering solutions. Additionally, integrating process intensification techniques, such as microreactor technology or continuous flow processes, into existing production frameworks poses both technical and economic challenges.
Lastly, meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations and sustainability goals adds another dimension to the technical challenges. Developing greener processes that reduce energy consumption, minimize waste generation, and utilize renewable feedstocks is becoming increasingly important. This includes exploring bio-based catalysts, implementing solvent-free reactions, and designing more efficient separation and purification methods to reduce the environmental footprint of ethyl propanoate production.
Current Methodologies
01 Catalytic esterification process
The esterification of propionic acid with ethanol to produce ethyl propanoate can be carried out using various catalysts. These catalysts enhance the reaction rate and selectivity, improving the overall efficiency of the process. Common catalysts include strong acids, ion exchange resins, and metal-based catalysts.- Catalytic esterification process: The esterification of propionic acid with ethanol to produce ethyl propanoate can be carried out using various catalysts. These catalysts can include strong acids, ion exchange resins, or solid acid catalysts. The process typically involves heating the reactants in the presence of the catalyst, often under reflux conditions, to drive the reaction to completion.
- Continuous flow esterification: Ethyl propanoate can be produced using continuous flow reactors, which offer advantages in terms of process efficiency and scalability. This method involves continuously feeding the reactants through a reactor system, often with integrated separation and purification steps. The continuous process can lead to higher yields and improved product quality compared to batch processes.
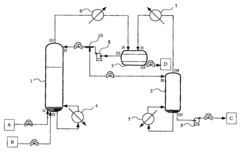
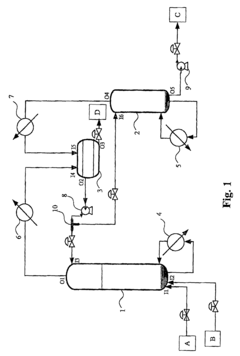
- Reactive distillation for esterification: Reactive distillation combines the reaction and separation steps in a single unit operation for the production of ethyl propanoate. This process involves carrying out the esterification reaction in a distillation column, where the product is continuously removed as it forms. This approach can help overcome equilibrium limitations and improve conversion rates.
- Enzymatic esterification process: Ethyl propanoate can be synthesized using enzymatic catalysis, typically employing lipases. This bio-catalytic approach offers advantages such as mild reaction conditions, high selectivity, and reduced environmental impact. The process often involves immobilized enzymes to facilitate catalyst recovery and reuse.
- Microwave-assisted esterification: Microwave irradiation can be used to enhance the esterification process for producing ethyl propanoate. This method typically results in faster reaction rates and potentially higher yields compared to conventional heating methods. The microwave-assisted process can be combined with various catalysts to further improve efficiency.
02 Continuous flow esterification
Continuous flow processes for the production of ethyl propanoate offer advantages over batch processes, including improved productivity and consistent product quality. These processes often involve the use of fixed-bed reactors or reactive distillation columns, allowing for efficient separation of the product from unreacted starting materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Azeotropic distillation for product purification
Azeotropic distillation techniques can be employed to purify ethyl propanoate and remove water formed during the esterification reaction. This method involves the use of entrainers to break the azeotrope between ethyl propanoate and water, allowing for more efficient separation and higher product purity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Green chemistry approaches
Environmentally friendly methods for ethyl propanoate production focus on using renewable feedstocks, minimizing waste generation, and reducing energy consumption. These approaches may include the use of biocatalysts, such as enzymes, or the development of solvent-free reaction conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process optimization and control
Optimization of reaction parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and reactant ratios, is crucial for maximizing ethyl propanoate yield and selectivity. Advanced process control strategies, including in-line monitoring and automated feedback systems, can be implemented to maintain optimal reaction conditions and ensure consistent product quality.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Players
The esterification process optimization for Ethyl Propanoate is in a mature stage of development, with a significant market presence and established technological foundations. The global market for esters, including Ethyl Propanoate, is substantial and growing, driven by increasing demand in various industries. Key players like Shell, Novozymes, and SINOPEC are at the forefront of research and development, leveraging their extensive expertise in catalysis and process engineering. Companies such as LanzaTech and Eastman Chemical are exploring innovative approaches to enhance efficiency and sustainability in esterification processes. The technology's maturity is evident in the diverse range of applications and the continuous improvements in catalysts and reaction conditions by industry leaders.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative approach to optimize the esterification process for ethyl propanoate production. Their method involves using a heterogeneous acid catalyst, specifically a sulfonated zirconia catalyst, which enhances the reaction efficiency and selectivity[1]. The process operates under mild conditions, typically at temperatures between 60-80°C and atmospheric pressure, reducing energy consumption. Sinopec's technique also incorporates a reactive distillation column, which combines reaction and separation steps, leading to improved conversion rates and product purity[2]. This integrated process allows for continuous operation, minimizing downtime and increasing overall productivity.
