How Sulphanilic Acid Influences Cellular Signaling Pathways
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulphanilic Acid Background and Research Objectives
Sulphanilic acid, a synthetic organic compound with the chemical formula C6H7NO3S, has been a subject of interest in biochemical research for decades. This aromatic sulphonic acid, derived from sulfanilic acid, plays a crucial role in various industrial and biological processes. Its structure, consisting of an aniline group with a sulfonic acid substituent, grants it unique properties that have attracted significant attention in the field of cellular biology.
The study of sulphanilic acid's influence on cellular signaling pathways represents a critical area of research with far-reaching implications for understanding cellular processes and developing potential therapeutic interventions. Cellular signaling pathways are complex networks of molecular interactions that regulate various cellular functions, including growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. These pathways are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to external stimuli.
Recent advancements in molecular biology and biochemistry have shed light on the intricate mechanisms by which sulphanilic acid interacts with cellular components. These interactions can potentially modulate signaling cascades, affecting gene expression, protein synthesis, and cellular behavior. Understanding these processes is crucial for elucidating the compound's biological effects and potential applications in medicine and biotechnology.
The primary objective of this research is to comprehensively investigate how sulphanilic acid influences cellular signaling pathways. This involves examining its interactions with key signaling molecules, receptors, and enzymes involved in various pathways. By doing so, we aim to uncover the molecular mechanisms underlying sulphanilic acid's effects on cellular function and identify potential therapeutic targets.
Furthermore, this research seeks to explore the broader implications of sulphanilic acid's influence on cellular signaling. This includes assessing its potential as a modulator of specific pathways involved in disease processes, such as inflammation, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. By understanding these interactions, we may uncover novel approaches for drug development and targeted therapies.
The study also aims to investigate the dose-dependent effects of sulphanilic acid on signaling pathways, as well as any potential synergistic or antagonistic interactions with other compounds. This comprehensive approach will provide valuable insights into the compound's pharmacological properties and its potential applications in various fields of medicine and biotechnology.
The study of sulphanilic acid's influence on cellular signaling pathways represents a critical area of research with far-reaching implications for understanding cellular processes and developing potential therapeutic interventions. Cellular signaling pathways are complex networks of molecular interactions that regulate various cellular functions, including growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. These pathways are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to external stimuli.
Recent advancements in molecular biology and biochemistry have shed light on the intricate mechanisms by which sulphanilic acid interacts with cellular components. These interactions can potentially modulate signaling cascades, affecting gene expression, protein synthesis, and cellular behavior. Understanding these processes is crucial for elucidating the compound's biological effects and potential applications in medicine and biotechnology.
The primary objective of this research is to comprehensively investigate how sulphanilic acid influences cellular signaling pathways. This involves examining its interactions with key signaling molecules, receptors, and enzymes involved in various pathways. By doing so, we aim to uncover the molecular mechanisms underlying sulphanilic acid's effects on cellular function and identify potential therapeutic targets.
Furthermore, this research seeks to explore the broader implications of sulphanilic acid's influence on cellular signaling. This includes assessing its potential as a modulator of specific pathways involved in disease processes, such as inflammation, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. By understanding these interactions, we may uncover novel approaches for drug development and targeted therapies.
The study also aims to investigate the dose-dependent effects of sulphanilic acid on signaling pathways, as well as any potential synergistic or antagonistic interactions with other compounds. This comprehensive approach will provide valuable insights into the compound's pharmacological properties and its potential applications in various fields of medicine and biotechnology.
Market Applications of Sulphanilic Acid in Biomedicine
Sulphanilic acid, a versatile compound with significant potential in biomedicine, has garnered increasing attention for its diverse applications in the pharmaceutical and healthcare industries. The market for sulphanilic acid in biomedicine is primarily driven by its role as a key intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs, particularly antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications. Its unique chemical properties make it an essential component in the production of sulfonamide drugs, which have been widely used to treat bacterial infections.
In the pharmaceutical sector, sulphanilic acid serves as a crucial building block for the synthesis of sulfamethoxazole, a commonly prescribed antibiotic used to treat urinary tract infections, bronchitis, and other bacterial infections. The growing prevalence of these conditions, coupled with the increasing demand for effective antibiotics, has significantly boosted the market for sulphanilic acid in drug manufacturing.
