How Polypropylene Facilitates Traditional Packaging Alternatives
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polypropylene Evolution
Polypropylene, a versatile thermoplastic polymer, has undergone significant evolution since its discovery in the 1950s. Initially developed as a byproduct of petroleum refining, polypropylene quickly gained prominence in the packaging industry due to its unique properties and cost-effectiveness.
In the early stages of its development, polypropylene was primarily used for simple packaging applications such as bags and containers. However, as manufacturing techniques improved, its potential for more complex packaging solutions became apparent. The 1960s and 1970s saw rapid advancements in polypropylene production, leading to enhanced material properties and expanded applications.
The 1980s marked a turning point in polypropylene evolution with the introduction of metallocene catalysts. This innovation allowed for greater control over the polymer's molecular structure, resulting in improved strength, clarity, and processability. Consequently, polypropylene began to replace traditional materials in various packaging applications, including food containers, beverage bottles, and flexible packaging.
The 1990s and early 2000s witnessed further refinements in polypropylene technology. The development of advanced additives and fillers enabled manufacturers to tailor the material's properties for specific packaging requirements. This led to the creation of high-barrier polypropylene films, which offered enhanced protection against moisture and oxygen, making them suitable for sensitive food products.
In recent years, the focus of polypropylene evolution has shifted towards sustainability and recyclability. The packaging industry has been under increasing pressure to reduce its environmental impact, and polypropylene has emerged as a viable alternative to less recyclable materials. Innovations in polypropylene recycling technologies have made it possible to create closed-loop systems, where post-consumer polypropylene packaging can be effectively recycled into new products.
The latest advancements in polypropylene technology include the development of bio-based and biodegradable variants. These innovations aim to address concerns about fossil fuel dependency and plastic waste accumulation. While still in the early stages, these sustainable polypropylene alternatives show promise for future packaging applications.
As polypropylene continues to evolve, its role in facilitating traditional packaging alternatives is becoming increasingly significant. The material's versatility, coupled with ongoing technological advancements, positions polypropylene as a key player in the transition towards more sustainable and efficient packaging solutions.
In the early stages of its development, polypropylene was primarily used for simple packaging applications such as bags and containers. However, as manufacturing techniques improved, its potential for more complex packaging solutions became apparent. The 1960s and 1970s saw rapid advancements in polypropylene production, leading to enhanced material properties and expanded applications.
The 1980s marked a turning point in polypropylene evolution with the introduction of metallocene catalysts. This innovation allowed for greater control over the polymer's molecular structure, resulting in improved strength, clarity, and processability. Consequently, polypropylene began to replace traditional materials in various packaging applications, including food containers, beverage bottles, and flexible packaging.
The 1990s and early 2000s witnessed further refinements in polypropylene technology. The development of advanced additives and fillers enabled manufacturers to tailor the material's properties for specific packaging requirements. This led to the creation of high-barrier polypropylene films, which offered enhanced protection against moisture and oxygen, making them suitable for sensitive food products.
In recent years, the focus of polypropylene evolution has shifted towards sustainability and recyclability. The packaging industry has been under increasing pressure to reduce its environmental impact, and polypropylene has emerged as a viable alternative to less recyclable materials. Innovations in polypropylene recycling technologies have made it possible to create closed-loop systems, where post-consumer polypropylene packaging can be effectively recycled into new products.
The latest advancements in polypropylene technology include the development of bio-based and biodegradable variants. These innovations aim to address concerns about fossil fuel dependency and plastic waste accumulation. While still in the early stages, these sustainable polypropylene alternatives show promise for future packaging applications.
As polypropylene continues to evolve, its role in facilitating traditional packaging alternatives is becoming increasingly significant. The material's versatility, coupled with ongoing technological advancements, positions polypropylene as a key player in the transition towards more sustainable and efficient packaging solutions.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for polypropylene in traditional packaging alternatives has been steadily increasing due to its versatile properties and cost-effectiveness. As consumers and businesses become more environmentally conscious, there is a growing shift towards sustainable packaging solutions. Polypropylene, with its recyclability and durability, has emerged as a viable option to meet this demand.
