How Magnesium Carbonate Affects the Flavor Profile of Dairy Products
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Magnesium Carbonate in Dairy: Background and Objectives
Magnesium carbonate has been a subject of increasing interest in the dairy industry due to its potential impact on the flavor profile of various dairy products. This compound, naturally occurring in some water sources and intentionally added in others, has garnered attention for its multifaceted role in dairy processing and consumption. The evolution of dairy technology has led to a growing awareness of how mineral components can influence not only the nutritional value but also the sensory characteristics of dairy products.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively examine how magnesium carbonate affects the flavor profile of dairy products. This investigation aims to uncover the mechanisms by which this compound interacts with dairy components, altering taste, aroma, and overall sensory perception. Understanding these interactions is crucial for optimizing product formulations and enhancing consumer acceptance in an increasingly competitive market.
Historical context provides valuable insights into the progression of this field. Initially, the focus was predominantly on the nutritional aspects of minerals in dairy. However, as consumer preferences evolved and production techniques advanced, the industry began to recognize the significance of mineral composition in shaping flavor profiles. This shift in perspective has prompted a more nuanced approach to dairy product development, considering both nutritional value and sensory appeal.
The dairy industry's technological trajectory has been marked by continuous innovation, with flavor enhancement techniques becoming increasingly sophisticated. Magnesium carbonate's role in this landscape has emerged as a critical area of study, intersecting with broader trends in food science and consumer health consciousness. As the industry moves towards cleaner labels and more natural ingredients, understanding the intrinsic properties of compounds like magnesium carbonate becomes paramount.
Current market demands reflect a growing consumer interest in dairy products with enhanced nutritional profiles and superior taste experiences. This has led to a surge in research and development efforts focused on manipulating mineral content to achieve desired flavor outcomes. The challenge lies in balancing these sensory improvements with maintaining the authentic taste of dairy that consumers expect and appreciate.
As we delve deeper into this technical exploration, we aim to elucidate the specific mechanisms by which magnesium carbonate influences dairy flavor, identify potential applications across various dairy product categories, and anticipate future trends in this dynamic field. This research seeks to provide a foundation for innovative product development strategies that leverage the flavor-modifying properties of magnesium carbonate while addressing the evolving needs of the global dairy market.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively examine how magnesium carbonate affects the flavor profile of dairy products. This investigation aims to uncover the mechanisms by which this compound interacts with dairy components, altering taste, aroma, and overall sensory perception. Understanding these interactions is crucial for optimizing product formulations and enhancing consumer acceptance in an increasingly competitive market.
Historical context provides valuable insights into the progression of this field. Initially, the focus was predominantly on the nutritional aspects of minerals in dairy. However, as consumer preferences evolved and production techniques advanced, the industry began to recognize the significance of mineral composition in shaping flavor profiles. This shift in perspective has prompted a more nuanced approach to dairy product development, considering both nutritional value and sensory appeal.
The dairy industry's technological trajectory has been marked by continuous innovation, with flavor enhancement techniques becoming increasingly sophisticated. Magnesium carbonate's role in this landscape has emerged as a critical area of study, intersecting with broader trends in food science and consumer health consciousness. As the industry moves towards cleaner labels and more natural ingredients, understanding the intrinsic properties of compounds like magnesium carbonate becomes paramount.
Current market demands reflect a growing consumer interest in dairy products with enhanced nutritional profiles and superior taste experiences. This has led to a surge in research and development efforts focused on manipulating mineral content to achieve desired flavor outcomes. The challenge lies in balancing these sensory improvements with maintaining the authentic taste of dairy that consumers expect and appreciate.
As we delve deeper into this technical exploration, we aim to elucidate the specific mechanisms by which magnesium carbonate influences dairy flavor, identify potential applications across various dairy product categories, and anticipate future trends in this dynamic field. This research seeks to provide a foundation for innovative product development strategies that leverage the flavor-modifying properties of magnesium carbonate while addressing the evolving needs of the global dairy market.
Market Analysis of Fortified Dairy Products
The fortified dairy products market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health and wellness. This segment encompasses a wide range of products, including milk, yogurt, cheese, and other dairy-based items enriched with various nutrients, vitamins, and minerals. Among these, magnesium-fortified dairy products have gained particular attention due to the essential role of magnesium in human health.
Market research indicates that the global fortified dairy products market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to be substantial over the next five years. This growth is attributed to several factors, including rising health consciousness, increasing disposable incomes, and a growing aging population seeking functional foods to support their health.
