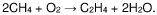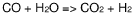Ethyl Propanoate Solvation Dynamics in Ionic Liquids
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ionic Liquid Solvation Background and Objectives
Ionic liquids have emerged as a fascinating class of solvents with unique properties that set them apart from conventional molecular solvents. These room-temperature molten salts have garnered significant attention in recent decades due to their remarkable characteristics, including negligible vapor pressure, high thermal stability, and tunable physicochemical properties. The study of solvation dynamics in ionic liquids has become a critical area of research, offering insights into the fundamental interactions between solutes and these complex liquid environments.
The investigation of ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics in ionic liquids represents a specific focus within this broader field. Ethyl propanoate, an ester commonly used in various industrial applications, serves as an excellent model compound for understanding the behavior of organic molecules in ionic liquid systems. By examining the solvation dynamics of this molecule, researchers aim to elucidate the intricate interplay between solute-solvent interactions and the unique structural features of ionic liquids.
The evolution of ionic liquid research has been marked by significant milestones, from their initial synthesis and characterization to their application in diverse fields such as electrochemistry, catalysis, and separation processes. As the field has progressed, the focus has shifted towards understanding the molecular-level interactions and dynamics within these systems, which is crucial for optimizing their performance in various applications.
The primary objective of studying ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics in ionic liquids is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing solute behavior in these complex environments. This includes investigating how the ionic liquid's structure, composition, and properties affect the solvation process, as well as exploring the time-dependent evolution of the solvation shell around the ethyl propanoate molecule.
Furthermore, this research aims to elucidate the role of specific ionic liquid components, such as the cation and anion structures, in determining solvation dynamics. By systematically varying these components, researchers seek to establish structure-property relationships that can guide the design of tailored ionic liquids for specific applications.
Another crucial objective is to develop and refine experimental and computational techniques for probing solvation dynamics in ionic liquids. This includes advancing spectroscopic methods, such as time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy, and enhancing molecular dynamics simulations to accurately capture the complex interactions within these systems.
Ultimately, the insights gained from studying ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics in ionic liquids are expected to contribute to the broader understanding of solute-solvent interactions in non-conventional media. This knowledge has far-reaching implications, potentially leading to the development of more efficient and sustainable processes in areas such as chemical synthesis, energy storage, and environmental remediation.
The investigation of ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics in ionic liquids represents a specific focus within this broader field. Ethyl propanoate, an ester commonly used in various industrial applications, serves as an excellent model compound for understanding the behavior of organic molecules in ionic liquid systems. By examining the solvation dynamics of this molecule, researchers aim to elucidate the intricate interplay between solute-solvent interactions and the unique structural features of ionic liquids.
The evolution of ionic liquid research has been marked by significant milestones, from their initial synthesis and characterization to their application in diverse fields such as electrochemistry, catalysis, and separation processes. As the field has progressed, the focus has shifted towards understanding the molecular-level interactions and dynamics within these systems, which is crucial for optimizing their performance in various applications.
The primary objective of studying ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics in ionic liquids is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing solute behavior in these complex environments. This includes investigating how the ionic liquid's structure, composition, and properties affect the solvation process, as well as exploring the time-dependent evolution of the solvation shell around the ethyl propanoate molecule.
Furthermore, this research aims to elucidate the role of specific ionic liquid components, such as the cation and anion structures, in determining solvation dynamics. By systematically varying these components, researchers seek to establish structure-property relationships that can guide the design of tailored ionic liquids for specific applications.
Another crucial objective is to develop and refine experimental and computational techniques for probing solvation dynamics in ionic liquids. This includes advancing spectroscopic methods, such as time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy, and enhancing molecular dynamics simulations to accurately capture the complex interactions within these systems.
Ultimately, the insights gained from studying ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics in ionic liquids are expected to contribute to the broader understanding of solute-solvent interactions in non-conventional media. This knowledge has far-reaching implications, potentially leading to the development of more efficient and sustainable processes in areas such as chemical synthesis, energy storage, and environmental remediation.
Market Analysis for Ionic Liquid Applications
The market for ionic liquids has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by their unique properties and diverse applications across various industries. These versatile compounds, composed of organic cations and inorganic or organic anions, offer numerous advantages over traditional solvents, including low volatility, high thermal stability, and excellent solvation capabilities.