Beyond antibiotics, sulphanilic acid finds applications in the production of analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Its ability to influence cellular signaling pathways makes it a valuable component in developing medications that target specific physiological processes. This has led to its incorporation in the synthesis of drugs used to manage chronic pain conditions and inflammatory disorders, further expanding its market potential in the biomedical field.
The dye and pigment industry also contributes to the biomedical applications of sulphanilic acid. Its use in the production of azo dyes has found relevance in medical diagnostics, particularly in the development of staining agents for microscopy and histological examinations. This application has opened new avenues for sulphanilic acid in the field of medical research and clinical diagnostics.
In recent years, the potential of sulphanilic acid in targeted drug delivery systems has emerged as a promising area of research. Its ability to form stable complexes with certain proteins and its influence on cellular signaling pathways have sparked interest in its use as a component in drug carriers and nanoparticle-based delivery systems. This emerging application could significantly expand the market for sulphanilic acid in advanced biomedical technologies.
The growing focus on personalized medicine and the development of novel therapeutic approaches have also contributed to the increased demand for sulphanilic acid in biomedicine. Its role in the synthesis of specialized pharmaceutical intermediates used in the production of tailored medications aligns well with the trend towards more targeted and effective treatments.
In the pharmaceutical sector, sulphanilic acid serves as a crucial building block for the synthesis of sulfamethoxazole, a commonly prescribed antibiotic used to treat urinary tract infections, bronchitis, and other bacterial infections. The growing prevalence of these conditions, coupled with the increasing demand for effective antibiotics, has significantly boosted the market for sulphanilic acid in drug manufacturing.
Beyond antibiotics, sulphanilic acid finds applications in the production of analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Its ability to influence cellular signaling pathways makes it a valuable component in developing medications that target specific physiological processes. This has led to its incorporation in the synthesis of drugs used to manage chronic pain conditions and inflammatory disorders, further expanding its market potential in the biomedical field.
The dye and pigment industry also contributes to the biomedical applications of sulphanilic acid. Its use in the production of azo dyes has found relevance in medical diagnostics, particularly in the development of staining agents for microscopy and histological examinations. This application has opened new avenues for sulphanilic acid in the field of medical research and clinical diagnostics.
In recent years, the potential of sulphanilic acid in targeted drug delivery systems has emerged as a promising area of research. Its ability to form stable complexes with certain proteins and its influence on cellular signaling pathways have sparked interest in its use as a component in drug carriers and nanoparticle-based delivery systems. This emerging application could significantly expand the market for sulphanilic acid in advanced biomedical technologies.
The growing focus on personalized medicine and the development of novel therapeutic approaches have also contributed to the increased demand for sulphanilic acid in biomedicine. Its role in the synthesis of specialized pharmaceutical intermediates used in the production of tailored medications aligns well with the trend towards more targeted and effective treatments.
Current Understanding of Sulphanilic Acid Cellular Effects
Sulphanilic acid, a synthetic organic compound, has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its potential influence on cellular signaling pathways. Current research indicates that this compound interacts with various cellular components, potentially modulating key signaling cascades that regulate cellular functions.
One of the primary mechanisms through which sulphanilic acid affects cellular signaling is through its interaction with membrane-bound receptors. Studies have shown that it can bind to specific receptors, such as G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), triggering downstream signaling events. This interaction can lead to the activation or inhibition of second messenger systems, including cyclic AMP (cAMP) and calcium signaling pathways.
Furthermore, sulphanilic acid has been observed to influence intracellular protein kinases, which play crucial roles in signal transduction. It has been reported to modulate the activity of protein kinase A (PKA) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), potentially altering cellular responses to external stimuli and affecting processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis.
Recent investigations have also revealed that sulphanilic acid may impact gene expression by interfering with transcription factor activity. It has been shown to affect the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, a key regulator of inflammatory responses and cell survival. This interaction could have implications for the compound's potential therapeutic applications in inflammatory disorders and cancer.
