How Sulphanilic Acid Facilitates Biocatalytic Processes
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulphanilic Acid in Biocatalysis: Background and Objectives
Sulphanilic acid, a versatile aromatic compound, has emerged as a significant facilitator in biocatalytic processes over the past few decades. This organic molecule, characterized by its sulfonated aniline structure, has garnered attention in the field of biotechnology due to its unique chemical properties and potential applications in enzymatic reactions.
The journey of sulphanilic acid in biocatalysis can be traced back to the early 1980s when researchers began exploring its role as a cofactor in certain enzymatic reactions. Initially, its use was limited to a narrow range of applications, primarily in the synthesis of dyes and pharmaceuticals. However, as the field of biocatalysis expanded, so did the understanding of sulphanilic acid's potential.
The primary objective of incorporating sulphanilic acid into biocatalytic processes is to enhance the efficiency and selectivity of enzymatic reactions. This compound has shown remarkable ability to modulate enzyme activity, often leading to improved yields and reduced reaction times. Furthermore, its use has been associated with increased stability of enzymes under various reaction conditions, thereby extending the operational life of biocatalysts.
One of the key advantages of sulphanilic acid in biocatalysis is its ability to act as a bridging molecule between enzymes and substrates. This property has opened up new possibilities in the design of multi-enzyme cascades, where sulphanilic acid serves as a crucial link in complex reaction pathways. Such cascades are particularly valuable in the production of fine chemicals and pharmaceutical intermediates.
The evolution of sulphanilic acid's role in biocatalysis has been closely tied to advancements in enzyme engineering and directed evolution techniques. As researchers gained deeper insights into enzyme structures and mechanisms, they were able to tailor enzymes to work more effectively with sulphanilic acid as a cofactor or substrate analog.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards understanding the molecular interactions between sulphanilic acid and various enzyme classes. This has led to the development of novel biocatalytic systems that exploit these interactions for improved catalytic performance. Additionally, computational studies have begun to shed light on the electronic and steric factors that govern sulphanilic acid's behavior in enzymatic environments.
Looking ahead, the integration of sulphanilic acid in biocatalytic processes aims to address several challenges in industrial biotechnology. These include the need for more sustainable and environmentally friendly chemical synthesis routes, the demand for highly selective transformations in complex molecular settings, and the push towards more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes in the pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries.
The journey of sulphanilic acid in biocatalysis can be traced back to the early 1980s when researchers began exploring its role as a cofactor in certain enzymatic reactions. Initially, its use was limited to a narrow range of applications, primarily in the synthesis of dyes and pharmaceuticals. However, as the field of biocatalysis expanded, so did the understanding of sulphanilic acid's potential.
The primary objective of incorporating sulphanilic acid into biocatalytic processes is to enhance the efficiency and selectivity of enzymatic reactions. This compound has shown remarkable ability to modulate enzyme activity, often leading to improved yields and reduced reaction times. Furthermore, its use has been associated with increased stability of enzymes under various reaction conditions, thereby extending the operational life of biocatalysts.
One of the key advantages of sulphanilic acid in biocatalysis is its ability to act as a bridging molecule between enzymes and substrates. This property has opened up new possibilities in the design of multi-enzyme cascades, where sulphanilic acid serves as a crucial link in complex reaction pathways. Such cascades are particularly valuable in the production of fine chemicals and pharmaceutical intermediates.
The evolution of sulphanilic acid's role in biocatalysis has been closely tied to advancements in enzyme engineering and directed evolution techniques. As researchers gained deeper insights into enzyme structures and mechanisms, they were able to tailor enzymes to work more effectively with sulphanilic acid as a cofactor or substrate analog.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards understanding the molecular interactions between sulphanilic acid and various enzyme classes. This has led to the development of novel biocatalytic systems that exploit these interactions for improved catalytic performance. Additionally, computational studies have begun to shed light on the electronic and steric factors that govern sulphanilic acid's behavior in enzymatic environments.
Looking ahead, the integration of sulphanilic acid in biocatalytic processes aims to address several challenges in industrial biotechnology. These include the need for more sustainable and environmentally friendly chemical synthesis routes, the demand for highly selective transformations in complex molecular settings, and the push towards more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes in the pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries.