In the food packaging sector, polypropylene has gained significant traction. Its ability to withstand high temperatures, resist moisture, and provide excellent barrier properties makes it ideal for microwave-safe containers, ready-to-eat meal packaging, and fresh produce containers. The global food packaging market, which heavily utilizes polypropylene, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2021 to 2028.
The beverage industry has also embraced polypropylene for bottle caps, labels, and shrink sleeves. As the demand for bottled water and other packaged beverages continues to rise, particularly in developing countries, the market for polypropylene in this sector is expected to expand significantly.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, polypropylene is increasingly being used for packaging creams, lotions, and other beauty products. Its clarity, chemical resistance, and ability to be molded into various shapes make it an attractive option for brands looking to enhance their product presentation while maintaining functionality.
The pharmaceutical sector represents another growing market for polypropylene packaging. With its excellent moisture barrier properties and compatibility with sterilization processes, polypropylene is widely used in blister packs, pill bottles, and medical device packaging. The global pharmaceutical packaging market, which includes polypropylene products, is expected to reach $188.79 billion by 2028.
E-commerce has further fueled the demand for polypropylene packaging. As online shopping continues to grow, there is an increased need for lightweight, durable, and cost-effective packaging materials. Polypropylene's strength-to-weight ratio makes it an excellent choice for shipping mailers, protective wraps, and void fill materials.
The automotive industry has also contributed to the rising demand for polypropylene in packaging. As car manufacturers seek to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency, they are turning to polypropylene for packaging and protecting automotive parts during transportation and storage.
Despite the growing demand, challenges remain. The fluctuating prices of raw materials and increasing environmental regulations may impact the market. However, ongoing research and development in bio-based polypropylene and advanced recycling technologies are expected to address these concerns and further drive market growth in the coming years.
In the food packaging sector, polypropylene has gained significant traction. Its ability to withstand high temperatures, resist moisture, and provide excellent barrier properties makes it ideal for microwave-safe containers, ready-to-eat meal packaging, and fresh produce containers. The global food packaging market, which heavily utilizes polypropylene, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2021 to 2028.
The beverage industry has also embraced polypropylene for bottle caps, labels, and shrink sleeves. As the demand for bottled water and other packaged beverages continues to rise, particularly in developing countries, the market for polypropylene in this sector is expected to expand significantly.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, polypropylene is increasingly being used for packaging creams, lotions, and other beauty products. Its clarity, chemical resistance, and ability to be molded into various shapes make it an attractive option for brands looking to enhance their product presentation while maintaining functionality.
The pharmaceutical sector represents another growing market for polypropylene packaging. With its excellent moisture barrier properties and compatibility with sterilization processes, polypropylene is widely used in blister packs, pill bottles, and medical device packaging. The global pharmaceutical packaging market, which includes polypropylene products, is expected to reach $188.79 billion by 2028.
E-commerce has further fueled the demand for polypropylene packaging. As online shopping continues to grow, there is an increased need for lightweight, durable, and cost-effective packaging materials. Polypropylene's strength-to-weight ratio makes it an excellent choice for shipping mailers, protective wraps, and void fill materials.
The automotive industry has also contributed to the rising demand for polypropylene in packaging. As car manufacturers seek to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency, they are turning to polypropylene for packaging and protecting automotive parts during transportation and storage.
Despite the growing demand, challenges remain. The fluctuating prices of raw materials and increasing environmental regulations may impact the market. However, ongoing research and development in bio-based polypropylene and advanced recycling technologies are expected to address these concerns and further drive market growth in the coming years.
Current Challenges
Polypropylene (PP) has long been a staple in traditional packaging, but its continued use faces several challenges in the current environmental and regulatory landscape. One of the primary issues is the growing concern over plastic pollution and its impact on ecosystems. As a petroleum-based plastic, PP contributes to the accumulation of non-biodegradable waste in landfills and oceans, leading to increased public pressure for more sustainable alternatives.