Strengths: High catalytic efficiency, improved product purity, and reduced energy consumption. Weaknesses: Potential catalyst deactivation over time, requiring periodic regeneration or replacement.
Eastman Chemical Co.
Technical Solution: Eastman Chemical Co. has developed a novel approach to ethyl propanoate esterification using a proprietary solid acid catalyst. Their process employs a fixed-bed reactor system with the catalyst, allowing for continuous operation and easy catalyst recovery[3]. The reaction is carried out at moderate temperatures (70-90°C) and pressures (1-5 bar), optimizing energy efficiency. Eastman's method incorporates an innovative water removal technique, utilizing a selective membrane system to shift the equilibrium towards product formation[4]. This approach significantly enhances conversion rates, typically achieving over 95% yield. Additionally, the company has implemented advanced process control systems, utilizing real-time monitoring and adjustment of reaction parameters to maintain optimal conditions throughout the esterification process.
Strengths: High product yield, continuous operation, and efficient water removal. Weaknesses: Potential membrane fouling issues and higher initial capital investment for the specialized equipment.
Key Innovations
Method and apparatus for esterification
PatentInactiveUS7857944B2
Innovation
- A method and apparatus involving a reactive distillation column with a solid catalyst, a separation device, and a stripper, where the acid and alcohol are mixed at the bottom section to produce a vapor mixture, cooled and separated to isolate an ester product of high purity, with specific temperature and pressure controls, and a T-typed bypass for recycling, optimizing the separation process based on thermodynamic characteristics.
Method for preparing a carboxylic acid ester
PatentWO2011095872A1
Innovation
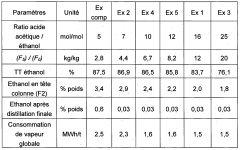
- A process involving an esterification reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol with a molar ratio of at least 7, in the presence of an acid catalyst, preferably using a protonic acid catalyst like sulphonic resins or strong acids, and employing a continuous or discontinuous distillation method to separate and recycle reactants, optimizing energy use and product purity.
Process Optimization
Process optimization for the esterification of ethyl propanoate involves a systematic approach to enhance reaction efficiency, yield, and product quality. The optimization process typically focuses on several key parameters that significantly influence the reaction outcome.
Temperature control plays a crucial role in the esterification process. The reaction rate generally increases with temperature, but excessive heat can lead to side reactions or product degradation. Optimal temperature ranges are typically between 50-80°C, with precise control maintained throughout the reaction duration. Advanced temperature control systems, such as jacketed reactors with programmable temperature profiles, can be employed to achieve precise thermal management.
Reaction time is another critical factor in process optimization. While longer reaction times can increase conversion rates, they may also lead to increased energy consumption and reduced reactor throughput. Kinetic studies are often conducted to determine the optimal reaction time that balances conversion efficiency with process economics. In many cases, a reaction time of 2-4 hours is found to be sufficient for high conversion rates.
Catalyst selection and concentration significantly impact the esterification process. Commonly used catalysts include sulfuric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, and ion exchange resins. The catalyst type and concentration must be optimized to maximize reaction rate while minimizing side reactions and product contamination. Heterogeneous catalysts, such as Amberlyst-15, have gained popularity due to their ease of separation and potential for reuse.
