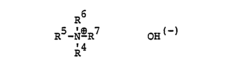How Isocyanates Reach Innovative Standardization Benchmarks?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Tech Evolution
The evolution of isocyanate technology has been marked by significant milestones and continuous innovation over the past century. Initially discovered in 1849 by Wurtz, isocyanates remained largely unexplored until the 1930s when their potential for polymer synthesis was recognized. This breakthrough led to the development of polyurethanes, revolutionizing various industries.
The 1940s and 1950s saw rapid advancements in isocyanate chemistry, with the introduction of toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI). These compounds became the backbone of the polyurethane industry, enabling the production of flexible and rigid foams, elastomers, and coatings. The subsequent decades witnessed a focus on improving production processes and expanding applications.
In the 1970s and 1980s, environmental and health concerns prompted research into safer isocyanate handling and usage. This period saw the development of blocked isocyanates and water-based systems, addressing issues related to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and worker exposure. Concurrently, efforts to enhance the performance of isocyanate-based products led to the creation of specialized formulations for specific applications.
The 1990s and early 2000s marked a shift towards sustainability and eco-friendly solutions. Bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources emerged as alternatives to petroleum-based products. Additionally, advancements in catalysis and process technology improved the efficiency and selectivity of isocyanate production.
Recent years have seen a focus on nanotechnology and smart materials. Isocyanate-based nanocomposites and self-healing polymers have opened new avenues for high-performance materials. The integration of isocyanates with other emerging technologies, such as 3D printing and wearable electronics, has further expanded their application scope.
Standardization efforts have played a crucial role in the evolution of isocyanate technology. Industry-wide initiatives have led to the establishment of safety protocols, quality control measures, and performance benchmarks. These standards have not only improved product consistency and reliability but also facilitated global trade and collaboration in research and development.
Looking ahead, the isocyanate industry is poised for further innovation. Current research focuses on developing isocyanates with reduced environmental impact, improved safety profiles, and enhanced performance characteristics. The pursuit of innovative standardization benchmarks continues to drive advancements in production methods, analytical techniques, and application-specific formulations, ensuring that isocyanates remain at the forefront of materials science and chemical engineering.
The 1940s and 1950s saw rapid advancements in isocyanate chemistry, with the introduction of toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI). These compounds became the backbone of the polyurethane industry, enabling the production of flexible and rigid foams, elastomers, and coatings. The subsequent decades witnessed a focus on improving production processes and expanding applications.
In the 1970s and 1980s, environmental and health concerns prompted research into safer isocyanate handling and usage. This period saw the development of blocked isocyanates and water-based systems, addressing issues related to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and worker exposure. Concurrently, efforts to enhance the performance of isocyanate-based products led to the creation of specialized formulations for specific applications.
The 1990s and early 2000s marked a shift towards sustainability and eco-friendly solutions. Bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources emerged as alternatives to petroleum-based products. Additionally, advancements in catalysis and process technology improved the efficiency and selectivity of isocyanate production.
Recent years have seen a focus on nanotechnology and smart materials. Isocyanate-based nanocomposites and self-healing polymers have opened new avenues for high-performance materials. The integration of isocyanates with other emerging technologies, such as 3D printing and wearable electronics, has further expanded their application scope.
Standardization efforts have played a crucial role in the evolution of isocyanate technology. Industry-wide initiatives have led to the establishment of safety protocols, quality control measures, and performance benchmarks. These standards have not only improved product consistency and reliability but also facilitated global trade and collaboration in research and development.
Looking ahead, the isocyanate industry is poised for further innovation. Current research focuses on developing isocyanates with reduced environmental impact, improved safety profiles, and enhanced performance characteristics. The pursuit of innovative standardization benchmarks continues to drive advancements in production methods, analytical techniques, and application-specific formulations, ensuring that isocyanates remain at the forefront of materials science and chemical engineering.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for isocyanates has been steadily growing, driven by their versatile applications across various industries. The global isocyanate market is experiencing robust expansion, primarily fueled by the increasing use of polyurethanes in construction, automotive, and furniture sectors. As these industries continue to evolve and seek innovative solutions, the demand for high-performance isocyanates that meet stringent standardization benchmarks is on the rise.