Recycling infrastructure for PP remains inadequate in many regions, hindering efforts to create a circular economy for this material. While PP is technically recyclable, the process is often economically unfeasible due to contamination issues and the lack of efficient sorting technologies. This results in a significant portion of PP packaging ending up in waste streams rather than being recycled.
The volatility of oil prices directly affects the cost of PP production, creating uncertainty for manufacturers and potentially impacting the competitiveness of PP-based packaging solutions. This economic challenge is compounded by the emergence of bio-based and biodegradable alternatives, which are gaining traction in the market despite higher production costs.
Regulatory pressures are mounting, with many countries implementing or considering bans on single-use plastics, including some PP products. This shifting legislative landscape requires packaging manufacturers to adapt quickly, potentially necessitating significant investments in new materials and production processes.
Consumer preferences are evolving towards more environmentally friendly packaging options, driven by increased awareness of plastic pollution. This shift in demand poses a challenge for companies heavily reliant on PP packaging to maintain market share and brand loyalty.
The development of PP packaging with enhanced barrier properties remains a technical challenge. While PP offers good moisture resistance, it struggles to provide adequate oxygen and aroma barriers for certain food and beverage applications without additional treatments or layers, which can complicate recycling efforts.
Lastly, the carbon footprint associated with PP production and transportation is under scrutiny as companies and consumers alike seek to reduce their environmental impact. The energy-intensive nature of PP manufacturing processes contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, conflicting with global efforts to combat climate change.
Addressing these challenges requires innovation in material science, improvements in recycling technologies, and a concerted effort to develop more sustainable packaging solutions that can match the performance and cost-effectiveness of traditional PP packaging.
Recycling infrastructure for PP remains inadequate in many regions, hindering efforts to create a circular economy for this material. While PP is technically recyclable, the process is often economically unfeasible due to contamination issues and the lack of efficient sorting technologies. This results in a significant portion of PP packaging ending up in waste streams rather than being recycled.
The volatility of oil prices directly affects the cost of PP production, creating uncertainty for manufacturers and potentially impacting the competitiveness of PP-based packaging solutions. This economic challenge is compounded by the emergence of bio-based and biodegradable alternatives, which are gaining traction in the market despite higher production costs.
Regulatory pressures are mounting, with many countries implementing or considering bans on single-use plastics, including some PP products. This shifting legislative landscape requires packaging manufacturers to adapt quickly, potentially necessitating significant investments in new materials and production processes.
Consumer preferences are evolving towards more environmentally friendly packaging options, driven by increased awareness of plastic pollution. This shift in demand poses a challenge for companies heavily reliant on PP packaging to maintain market share and brand loyalty.
The development of PP packaging with enhanced barrier properties remains a technical challenge. While PP offers good moisture resistance, it struggles to provide adequate oxygen and aroma barriers for certain food and beverage applications without additional treatments or layers, which can complicate recycling efforts.
Lastly, the carbon footprint associated with PP production and transportation is under scrutiny as companies and consumers alike seek to reduce their environmental impact. The energy-intensive nature of PP manufacturing processes contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, conflicting with global efforts to combat climate change.
Addressing these challenges requires innovation in material science, improvements in recycling technologies, and a concerted effort to develop more sustainable packaging solutions that can match the performance and cost-effectiveness of traditional PP packaging.
Existing PP Solutions
01 Polypropylene synthesis and production methods
Various methods for synthesizing and producing polypropylene, including catalytic processes, polymerization techniques, and reactor designs. These methods aim to improve the efficiency and quality of polypropylene production.- Polypropylene synthesis and production methods: Various methods for synthesizing and producing polypropylene, including polymerization techniques, catalyst systems, and process improvements to enhance yield and quality of the resulting polymer.
- Polypropylene compositions and blends: Development of polypropylene compositions and blends with other materials to enhance specific properties such as strength, flexibility, or heat resistance for various applications.
- Polypropylene modification techniques: Methods for modifying polypropylene through chemical or physical processes to improve its characteristics, such as impact resistance, weatherability, or compatibility with other materials.