Reactant ratio optimization is essential for achieving high yields and minimizing waste. While the stoichiometric ratio of ethanol to propionic acid is 1:1, an excess of one reactant (typically ethanol) is often used to drive the equilibrium towards product formation. The optimal ratio is determined through experimental studies and can vary depending on other process conditions.
Water removal is a critical aspect of process optimization, as the esterification reaction produces water as a byproduct. Effective water removal shifts the equilibrium towards product formation, improving yield and reaction rate. Techniques such as azeotropic distillation, pervaporation, or the use of molecular sieves can be employed to continuously remove water from the reaction mixture.
Mixing and mass transfer optimization ensure uniform distribution of reactants and catalyst throughout the reaction vessel. Efficient mixing reduces mass transfer limitations and promotes higher reaction rates. Advanced reactor designs, such as static mixers or high-shear impellers, can be utilized to enhance mixing efficiency.
Process intensification techniques, such as reactive distillation or microreactor technology, can be applied to further optimize the esterification process. These approaches combine reaction and separation steps, leading to improved efficiency, reduced equipment size, and lower energy consumption.
Temperature control plays a crucial role in the esterification process. The reaction rate generally increases with temperature, but excessive heat can lead to side reactions or product degradation. Optimal temperature ranges are typically between 50-80°C, with precise control maintained throughout the reaction duration. Advanced temperature control systems, such as jacketed reactors with programmable temperature profiles, can be employed to achieve precise thermal management.
Reaction time is another critical factor in process optimization. While longer reaction times can increase conversion rates, they may also lead to increased energy consumption and reduced reactor throughput. Kinetic studies are often conducted to determine the optimal reaction time that balances conversion efficiency with process economics. In many cases, a reaction time of 2-4 hours is found to be sufficient for high conversion rates.
Catalyst selection and concentration significantly impact the esterification process. Commonly used catalysts include sulfuric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, and ion exchange resins. The catalyst type and concentration must be optimized to maximize reaction rate while minimizing side reactions and product contamination. Heterogeneous catalysts, such as Amberlyst-15, have gained popularity due to their ease of separation and potential for reuse.
Reactant ratio optimization is essential for achieving high yields and minimizing waste. While the stoichiometric ratio of ethanol to propionic acid is 1:1, an excess of one reactant (typically ethanol) is often used to drive the equilibrium towards product formation. The optimal ratio is determined through experimental studies and can vary depending on other process conditions.
Water removal is a critical aspect of process optimization, as the esterification reaction produces water as a byproduct. Effective water removal shifts the equilibrium towards product formation, improving yield and reaction rate. Techniques such as azeotropic distillation, pervaporation, or the use of molecular sieves can be employed to continuously remove water from the reaction mixture.
Mixing and mass transfer optimization ensure uniform distribution of reactants and catalyst throughout the reaction vessel. Efficient mixing reduces mass transfer limitations and promotes higher reaction rates. Advanced reactor designs, such as static mixers or high-shear impellers, can be utilized to enhance mixing efficiency.
Process intensification techniques, such as reactive distillation or microreactor technology, can be applied to further optimize the esterification process. These approaches combine reaction and separation steps, leading to improved efficiency, reduced equipment size, and lower energy consumption.
Catalyst Developments
Catalyst developments have played a crucial role in optimizing the esterification process for ethyl propanoate production. Over the years, researchers have made significant strides in improving catalyst efficiency, selectivity, and reusability, leading to enhanced process performance and reduced environmental impact.
Traditional acid catalysts, such as sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, have been widely used in esterification reactions. However, these homogeneous catalysts pose challenges in terms of product separation, corrosion, and environmental concerns. To address these issues, heterogeneous catalysts have gained considerable attention in recent years.
Solid acid catalysts, including ion-exchange resins, zeolites, and functionalized mesoporous materials, have emerged as promising alternatives. These catalysts offer advantages such as easy separation, reusability, and reduced corrosion. For instance, Amberlyst-15, a sulfonated polystyrene resin, has shown excellent catalytic activity in ethyl propanoate synthesis, with high conversion rates and selectivity.