Market Analysis for Biocatalytic Processes
The biocatalytic processes market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly manufacturing methods across various industries. The global market for biocatalysts is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding industry averages. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising adoption of biocatalysts in pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and chemical industries.
In the pharmaceutical sector, biocatalytic processes are gaining traction due to their ability to produce complex drug intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) with high selectivity and efficiency. The increasing focus on green chemistry and the need for cost-effective drug manufacturing processes are driving the demand for biocatalysts in this sector.
The food and beverage industry is another key market for biocatalytic processes, particularly in the production of flavors, fragrances, and functional ingredients. Consumers' growing preference for natural and clean-label products has led to increased adoption of enzyme-based processes in food manufacturing, further boosting the market growth.
In the chemical industry, biocatalytic processes are being increasingly utilized for the production of fine chemicals, polymers, and specialty chemicals. The ability of biocatalysts to operate under mild conditions and their high specificity make them attractive alternatives to traditional chemical catalysts, especially in the context of sustainable manufacturing practices.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for biocatalytic processes, owing to stringent environmental regulations and a strong presence of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing investments in biotechnology, and growing awareness of sustainable manufacturing practices.
The market for biocatalytic processes is characterized by ongoing research and development activities aimed at discovering novel enzymes and improving existing biocatalytic systems. This includes efforts to enhance enzyme stability, broaden substrate specificity, and develop more efficient immobilization techniques. The integration of biocatalysis with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, is expected to further drive innovation in this field.
As the demand for sustainable and efficient manufacturing processes continues to grow, the market for biocatalytic processes is poised for substantial expansion. The increasing focus on circular economy principles and the need to reduce carbon footprints across industries are likely to create new opportunities for biocatalytic applications in the coming years.
In the pharmaceutical sector, biocatalytic processes are gaining traction due to their ability to produce complex drug intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) with high selectivity and efficiency. The increasing focus on green chemistry and the need for cost-effective drug manufacturing processes are driving the demand for biocatalysts in this sector.
The food and beverage industry is another key market for biocatalytic processes, particularly in the production of flavors, fragrances, and functional ingredients. Consumers' growing preference for natural and clean-label products has led to increased adoption of enzyme-based processes in food manufacturing, further boosting the market growth.
In the chemical industry, biocatalytic processes are being increasingly utilized for the production of fine chemicals, polymers, and specialty chemicals. The ability of biocatalysts to operate under mild conditions and their high specificity make them attractive alternatives to traditional chemical catalysts, especially in the context of sustainable manufacturing practices.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for biocatalytic processes, owing to stringent environmental regulations and a strong presence of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing investments in biotechnology, and growing awareness of sustainable manufacturing practices.
The market for biocatalytic processes is characterized by ongoing research and development activities aimed at discovering novel enzymes and improving existing biocatalytic systems. This includes efforts to enhance enzyme stability, broaden substrate specificity, and develop more efficient immobilization techniques. The integration of biocatalysis with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, is expected to further drive innovation in this field.
As the demand for sustainable and efficient manufacturing processes continues to grow, the market for biocatalytic processes is poised for substantial expansion. The increasing focus on circular economy principles and the need to reduce carbon footprints across industries are likely to create new opportunities for biocatalytic applications in the coming years.
Current State and Challenges in Sulphanilic Acid Biocatalysis
The current state of sulphanilic acid biocatalysis is characterized by significant advancements in enzyme engineering and process optimization. Researchers have made substantial progress in developing efficient biocatalytic systems for the production and transformation of sulphanilic acid, a valuable compound in various industries. Enzyme-catalyzed reactions involving sulphanilic acid have shown improved selectivity, yield, and environmental sustainability compared to traditional chemical synthesis methods.
However, several challenges persist in the field of sulphanilic acid biocatalysis. One major hurdle is the limited stability of enzymes in the presence of sulphanilic acid and its derivatives. The acidic nature of these compounds can lead to enzyme denaturation, reducing catalytic efficiency and process longevity. Scientists are actively exploring protein engineering techniques to enhance enzyme stability and tolerance to harsh reaction conditions.