In the context of ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics, ionic liquids present a promising alternative to conventional solvents. The market for ionic liquids in this specific application is closely tied to the broader chemical and pharmaceutical industries, where solvation processes play a crucial role in synthesis, extraction, and purification.
The global ionic liquids market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% in the coming years. This growth is primarily attributed to the increasing demand for green solvents and the rising adoption of ionic liquids in various industrial processes. The pharmaceutical and chemical sectors are expected to be the major contributors to this market expansion.
The use of ionic liquids for ethyl propanoate solvation offers several advantages, including enhanced selectivity, improved reaction rates, and potential for recycling. These benefits are particularly attractive to industries seeking to optimize their processes and reduce environmental impact. As a result, the market for ionic liquids in this specific application is anticipated to grow steadily.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the ionic liquids market, owing to their advanced chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in research and development.
Key market players in the ionic liquids sector include BASF SE, Merck KGaA, Evonik Industries, and Ionic Liquids Technologies GmbH. These companies are actively investing in research and development to expand their product portfolios and cater to the growing demand for specialized ionic liquids, including those suitable for ethyl propanoate solvation.
The market for ionic liquids in ethyl propanoate solvation applications faces some challenges, such as high production costs and limited awareness among potential end-users. However, ongoing research and development efforts are expected to address these issues, potentially leading to more cost-effective production methods and wider adoption across industries.
In the context of ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics, ionic liquids present a promising alternative to conventional solvents. The market for ionic liquids in this specific application is closely tied to the broader chemical and pharmaceutical industries, where solvation processes play a crucial role in synthesis, extraction, and purification.
The global ionic liquids market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% in the coming years. This growth is primarily attributed to the increasing demand for green solvents and the rising adoption of ionic liquids in various industrial processes. The pharmaceutical and chemical sectors are expected to be the major contributors to this market expansion.
The use of ionic liquids for ethyl propanoate solvation offers several advantages, including enhanced selectivity, improved reaction rates, and potential for recycling. These benefits are particularly attractive to industries seeking to optimize their processes and reduce environmental impact. As a result, the market for ionic liquids in this specific application is anticipated to grow steadily.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the ionic liquids market, owing to their advanced chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in research and development.
Key market players in the ionic liquids sector include BASF SE, Merck KGaA, Evonik Industries, and Ionic Liquids Technologies GmbH. These companies are actively investing in research and development to expand their product portfolios and cater to the growing demand for specialized ionic liquids, including those suitable for ethyl propanoate solvation.
The market for ionic liquids in ethyl propanoate solvation applications faces some challenges, such as high production costs and limited awareness among potential end-users. However, ongoing research and development efforts are expected to address these issues, potentially leading to more cost-effective production methods and wider adoption across industries.
Current Challenges in Ethyl Propanoate Solvation
The solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate in ionic liquids present several significant challenges that researchers are currently grappling with. One of the primary difficulties lies in understanding the complex interactions between the solute molecules and the unique ionic environment provided by ionic liquids. Unlike conventional solvents, ionic liquids possess a heterogeneous structure with distinct polar and non-polar domains, which significantly influences the solvation process.
A major challenge is accurately modeling and predicting the solvation behavior of ethyl propanoate in various ionic liquids. The diverse range of cation and anion combinations in ionic liquids creates a vast parameter space, making it difficult to develop comprehensive models that can account for all possible interactions. This complexity is further compounded by the fact that the solvation dynamics can be highly dependent on the specific ionic liquid composition and structure.
Another significant hurdle is the experimental characterization of the solvation process at the molecular level. Traditional spectroscopic techniques often struggle to provide detailed information about the local environment and dynamics of ethyl propanoate molecules within the ionic liquid matrix. This limitation hampers our ability to fully understand the solvation mechanisms and the factors that influence them.
The time-dependent nature of the solvation process adds another layer of complexity to the research. Capturing the ultrafast dynamics of solvent reorganization around the ethyl propanoate molecules requires sophisticated time-resolved spectroscopic techniques, which are not always readily available or easily implemented for ionic liquid systems.
Furthermore, the high viscosity of many ionic liquids poses challenges for both experimental measurements and theoretical simulations. The slow molecular motions in viscous ionic liquids can lead to extended equilibration times and sluggish dynamics, making it difficult to observe and analyze the solvation process on relevant timescales.
The potential for specific interactions between ethyl propanoate and ionic liquid components, such as hydrogen bonding or π-π stacking, adds another dimension to the complexity of the system. These interactions can significantly influence the solvation dynamics but are often challenging to isolate and quantify experimentally or computationally.