Regionally, North America and Europe currently dominate the fortified dairy products market, owing to well-established dairy industries and high consumer awareness. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by changing dietary habits, urbanization, and increasing health concerns in countries like China and India.
Consumer preferences within the fortified dairy market are evolving, with a noticeable shift towards products that offer multiple health benefits without compromising on taste. This trend has led to increased demand for dairy products fortified with magnesium carbonate, as it not only enhances the nutritional profile but also potentially influences the flavor characteristics of the products.
Market segmentation reveals that yogurt and milk are the leading product categories in the fortified dairy sector. Yogurt, in particular, has seen substantial growth due to its versatility and perceived health benefits. The introduction of magnesium-fortified yogurt variants has been well-received by health-conscious consumers looking for products that support bone health, muscle function, and overall well-being.
Key market players in the fortified dairy industry have been actively investing in research and development to create innovative products that meet consumer demands for both nutrition and taste. Companies are exploring various formulations and processing techniques to optimize the integration of magnesium carbonate into dairy products while maintaining or enhancing flavor profiles.
Consumer surveys indicate a growing interest in understanding the specific health benefits of fortified dairy products. This has led to increased marketing efforts focused on educating consumers about the role of magnesium in the body and the advantages of consuming magnesium-fortified dairy products. As a result, product labeling and packaging have become crucial differentiators in the market, with clear communication of nutritional benefits being a key factor in consumer decision-making.
The market analysis also highlights the importance of distribution channels in the success of fortified dairy products. Supermarkets and hypermarkets remain the primary retail outlets, but there is a notable increase in online sales, especially in the wake of the global pandemic. This shift in purchasing behavior has prompted dairy companies to enhance their e-commerce presence and develop direct-to-consumer strategies for their fortified product lines.
Market research indicates that the global fortified dairy products market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to be substantial over the next five years. This growth is attributed to several factors, including rising health consciousness, increasing disposable incomes, and a growing aging population seeking functional foods to support their health.
Regionally, North America and Europe currently dominate the fortified dairy products market, owing to well-established dairy industries and high consumer awareness. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by changing dietary habits, urbanization, and increasing health concerns in countries like China and India.
Consumer preferences within the fortified dairy market are evolving, with a noticeable shift towards products that offer multiple health benefits without compromising on taste. This trend has led to increased demand for dairy products fortified with magnesium carbonate, as it not only enhances the nutritional profile but also potentially influences the flavor characteristics of the products.
Market segmentation reveals that yogurt and milk are the leading product categories in the fortified dairy sector. Yogurt, in particular, has seen substantial growth due to its versatility and perceived health benefits. The introduction of magnesium-fortified yogurt variants has been well-received by health-conscious consumers looking for products that support bone health, muscle function, and overall well-being.
Key market players in the fortified dairy industry have been actively investing in research and development to create innovative products that meet consumer demands for both nutrition and taste. Companies are exploring various formulations and processing techniques to optimize the integration of magnesium carbonate into dairy products while maintaining or enhancing flavor profiles.
Consumer surveys indicate a growing interest in understanding the specific health benefits of fortified dairy products. This has led to increased marketing efforts focused on educating consumers about the role of magnesium in the body and the advantages of consuming magnesium-fortified dairy products. As a result, product labeling and packaging have become crucial differentiators in the market, with clear communication of nutritional benefits being a key factor in consumer decision-making.
The market analysis also highlights the importance of distribution channels in the success of fortified dairy products. Supermarkets and hypermarkets remain the primary retail outlets, but there is a notable increase in online sales, especially in the wake of the global pandemic. This shift in purchasing behavior has prompted dairy companies to enhance their e-commerce presence and develop direct-to-consumer strategies for their fortified product lines.
Current Applications and Challenges in Dairy Fortification
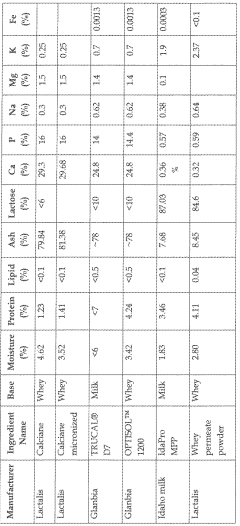
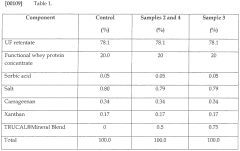
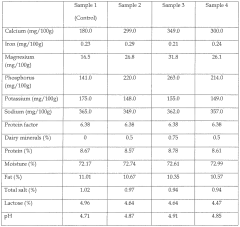
Magnesium carbonate has emerged as a significant additive in dairy fortification, offering both nutritional benefits and potential flavor enhancements. Currently, its applications in the dairy industry are diverse and expanding. Many dairy manufacturers are incorporating magnesium carbonate into milk, yogurt, and cheese products to increase their mineral content and improve overall nutritional profiles.