- Polypropylene applications in packaging and films: Utilization of polypropylene in packaging materials and film production, including techniques for improving barrier properties, printability, and overall performance in these applications.
- Recycling and sustainability of polypropylene: Innovations in recycling polypropylene and developing more sustainable production methods, including the use of bio-based feedstocks and improving the recyclability of polypropylene products.
02 Polypropylene compositions and blends
Development of polypropylene compositions and blends with enhanced properties, such as improved strength, flexibility, or thermal resistance. These compositions may include additives, fillers, or other polymers to achieve desired characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polypropylene applications in packaging and films
Use of polypropylene in packaging materials and films, including food packaging, flexible packaging, and multilayer films. These applications leverage polypropylene's properties such as clarity, moisture resistance, and barrier properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Polypropylene fiber and textile applications
Development of polypropylene fibers and their use in textile applications, including nonwoven fabrics, carpets, and clothing. These applications take advantage of polypropylene's lightweight, durability, and moisture-wicking properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Recycling and sustainability of polypropylene
Methods and technologies for recycling polypropylene products, as well as developing more sustainable production processes and bio-based alternatives. These efforts aim to reduce the environmental impact of polypropylene and improve its lifecycle sustainability.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The polypropylene packaging market is in a mature growth stage, with a global market size expected to reach $28.3 billion by 2027. The industry is characterized by intense competition among established players like Prime Polymer, Mitsui Chemicals, and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. These companies are focusing on technological advancements to improve product performance and sustainability. The technology's maturity is evident in its widespread adoption across various industries, with companies like L'Oréal and General Motors incorporating polypropylene in their packaging solutions. However, there is ongoing research and development, particularly in areas of biodegradability and recycling, as exemplified by innovations from companies such as Borealis AG and ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced polypropylene (PP) grades for traditional packaging alternatives. Their technology focuses on enhancing PP's barrier properties and mechanical strength. They have introduced a multi-layer PP film technology that combines different PP grades to achieve superior moisture and oxygen barrier properties[1]. This innovation allows for the creation of packaging materials that can extend the shelf life of food products while maintaining recyclability. Sinopec has also developed a proprietary catalyst system that enables the production of high-performance PP with improved clarity and impact resistance[2], making it suitable for rigid packaging applications.
Strengths: Improved barrier properties, enhanced recyclability, and versatility in packaging applications. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional PP, potential limitations in extreme temperature applications.
Borealis AG
Technical Solution: Borealis AG has pioneered the development of random copolymer polypropylene (rPP) technology for packaging applications. Their Bormed™ rPP grades offer exceptional clarity and low extractables, making them ideal for medical and food packaging[3]. The company has also introduced a proprietary Borstar® technology that allows for the production of bimodal PP with enhanced stiffness and impact balance[4]. This technology enables the creation of lighter weight packaging without compromising strength. Additionally, Borealis has developed advanced PP compounds with improved heat resistance and sealing properties, addressing the needs of hot-fill and retort packaging applications[5].
Strengths: High purity grades for sensitive applications, excellent balance of properties, and reduced material usage. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to standard PP grades, limited availability in some regions.
Innovative PP Tech
Polypropylene resin composition
PatentInactiveEP1397432A2
Innovation
- A polypropylene resin composition is developed by blending a small amount of olefin copolymer rubber or polyethylene resin with a polypropylene resin, followed by ionization ray irradiation or organic peroxide treatment, and incorporating specific metal compounds and nucleating agents to enhance melt tension and maintain it during recycling without causing coloring or odor.
Polypropylene-based packaging material
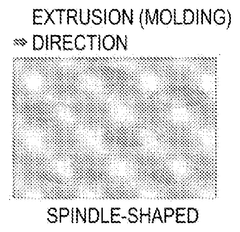
PatentPendingUS20240400816A1
Innovation
- A polypropylene-based packaging material with a phase dispersion structure featuring a spindle-shaped polypropylene-based elastomer domain in a polypropylene matrix, combined with an ethylene-propylene block copolymer and homopolypropylene, which adjusts viscosity for improved moldability and surface roughness, is used. This material is integrated into a layered body with specific molecular weight ranges and compositions to enhance drop impact resistance, slipperiness, and flavor barrier properties.