Lastly, the translation of fundamental research findings into practical applications remains a significant challenge. While understanding the solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate in ionic liquids is crucial for various industrial processes, bridging the gap between theoretical insights and real-world applications requires overcoming numerous technical and engineering hurdles.
A major challenge is accurately modeling and predicting the solvation behavior of ethyl propanoate in various ionic liquids. The diverse range of cation and anion combinations in ionic liquids creates a vast parameter space, making it difficult to develop comprehensive models that can account for all possible interactions. This complexity is further compounded by the fact that the solvation dynamics can be highly dependent on the specific ionic liquid composition and structure.
Another significant hurdle is the experimental characterization of the solvation process at the molecular level. Traditional spectroscopic techniques often struggle to provide detailed information about the local environment and dynamics of ethyl propanoate molecules within the ionic liquid matrix. This limitation hampers our ability to fully understand the solvation mechanisms and the factors that influence them.
The time-dependent nature of the solvation process adds another layer of complexity to the research. Capturing the ultrafast dynamics of solvent reorganization around the ethyl propanoate molecules requires sophisticated time-resolved spectroscopic techniques, which are not always readily available or easily implemented for ionic liquid systems.
Furthermore, the high viscosity of many ionic liquids poses challenges for both experimental measurements and theoretical simulations. The slow molecular motions in viscous ionic liquids can lead to extended equilibration times and sluggish dynamics, making it difficult to observe and analyze the solvation process on relevant timescales.
The potential for specific interactions between ethyl propanoate and ionic liquid components, such as hydrogen bonding or π-π stacking, adds another dimension to the complexity of the system. These interactions can significantly influence the solvation dynamics but are often challenging to isolate and quantify experimentally or computationally.
Lastly, the translation of fundamental research findings into practical applications remains a significant challenge. While understanding the solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate in ionic liquids is crucial for various industrial processes, bridging the gap between theoretical insights and real-world applications requires overcoming numerous technical and engineering hurdles.
Existing Solvation Dynamics Models
01 Molecular dynamics simulations of ethyl propanoate solvation
Computational methods are used to study the solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate. These simulations provide insights into the behavior of the molecule in various solvents, including its interactions, conformational changes, and energetics. The results can be used to predict and understand the solvation properties of ethyl propanoate in different environments.- Molecular dynamics simulations of ethyl propanoate solvation: Computational methods are used to study the solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate. These simulations provide insights into the behavior of the molecule in different solvents, including its interactions, conformational changes, and energy profiles. The results can be used to predict and understand the solvation properties of ethyl propanoate in various environments.
- Experimental techniques for studying ethyl propanoate solvation: Various experimental methods are employed to investigate the solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate. These may include spectroscopic techniques such as NMR, IR, and Raman spectroscopy, as well as calorimetric measurements. These experiments provide valuable data on the interactions between ethyl propanoate and solvent molecules, helping to elucidate the solvation process.
- Solvent effects on the properties of ethyl propanoate: The choice of solvent can significantly impact the properties and behavior of ethyl propanoate. Studies focus on how different solvents affect the molecule's structure, reactivity, and physical properties. This information is crucial for understanding and predicting the behavior of ethyl propanoate in various applications, such as in chemical synthesis or as a solvent itself.
- Solvation dynamics in mixtures containing ethyl propanoate: Research explores the solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate in complex mixtures or multi-component systems. This includes studying how ethyl propanoate interacts with other solutes in solution, as well as its behavior in mixed solvents. Understanding these dynamics is important for applications where ethyl propanoate is used in combination with other compounds.
- Applications of ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics: Knowledge of ethyl propanoate's solvation dynamics is applied in various fields. This includes its use in chemical processes, pharmaceutical formulations, and as a model compound for studying ester solvation. The understanding of its solvation behavior helps in optimizing processes and developing new applications where ethyl propanoate or similar esters are involved.