In milk fortification, magnesium carbonate is often used in combination with other minerals to create balanced, nutrient-rich products. It serves as an excellent source of magnesium, which is essential for bone health, muscle function, and various metabolic processes. Yogurt manufacturers are also exploring the use of magnesium carbonate to enhance the mineral content of their products while potentially influencing texture and stability.
The cheese industry has shown particular interest in magnesium carbonate for its potential to affect both nutritional value and flavor development during the aging process. Some artisanal cheesemakers are experimenting with magnesium carbonate as a ripening agent, believing it may contribute to unique flavor profiles in certain cheese varieties.
Despite these promising applications, the dairy industry faces several challenges in effectively incorporating magnesium carbonate. One primary concern is maintaining product consistency and quality across different formulations. The addition of magnesium carbonate can potentially alter the pH of dairy products, affecting their taste, texture, and shelf life. Manufacturers must carefully balance the amount added to achieve desired nutritional benefits without compromising sensory attributes.
Another significant challenge lies in consumer acceptance. While there is growing awareness of the importance of mineral fortification, some consumers may be skeptical of additives they perceive as "artificial" or "unnecessary." This necessitates clear communication about the benefits of magnesium carbonate fortification and transparency in labeling practices.
Regulatory compliance presents an additional hurdle. Different countries have varying regulations regarding the use of mineral additives in dairy products. Manufacturers must navigate these complex regulatory landscapes to ensure their fortified products meet local standards and can be marketed internationally.
Furthermore, the interaction between magnesium carbonate and other components in dairy products is not fully understood. Research is ongoing to determine how it may affect the bioavailability of other nutrients or influence the overall nutritional profile of fortified dairy products. This knowledge gap presents both a challenge and an opportunity for further scientific investigation and product development.
In milk fortification, magnesium carbonate is often used in combination with other minerals to create balanced, nutrient-rich products. It serves as an excellent source of magnesium, which is essential for bone health, muscle function, and various metabolic processes. Yogurt manufacturers are also exploring the use of magnesium carbonate to enhance the mineral content of their products while potentially influencing texture and stability.
The cheese industry has shown particular interest in magnesium carbonate for its potential to affect both nutritional value and flavor development during the aging process. Some artisanal cheesemakers are experimenting with magnesium carbonate as a ripening agent, believing it may contribute to unique flavor profiles in certain cheese varieties.
Despite these promising applications, the dairy industry faces several challenges in effectively incorporating magnesium carbonate. One primary concern is maintaining product consistency and quality across different formulations. The addition of magnesium carbonate can potentially alter the pH of dairy products, affecting their taste, texture, and shelf life. Manufacturers must carefully balance the amount added to achieve desired nutritional benefits without compromising sensory attributes.
Another significant challenge lies in consumer acceptance. While there is growing awareness of the importance of mineral fortification, some consumers may be skeptical of additives they perceive as "artificial" or "unnecessary." This necessitates clear communication about the benefits of magnesium carbonate fortification and transparency in labeling practices.
Regulatory compliance presents an additional hurdle. Different countries have varying regulations regarding the use of mineral additives in dairy products. Manufacturers must navigate these complex regulatory landscapes to ensure their fortified products meet local standards and can be marketed internationally.
Furthermore, the interaction between magnesium carbonate and other components in dairy products is not fully understood. Research is ongoing to determine how it may affect the bioavailability of other nutrients or influence the overall nutritional profile of fortified dairy products. This knowledge gap presents both a challenge and an opportunity for further scientific investigation and product development.
Existing Methods for Magnesium Carbonate Incorporation
01 Taste masking properties
Magnesium carbonate is used in various formulations to mask unpleasant tastes or flavors. It can neutralize acidic components and reduce bitterness in pharmaceutical and food products, improving overall palatability without significantly altering the intended flavor profile.- Taste masking properties: Magnesium carbonate is used in various formulations to mask unpleasant tastes or flavors. Its ability to neutralize acidic components and absorb odors makes it effective in improving the overall flavor profile of products, particularly in pharmaceuticals and food applications.