Environmental Impact
Polypropylene, a versatile thermoplastic polymer, has gained significant attention in the packaging industry due to its potential to facilitate traditional packaging alternatives. However, its environmental impact remains a critical concern that warrants thorough examination.
The production of polypropylene involves the use of fossil fuels, primarily natural gas or crude oil, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. The manufacturing process also requires substantial energy inputs, further exacerbating its carbon footprint. Despite these initial environmental costs, polypropylene's durability and recyclability offer potential long-term benefits that may offset its production-related impacts.
One of the key environmental advantages of polypropylene is its recyclability. When properly collected and processed, polypropylene can be recycled multiple times without significant degradation in quality. This characteristic reduces the need for virgin material production and helps conserve natural resources. However, the actual recycling rates for polypropylene packaging remain relatively low in many regions, primarily due to inadequate collection infrastructure and consumer awareness.
Polypropylene's lightweight nature contributes to reduced transportation-related emissions compared to heavier packaging materials. This attribute can lead to lower fuel consumption and decreased carbon emissions throughout the supply chain. Additionally, polypropylene's resistance to moisture and chemicals often results in extended product shelf life, potentially reducing food waste and the associated environmental impacts.
The end-of-life management of polypropylene packaging presents both challenges and opportunities. While it is technically recyclable, improper disposal can lead to environmental pollution, particularly in marine ecosystems. Microplastic pollution from degraded polypropylene products poses a growing concern for aquatic life and potentially human health. However, advancements in biodegradable additives and chemical recycling technologies offer promising solutions to mitigate these issues.
When comparing polypropylene to traditional packaging materials, its environmental performance varies depending on the specific application and lifecycle considerations. In some cases, polypropylene may offer improved sustainability metrics compared to materials like glass or metal, particularly in terms of energy consumption and transportation efficiency. However, the overall environmental impact depends heavily on factors such as production methods, recycling rates, and end-of-life management practices.
As the packaging industry continues to evolve, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the environmental profile of polypropylene. These initiatives include improving recycling technologies, developing bio-based alternatives, and optimizing production processes to reduce energy consumption and emissions. The success of these efforts will play a crucial role in determining the long-term sustainability of polypropylene as a packaging material.
The production of polypropylene involves the use of fossil fuels, primarily natural gas or crude oil, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. The manufacturing process also requires substantial energy inputs, further exacerbating its carbon footprint. Despite these initial environmental costs, polypropylene's durability and recyclability offer potential long-term benefits that may offset its production-related impacts.
One of the key environmental advantages of polypropylene is its recyclability. When properly collected and processed, polypropylene can be recycled multiple times without significant degradation in quality. This characteristic reduces the need for virgin material production and helps conserve natural resources. However, the actual recycling rates for polypropylene packaging remain relatively low in many regions, primarily due to inadequate collection infrastructure and consumer awareness.
Polypropylene's lightweight nature contributes to reduced transportation-related emissions compared to heavier packaging materials. This attribute can lead to lower fuel consumption and decreased carbon emissions throughout the supply chain. Additionally, polypropylene's resistance to moisture and chemicals often results in extended product shelf life, potentially reducing food waste and the associated environmental impacts.
The end-of-life management of polypropylene packaging presents both challenges and opportunities. While it is technically recyclable, improper disposal can lead to environmental pollution, particularly in marine ecosystems. Microplastic pollution from degraded polypropylene products poses a growing concern for aquatic life and potentially human health. However, advancements in biodegradable additives and chemical recycling technologies offer promising solutions to mitigate these issues.
When comparing polypropylene to traditional packaging materials, its environmental performance varies depending on the specific application and lifecycle considerations. In some cases, polypropylene may offer improved sustainability metrics compared to materials like glass or metal, particularly in terms of energy consumption and transportation efficiency. However, the overall environmental impact depends heavily on factors such as production methods, recycling rates, and end-of-life management practices.