02 Experimental techniques for studying ethyl propanoate solvation
Various experimental methods are employed to investigate the solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate. These may include spectroscopic techniques such as NMR, IR, and Raman spectroscopy, as well as calorimetric and chromatographic methods. These experiments provide valuable data on the solvation behavior of ethyl propanoate in different solvents and under various conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics in chemical processes
Understanding the solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate is crucial for various chemical processes. This knowledge is applied in areas such as reaction optimization, solvent selection for extractions or separations, and formulation of products containing ethyl propanoate. The solvation behavior influences the reactivity, stability, and physical properties of the compound in different media.Expand Specific Solutions04 Influence of solvent properties on ethyl propanoate solvation
The solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate are significantly affected by the properties of the solvent. Factors such as polarity, hydrogen bonding ability, and dielectric constant of the solvent play crucial roles in determining the solvation behavior. Studies focus on how these solvent properties impact the structure, energetics, and dynamics of ethyl propanoate in solution.Expand Specific Solutions05 Theoretical models for predicting ethyl propanoate solvation behavior
Theoretical models are developed to predict the solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate in various solvents. These models may incorporate quantum mechanical calculations, statistical mechanics, and machine learning approaches. They aim to provide accurate predictions of solvation energies, conformational preferences, and other relevant properties of ethyl propanoate in different solvent environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Ionic Liquid Research
The field of ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics in ionic liquids is in an early developmental stage, characterized by ongoing research and exploration. The market size remains relatively small, primarily driven by academic and industrial research interests. Technologically, the area is still evolving, with various institutions and companies contributing to its advancement. Zhejiang University and China University of Petroleum (East China) are among the key academic players, while companies like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. and Firmenich SA are likely involved in industrial applications. The technology's maturity is moderate, with ongoing efforts to understand and optimize solvation dynamics for potential applications in chemical processes and product development.
Zhejiang University
Technical Solution: Zhejiang University has conducted extensive research on the solvation dynamics of Ethyl Propanoate in ionic liquids. Their approach involves using advanced spectroscopic techniques, including time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulations, to study the solute-solvent interactions at a molecular level[1]. They have developed a multi-scale modeling framework that combines quantum mechanical calculations with classical molecular dynamics to accurately predict the solvation behavior of Ethyl Propanoate in various ionic liquids[2]. This method allows for the investigation of both short-range and long-range interactions, providing a comprehensive understanding of the solvation process[3].
Strengths: Advanced spectroscopic techniques and multi-scale modeling approach provide detailed insights into molecular interactions. Weaknesses: May require significant computational resources and specialized equipment.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a novel approach to studying Ethyl Propanoate solvation dynamics in ionic liquids, focusing on its applications in the petroleum industry. Their method combines experimental techniques with molecular simulation to investigate the behavior of Ethyl Propanoate in task-specific ionic liquids designed for enhanced oil recovery and catalytic processes[4]. Sinopec has created a proprietary database of ionic liquid properties and their interactions with various organic compounds, including Ethyl Propanoate, which aids in predicting and optimizing solvation processes for industrial applications[5]. They have also implemented machine learning algorithms to analyze large datasets of solvation dynamics, enabling rapid screening of potential ionic liquid solvents for specific applications[6].
Strengths: Industry-focused research with direct applications in petroleum processes. Extensive database and machine learning integration for efficient solvent screening. Weaknesses: May be limited to petroleum-specific applications and proprietary data.
Breakthrough Studies in Ethyl Propanoate Solvation
Ionic liquid with 4-hexadecyl-4-methylmorpholinium cation and (RS)-2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoate anion, method of its preparation and use as a washing-disinfecting agent
PatentInactivePL430227A1
Innovation
- Novel ionic liquid composition with 4-hexadecyl-4-methylmorpholinium cation and (RS)-2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoate anion.
- Simple and efficient method for preparing the ionic liquid using readily available precursors.
- Dual functionality of the ionic liquid as both a cleaning and disinfecting agent.
Process for the conversion of methane into propanal
PatentWO2018005074A1
Innovation
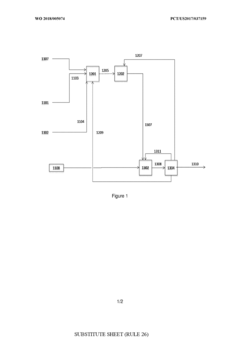
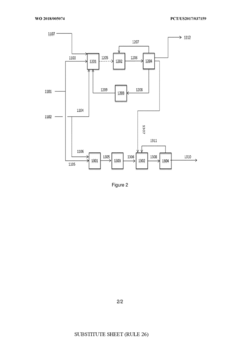
- A process involving oxidative coupling of methane with oxygen in a gas phase reaction, followed by hydroformylation in a second reactor, where the molar ratios of syngas to ethylene and CO2 to ethane are optimized by adjusting the H2 to CO ratio using steam co-feeding and water gas shift reactions, eliminating the need for separate syngas production and separation steps.