- Texture enhancement in food products: Magnesium carbonate is utilized as a texturizing agent in food products. It can improve the mouthfeel and consistency of various foods, contributing to a smoother texture and better overall sensory experience.
- pH regulation and flavor stability: The use of magnesium carbonate in food and beverage formulations helps regulate pH levels, which in turn stabilizes flavors and prevents degradation of taste over time. This property is particularly useful in extending the shelf life of products while maintaining their intended flavor profile.
- Flavor carrier and enhancer: Magnesium carbonate can act as a carrier for flavors and aromas, helping to distribute them evenly throughout a product. It may also enhance certain flavor notes, particularly in beverages and confectionery items, by interacting with other ingredients to create a more complex taste profile.
- Antacid properties influencing flavor perception: The antacid properties of magnesium carbonate can influence flavor perception by neutralizing acids in the mouth. This can reduce the perception of sourness or bitterness in certain foods and beverages, leading to a more balanced and pleasant flavor profile.
02 Texture modification in food products
Magnesium carbonate can be utilized as a texturizing agent in food products. It can improve the mouthfeel, consistency, and stability of various food items, particularly in powdered or dry formulations, without imparting a strong flavor of its own.Expand Specific Solutions03 pH adjustment and buffering
In food and beverage applications, magnesium carbonate acts as a pH regulator and buffering agent. This property allows it to stabilize flavors and prevent unwanted taste changes in products over time, maintaining a consistent flavor profile throughout the product's shelf life.Expand Specific Solutions04 Flavor enhancement in mineral water
Magnesium carbonate is used in the production of mineral water to enhance its flavor profile. It can contribute to a slightly alkaline taste and provide a mineral character to the water, improving its overall sensory attributes without overpowering the natural taste.Expand Specific Solutions05 Interaction with other flavor compounds
When used in complex formulations, magnesium carbonate can interact with other flavor compounds. These interactions may lead to subtle changes in the overall flavor profile of the product, potentially enhancing certain notes or reducing others, which can be leveraged in flavor development.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Dairy Fortification Technology
The market for magnesium carbonate's impact on dairy product flavor profiles is in its early development stage, with growing interest from major players in the food and beverage industry. The global dairy market, valued at over $700 billion, provides a substantial backdrop for this niche research area. Companies like Nestlé, Yili, and Fonterra are likely at the forefront, leveraging their R&D capabilities to explore this technology. Flavor specialists such as Givaudan and Firmenich may also be contributing their expertise. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with academic institutions like Louisiana State University potentially collaborating with industry leaders to advance understanding and applications in this field.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Technical Solution: Nestlé has developed a proprietary process for incorporating magnesium carbonate into dairy products to enhance flavor profiles. Their method involves a fine-tuned addition of magnesium carbonate during the production process, which helps to balance acidity and create a smoother mouthfeel in products like yogurt and cheese[1]. The company has also explored the use of magnesium carbonate as a mineral fortification agent, potentially improving the nutritional value of dairy products while maintaining desirable taste characteristics[2]. Nestlé's research has shown that careful control of magnesium carbonate levels can enhance the perception of creaminess in low-fat dairy products, addressing consumer demands for healthier options without compromising on taste[3].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, global market presence, and ability to implement innovations across a wide range of products. Weaknesses: Potential for increased production costs and the need for careful control of magnesium carbonate levels to avoid negative taste impacts.
Givaudan SA
Technical Solution: Givaudan has developed a sophisticated flavor modulation system that incorporates magnesium carbonate to enhance the taste profile of dairy products. Their approach involves using magnesium carbonate as a pH buffer and flavor enhancer, which helps to reduce sourness and bitterness in fermented dairy products[1]. The company's research has shown that controlled addition of magnesium carbonate can improve the overall flavor balance and mouthfeel of products like cheese and yogurt[2]. Givaudan's technology also focuses on masking off-notes that can occur in fortified dairy products, allowing for the addition of functional ingredients without compromising taste[3]. Their flavor scientists have created proprietary blends that synergize with magnesium carbonate to create unique and appealing flavor profiles in dairy applications.
Strengths: Specialized expertise in flavor science, ability to create custom solutions for different dairy products. Weaknesses: Reliance on dairy manufacturers to implement their solutions, potential limitations in addressing non-flavor related aspects of magnesium carbonate use.