As the packaging industry continues to evolve, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the environmental profile of polypropylene. These initiatives include improving recycling technologies, developing bio-based alternatives, and optimizing production processes to reduce energy consumption and emissions. The success of these efforts will play a crucial role in determining the long-term sustainability of polypropylene as a packaging material.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding polypropylene in traditional packaging alternatives is complex and evolving, reflecting growing environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives worldwide. Governments and international organizations are increasingly implementing regulations to address plastic waste and promote more sustainable packaging solutions.
In the European Union, the Single-Use Plastics Directive, implemented in 2019, aims to reduce the impact of certain plastic products on the environment. This directive has significant implications for polypropylene packaging, as it sets targets for recycling and mandates the use of recycled content in certain plastic products. The EU's Circular Economy Action Plan further reinforces these efforts by promoting design for recyclability and setting ambitious recycling targets for plastic packaging.
In the United States, regulations vary by state, but there is a growing trend towards stricter controls on plastic packaging. California, for instance, has enacted legislation requiring all plastic packaging to be recyclable, reusable, or compostable by 2032. This has spurred innovation in polypropylene packaging design and recycling technologies.
Asian countries are also taking steps to address plastic pollution. China's ban on importing plastic waste has led to increased focus on domestic recycling capabilities, including for polypropylene packaging. Japan has implemented a comprehensive recycling system that includes polypropylene, setting high recycling rate targets for various plastic materials.
International agreements, such as the Basel Convention's Plastic Waste Amendments, have implications for the global trade of plastic waste, including polypropylene. These regulations aim to make global trade in plastic waste more transparent and better regulated, potentially affecting the supply chain for recycled polypropylene.
The regulatory landscape is also driving innovation in polypropylene packaging alternatives. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes, implemented in various forms across different jurisdictions, are pushing manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of their packaging products. This has led to increased investment in recyclable polypropylene formulations and mono-material packaging solutions that are easier to recycle.
As regulations continue to evolve, the polypropylene packaging industry faces both challenges and opportunities. Compliance with increasingly stringent environmental standards requires ongoing adaptation and innovation. However, these regulations also create market opportunities for sustainable packaging solutions, driving research and development in areas such as bio-based polypropylene alternatives and advanced recycling technologies.
In the European Union, the Single-Use Plastics Directive, implemented in 2019, aims to reduce the impact of certain plastic products on the environment. This directive has significant implications for polypropylene packaging, as it sets targets for recycling and mandates the use of recycled content in certain plastic products. The EU's Circular Economy Action Plan further reinforces these efforts by promoting design for recyclability and setting ambitious recycling targets for plastic packaging.
In the United States, regulations vary by state, but there is a growing trend towards stricter controls on plastic packaging. California, for instance, has enacted legislation requiring all plastic packaging to be recyclable, reusable, or compostable by 2032. This has spurred innovation in polypropylene packaging design and recycling technologies.
Asian countries are also taking steps to address plastic pollution. China's ban on importing plastic waste has led to increased focus on domestic recycling capabilities, including for polypropylene packaging. Japan has implemented a comprehensive recycling system that includes polypropylene, setting high recycling rate targets for various plastic materials.
International agreements, such as the Basel Convention's Plastic Waste Amendments, have implications for the global trade of plastic waste, including polypropylene. These regulations aim to make global trade in plastic waste more transparent and better regulated, potentially affecting the supply chain for recycled polypropylene.
The regulatory landscape is also driving innovation in polypropylene packaging alternatives. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes, implemented in various forms across different jurisdictions, are pushing manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of their packaging products. This has led to increased investment in recyclable polypropylene formulations and mono-material packaging solutions that are easier to recycle.
As regulations continue to evolve, the polypropylene packaging industry faces both challenges and opportunities. Compliance with increasingly stringent environmental standards requires ongoing adaptation and innovation. However, these regulations also create market opportunities for sustainable packaging solutions, driving research and development in areas such as bio-based polypropylene alternatives and advanced recycling technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!