In the construction industry, isocyanates play a crucial role in the production of insulation materials, sealants, and adhesives. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient buildings and sustainable construction practices has led to a surge in demand for advanced insulation solutions, thereby boosting the market for isocyanates. Similarly, the automotive sector's shift towards lightweight materials and improved fuel efficiency has increased the adoption of polyurethane-based components, further driving the demand for isocyanates.
The furniture industry represents another significant market for isocyanates, particularly in the production of flexible and rigid foams used in upholstery and mattresses. As consumer preferences evolve towards more comfortable and durable furniture, manufacturers are increasingly turning to isocyanate-based materials to meet these demands.
Market trends indicate a growing preference for eco-friendly and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) isocyanate formulations. This shift is largely driven by stringent environmental regulations and increasing consumer awareness about sustainability. Consequently, there is a rising demand for bio-based isocyanates and water-based polyurethane systems, presenting new opportunities for innovation in the isocyanate market.
The healthcare and medical device industries are emerging as promising growth areas for isocyanates. The use of polyurethanes in medical applications, such as wound dressings, catheters, and prosthetics, is expanding, creating new avenues for isocyanate manufacturers to explore.
As industries strive to meet higher performance standards and regulatory requirements, there is an increasing focus on developing isocyanates that can achieve innovative standardization benchmarks. This trend is driving research and development efforts towards creating isocyanates with enhanced properties, such as improved thermal stability, chemical resistance, and durability.
The market demand analysis reveals a clear trajectory towards more specialized and high-performance isocyanates. Manufacturers are under pressure to develop products that not only meet current industry standards but also anticipate future regulatory changes and performance requirements. This dynamic is fostering a competitive landscape where innovation in isocyanate technology is becoming a key differentiator for market players.
In the construction industry, isocyanates play a crucial role in the production of insulation materials, sealants, and adhesives. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient buildings and sustainable construction practices has led to a surge in demand for advanced insulation solutions, thereby boosting the market for isocyanates. Similarly, the automotive sector's shift towards lightweight materials and improved fuel efficiency has increased the adoption of polyurethane-based components, further driving the demand for isocyanates.
The furniture industry represents another significant market for isocyanates, particularly in the production of flexible and rigid foams used in upholstery and mattresses. As consumer preferences evolve towards more comfortable and durable furniture, manufacturers are increasingly turning to isocyanate-based materials to meet these demands.
Market trends indicate a growing preference for eco-friendly and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) isocyanate formulations. This shift is largely driven by stringent environmental regulations and increasing consumer awareness about sustainability. Consequently, there is a rising demand for bio-based isocyanates and water-based polyurethane systems, presenting new opportunities for innovation in the isocyanate market.
The healthcare and medical device industries are emerging as promising growth areas for isocyanates. The use of polyurethanes in medical applications, such as wound dressings, catheters, and prosthetics, is expanding, creating new avenues for isocyanate manufacturers to explore.
As industries strive to meet higher performance standards and regulatory requirements, there is an increasing focus on developing isocyanates that can achieve innovative standardization benchmarks. This trend is driving research and development efforts towards creating isocyanates with enhanced properties, such as improved thermal stability, chemical resistance, and durability.
The market demand analysis reveals a clear trajectory towards more specialized and high-performance isocyanates. Manufacturers are under pressure to develop products that not only meet current industry standards but also anticipate future regulatory changes and performance requirements. This dynamic is fostering a competitive landscape where innovation in isocyanate technology is becoming a key differentiator for market players.
Current Challenges
The standardization of isocyanates faces several significant challenges in the current landscape. One of the primary obstacles is the diverse range of isocyanate compounds and their applications across multiple industries. This diversity makes it difficult to establish universal benchmarks that can be applied consistently across all sectors.
The reactive nature of isocyanates presents another major challenge. These compounds are highly sensitive to environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of other chemicals. This reactivity complicates the development of standardized testing methods and storage protocols, as slight variations in conditions can lead to significant differences in results.