Another significant challenge is the optimization of reaction kinetics and substrate specificity. While biocatalytic processes offer high selectivity, achieving commercially viable reaction rates and product yields remains a key focus area. Researchers are investigating various approaches, including directed evolution and rational design, to improve enzyme performance and broaden substrate scope.
Scale-up and process integration present additional challenges in sulphanilic acid biocatalysis. Transitioning from laboratory-scale experiments to industrial-scale production often requires overcoming issues related to mass transfer, product inhibition, and downstream processing. Engineers are working on developing novel reactor designs and separation techniques to address these challenges and improve overall process efficiency.
The recovery and recycling of enzymes in sulphanilic acid biocatalytic processes also pose significant challenges. Immobilization techniques are being explored to enhance enzyme stability and facilitate enzyme recovery, but further improvements are needed to make these processes economically viable at industrial scales.
Regulatory and safety considerations add another layer of complexity to the development of sulphanilic acid biocatalytic processes. Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and addressing potential health hazards associated with sulphanilic acid and its derivatives require careful process design and risk assessment.
Despite these challenges, the field of sulphanilic acid biocatalysis continues to advance, driven by the potential for more sustainable and efficient production methods. Collaborative efforts between academic researchers and industry partners are accelerating progress in addressing these challenges and pushing the boundaries of biocatalytic applications in this domain.
However, several challenges persist in the field of sulphanilic acid biocatalysis. One major hurdle is the limited stability of enzymes in the presence of sulphanilic acid and its derivatives. The acidic nature of these compounds can lead to enzyme denaturation, reducing catalytic efficiency and process longevity. Scientists are actively exploring protein engineering techniques to enhance enzyme stability and tolerance to harsh reaction conditions.
Another significant challenge is the optimization of reaction kinetics and substrate specificity. While biocatalytic processes offer high selectivity, achieving commercially viable reaction rates and product yields remains a key focus area. Researchers are investigating various approaches, including directed evolution and rational design, to improve enzyme performance and broaden substrate scope.
Scale-up and process integration present additional challenges in sulphanilic acid biocatalysis. Transitioning from laboratory-scale experiments to industrial-scale production often requires overcoming issues related to mass transfer, product inhibition, and downstream processing. Engineers are working on developing novel reactor designs and separation techniques to address these challenges and improve overall process efficiency.
The recovery and recycling of enzymes in sulphanilic acid biocatalytic processes also pose significant challenges. Immobilization techniques are being explored to enhance enzyme stability and facilitate enzyme recovery, but further improvements are needed to make these processes economically viable at industrial scales.
Regulatory and safety considerations add another layer of complexity to the development of sulphanilic acid biocatalytic processes. Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and addressing potential health hazards associated with sulphanilic acid and its derivatives require careful process design and risk assessment.
Despite these challenges, the field of sulphanilic acid biocatalysis continues to advance, driven by the potential for more sustainable and efficient production methods. Collaborative efforts between academic researchers and industry partners are accelerating progress in addressing these challenges and pushing the boundaries of biocatalytic applications in this domain.
Existing Sulphanilic Acid-Based Biocatalytic Solutions
01 Synthesis and production methods of sulphanilic acid
Various methods for synthesizing and producing sulphanilic acid are described, including different reaction conditions, catalysts, and starting materials. These processes aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in the production of sulphanilic acid for industrial applications.- Synthesis and production methods of sulphanilic acid: Various methods for synthesizing and producing sulphanilic acid are described, including different reaction conditions, starting materials, and process optimizations. These methods aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in the production of sulphanilic acid for industrial applications.
- Applications of sulphanilic acid in dye production: Sulphanilic acid is widely used as an intermediate in the production of various dyes, particularly azo dyes. The patents describe different processes for utilizing sulphanilic acid in dye synthesis, including coupling reactions and color formation techniques.
- Purification and treatment of sulphanilic acid: Several methods for purifying and treating sulphanilic acid are presented, including crystallization techniques, filtration processes, and chemical treatments. These processes aim to improve the quality and purity of sulphanilic acid for specific applications.
- Derivatives and modifications of sulphanilic acid: Various patents describe the synthesis and applications of sulphanilic acid derivatives and modified forms. These include sulfonation processes, salt formation, and the creation of new compounds based on sulphanilic acid for use in different industries.
