How Carboxylic Acid Reduces Waste in Industrial Processes?
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Carboxylic Acid Background and Objectives
Carboxylic acids have played a pivotal role in industrial processes for decades, serving as versatile compounds with a wide range of applications. These organic acids, characterized by their -COOH functional group, have gained significant attention in recent years due to their potential to reduce waste and improve efficiency in various industrial sectors.
The evolution of carboxylic acid utilization in industry can be traced back to the early 20th century, with initial applications primarily in the food and pharmaceutical industries. As research progressed, the unique properties of carboxylic acids, such as their ability to form esters and salts, led to their adoption in diverse fields including polymer production, lubricants, and surfactants.
In the context of waste reduction, carboxylic acids have emerged as a promising solution to several industrial challenges. Their ability to act as green solvents, catalysts, and reagents aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes. This shift towards more sustainable practices has been driven by increasing environmental regulations, consumer demand for eco-friendly products, and the need for cost-effective production methods.
The primary objective of utilizing carboxylic acids in waste reduction is to minimize the environmental impact of industrial processes while maintaining or improving product quality and production efficiency. This goal encompasses several key aspects, including the reduction of harmful byproducts, the development of more efficient reaction pathways, and the implementation of circular economy principles in manufacturing.
One of the most significant trends in this field is the exploration of bio-based carboxylic acids derived from renewable resources. This approach not only addresses waste reduction but also contributes to the broader goal of reducing dependence on fossil-based raw materials. Researchers and industry leaders are actively investigating the production of carboxylic acids from biomass feedstocks, agricultural waste, and even carbon dioxide, presenting exciting opportunities for sustainable chemical production.
As we delve deeper into the potential of carboxylic acids in waste reduction, it is crucial to consider the technological advancements that have enabled their more efficient production and application. Innovations in biotechnology, process engineering, and catalysis have opened new avenues for the synthesis and utilization of these compounds, paving the way for more sustainable industrial practices.
The journey towards fully realizing the waste-reducing potential of carboxylic acids is ongoing, with challenges still to be addressed. These include scaling up production of bio-based acids, optimizing reaction conditions for specific applications, and developing more efficient separation and purification techniques. However, the progress made thus far and the continued research efforts in this field suggest a promising future for carboxylic acids as key players in the transition towards more sustainable industrial processes.
The evolution of carboxylic acid utilization in industry can be traced back to the early 20th century, with initial applications primarily in the food and pharmaceutical industries. As research progressed, the unique properties of carboxylic acids, such as their ability to form esters and salts, led to their adoption in diverse fields including polymer production, lubricants, and surfactants.
In the context of waste reduction, carboxylic acids have emerged as a promising solution to several industrial challenges. Their ability to act as green solvents, catalysts, and reagents aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes. This shift towards more sustainable practices has been driven by increasing environmental regulations, consumer demand for eco-friendly products, and the need for cost-effective production methods.
The primary objective of utilizing carboxylic acids in waste reduction is to minimize the environmental impact of industrial processes while maintaining or improving product quality and production efficiency. This goal encompasses several key aspects, including the reduction of harmful byproducts, the development of more efficient reaction pathways, and the implementation of circular economy principles in manufacturing.
One of the most significant trends in this field is the exploration of bio-based carboxylic acids derived from renewable resources. This approach not only addresses waste reduction but also contributes to the broader goal of reducing dependence on fossil-based raw materials. Researchers and industry leaders are actively investigating the production of carboxylic acids from biomass feedstocks, agricultural waste, and even carbon dioxide, presenting exciting opportunities for sustainable chemical production.
As we delve deeper into the potential of carboxylic acids in waste reduction, it is crucial to consider the technological advancements that have enabled their more efficient production and application. Innovations in biotechnology, process engineering, and catalysis have opened new avenues for the synthesis and utilization of these compounds, paving the way for more sustainable industrial practices.
The journey towards fully realizing the waste-reducing potential of carboxylic acids is ongoing, with challenges still to be addressed. These include scaling up production of bio-based acids, optimizing reaction conditions for specific applications, and developing more efficient separation and purification techniques. However, the progress made thus far and the continued research efforts in this field suggest a promising future for carboxylic acids as key players in the transition towards more sustainable industrial processes.