Safety concerns also pose a substantial hurdle in the standardization process. Isocyanates are known for their potential health hazards, particularly respiratory sensitization and occupational asthma. Establishing safety standards that adequately protect workers while maintaining practical usability in industrial settings requires a delicate balance.
The global nature of the isocyanate market introduces regulatory complexities. Different countries and regions have varying regulations and standards for isocyanate use and handling. Harmonizing these diverse regulatory frameworks to create internationally recognized benchmarks is a formidable task that requires extensive collaboration and negotiation.
Technological advancements in isocyanate chemistry further complicate standardization efforts. As new formulations and applications emerge, existing standards may quickly become obsolete. The rapid pace of innovation necessitates a flexible and adaptable approach to standardization that can keep pace with technological progress.
Environmental concerns add another layer of complexity to the standardization process. The push for more sustainable and eco-friendly practices in chemical manufacturing has led to increased scrutiny of isocyanate production and use. Incorporating environmental considerations into standardization benchmarks while maintaining product performance is a significant challenge.
Finally, the lack of comprehensive data on long-term effects and exposure limits for various isocyanate compounds hinders the development of evidence-based standards. Conducting extensive research to fill these knowledge gaps is both time-consuming and resource-intensive, yet crucial for establishing reliable and scientifically sound benchmarks.
The reactive nature of isocyanates presents another major challenge. These compounds are highly sensitive to environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of other chemicals. This reactivity complicates the development of standardized testing methods and storage protocols, as slight variations in conditions can lead to significant differences in results.
Safety concerns also pose a substantial hurdle in the standardization process. Isocyanates are known for their potential health hazards, particularly respiratory sensitization and occupational asthma. Establishing safety standards that adequately protect workers while maintaining practical usability in industrial settings requires a delicate balance.
The global nature of the isocyanate market introduces regulatory complexities. Different countries and regions have varying regulations and standards for isocyanate use and handling. Harmonizing these diverse regulatory frameworks to create internationally recognized benchmarks is a formidable task that requires extensive collaboration and negotiation.
Technological advancements in isocyanate chemistry further complicate standardization efforts. As new formulations and applications emerge, existing standards may quickly become obsolete. The rapid pace of innovation necessitates a flexible and adaptable approach to standardization that can keep pace with technological progress.
Environmental concerns add another layer of complexity to the standardization process. The push for more sustainable and eco-friendly practices in chemical manufacturing has led to increased scrutiny of isocyanate production and use. Incorporating environmental considerations into standardization benchmarks while maintaining product performance is a significant challenge.
Finally, the lack of comprehensive data on long-term effects and exposure limits for various isocyanate compounds hinders the development of evidence-based standards. Conducting extensive research to fill these knowledge gaps is both time-consuming and resource-intensive, yet crucial for establishing reliable and scientifically sound benchmarks.
Existing Solutions
01 Standardization of isocyanate measurement methods
Development and implementation of standardized methods for measuring isocyanate concentrations in various applications. This includes techniques for sampling, analysis, and quantification of isocyanates in air, materials, and products. Standardization ensures consistency and comparability of results across different laboratories and industries.- Standardization of isocyanate measurement methods: Development of standardized methods for measuring isocyanate concentrations in various environments. This includes techniques for sampling, analysis, and quantification of isocyanates to ensure consistent and accurate results across different laboratories and industries.
- Quality control standards for isocyanate-based products: Establishment of quality control standards for products containing isocyanates, such as polyurethanes and coatings. This involves defining acceptable ranges for isocyanate content, reactivity, and purity to ensure product consistency and performance.
- Standardization of isocyanate handling and safety protocols: Development of standardized safety protocols for handling, storage, and disposal of isocyanates in industrial settings. This includes guidelines for personal protective equipment, ventilation requirements, and emergency response procedures to minimize health and environmental risks.
- Isocyanate characterization and classification standards: Establishment of standardized methods for characterizing and classifying different types of isocyanates based on their chemical structure, reactivity, and physical properties. This aids in proper identification, labeling, and application of isocyanates in various industries.