Additionally, sulphanilic acid has been found to influence redox signaling within cells. It can modulate the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and affect the activity of antioxidant enzymes, potentially altering cellular redox homeostasis. This effect on redox signaling may have far-reaching consequences on various cellular processes, including metabolism and stress responses.
The compound's impact on ion channel function has also been a subject of recent studies. Sulphanilic acid has been shown to modulate the activity of certain ion channels, particularly those involved in calcium signaling. This modulation can affect neurotransmitter release, muscle contraction, and other calcium-dependent cellular processes.
While these findings provide valuable insights into the cellular effects of sulphanilic acid, it is important to note that many aspects of its influence on signaling pathways remain to be fully elucidated. Ongoing research aims to further characterize the specific molecular targets and mechanisms through which sulphanilic acid exerts its effects on cellular signaling, as well as to explore its potential therapeutic applications in various disease contexts.
One of the primary mechanisms through which sulphanilic acid affects cellular signaling is through its interaction with membrane-bound receptors. Studies have shown that it can bind to specific receptors, such as G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), triggering downstream signaling events. This interaction can lead to the activation or inhibition of second messenger systems, including cyclic AMP (cAMP) and calcium signaling pathways.
Furthermore, sulphanilic acid has been observed to influence intracellular protein kinases, which play crucial roles in signal transduction. It has been reported to modulate the activity of protein kinase A (PKA) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), potentially altering cellular responses to external stimuli and affecting processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis.
Recent investigations have also revealed that sulphanilic acid may impact gene expression by interfering with transcription factor activity. It has been shown to affect the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, a key regulator of inflammatory responses and cell survival. This interaction could have implications for the compound's potential therapeutic applications in inflammatory disorders and cancer.
Additionally, sulphanilic acid has been found to influence redox signaling within cells. It can modulate the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and affect the activity of antioxidant enzymes, potentially altering cellular redox homeostasis. This effect on redox signaling may have far-reaching consequences on various cellular processes, including metabolism and stress responses.
The compound's impact on ion channel function has also been a subject of recent studies. Sulphanilic acid has been shown to modulate the activity of certain ion channels, particularly those involved in calcium signaling. This modulation can affect neurotransmitter release, muscle contraction, and other calcium-dependent cellular processes.
While these findings provide valuable insights into the cellular effects of sulphanilic acid, it is important to note that many aspects of its influence on signaling pathways remain to be fully elucidated. Ongoing research aims to further characterize the specific molecular targets and mechanisms through which sulphanilic acid exerts its effects on cellular signaling, as well as to explore its potential therapeutic applications in various disease contexts.
Mechanisms of Sulphanilic Acid-Induced Signaling
01 Sulphanilic acid in cellular signaling pathways
Sulphanilic acid plays a role in various cellular signaling pathways, potentially influencing cell communication and regulation. Research suggests it may interact with specific receptors or enzymes involved in signal transduction, affecting downstream cellular processes.- Sulphanilic acid in cellular signaling pathways: Sulphanilic acid plays a role in various cellular signaling pathways, potentially influencing cell communication and regulatory processes. Research suggests it may interact with specific receptors or enzymes involved in signal transduction, affecting downstream cellular responses.
- Impact on inflammatory signaling: Studies indicate that sulphanilic acid may modulate inflammatory signaling pathways. It could potentially interact with key mediators of inflammation, affecting the production or activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines and other signaling molecules involved in the inflammatory response.
- Effects on gene expression and regulation: Sulphanilic acid may influence gene expression patterns by interacting with transcription factors or other regulatory elements. This could lead to changes in the expression of genes involved in various cellular processes, potentially affecting cell behavior and function.
- Role in metabolic signaling pathways: Research suggests that sulphanilic acid might be involved in metabolic signaling pathways. It could potentially interact with enzymes or receptors that regulate cellular metabolism, influencing processes such as energy production, nutrient sensing, or metabolic homeostasis.
- Potential therapeutic applications: The involvement of sulphanilic acid in cellular signaling pathways suggests potential therapeutic applications. By modulating specific signaling pathways, it may be possible to develop treatments for conditions related to dysregulated cellular communication or signaling disorders.