- Industrial applications of sulphanilic acid: Sulphanilic acid finds applications in various industries beyond dye production. Patents describe its use in pharmaceuticals, polymer production, and as a reagent in analytical chemistry. These applications showcase the versatility of sulphanilic acid in different industrial processes.
02 Applications of sulphanilic acid in dye production
Sulphanilic acid is widely used as an intermediate in the production of various dyes and pigments. It serves as a key component in the synthesis of azo dyes, which are important in the textile and printing industries. The patents describe different dye formulations and manufacturing processes utilizing sulphanilic acid.Expand Specific Solutions03 Purification and treatment of sulphanilic acid
Several methods for purifying and treating sulphanilic acid are presented, including crystallization, filtration, and washing techniques. These processes aim to improve the quality and purity of sulphanilic acid for use in various applications, such as pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals.Expand Specific Solutions04 Derivatives and modifications of sulphanilic acid
The patents describe various derivatives and modifications of sulphanilic acid, including salts, esters, and complexes. These modified forms of sulphanilic acid offer improved properties or specific functionalities for use in different applications, such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial applications of sulphanilic acid
Sulphanilic acid finds applications in various industrial processes beyond dye production. The patents describe its use in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and other chemical products. Additionally, sulphanilic acid is utilized in water treatment, polymer production, and as a reagent in analytical chemistry.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sulphanilic Acid and Biocatalysis Industry
The biocatalytic processes facilitated by sulphanilic acid represent an emerging field in the intersection of chemistry and biotechnology. This sector is in its early growth stage, with increasing interest from both academic institutions and industry players. The market size is expanding, driven by the growing demand for sustainable and efficient chemical processes. Technologically, the field is rapidly evolving, with companies like Sanofi, BASF Corp., and Bayer CropScience LP investing in research and development. Academic institutions such as MIT and Rutgers University are also contributing significantly to advancing the technology. While not yet fully mature, the technology shows promising applications in pharmaceutical and agricultural industries, indicating a competitive landscape with potential for further innovation and market growth.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Technical Solution: MIT researchers have made significant advancements in understanding how sulphanilic acid facilitates biocatalytic processes at the molecular level. Their studies have revealed that sulphanilic acid can act as a molecular chaperone, stabilizing enzyme structures and preventing aggregation during biocatalytic reactions[7]. The team has also discovered novel applications of sulphanilic acid in directed evolution experiments, where it serves as a selection pressure to evolve enzymes with enhanced activity and stability[9]. Additionally, MIT has developed computational models to predict the optimal conditions for sulphanilic acid-assisted biocatalysis, enabling rapid optimization of industrial processes[11].
Strengths: Deep molecular understanding, novel applications in enzyme engineering, and predictive modeling capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential gaps between academic research and industrial implementation.
Rhodia Chimie
Technical Solution: Rhodia Chimie has pioneered the use of sulphanilic acid in biocatalytic processes for the production of specialty chemicals. Their approach involves using sulphanilic acid as a pH buffer and stabilizing agent in enzymatic reactions, particularly in the synthesis of aromatic compounds[2]. The company has developed a proprietary process that combines sulphanilic acid with specific biocatalysts to achieve highly selective transformations, reducing the need for costly purification steps[4]. Rhodia's technology also incorporates a unique recycling system for sulphanilic acid, making the overall process more sustainable and economically viable for large-scale applications[6].
Strengths: Highly selective transformations, reduced purification costs, and improved process sustainability. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in scaling up the technology and dependency on specific biocatalysts.
Core Innovations in Sulphanilic Acid Biocatalysis
Methods for modulating the levels of organic sulfur compounds in plants
PatentInactiveEP1153135B1
Innovation
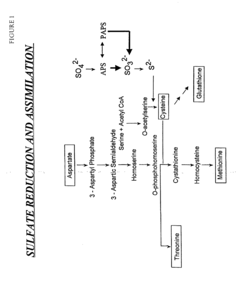
- Stably transforming plants with a DNA construct encoding a (P)APS reductase enzyme to alter the biosynthesis of organic sulfur compounds, such as cysteine and methionine, and reducing oxidative stress by enhancing sulfate reduction pathways.