- Standardization of isocyanate-based formulations: Development of standardized formulations and processing parameters for isocyanate-based products in specific applications. This includes guidelines for mixing ratios, curing conditions, and additives to ensure consistent product performance across different manufacturers.
02 Quality control and assurance for isocyanate-based products
Establishment of standardized quality control procedures for isocyanate-based products, including polyurethanes and coatings. This involves developing protocols for testing raw materials, monitoring production processes, and evaluating final product properties to ensure consistency and compliance with industry standards.Expand Specific Solutions03 Safety standards for handling and storage of isocyanates
Creation and implementation of safety standards for the handling, storage, and transportation of isocyanates. This includes guidelines for personal protective equipment, ventilation requirements, spill containment, and emergency response procedures to minimize risks associated with isocyanate exposure.Expand Specific Solutions04 Standardization of isocyanate-based formulations
Development of standardized formulations and processing parameters for isocyanate-based products across various industries. This includes establishing guidelines for mixing ratios, curing conditions, and additives to ensure consistent performance and properties of final products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and health impact assessment standards
Creation of standardized protocols for assessing the environmental and health impacts of isocyanates throughout their lifecycle. This includes methods for evaluating emissions, biodegradability, and potential long-term effects on human health and ecosystems, as well as establishing acceptable exposure limits and mitigation strategies.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The isocyanates industry is in a mature growth phase, characterized by steady demand and established market players. The global market size for isocyanates is substantial, driven by their widespread use in polyurethane production across various sectors. Technologically, the field is advancing towards innovative standardization benchmarks, with key players like Wanhua Chemical, BASF, Covestro, and Bayer leading research and development efforts. These companies are focusing on improving product performance, sustainability, and compliance with evolving regulatory standards. The competitive landscape is intense, with companies investing in R&D to differentiate their offerings and meet the increasing demand for eco-friendly and high-performance isocyanate products.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group has developed innovative isocyanate production processes that meet stringent environmental and safety standards. Their approach includes the use of advanced catalysts and optimized reaction conditions to improve yield and reduce byproducts. The company has implemented a closed-loop production system that minimizes emissions and maximizes resource efficiency[1]. They have also developed proprietary technology for the production of low-monomer content polyisocyanates, which significantly reduces worker exposure risks and improves product safety[2]. Wanhua's continuous investment in R&D has led to the development of novel isocyanate grades with enhanced performance characteristics, such as improved durability and weather resistance[3].
Strengths: Advanced production technology, strong focus on sustainability, and diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Potential dependency on raw material supply and exposure to market volatility.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has pioneered several breakthrough technologies in isocyanate production, focusing on sustainability and efficiency. Their gas-phase phosgenation process for TDI (toluene diisocyanate) production has set new industry benchmarks for energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprint[4]. BASF has also developed a novel MDI (methylene diphenyl diisocyanate) production method that utilizes a more environmentally friendly aniline production process, reducing overall environmental impact[5]. The company's commitment to green chemistry has led to the development of bio-based isocyanates, derived from renewable resources, which align with circular economy principles[6]. BASF's innovative approach extends to product application, with the development of low-emission isocyanate formulations for automotive and construction industries.
Strengths: Industry-leading R&D capabilities, strong focus on sustainable chemistry, and global market presence. Weaknesses: High capital investment requirements for new technologies and potential regulatory challenges in some markets.
Core Innovations
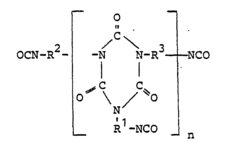
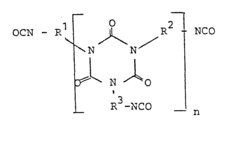
Process for the preparation of isocyanurates containing isocyanate groups the products obtained by the process and their application as isocyanate component in polyurethane lacquers
PatentInactiveEP0047452A1
Innovation
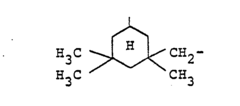
- A process involving the catalytic trimerization of a mixture of hexamethylene diisocyanate and 1-isocyanato-3,3,5-trimethyl-5-isocyanatomethyl-cyclohexane (IPDI) to produce isocyanato-isocyanurates with a specific molar ratio, which allows for clear, low-viscosity solutions in weakly polar solvents and enhanced hardness and elasticity, even at low temperatures.