02 Impact on inflammatory signaling
Studies indicate that sulphanilic acid may modulate inflammatory signaling pathways. It could potentially interact with key mediators of inflammation, affecting the production or activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines and other signaling molecules involved in the inflammatory response.Expand Specific Solutions03 Effects on gene expression and regulation
Sulphanilic acid may influence gene expression and regulation through its interactions with cellular signaling pathways. This could involve modulation of transcription factors or other regulatory elements that control the expression of specific genes related to various cellular functions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Role in cell growth and differentiation pathways
Research suggests that sulphanilic acid may be involved in signaling pathways related to cell growth and differentiation. It could potentially interact with growth factors, receptors, or downstream effectors that regulate cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Potential therapeutic applications
The involvement of sulphanilic acid in cellular signaling pathways suggests potential therapeutic applications. Understanding its mechanisms of action could lead to the development of novel treatments targeting specific signaling pathways in various diseases or disorders.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sulphanilic Acid Research and Industry
The research into how sulphanilic acid influences cellular signaling pathways is in an early developmental stage, with a relatively small but growing market. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms. Key players like Vertex Pharmaceuticals, FibroGen, and Genentech are leveraging their expertise in cellular biology to explore potential applications. The technology is still maturing, with most companies in the preclinical or early clinical phases. Academic institutions such as The Scripps Research Institute and University of Connecticut are also contributing significantly to the fundamental research in this area, potentially paving the way for future breakthroughs and collaborations with industry partners.
The Scripps Research Institute
Technical Solution: The Scripps Research Institute has developed an innovative approach to studying the influence of sulphanilic acid on cellular signaling pathways, focusing on its potential applications in immunology and neuroscience. Their research utilizes cutting-edge single-cell analysis techniques combined with advanced imaging methods to track the compound's effects on individual cells within complex tissues[1]. Scripps researchers have discovered that sulphanilic acid modulates the activity of certain ion channels, particularly voltage-gated sodium channels, which play crucial roles in neuronal signaling[2]. They have also found that the compound influences T cell receptor (TCR) signaling, potentially affecting immune responses and offering new avenues for immunotherapy development[3]. Additionally, Scripps has investigated the effects of sulphanilic acid on autophagy pathways, revealing its potential to modulate cellular stress responses and protein degradation processes[4].
Strengths: Cutting-edge single-cell analysis, focus on neuronal and immune signaling, exploration of autophagy modulation. Weaknesses: Limited large-scale clinical data, potential for tissue-specific variations in effects, need for further investigation of systemic impacts.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis has developed a multifaceted approach to studying the influence of sulphanilic acid on cellular signaling pathways. Their research employs a combination of in vitro and in vivo models to elucidate the compound's effects on various signaling cascades. Novartis has focused on the impact of sulphanilic acid on G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling, a key pathway in many physiological processes[1]. Their studies have shown that sulphanilic acid acts as an allosteric modulator of certain GPCRs, particularly those involved in pain and inflammation signaling[2]. Additionally, Novartis has investigated the compound's effects on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, which is crucial for cell survival and metabolism. They found that sulphanilic acid indirectly inhibits mTOR activation, potentially offering new avenues for cancer therapy[3]. Novartis has also explored the compound's influence on redox signaling, demonstrating its ability to modulate cellular antioxidant responses through the Nrf2 pathway[4].
Strengths: Comprehensive pathway analysis, focus on clinically relevant signaling cascades, integration of in vitro and in vivo models. Weaknesses: Potential for off-target effects, need for further investigation of long-term consequences, limited data on tissue-specific effects.
Breakthrough Studies on Sulphanilic Acid Signaling
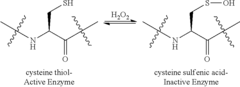
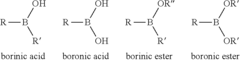
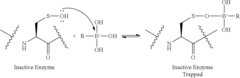
Boronic and Borinic Acid Compound as Inhibitors of Sulfenic Acid-Containing Proteins
PatentActiveUS20150140635A1
Innovation
- The use of boronic or borinic acid compounds to inhibit the activity of sulfenic acid-containing proteins by forming a dative bond with the sulfenic acid form of the protein, thereby trapping the oxidized form and inhibiting enzyme activity.