Method for bio-oxidative desulfurization of liquid hydrocarbon fuels and product thereof
PatentInactiveUS20090217571A1
Innovation
- Employing lipase enzymes as biocatalysts in a bio-oxidative process with incremental hydrogen peroxide and carboxylic acid to oxidize sulfur compounds to sulfoxides and sulfones, which can be selectively removed from fossil fuels without the need for water or co-factors, using solvents like methanol or DMSO for extraction.
Environmental Impact of Sulphanilic Acid in Biocatalysis
The use of sulphanilic acid in biocatalytic processes has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. This compound, while instrumental in facilitating various enzymatic reactions, can potentially impact ecosystems if not properly managed.
Sulphanilic acid, when used in biocatalysis, often results in reduced energy consumption and waste generation compared to traditional chemical synthesis methods. This is due to the specificity and efficiency of enzymatic reactions, which typically operate under milder conditions. Consequently, the carbon footprint associated with biocatalytic processes utilizing sulphanilic acid is generally lower than conventional approaches.
However, the release of sulphanilic acid into the environment can lead to adverse effects. As a synthetic compound, it may not be readily biodegradable, potentially persisting in aquatic ecosystems. This persistence can disrupt natural habitats and affect aquatic organisms, particularly if discharged in high concentrations.
The compound's aromatic structure and sulfonic acid group contribute to its potential toxicity. Studies have shown that sulphanilic acid can exhibit ecotoxicological effects on certain aquatic species, including algae and fish. Therefore, proper waste management and treatment protocols are crucial to mitigate these risks.
On the positive side, the use of sulphanilic acid in biocatalysis often leads to improved atom economy and reduced use of hazardous solvents. This can result in a net positive environmental impact when compared to traditional chemical processes that may require more aggressive reagents and generate more toxic by-products.
The environmental fate of sulphanilic acid is also influenced by its chemical properties. Its solubility in water and resistance to hydrolysis mean that it can be transported in aqueous environments, potentially affecting a wider area if released untreated. However, this property also makes it amenable to certain water treatment technologies.
Efforts to minimize the environmental impact of sulphanilic acid in biocatalytic processes include the development of closed-loop systems, where the compound is recycled and reused. Additionally, advanced wastewater treatment methods, such as advanced oxidation processes and membrane filtration, have shown promise in removing sulphanilic acid from effluents.
In conclusion, while sulphanilic acid offers significant benefits in biocatalytic processes, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. Balancing the advantages of improved reaction efficiency and reduced overall chemical waste with the potential risks of environmental persistence and ecotoxicity is crucial for sustainable industrial practices.
Sulphanilic acid, when used in biocatalysis, often results in reduced energy consumption and waste generation compared to traditional chemical synthesis methods. This is due to the specificity and efficiency of enzymatic reactions, which typically operate under milder conditions. Consequently, the carbon footprint associated with biocatalytic processes utilizing sulphanilic acid is generally lower than conventional approaches.
However, the release of sulphanilic acid into the environment can lead to adverse effects. As a synthetic compound, it may not be readily biodegradable, potentially persisting in aquatic ecosystems. This persistence can disrupt natural habitats and affect aquatic organisms, particularly if discharged in high concentrations.
The compound's aromatic structure and sulfonic acid group contribute to its potential toxicity. Studies have shown that sulphanilic acid can exhibit ecotoxicological effects on certain aquatic species, including algae and fish. Therefore, proper waste management and treatment protocols are crucial to mitigate these risks.
On the positive side, the use of sulphanilic acid in biocatalysis often leads to improved atom economy and reduced use of hazardous solvents. This can result in a net positive environmental impact when compared to traditional chemical processes that may require more aggressive reagents and generate more toxic by-products.
The environmental fate of sulphanilic acid is also influenced by its chemical properties. Its solubility in water and resistance to hydrolysis mean that it can be transported in aqueous environments, potentially affecting a wider area if released untreated. However, this property also makes it amenable to certain water treatment technologies.
Efforts to minimize the environmental impact of sulphanilic acid in biocatalytic processes include the development of closed-loop systems, where the compound is recycled and reused. Additionally, advanced wastewater treatment methods, such as advanced oxidation processes and membrane filtration, have shown promise in removing sulphanilic acid from effluents.