Environmental Impact of Ionic Liquids
The environmental impact of ionic liquids (ILs) in the context of ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics is a critical consideration for their widespread application. ILs have gained significant attention as potential green solvents due to their unique properties, including low volatility and high thermal stability. However, their environmental implications require careful examination.
One of the primary environmental advantages of ILs in ethyl propanoate solvation is their negligible vapor pressure. This characteristic significantly reduces air pollution and exposure risks associated with volatile organic compounds (VOCs) typically used in traditional solvents. The reduced evaporation also leads to lower solvent losses, potentially decreasing the overall environmental footprint of industrial processes involving ethyl propanoate.
Despite these benefits, the environmental impact of ILs is not entirely benign. The synthesis of ILs often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially harmful precursors. This raises concerns about the life cycle assessment of ILs, particularly when considering their production on an industrial scale for ethyl propanoate solvation applications.
Water solubility is another crucial factor in assessing the environmental impact of ILs. Some ILs used in ethyl propanoate solvation may be water-soluble, potentially leading to aquatic ecosystem contamination if not properly managed. The persistence of ILs in the environment is a growing concern, as many are not readily biodegradable and may accumulate in water bodies or soil.
Toxicity studies on various ILs have shown mixed results, with some exhibiting low toxicity while others demonstrate potential harmful effects on aquatic organisms. The structural diversity of ILs complicates generalizations about their ecotoxicological profiles, necessitating case-by-case evaluations for different IL-ethyl propanoate systems.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of ILs in ethyl propanoate solvation include the development of bio-based ILs derived from renewable resources. These green ILs aim to reduce the carbon footprint and improve biodegradability. Additionally, research into IL recycling and recovery methods is crucial for minimizing waste and enhancing the sustainability of IL-based processes.
The potential for ILs to enable more efficient and selective chemical processes in ethyl propanoate solvation may indirectly contribute to environmental benefits. By improving reaction yields and reducing byproduct formation, ILs could lead to overall reductions in energy consumption and waste generation in chemical manufacturing.
In conclusion, while ILs offer promising environmental advantages in ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics, their full environmental impact remains complex and multifaceted. Continued research into greener IL synthesis, improved toxicity profiles, and effective recycling strategies is essential to maximize the environmental benefits of ILs in this application.
One of the primary environmental advantages of ILs in ethyl propanoate solvation is their negligible vapor pressure. This characteristic significantly reduces air pollution and exposure risks associated with volatile organic compounds (VOCs) typically used in traditional solvents. The reduced evaporation also leads to lower solvent losses, potentially decreasing the overall environmental footprint of industrial processes involving ethyl propanoate.
Despite these benefits, the environmental impact of ILs is not entirely benign. The synthesis of ILs often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially harmful precursors. This raises concerns about the life cycle assessment of ILs, particularly when considering their production on an industrial scale for ethyl propanoate solvation applications.
Water solubility is another crucial factor in assessing the environmental impact of ILs. Some ILs used in ethyl propanoate solvation may be water-soluble, potentially leading to aquatic ecosystem contamination if not properly managed. The persistence of ILs in the environment is a growing concern, as many are not readily biodegradable and may accumulate in water bodies or soil.
Toxicity studies on various ILs have shown mixed results, with some exhibiting low toxicity while others demonstrate potential harmful effects on aquatic organisms. The structural diversity of ILs complicates generalizations about their ecotoxicological profiles, necessitating case-by-case evaluations for different IL-ethyl propanoate systems.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of ILs in ethyl propanoate solvation include the development of bio-based ILs derived from renewable resources. These green ILs aim to reduce the carbon footprint and improve biodegradability. Additionally, research into IL recycling and recovery methods is crucial for minimizing waste and enhancing the sustainability of IL-based processes.
The potential for ILs to enable more efficient and selective chemical processes in ethyl propanoate solvation may indirectly contribute to environmental benefits. By improving reaction yields and reducing byproduct formation, ILs could lead to overall reductions in energy consumption and waste generation in chemical manufacturing.
In conclusion, while ILs offer promising environmental advantages in ethyl propanoate solvation dynamics, their full environmental impact remains complex and multifaceted. Continued research into greener IL synthesis, improved toxicity profiles, and effective recycling strategies is essential to maximize the environmental benefits of ILs in this application.