Isocyanato-isocyanurates, process for their preparation and their use in polyurethane lacquers as isocyanate component
PatentInactiveEP0039864A1
Innovation
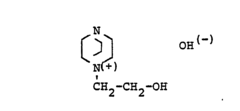
- Development of new isocyanato-isocyanurates with high melting points and improved solvent compatibility through the catalytic trimerization of diisocyanates, specifically using bis-(isocyanatomethyl)-tricyclo[5,2,1,0,2,6]-decane, with quaternary ammonium hydroxides as catalysts, and optionally blocking isocyanate groups for enhanced reactivity and stability.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding isocyanates plays a crucial role in driving innovative standardization benchmarks. Governments and international organizations have established comprehensive regulations to ensure the safe production, handling, and use of isocyanates across various industries. These regulations have evolved over time, reflecting advancements in scientific understanding and technological capabilities.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set stringent exposure limits for isocyanates in workplace environments. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) provides additional guidelines and recommendations for best practices in handling these chemicals. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates isocyanates under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), focusing on environmental impact and consumer safety.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which includes specific provisions for isocyanates. This comprehensive framework requires manufacturers and importers to register chemical substances and provide detailed safety information. The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation further ensures consistent hazard communication across EU member states.
International standards organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), have developed specific standards for isocyanate testing, quality control, and performance evaluation. These standards provide a common language and methodology for industry stakeholders, facilitating global trade and ensuring product consistency.
The regulatory landscape has prompted innovative approaches to isocyanate standardization. Companies are investing in advanced analytical techniques and monitoring systems to ensure compliance with increasingly stringent regulations. This has led to the development of more sensitive detection methods, improved personal protective equipment, and enhanced process control systems.
Emerging trends in isocyanate regulation include a focus on sustainable alternatives and green chemistry principles. Regulatory bodies are encouraging the development of bio-based isocyanates and exploring ways to reduce the environmental footprint of isocyanate production. This shift is driving research into novel synthesis routes and alternative raw materials, pushing the boundaries of isocyanate chemistry.
As global awareness of health and environmental concerns grows, regulatory frameworks are becoming more harmonized across different regions. This trend towards international alignment is fostering collaboration between industry players, research institutions, and regulatory bodies, leading to more robust and universally applicable standardization benchmarks for isocyanates.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set stringent exposure limits for isocyanates in workplace environments. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) provides additional guidelines and recommendations for best practices in handling these chemicals. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates isocyanates under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), focusing on environmental impact and consumer safety.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which includes specific provisions for isocyanates. This comprehensive framework requires manufacturers and importers to register chemical substances and provide detailed safety information. The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation further ensures consistent hazard communication across EU member states.
International standards organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), have developed specific standards for isocyanate testing, quality control, and performance evaluation. These standards provide a common language and methodology for industry stakeholders, facilitating global trade and ensuring product consistency.
The regulatory landscape has prompted innovative approaches to isocyanate standardization. Companies are investing in advanced analytical techniques and monitoring systems to ensure compliance with increasingly stringent regulations. This has led to the development of more sensitive detection methods, improved personal protective equipment, and enhanced process control systems.
Emerging trends in isocyanate regulation include a focus on sustainable alternatives and green chemistry principles. Regulatory bodies are encouraging the development of bio-based isocyanates and exploring ways to reduce the environmental footprint of isocyanate production. This shift is driving research into novel synthesis routes and alternative raw materials, pushing the boundaries of isocyanate chemistry.
As global awareness of health and environmental concerns grows, regulatory frameworks are becoming more harmonized across different regions. This trend towards international alignment is fostering collaboration between industry players, research institutions, and regulatory bodies, leading to more robust and universally applicable standardization benchmarks for isocyanates.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of isocyanates and their standardization processes is a critical consideration in the pursuit of innovative benchmarks. Isocyanates, widely used in the production of polyurethanes, have significant implications for both human health and ecological systems. The standardization of these compounds must therefore address their potential environmental effects throughout their lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with isocyanates is their potential for air pollution. During manufacturing processes and product use, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can be released, contributing to smog formation and air quality degradation. Innovative standardization benchmarks must focus on reducing these emissions through improved production techniques and stricter handling protocols.