Flavor Profile Impact: Key Research Findings
Flavor modulating compositions
PatentWO2025099060A1
Innovation
- The use of a flavor modulating composition comprising magnesium salts and calcium salts, specifically magnesium chloride and calcium chloride, in amounts effective to improve the organoleptic properties of non-animal protein containing consumables, thereby enhancing mouthfeel, reducing bitter and beany notes, and improving drinkability.
Dairy products with added dairy minerals and methods of producing dairy products with added dairy minerals
PatentWO2013116621A1
Innovation
- Incorporating dairy minerals like potassium, magnesium, and calcium in specific ratios to the cheese-making process to enhance the flavor profile of dairy products, providing a fresh dairy flavor note and improving the overall taste experience.
Regulatory Framework for Dairy Fortification
The regulatory framework for dairy fortification plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of adding magnesium carbonate to dairy products. This framework encompasses a complex set of guidelines, standards, and regulations that govern the use of fortifying agents in food products, particularly in the dairy industry.
At the international level, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides global standards for food safety and quality. These standards include guidelines for the fortification of foods, including dairy products, with essential nutrients and minerals such as magnesium carbonate.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of food additives, including those used in dairy fortification. The FDA's Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status is a key consideration for the use of magnesium carbonate in dairy products. Manufacturers must ensure that the addition of magnesium carbonate complies with FDA regulations and does not compromise the safety or quality of the final product.
The European Union (EU) has its own set of regulations governing food additives and fortification. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) provides scientific opinions on the safety and efficacy of food additives, including magnesium carbonate. EU regulations specify the conditions under which magnesium carbonate can be added to dairy products, including maximum permitted levels and labeling requirements.
Many countries have specific national regulations that address dairy fortification. These regulations often define the types of nutrients that can be added, the permissible levels of fortification, and the labeling requirements for fortified dairy products. Compliance with these regulations is essential for manufacturers looking to introduce magnesium carbonate-fortified dairy products to the market.
Regulatory bodies also consider the potential impact of fortification on public health. They assess the nutritional needs of the population and evaluate the potential risks and benefits of adding specific nutrients to dairy products. This assessment helps in determining appropriate fortification levels and ensuring that the addition of magnesium carbonate does not lead to excessive intake or adverse health effects.
Labeling requirements form a significant part of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must accurately declare the presence of magnesium carbonate on product labels, along with any relevant nutritional information or health claims. These requirements ensure transparency and enable consumers to make informed choices about their dairy product consumption.
As research continues to evolve regarding the effects of magnesium carbonate on the flavor profile of dairy products, regulatory frameworks may adapt to incorporate new findings. This ongoing process ensures that regulations remain up-to-date and continue to protect consumer health while allowing for innovation in the dairy industry.
At the international level, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides global standards for food safety and quality. These standards include guidelines for the fortification of foods, including dairy products, with essential nutrients and minerals such as magnesium carbonate.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of food additives, including those used in dairy fortification. The FDA's Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status is a key consideration for the use of magnesium carbonate in dairy products. Manufacturers must ensure that the addition of magnesium carbonate complies with FDA regulations and does not compromise the safety or quality of the final product.
The European Union (EU) has its own set of regulations governing food additives and fortification. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) provides scientific opinions on the safety and efficacy of food additives, including magnesium carbonate. EU regulations specify the conditions under which magnesium carbonate can be added to dairy products, including maximum permitted levels and labeling requirements.
Many countries have specific national regulations that address dairy fortification. These regulations often define the types of nutrients that can be added, the permissible levels of fortification, and the labeling requirements for fortified dairy products. Compliance with these regulations is essential for manufacturers looking to introduce magnesium carbonate-fortified dairy products to the market.
Regulatory bodies also consider the potential impact of fortification on public health. They assess the nutritional needs of the population and evaluate the potential risks and benefits of adding specific nutrients to dairy products. This assessment helps in determining appropriate fortification levels and ensuring that the addition of magnesium carbonate does not lead to excessive intake or adverse health effects.
Labeling requirements form a significant part of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must accurately declare the presence of magnesium carbonate on product labels, along with any relevant nutritional information or health claims. These requirements ensure transparency and enable consumers to make informed choices about their dairy product consumption.
As research continues to evolve regarding the effects of magnesium carbonate on the flavor profile of dairy products, regulatory frameworks may adapt to incorporate new findings. This ongoing process ensures that regulations remain up-to-date and continue to protect consumer health while allowing for innovation in the dairy industry.
Consumer Perception and Acceptance Studies
Consumer perception and acceptance studies play a crucial role in understanding how magnesium carbonate affects the flavor profile of dairy products. These studies provide valuable insights into the sensory experiences of consumers and their willingness to accept products containing this additive.