Computational Methods in Solvation Dynamics
Computational methods play a crucial role in understanding solvation dynamics in ionic liquids, particularly for systems involving ethyl propanoate. These methods provide valuable insights into the complex interactions between solute molecules and the ionic liquid environment, offering a detailed molecular-level perspective that complements experimental studies.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are widely employed to investigate the solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate in ionic liquids. These simulations allow researchers to track the motion of individual atoms and molecules over time, providing information on solvent reorganization, diffusion processes, and local structural changes. Advanced MD techniques, such as ab initio MD, incorporate quantum mechanical calculations to more accurately represent electronic interactions and chemical reactivity.
Density functional theory (DFT) calculations are essential for studying the electronic structure and energetics of ethyl propanoate and its interactions with ionic liquid components. DFT methods can provide accurate predictions of molecular geometries, binding energies, and charge distributions, which are crucial for understanding solvation processes at the atomic level.
Time-dependent DFT (TD-DFT) calculations are particularly useful for investigating the excited-state properties of ethyl propanoate in ionic liquids. These calculations can predict electronic transitions and spectroscopic properties, allowing researchers to interpret experimental data and gain insights into solvent-induced changes in the electronic structure of the solute.
Quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) methods combine the accuracy of quantum mechanical calculations with the efficiency of classical molecular mechanics. This approach is particularly valuable for studying large systems, where the ethyl propanoate and its immediate solvation shell can be treated quantum mechanically, while the bulk ionic liquid is represented by a classical force field.
Continuum solvation models, such as the polarizable continuum model (PCM) or conductor-like screening model (COSMO), provide a computationally efficient way to account for long-range solvent effects. These models represent the ionic liquid as a continuous dielectric medium, allowing for rapid calculations of solvation free energies and other thermodynamic properties.
Advanced sampling techniques, such as metadynamics or umbrella sampling, are employed to explore rare events and calculate free energy profiles associated with solvation processes. These methods enable researchers to overcome energy barriers and sample configurations that may be inaccessible in standard MD simulations, providing a more complete picture of the solvation dynamics.
Machine learning approaches are increasingly being applied to solvation dynamics studies. Neural networks and other machine learning algorithms can be trained on large datasets of molecular simulations or experimental results to predict solvation properties and dynamics, potentially accelerating the discovery of new ionic liquid systems with tailored properties for specific applications.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are widely employed to investigate the solvation dynamics of ethyl propanoate in ionic liquids. These simulations allow researchers to track the motion of individual atoms and molecules over time, providing information on solvent reorganization, diffusion processes, and local structural changes. Advanced MD techniques, such as ab initio MD, incorporate quantum mechanical calculations to more accurately represent electronic interactions and chemical reactivity.
Density functional theory (DFT) calculations are essential for studying the electronic structure and energetics of ethyl propanoate and its interactions with ionic liquid components. DFT methods can provide accurate predictions of molecular geometries, binding energies, and charge distributions, which are crucial for understanding solvation processes at the atomic level.
Time-dependent DFT (TD-DFT) calculations are particularly useful for investigating the excited-state properties of ethyl propanoate in ionic liquids. These calculations can predict electronic transitions and spectroscopic properties, allowing researchers to interpret experimental data and gain insights into solvent-induced changes in the electronic structure of the solute.
Quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) methods combine the accuracy of quantum mechanical calculations with the efficiency of classical molecular mechanics. This approach is particularly valuable for studying large systems, where the ethyl propanoate and its immediate solvation shell can be treated quantum mechanically, while the bulk ionic liquid is represented by a classical force field.
Continuum solvation models, such as the polarizable continuum model (PCM) or conductor-like screening model (COSMO), provide a computationally efficient way to account for long-range solvent effects. These models represent the ionic liquid as a continuous dielectric medium, allowing for rapid calculations of solvation free energies and other thermodynamic properties.
Advanced sampling techniques, such as metadynamics or umbrella sampling, are employed to explore rare events and calculate free energy profiles associated with solvation processes. These methods enable researchers to overcome energy barriers and sample configurations that may be inaccessible in standard MD simulations, providing a more complete picture of the solvation dynamics.
Machine learning approaches are increasingly being applied to solvation dynamics studies. Neural networks and other machine learning algorithms can be trained on large datasets of molecular simulations or experimental results to predict solvation properties and dynamics, potentially accelerating the discovery of new ionic liquid systems with tailored properties for specific applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!