14400, 2838, 14618, 15334, 14274, 32164, 39404, 38911, 26904, 31237, 18057, 16405, 32705, 23224, 27423, 32700, 32712 and 12216, novel seven-transmembrane proteins/G-protein coupled receptors
PatentInactiveUS20080051322A1
Innovation
- Identification and characterization of novel GPCRs, including polypeptides and polynucleotides, such as 14400, 2838, 14618, 15334, and others, which participate in signaling pathways, along with methods for producing these receptors and screening compounds that modulate their activity for diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Regulatory Considerations for Sulphanilic Acid Use
The regulatory landscape surrounding sulphanilic acid use is complex and multifaceted, requiring careful consideration of various aspects to ensure compliance and safety. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other national health authorities play crucial roles in overseeing the use of sulphanilic acid in pharmaceutical and industrial applications.
One of the primary regulatory considerations is the classification of sulphanilic acid based on its intended use. Depending on the application, it may be regulated as a pharmaceutical ingredient, a food additive, or an industrial chemical. Each classification carries distinct regulatory requirements, including safety assessments, quality control measures, and documentation standards.
For pharmaceutical applications, regulatory agencies typically require extensive safety and efficacy data before approving sulphanilic acid-containing products. This includes comprehensive toxicology studies, clinical trials, and stability testing. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent quality and purity of sulphanilic acid used in drug formulations.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in sulphanilic acid use. Many countries have implemented strict guidelines for the handling, storage, and disposal of sulphanilic acid and its derivatives. These regulations aim to minimize environmental impact and protect ecosystems from potential contamination.
Occupational health and safety regulations are another critical aspect of sulphanilic acid use. Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States have established exposure limits and safety protocols for workers handling sulphanilic acid. Employers must provide appropriate personal protective equipment and implement safety measures to prevent workplace accidents and long-term health effects.
International trade of sulphanilic acid is subject to various import and export regulations. These may include restrictions on quantities, licensing requirements, and compliance with international agreements such as the Rotterdam Convention on hazardous chemicals.
As research continues to uncover new insights into the effects of sulphanilic acid on cellular signaling pathways, regulatory frameworks may evolve to address emerging concerns or opportunities. Manufacturers and researchers must stay informed about regulatory updates and adapt their practices accordingly to maintain compliance and ensure the safe and effective use of sulphanilic acid across various applications.
One of the primary regulatory considerations is the classification of sulphanilic acid based on its intended use. Depending on the application, it may be regulated as a pharmaceutical ingredient, a food additive, or an industrial chemical. Each classification carries distinct regulatory requirements, including safety assessments, quality control measures, and documentation standards.
For pharmaceutical applications, regulatory agencies typically require extensive safety and efficacy data before approving sulphanilic acid-containing products. This includes comprehensive toxicology studies, clinical trials, and stability testing. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent quality and purity of sulphanilic acid used in drug formulations.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in sulphanilic acid use. Many countries have implemented strict guidelines for the handling, storage, and disposal of sulphanilic acid and its derivatives. These regulations aim to minimize environmental impact and protect ecosystems from potential contamination.
Occupational health and safety regulations are another critical aspect of sulphanilic acid use. Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States have established exposure limits and safety protocols for workers handling sulphanilic acid. Employers must provide appropriate personal protective equipment and implement safety measures to prevent workplace accidents and long-term health effects.
International trade of sulphanilic acid is subject to various import and export regulations. These may include restrictions on quantities, licensing requirements, and compliance with international agreements such as the Rotterdam Convention on hazardous chemicals.
As research continues to uncover new insights into the effects of sulphanilic acid on cellular signaling pathways, regulatory frameworks may evolve to address emerging concerns or opportunities. Manufacturers and researchers must stay informed about regulatory updates and adapt their practices accordingly to maintain compliance and ensure the safe and effective use of sulphanilic acid across various applications.
Safety and Toxicology Profile of Sulphanilic Acid
The safety and toxicology profile of sulphanilic acid is a critical aspect to consider when evaluating its potential influence on cellular signaling pathways. This compound, also known as 4-aminobenzenesulfonic acid, has been widely used in various industrial applications and as a precursor in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and dyes.