Research has shown that the addition of magnesium carbonate to dairy products can have both positive and negative effects on consumer perception. One of the primary benefits observed is the enhanced mouthfeel and texture of certain dairy products. Consumers have reported a smoother, creamier texture in products such as yogurt and ice cream when magnesium carbonate is present in appropriate quantities.
However, the impact on flavor is more nuanced. Some studies have indicated that magnesium carbonate can impart a slight mineral taste to dairy products, which may be perceived differently by various consumer groups. While some consumers find this mineral note to be pleasant and associate it with a "natural" or "healthy" product, others may perceive it as an off-flavor or an undesirable characteristic.
Acceptance studies have revealed that the level of magnesium carbonate used in dairy products is critical to consumer satisfaction. Low concentrations often go unnoticed, while higher concentrations can lead to decreased acceptance due to more pronounced flavor alterations. The threshold for detection and acceptance varies among different dairy products and consumer demographics.
Interestingly, consumer education and product positioning can significantly influence acceptance. When consumers are informed about the potential health benefits of magnesium carbonate in dairy products, their acceptance tends to increase. This suggests that marketing strategies and product labeling play a crucial role in shaping consumer perceptions.
Age and cultural factors also impact consumer acceptance. Younger consumers and those from cultures with a tradition of consuming fermented dairy products tend to be more accepting of the flavor changes induced by magnesium carbonate. In contrast, older consumers and those from regions where fresh dairy flavors are preferred may show lower acceptance rates.
Sensory evaluation techniques, such as descriptive analysis and consumer preference mapping, have been employed to better understand the specific flavor attributes affected by magnesium carbonate. These studies have identified key sensory descriptors associated with magnesium carbonate addition, including "chalky," "mineral," and "slightly astringent."
Long-term consumer studies have shown that repeated exposure to dairy products containing magnesium carbonate can lead to increased acceptance over time. This suggests that consumer palates may adapt to the altered flavor profile, potentially expanding the market for such products.
In conclusion, consumer perception and acceptance studies provide essential data for dairy product manufacturers considering the use of magnesium carbonate. These studies guide product development, inform marketing strategies, and help predict market success for dairy products with modified flavor profiles due to magnesium carbonate addition.
Research has shown that the addition of magnesium carbonate to dairy products can have both positive and negative effects on consumer perception. One of the primary benefits observed is the enhanced mouthfeel and texture of certain dairy products. Consumers have reported a smoother, creamier texture in products such as yogurt and ice cream when magnesium carbonate is present in appropriate quantities.
However, the impact on flavor is more nuanced. Some studies have indicated that magnesium carbonate can impart a slight mineral taste to dairy products, which may be perceived differently by various consumer groups. While some consumers find this mineral note to be pleasant and associate it with a "natural" or "healthy" product, others may perceive it as an off-flavor or an undesirable characteristic.
Acceptance studies have revealed that the level of magnesium carbonate used in dairy products is critical to consumer satisfaction. Low concentrations often go unnoticed, while higher concentrations can lead to decreased acceptance due to more pronounced flavor alterations. The threshold for detection and acceptance varies among different dairy products and consumer demographics.
Interestingly, consumer education and product positioning can significantly influence acceptance. When consumers are informed about the potential health benefits of magnesium carbonate in dairy products, their acceptance tends to increase. This suggests that marketing strategies and product labeling play a crucial role in shaping consumer perceptions.
Age and cultural factors also impact consumer acceptance. Younger consumers and those from cultures with a tradition of consuming fermented dairy products tend to be more accepting of the flavor changes induced by magnesium carbonate. In contrast, older consumers and those from regions where fresh dairy flavors are preferred may show lower acceptance rates.
Sensory evaluation techniques, such as descriptive analysis and consumer preference mapping, have been employed to better understand the specific flavor attributes affected by magnesium carbonate. These studies have identified key sensory descriptors associated with magnesium carbonate addition, including "chalky," "mineral," and "slightly astringent."
Long-term consumer studies have shown that repeated exposure to dairy products containing magnesium carbonate can lead to increased acceptance over time. This suggests that consumer palates may adapt to the altered flavor profile, potentially expanding the market for such products.
In conclusion, consumer perception and acceptance studies provide essential data for dairy product manufacturers considering the use of magnesium carbonate. These studies guide product development, inform marketing strategies, and help predict market success for dairy products with modified flavor profiles due to magnesium carbonate addition.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!