Industrial Waste Reduction Market Analysis
The industrial waste reduction market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental regulations, corporate sustainability initiatives, and the rising costs of waste disposal. The global market for industrial waste management was valued at $1.3 trillion in 2020 and is projected to reach $2.5 trillion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% during this period.
Within this broader market, the segment focusing on chemical waste reduction, particularly through the use of carboxylic acids, is gaining traction. Carboxylic acids have shown promising results in reducing waste in various industrial processes, leading to increased demand for related technologies and solutions. The market for carboxylic acid-based waste reduction solutions is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2021 to 2026.
Key industries driving this market growth include chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and metal fabrication. These sectors are increasingly adopting carboxylic acid-based solutions to minimize waste generation, improve resource efficiency, and comply with stringent environmental regulations. For instance, the pharmaceutical industry, which generates significant amounts of chemical waste, is expected to increase its investment in waste reduction technologies by 12% annually over the next five years.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the industrial waste reduction market, accounting for approximately 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, with a projected CAGR of 9.2% from 2021 to 2026, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing environmental awareness in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Major chemical companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the efficiency of carboxylic acid-based waste reduction processes. Simultaneously, several startups are emerging with novel applications of carboxylic acids in waste treatment, attracting significant venture capital funding.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the market faces challenges such as high initial implementation costs and the need for specialized expertise. However, the long-term cost savings and environmental benefits are expected to outweigh these challenges, driving continued market expansion. As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability and circular economy principles, the demand for effective waste reduction solutions, including those based on carboxylic acids, is poised for sustained growth in the coming years.
Within this broader market, the segment focusing on chemical waste reduction, particularly through the use of carboxylic acids, is gaining traction. Carboxylic acids have shown promising results in reducing waste in various industrial processes, leading to increased demand for related technologies and solutions. The market for carboxylic acid-based waste reduction solutions is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2021 to 2026.
Key industries driving this market growth include chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and metal fabrication. These sectors are increasingly adopting carboxylic acid-based solutions to minimize waste generation, improve resource efficiency, and comply with stringent environmental regulations. For instance, the pharmaceutical industry, which generates significant amounts of chemical waste, is expected to increase its investment in waste reduction technologies by 12% annually over the next five years.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the industrial waste reduction market, accounting for approximately 60% of the global market share. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, with a projected CAGR of 9.2% from 2021 to 2026, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing environmental awareness in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Major chemical companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the efficiency of carboxylic acid-based waste reduction processes. Simultaneously, several startups are emerging with novel applications of carboxylic acids in waste treatment, attracting significant venture capital funding.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the market faces challenges such as high initial implementation costs and the need for specialized expertise. However, the long-term cost savings and environmental benefits are expected to outweigh these challenges, driving continued market expansion. As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability and circular economy principles, the demand for effective waste reduction solutions, including those based on carboxylic acids, is poised for sustained growth in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Industrial Waste Management
Industrial waste management faces numerous challenges in today's complex manufacturing landscape. One of the most pressing issues is the sheer volume of waste generated by industrial processes. As global production continues to increase, so does the amount of waste, putting immense pressure on existing disposal systems and environmental resources.
The diversity of waste types presents another significant challenge. Industrial processes produce a wide range of waste materials, including chemical byproducts, solid residues, and contaminated water. Each type of waste requires specific handling, treatment, and disposal methods, making waste management a complex and resource-intensive task.
Hazardous waste management remains a critical concern. Many industrial processes generate toxic, corrosive, or otherwise dangerous substances that pose serious risks to human health and the environment. Proper handling, storage, and disposal of these materials require specialized facilities and expertise, which can be costly and difficult to implement effectively.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to industrial waste management. Companies must navigate a maze of local, national, and international regulations governing waste handling and disposal. Keeping up with evolving standards and ensuring compliance across multiple jurisdictions can be challenging and resource-intensive for businesses.
The environmental impact of industrial waste is a growing concern. Improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, air pollution, and long-term ecological damage. As public awareness of environmental issues increases, industries face mounting pressure to adopt more sustainable waste management practices.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant challenge in industrial waste management. Implementing advanced treatment technologies and environmentally friendly disposal methods often requires substantial investment. Balancing these costs with operational efficiency and profitability is a constant struggle for many industries.