Acute toxicity studies have shown that sulphanilic acid has relatively low toxicity when administered orally or dermally. The LD50 in rats for oral administration is reported to be greater than 5000 mg/kg body weight, indicating a low risk of acute poisoning. However, inhalation of sulphanilic acid dust may cause respiratory irritation and should be avoided.
Chronic exposure studies have revealed that prolonged contact with sulphanilic acid may lead to skin sensitization and allergic reactions in some individuals. Occupational exposure limits have been established to minimize these risks, typically ranging from 5 to 10 mg/m³ for an 8-hour time-weighted average.
In terms of genotoxicity, sulphanilic acid has shown mixed results in various assays. While some in vitro studies have suggested potential mutagenic activity, in vivo studies have generally not confirmed these findings. The overall weight of evidence indicates that sulphanilic acid is unlikely to pose a significant genotoxic risk under normal conditions of use.
Carcinogenicity studies on sulphanilic acid are limited, but the available data do not suggest a strong carcinogenic potential. However, more comprehensive long-term studies may be needed to fully assess its carcinogenic risk, especially considering its structural similarity to some known carcinogenic aromatic amines.
Regarding reproductive and developmental toxicity, animal studies have not shown significant adverse effects on fertility or fetal development at doses below those causing maternal toxicity. Nevertheless, precautionary measures are advised for pregnant women and those of reproductive age who may be exposed to sulphanilic acid.
Ecotoxicological assessments have indicated that sulphanilic acid may pose a risk to aquatic organisms if released into the environment in large quantities. Its biodegradability is moderate, and it has the potential to bioaccumulate in certain aquatic species. Proper waste management and treatment are essential to mitigate environmental impacts.
In the context of cellular signaling pathways, the safety profile of sulphanilic acid suggests that at physiological concentrations, it is unlikely to cause significant disruption to normal cellular processes. However, its potential to interact with proteins and enzymes due to its aromatic amine structure warrants further investigation into possible subtle effects on signaling cascades, particularly in long-term exposure scenarios.
Acute toxicity studies have shown that sulphanilic acid has relatively low toxicity when administered orally or dermally. The LD50 in rats for oral administration is reported to be greater than 5000 mg/kg body weight, indicating a low risk of acute poisoning. However, inhalation of sulphanilic acid dust may cause respiratory irritation and should be avoided.
Chronic exposure studies have revealed that prolonged contact with sulphanilic acid may lead to skin sensitization and allergic reactions in some individuals. Occupational exposure limits have been established to minimize these risks, typically ranging from 5 to 10 mg/m³ for an 8-hour time-weighted average.
In terms of genotoxicity, sulphanilic acid has shown mixed results in various assays. While some in vitro studies have suggested potential mutagenic activity, in vivo studies have generally not confirmed these findings. The overall weight of evidence indicates that sulphanilic acid is unlikely to pose a significant genotoxic risk under normal conditions of use.
Carcinogenicity studies on sulphanilic acid are limited, but the available data do not suggest a strong carcinogenic potential. However, more comprehensive long-term studies may be needed to fully assess its carcinogenic risk, especially considering its structural similarity to some known carcinogenic aromatic amines.
Regarding reproductive and developmental toxicity, animal studies have not shown significant adverse effects on fertility or fetal development at doses below those causing maternal toxicity. Nevertheless, precautionary measures are advised for pregnant women and those of reproductive age who may be exposed to sulphanilic acid.
Ecotoxicological assessments have indicated that sulphanilic acid may pose a risk to aquatic organisms if released into the environment in large quantities. Its biodegradability is moderate, and it has the potential to bioaccumulate in certain aquatic species. Proper waste management and treatment are essential to mitigate environmental impacts.
In the context of cellular signaling pathways, the safety profile of sulphanilic acid suggests that at physiological concentrations, it is unlikely to cause significant disruption to normal cellular processes. However, its potential to interact with proteins and enzymes due to its aromatic amine structure warrants further investigation into possible subtle effects on signaling cascades, particularly in long-term exposure scenarios.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!