In conclusion, while sulphanilic acid offers significant benefits in biocatalytic processes, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. Balancing the advantages of improved reaction efficiency and reduced overall chemical waste with the potential risks of environmental persistence and ecotoxicity is crucial for sustainable industrial practices.
Scalability and Industrial Applications
The scalability and industrial applications of sulphanilic acid in biocatalytic processes represent a significant area of interest for the chemical and biotechnology industries. As the demand for sustainable and efficient production methods grows, the ability to scale up biocatalytic processes facilitated by sulphanilic acid becomes increasingly important.
In terms of scalability, sulphanilic acid has shown promising results in laboratory-scale experiments, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing various biocatalytic reactions. However, transitioning from bench-scale to industrial-scale production presents several challenges. One of the primary considerations is the optimization of reaction conditions, including temperature, pH, and substrate concentrations, to maintain efficiency at larger scales.
The use of immobilized enzymes in conjunction with sulphanilic acid has emerged as a potential solution to improve scalability. This approach allows for easier separation of the catalyst from the reaction mixture and enables continuous processing, which is crucial for industrial-scale operations. Additionally, the development of flow reactors incorporating sulphanilic acid as a facilitator has shown potential for increasing productivity and reducing reaction times.
In industrial applications, sulphanilic acid's role in biocatalytic processes spans various sectors. In the pharmaceutical industry, it has been utilized to enhance the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) through enzymatic transformations. The textile industry has also benefited from sulphanilic acid-facilitated biocatalytic processes, particularly in the development of eco-friendly dyeing methods and the treatment of textile effluents.
The food and beverage sector has explored the use of sulphanilic acid in biocatalytic processes for the production of flavors, fragrances, and nutritional supplements. Its ability to improve the selectivity and yield of certain enzymatic reactions has made it valuable in the synthesis of complex organic compounds used in these industries.
Environmental applications have also emerged as a promising area for sulphanilic acid-facilitated biocatalysis. Wastewater treatment processes have incorporated this technology to degrade recalcitrant pollutants more effectively, offering a greener alternative to traditional chemical treatments.
As industries continue to seek more sustainable and cost-effective production methods, the scalability and industrial applications of sulphanilic acid in biocatalytic processes are likely to expand. Future developments may focus on enhancing the stability of enzyme-sulphanilic acid systems under industrial conditions and exploring novel applications in emerging fields such as biofuel production and the synthesis of advanced materials.
In terms of scalability, sulphanilic acid has shown promising results in laboratory-scale experiments, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing various biocatalytic reactions. However, transitioning from bench-scale to industrial-scale production presents several challenges. One of the primary considerations is the optimization of reaction conditions, including temperature, pH, and substrate concentrations, to maintain efficiency at larger scales.
The use of immobilized enzymes in conjunction with sulphanilic acid has emerged as a potential solution to improve scalability. This approach allows for easier separation of the catalyst from the reaction mixture and enables continuous processing, which is crucial for industrial-scale operations. Additionally, the development of flow reactors incorporating sulphanilic acid as a facilitator has shown potential for increasing productivity and reducing reaction times.
In industrial applications, sulphanilic acid's role in biocatalytic processes spans various sectors. In the pharmaceutical industry, it has been utilized to enhance the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) through enzymatic transformations. The textile industry has also benefited from sulphanilic acid-facilitated biocatalytic processes, particularly in the development of eco-friendly dyeing methods and the treatment of textile effluents.
The food and beverage sector has explored the use of sulphanilic acid in biocatalytic processes for the production of flavors, fragrances, and nutritional supplements. Its ability to improve the selectivity and yield of certain enzymatic reactions has made it valuable in the synthesis of complex organic compounds used in these industries.
Environmental applications have also emerged as a promising area for sulphanilic acid-facilitated biocatalysis. Wastewater treatment processes have incorporated this technology to degrade recalcitrant pollutants more effectively, offering a greener alternative to traditional chemical treatments.
As industries continue to seek more sustainable and cost-effective production methods, the scalability and industrial applications of sulphanilic acid in biocatalytic processes are likely to expand. Future developments may focus on enhancing the stability of enzyme-sulphanilic acid systems under industrial conditions and exploring novel applications in emerging fields such as biofuel production and the synthesis of advanced materials.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!