Resource recovery and circular economy principles present both opportunities and challenges. While there is increasing emphasis on recycling and reusing industrial waste, implementing effective recovery systems can be technically complex and economically challenging. Developing viable markets for recovered materials and byproducts is crucial for the success of these initiatives.
Finally, the lack of standardized waste management practices across industries and regions hinders progress. Inconsistent approaches to waste classification, treatment, and disposal make it difficult to implement large-scale, coordinated waste management strategies. Addressing this challenge requires improved collaboration between industries, governments, and waste management experts to develop and implement best practices.
The diversity of waste types presents another significant challenge. Industrial processes produce a wide range of waste materials, including chemical byproducts, solid residues, and contaminated water. Each type of waste requires specific handling, treatment, and disposal methods, making waste management a complex and resource-intensive task.
Hazardous waste management remains a critical concern. Many industrial processes generate toxic, corrosive, or otherwise dangerous substances that pose serious risks to human health and the environment. Proper handling, storage, and disposal of these materials require specialized facilities and expertise, which can be costly and difficult to implement effectively.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to industrial waste management. Companies must navigate a maze of local, national, and international regulations governing waste handling and disposal. Keeping up with evolving standards and ensuring compliance across multiple jurisdictions can be challenging and resource-intensive for businesses.
The environmental impact of industrial waste is a growing concern. Improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, air pollution, and long-term ecological damage. As public awareness of environmental issues increases, industries face mounting pressure to adopt more sustainable waste management practices.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant challenge in industrial waste management. Implementing advanced treatment technologies and environmentally friendly disposal methods often requires substantial investment. Balancing these costs with operational efficiency and profitability is a constant struggle for many industries.
Resource recovery and circular economy principles present both opportunities and challenges. While there is increasing emphasis on recycling and reusing industrial waste, implementing effective recovery systems can be technically complex and economically challenging. Developing viable markets for recovered materials and byproducts is crucial for the success of these initiatives.
Finally, the lack of standardized waste management practices across industries and regions hinders progress. Inconsistent approaches to waste classification, treatment, and disposal make it difficult to implement large-scale, coordinated waste management strategies. Addressing this challenge requires improved collaboration between industries, governments, and waste management experts to develop and implement best practices.
Carboxylic Acid-Based Waste Reduction Methods
01 Treatment and disposal methods for carboxylic acid waste
Various methods are employed to treat and dispose of carboxylic acid waste, including chemical neutralization, biological treatment, and incineration. These processes aim to reduce the acidity and environmental impact of the waste before disposal or potential reuse.- Treatment and disposal of carboxylic acid waste: Various methods are employed for treating and disposing of carboxylic acid waste. These may include chemical neutralization, biological treatment, or advanced oxidation processes. The goal is to reduce the acidity and toxicity of the waste before disposal or potential reuse.
- Recovery and purification of carboxylic acids from waste streams: Techniques are developed to recover and purify carboxylic acids from industrial waste streams. These may involve extraction, distillation, or membrane separation processes. The recovered acids can be reused in various applications, reducing waste and improving resource efficiency.
- Conversion of carboxylic acid waste into valuable products:
- Microbial degradation of carboxylic acid waste: Biological methods using specific microorganisms are employed to degrade carboxylic acid waste. These processes can be more environmentally friendly and cost-effective compared to chemical treatments. The microbes metabolize the acids, reducing their concentration in the waste stream.
- Catalytic processes for carboxylic acid waste treatment: Catalytic reactions are developed to transform carboxylic acid waste into less harmful or more valuable compounds. These processes can involve hydrogenation, decarboxylation, or other chemical transformations. The choice of catalyst and reaction conditions is crucial for the efficiency of the process.