Zeolites, particularly H-ZSM-5 and H-Beta, have also demonstrated remarkable performance in esterification reactions. Their unique pore structure and tunable acidity allow for enhanced selectivity and reduced side reactions. Recent studies have focused on modifying zeolites through metal incorporation or hierarchical structuring to further improve their catalytic properties.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) represent another class of catalysts that have gained attention in esterification processes. These highly porous materials offer large surface areas and tunable functionalities, making them suitable for catalyzing various organic transformations. Zr-based MOFs, such as UiO-66, have shown promising results in ethyl propanoate synthesis, exhibiting high conversion rates and excellent reusability.
Enzyme-based catalysts have also been explored as green alternatives for esterification reactions. Lipases, in particular, have demonstrated high catalytic activity and selectivity in the synthesis of ethyl propanoate. Immobilized lipases on various supports have been developed to enhance their stability and reusability, making them attractive options for industrial applications.
Recent advancements in nanotechnology have led to the development of nanostructured catalysts for esterification reactions. These materials, including nanoparticles, nanowires, and nanocomposites, offer enhanced surface area and improved mass transfer properties. For example, magnetic nanoparticles functionalized with acidic groups have shown excellent catalytic activity and easy recyclability in ethyl propanoate synthesis.
Continuous efforts are being made to develop novel catalysts with improved performance and sustainability. Researchers are exploring the potential of bio-based catalysts, such as carbon materials derived from biomass, as well as hybrid catalysts that combine the advantages of different catalytic systems. These developments aim to further optimize the esterification process for ethyl propanoate production, addressing challenges related to catalyst stability, selectivity, and environmental impact.
Traditional acid catalysts, such as sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, have been widely used in esterification reactions. However, these homogeneous catalysts pose challenges in terms of product separation, corrosion, and environmental concerns. To address these issues, heterogeneous catalysts have gained considerable attention in recent years.
Solid acid catalysts, including ion-exchange resins, zeolites, and functionalized mesoporous materials, have emerged as promising alternatives. These catalysts offer advantages such as easy separation, reusability, and reduced corrosion. For instance, Amberlyst-15, a sulfonated polystyrene resin, has shown excellent catalytic activity in ethyl propanoate synthesis, with high conversion rates and selectivity.
Zeolites, particularly H-ZSM-5 and H-Beta, have also demonstrated remarkable performance in esterification reactions. Their unique pore structure and tunable acidity allow for enhanced selectivity and reduced side reactions. Recent studies have focused on modifying zeolites through metal incorporation or hierarchical structuring to further improve their catalytic properties.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) represent another class of catalysts that have gained attention in esterification processes. These highly porous materials offer large surface areas and tunable functionalities, making them suitable for catalyzing various organic transformations. Zr-based MOFs, such as UiO-66, have shown promising results in ethyl propanoate synthesis, exhibiting high conversion rates and excellent reusability.
Enzyme-based catalysts have also been explored as green alternatives for esterification reactions. Lipases, in particular, have demonstrated high catalytic activity and selectivity in the synthesis of ethyl propanoate. Immobilized lipases on various supports have been developed to enhance their stability and reusability, making them attractive options for industrial applications.
Recent advancements in nanotechnology have led to the development of nanostructured catalysts for esterification reactions. These materials, including nanoparticles, nanowires, and nanocomposites, offer enhanced surface area and improved mass transfer properties. For example, magnetic nanoparticles functionalized with acidic groups have shown excellent catalytic activity and easy recyclability in ethyl propanoate synthesis.
Continuous efforts are being made to develop novel catalysts with improved performance and sustainability. Researchers are exploring the potential of bio-based catalysts, such as carbon materials derived from biomass, as well as hybrid catalysts that combine the advantages of different catalytic systems. These developments aim to further optimize the esterification process for ethyl propanoate production, addressing challenges related to catalyst stability, selectivity, and environmental impact.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!