Water contamination is another crucial environmental aspect to consider. Isocyanates can react with water to form potentially harmful byproducts, posing risks to aquatic ecosystems if not properly managed. Standardization efforts should encompass comprehensive wastewater treatment guidelines and spill prevention measures to mitigate these risks.
The persistence and bioaccumulation potential of isocyanates in the environment are also important factors. While many isocyanates degrade relatively quickly in the environment, some may persist longer or form stable compounds that can accumulate in living organisms. Innovative benchmarks should include rigorous testing protocols to assess the long-term environmental fate of these substances and their degradation products.
Waste management is a critical area where standardization can drive significant environmental improvements. The disposal of isocyanate-containing products and manufacturing waste requires careful consideration to prevent soil and groundwater contamination. Innovative benchmarks should promote circular economy principles, encouraging recycling and reuse where possible, and ensuring safe disposal methods for materials that cannot be reclaimed.
Energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with isocyanate production are also important environmental considerations. Standardization efforts should incentivize the development and adoption of more energy-efficient manufacturing processes and the use of renewable energy sources. This approach can help reduce the carbon footprint of isocyanate-based products throughout their lifecycle.
Biodiversity protection is another crucial aspect that innovative standardization benchmarks must address. The potential impacts of isocyanates on flora and fauna, particularly in sensitive ecosystems, should be thoroughly assessed. This may involve establishing buffer zones around manufacturing facilities, implementing stringent monitoring programs, and developing eco-friendly alternatives where feasible.
In conclusion, reaching innovative standardization benchmarks for isocyanates requires a holistic approach to environmental impact assessment and mitigation. By addressing air and water pollution, persistence and bioaccumulation, waste management, energy efficiency, and biodiversity protection, these standards can drive significant improvements in the environmental performance of isocyanate-based industries.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with isocyanates is their potential for air pollution. During manufacturing processes and product use, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can be released, contributing to smog formation and air quality degradation. Innovative standardization benchmarks must focus on reducing these emissions through improved production techniques and stricter handling protocols.
Water contamination is another crucial environmental aspect to consider. Isocyanates can react with water to form potentially harmful byproducts, posing risks to aquatic ecosystems if not properly managed. Standardization efforts should encompass comprehensive wastewater treatment guidelines and spill prevention measures to mitigate these risks.
The persistence and bioaccumulation potential of isocyanates in the environment are also important factors. While many isocyanates degrade relatively quickly in the environment, some may persist longer or form stable compounds that can accumulate in living organisms. Innovative benchmarks should include rigorous testing protocols to assess the long-term environmental fate of these substances and their degradation products.
Waste management is a critical area where standardization can drive significant environmental improvements. The disposal of isocyanate-containing products and manufacturing waste requires careful consideration to prevent soil and groundwater contamination. Innovative benchmarks should promote circular economy principles, encouraging recycling and reuse where possible, and ensuring safe disposal methods for materials that cannot be reclaimed.
Energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with isocyanate production are also important environmental considerations. Standardization efforts should incentivize the development and adoption of more energy-efficient manufacturing processes and the use of renewable energy sources. This approach can help reduce the carbon footprint of isocyanate-based products throughout their lifecycle.
Biodiversity protection is another crucial aspect that innovative standardization benchmarks must address. The potential impacts of isocyanates on flora and fauna, particularly in sensitive ecosystems, should be thoroughly assessed. This may involve establishing buffer zones around manufacturing facilities, implementing stringent monitoring programs, and developing eco-friendly alternatives where feasible.
In conclusion, reaching innovative standardization benchmarks for isocyanates requires a holistic approach to environmental impact assessment and mitigation. By addressing air and water pollution, persistence and bioaccumulation, waste management, energy efficiency, and biodiversity protection, these standards can drive significant improvements in the environmental performance of isocyanate-based industries.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!