02 Recovery and purification of carboxylic acids from waste streams
Techniques for recovering and purifying carboxylic acids from waste streams involve extraction, distillation, and membrane separation processes. These methods allow for the reclamation of valuable carboxylic acids, reducing waste and improving resource efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Conversion of carboxylic acid waste into useful products
Carboxylic acid waste can be converted into valuable products through various chemical and biological processes. This includes the production of biofuels, polymers, and other industrially useful compounds, effectively turning waste into resources.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental impact mitigation of carboxylic acid waste
Strategies to mitigate the environmental impact of carboxylic acid waste include developing eco-friendly disposal methods, implementing closed-loop recycling systems, and using green chemistry principles in production processes to minimize waste generation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical methods for carboxylic acid waste characterization
Advanced analytical techniques are used to characterize carboxylic acid waste, including spectroscopic methods, chromatography, and electrochemical analysis. These methods help in identifying the composition of waste streams, which is crucial for developing effective treatment and recovery strategies.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Industrial Chemical Solutions
The carboxylic acid waste reduction technology in industrial processes is in a mature development stage, with a significant market size due to its widespread applications across various industries. The market is characterized by established players and ongoing research for further optimization. Companies like Cargill, Shell Oil Co., and BASF Corp. are at the forefront, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities to enhance process efficiency and sustainability. The technology's maturity is evident in its integration into diverse industrial sectors, including petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. However, there's still room for innovation, particularly in areas of green chemistry and circular economy approaches, as demonstrated by the involvement of research institutions like Delft University of Technology and specialized firms such as Dioxide Materials, Inc.
Eastman Chemical Co.
Technical Solution: Eastman Chemical has developed a sustainable approach to carboxylic acid production that focuses on circular economy principles. Their process utilizes advanced molecular recycling technologies to convert waste plastics into raw materials for carboxylic acid synthesis[13]. This innovative method not only reduces waste in the production process but also addresses the broader issue of plastic waste[15]. Eastman's technology employs a proprietary catalyst system that enables efficient conversion of recycled feedstocks into high-purity carboxylic acids[14]. The process also incorporates advanced purification techniques, including membrane separation and crystallization, to ensure product quality while minimizing waste streams[16].
Strengths: Addresses plastic waste issues, promotes circular economy, and reduces reliance on virgin raw materials. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in ensuring consistent quality of recycled feedstocks and managing impurities in the recycling process.
Arkema France SA
Technical Solution: Arkema has developed a bio-based process for producing acrylic acid, a key carboxylic acid used in various industries. Their innovative approach utilizes renewable resources, specifically glycerol derived from vegetable oils, as a starting material[4]. The process involves a two-step conversion: first, glycerol is dehydrated to acrolein, and then acrolein is oxidized to acrylic acid using a proprietary catalyst[6]. This method not only reduces dependence on fossil-based raw materials but also significantly decreases carbon dioxide emissions compared to traditional petrochemical routes[7]. Arkema's process also incorporates advanced separation and purification techniques, which enhance product quality and reduce waste streams[8].
Strengths: Utilization of renewable resources, reduced carbon footprint, and improved sustainability. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up bio-based processes and ensuring consistent quality of renewable feedstocks.
Innovative Applications of Carboxylic Acid
Carboxylic acids prepared using a salt-splitting process
PatentWO2008042958A2
Innovation
- A process involving the combination of an ammonium salt of a β-hydroxy carboxylic acid with a non-aqueous solvent and water to form a single phase mixture, which is then heated to split the ammonium salt, producing the β-hydroxy carboxylic acid without generating waste salts and without the need for acidification or elaborate distillation, allowing for recycling of ammonia or amines and dehydration to form unsaturated carboxylic acids.
Method and apparatus for controlling feed of gaseous reaction component
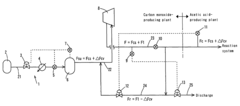
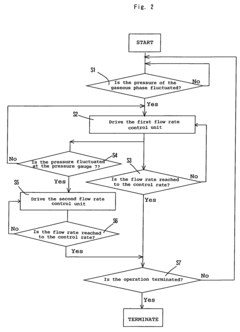
PatentInactiveUS7381837B2
Innovation
- A control method and apparatus that continuously supply carbon monoxide through a feed line with a reference flow rate, while circulating excess reactant via a circulation line to compensate for consumption fluctuations, maintaining system pressure and optimizing reactant utilization by adjusting feed flow rates based on pressure fluctuations in the reaction system.
Environmental Regulations and Compliance
The use of carboxylic acids in industrial processes has become increasingly subject to environmental regulations and compliance requirements. As industries strive to reduce waste and minimize their environmental impact, regulatory bodies have implemented stringent guidelines to ensure responsible use of these chemicals.
One of the primary areas of focus is the management of carboxylic acid emissions. Many countries have established air quality standards that limit the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including carboxylic acids. Industries are required to implement emission control technologies, such as scrubbers or thermal oxidizers, to capture and treat acid vapors before they are released into the atmosphere.
Wastewater discharge regulations also play a crucial role in governing the use of carboxylic acids. Effluent limitations have been set to control the pH levels and organic content of industrial wastewater. Companies must invest in appropriate treatment systems to neutralize acidic waste streams and remove organic contaminants before discharge.
The storage and handling of carboxylic acids are subject to strict safety regulations. Facilities must adhere to proper containment measures, including the use of corrosion-resistant materials and secondary containment systems to prevent accidental releases. Regular inspections and maintenance of storage tanks and transfer equipment are mandated to ensure compliance with these regulations.
Waste management regulations have also evolved to address the disposal of carboxylic acid-containing materials. Many jurisdictions classify these wastes as hazardous, requiring specialized handling, treatment, and disposal methods. Industries are encouraged to implement waste reduction strategies and explore recycling options to minimize the generation of hazardous waste.
Environmental impact assessments have become a standard requirement for new industrial projects involving carboxylic acids. These assessments evaluate the potential environmental consequences of proposed operations and outline mitigation measures to reduce adverse effects. Regulatory authorities use these assessments to make informed decisions on project approvals and to set specific compliance conditions.
Reporting and documentation requirements have increased to ensure transparency and accountability. Industries must maintain detailed records of carboxylic acid usage, waste generation, and disposal practices. Regular environmental audits and compliance reports are often mandated to demonstrate adherence to regulations and identify areas for improvement.
As global environmental concerns continue to grow, international agreements and standards are influencing national regulations on carboxylic acid use. Many countries are aligning their policies with global initiatives aimed at reducing industrial pollution and promoting sustainable practices. This harmonization of regulations is creating a more consistent regulatory landscape for multinational corporations operating in different regions.
One of the primary areas of focus is the management of carboxylic acid emissions. Many countries have established air quality standards that limit the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including carboxylic acids. Industries are required to implement emission control technologies, such as scrubbers or thermal oxidizers, to capture and treat acid vapors before they are released into the atmosphere.
Wastewater discharge regulations also play a crucial role in governing the use of carboxylic acids. Effluent limitations have been set to control the pH levels and organic content of industrial wastewater. Companies must invest in appropriate treatment systems to neutralize acidic waste streams and remove organic contaminants before discharge.
The storage and handling of carboxylic acids are subject to strict safety regulations. Facilities must adhere to proper containment measures, including the use of corrosion-resistant materials and secondary containment systems to prevent accidental releases. Regular inspections and maintenance of storage tanks and transfer equipment are mandated to ensure compliance with these regulations.
Waste management regulations have also evolved to address the disposal of carboxylic acid-containing materials. Many jurisdictions classify these wastes as hazardous, requiring specialized handling, treatment, and disposal methods. Industries are encouraged to implement waste reduction strategies and explore recycling options to minimize the generation of hazardous waste.
Environmental impact assessments have become a standard requirement for new industrial projects involving carboxylic acids. These assessments evaluate the potential environmental consequences of proposed operations and outline mitigation measures to reduce adverse effects. Regulatory authorities use these assessments to make informed decisions on project approvals and to set specific compliance conditions.
Reporting and documentation requirements have increased to ensure transparency and accountability. Industries must maintain detailed records of carboxylic acid usage, waste generation, and disposal practices. Regular environmental audits and compliance reports are often mandated to demonstrate adherence to regulations and identify areas for improvement.
As global environmental concerns continue to grow, international agreements and standards are influencing national regulations on carboxylic acid use. Many countries are aligning their policies with global initiatives aimed at reducing industrial pollution and promoting sustainable practices. This harmonization of regulations is creating a more consistent regulatory landscape for multinational corporations operating in different regions.
Economic Impact of Waste Reduction
The reduction of waste in industrial processes through the use of carboxylic acids has significant economic implications across various sectors. This approach not only minimizes environmental impact but also offers substantial cost savings and operational efficiencies for businesses.
One of the primary economic benefits is the reduction in raw material costs. By utilizing carboxylic acids to optimize chemical reactions and improve product yields, industries can significantly decrease the amount of input materials required. This leads to direct savings on procurement expenses and reduces the need for storage and handling of excess raw materials.
Furthermore, the implementation of carboxylic acid-based waste reduction strategies often results in improved process efficiency. This translates to lower energy consumption, reduced processing times, and increased production capacity. As a result, companies can achieve higher output levels with the same or fewer resources, enhancing their overall productivity and profitability.
The reduction of waste also leads to decreased disposal costs. Many industrial processes generate substantial amounts of by-products and waste materials that require expensive treatment or disposal methods. By minimizing waste generation through carboxylic acid applications, companies can significantly reduce their waste management expenses, including transportation, treatment, and landfill fees.
Additionally, the adoption of such waste reduction techniques can enhance a company's market position and brand value. As consumers and regulatory bodies increasingly prioritize environmental sustainability, businesses that demonstrate effective waste reduction practices may gain a competitive advantage. This can lead to increased market share, customer loyalty, and potentially higher profit margins for environmentally responsible products.
From a broader economic perspective, the widespread implementation of carboxylic acid-based waste reduction methods can stimulate innovation and growth in the chemical industry. This creates opportunities for the development of new technologies, specialized equipment, and services related to waste reduction, potentially fostering job creation and economic growth in related sectors.
Moreover, the economic benefits extend to the public sector as well. Reduced industrial waste can lead to lower environmental remediation costs for governments and decreased strain on public waste management infrastructure. This can result in more efficient allocation of public resources and potential tax savings for communities.
In conclusion, the economic impact of waste reduction through carboxylic acid applications is multifaceted and far-reaching. It offers direct financial benefits to industries through cost savings and efficiency gains, while also contributing to broader economic and environmental sustainability goals. As industries continue to seek ways to optimize their processes and reduce their environmental footprint, the economic incentives associated with carboxylic acid-based waste reduction strategies are likely to drive further adoption and innovation in this field.
One of the primary economic benefits is the reduction in raw material costs. By utilizing carboxylic acids to optimize chemical reactions and improve product yields, industries can significantly decrease the amount of input materials required. This leads to direct savings on procurement expenses and reduces the need for storage and handling of excess raw materials.
Furthermore, the implementation of carboxylic acid-based waste reduction strategies often results in improved process efficiency. This translates to lower energy consumption, reduced processing times, and increased production capacity. As a result, companies can achieve higher output levels with the same or fewer resources, enhancing their overall productivity and profitability.
The reduction of waste also leads to decreased disposal costs. Many industrial processes generate substantial amounts of by-products and waste materials that require expensive treatment or disposal methods. By minimizing waste generation through carboxylic acid applications, companies can significantly reduce their waste management expenses, including transportation, treatment, and landfill fees.
Additionally, the adoption of such waste reduction techniques can enhance a company's market position and brand value. As consumers and regulatory bodies increasingly prioritize environmental sustainability, businesses that demonstrate effective waste reduction practices may gain a competitive advantage. This can lead to increased market share, customer loyalty, and potentially higher profit margins for environmentally responsible products.
From a broader economic perspective, the widespread implementation of carboxylic acid-based waste reduction methods can stimulate innovation and growth in the chemical industry. This creates opportunities for the development of new technologies, specialized equipment, and services related to waste reduction, potentially fostering job creation and economic growth in related sectors.
Moreover, the economic benefits extend to the public sector as well. Reduced industrial waste can lead to lower environmental remediation costs for governments and decreased strain on public waste management infrastructure. This can result in more efficient allocation of public resources and potential tax savings for communities.
In conclusion, the economic impact of waste reduction through carboxylic acid applications is multifaceted and far-reaching. It offers direct financial benefits to industries through cost savings and efficiency gains, while also contributing to broader economic and environmental sustainability goals. As industries continue to seek ways to optimize their processes and reduce their environmental footprint, the economic incentives associated with carboxylic acid-based waste reduction strategies are likely to drive further adoption and innovation in this field.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!