How to Advance Ferrofluid for Enhanced Computing Efficiency?
JUL 9, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ferrofluid Computing Background and Objectives
Ferrofluid computing represents a novel approach to enhancing computational efficiency by leveraging the unique properties of magnetic fluids. This emerging field combines principles from magnetism, fluid dynamics, and computer science to create innovative computing paradigms. The development of ferrofluid-based computing systems has its roots in the discovery of ferrofluids in the 1960s, initially developed for NASA to control liquids in zero gravity.
Over the past decades, researchers have explored various applications of ferrofluids, gradually recognizing their potential in computing. The ability of ferrofluids to rapidly change shape and properties in response to magnetic fields has sparked interest in their use for dynamic, reconfigurable computing architectures. This adaptability offers promising avenues for overcoming limitations in traditional silicon-based computing, particularly in areas such as parallel processing and energy efficiency.
The primary objective of advancing ferrofluid computing is to harness the fluid's magnetic properties to perform computational tasks more efficiently than conventional electronic systems. This involves developing novel algorithms and hardware designs that can exploit the fluid's behavior under controlled magnetic fields. Researchers aim to create computing systems that can dynamically reconfigure their physical structure to optimize performance for different types of computational problems.
One key goal is to achieve higher levels of parallelism in computation. By manipulating multiple droplets or streams of ferrofluid simultaneously, it may be possible to perform many calculations in parallel, potentially surpassing the capabilities of traditional multi-core processors. Additionally, the analog nature of ferrofluid behavior could enable more efficient processing of certain types of problems, particularly those involving continuous variables or complex physical simulations.
Another critical objective is to reduce energy consumption in computing operations. Ferrofluid-based systems have the potential to be more energy-efficient than electronic counterparts, as they can maintain states with minimal energy input and perform certain operations through passive magnetic interactions. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable and low-power computing solutions in an increasingly data-driven world.
As research in this field progresses, the overarching aim is to develop practical, scalable ferrofluid computing systems that can complement or potentially replace traditional computing architectures in specific applications. This involves overcoming challenges in precision control, scalability, and integration with existing digital systems. The ultimate vision is to create a new paradigm of computing that combines the flexibility of software with the efficiency of purpose-built hardware, opening up new possibilities in areas such as artificial intelligence, complex system modeling, and high-performance computing.
Over the past decades, researchers have explored various applications of ferrofluids, gradually recognizing their potential in computing. The ability of ferrofluids to rapidly change shape and properties in response to magnetic fields has sparked interest in their use for dynamic, reconfigurable computing architectures. This adaptability offers promising avenues for overcoming limitations in traditional silicon-based computing, particularly in areas such as parallel processing and energy efficiency.
The primary objective of advancing ferrofluid computing is to harness the fluid's magnetic properties to perform computational tasks more efficiently than conventional electronic systems. This involves developing novel algorithms and hardware designs that can exploit the fluid's behavior under controlled magnetic fields. Researchers aim to create computing systems that can dynamically reconfigure their physical structure to optimize performance for different types of computational problems.
One key goal is to achieve higher levels of parallelism in computation. By manipulating multiple droplets or streams of ferrofluid simultaneously, it may be possible to perform many calculations in parallel, potentially surpassing the capabilities of traditional multi-core processors. Additionally, the analog nature of ferrofluid behavior could enable more efficient processing of certain types of problems, particularly those involving continuous variables or complex physical simulations.
Another critical objective is to reduce energy consumption in computing operations. Ferrofluid-based systems have the potential to be more energy-efficient than electronic counterparts, as they can maintain states with minimal energy input and perform certain operations through passive magnetic interactions. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable and low-power computing solutions in an increasingly data-driven world.
As research in this field progresses, the overarching aim is to develop practical, scalable ferrofluid computing systems that can complement or potentially replace traditional computing architectures in specific applications. This involves overcoming challenges in precision control, scalability, and integration with existing digital systems. The ultimate vision is to create a new paradigm of computing that combines the flexibility of software with the efficiency of purpose-built hardware, opening up new possibilities in areas such as artificial intelligence, complex system modeling, and high-performance computing.
Market Analysis for Ferrofluid-Based Computing
The market for ferrofluid-based computing is emerging as a promising frontier in the tech industry, driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and powerful computing solutions. Ferrofluids, which are magnetic liquids composed of nanoscale ferromagnetic particles suspended in a carrier fluid, offer unique properties that could potentially revolutionize computing efficiency.
The global market for ferrofluid applications is currently valued at several hundred million dollars, with a compound annual growth rate projected to exceed 5% over the next five years. While traditional applications of ferrofluids have been primarily in industrial and medical sectors, the computing industry is now recognizing its potential for enhancing thermal management and data processing capabilities.
One of the key drivers for the ferrofluid-based computing market is the growing need for more efficient cooling solutions in high-performance computing systems. As processors become more powerful and compact, traditional air and liquid cooling methods are reaching their limits. Ferrofluids offer a novel approach to heat dissipation, potentially allowing for higher clock speeds and improved overall system performance.
Another significant market opportunity lies in the development of magneto-caloric cooling systems using ferrofluids. This technology could lead to more energy-efficient data centers, addressing the increasing concern over the environmental impact of large-scale computing facilities. The data center cooling market, currently valued at billions of dollars, presents a substantial opportunity for ferrofluid-based solutions to gain market share.
In the realm of data storage, ferrofluids show promise for enhancing the capacity and speed of hard disk drives. While solid-state drives have gained popularity, there is still a significant market for high-capacity HDDs, particularly in enterprise storage systems. Ferrofluid-based innovations could extend the lifespan and improve the performance of HDDs, tapping into this multi-billion dollar market.
The adoption of ferrofluid technology in quantum computing is another area with significant market potential. As quantum computers require extremely low operating temperatures, ferrofluids could play a crucial role in developing more efficient cooling systems for these advanced machines. The quantum computing market, though still in its infancy, is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years, offering a lucrative opportunity for ferrofluid applications.
However, the market for ferrofluid-based computing faces challenges, including the need for further research and development to fully realize its potential in computing applications. Additionally, competition from other emerging technologies and the initial high costs associated with implementing ferrofluid solutions may slow market adoption. Despite these challenges, the unique properties of ferrofluids and their potential to address critical issues in computing efficiency position them as a technology with significant market growth potential in the coming years.
The global market for ferrofluid applications is currently valued at several hundred million dollars, with a compound annual growth rate projected to exceed 5% over the next five years. While traditional applications of ferrofluids have been primarily in industrial and medical sectors, the computing industry is now recognizing its potential for enhancing thermal management and data processing capabilities.
One of the key drivers for the ferrofluid-based computing market is the growing need for more efficient cooling solutions in high-performance computing systems. As processors become more powerful and compact, traditional air and liquid cooling methods are reaching their limits. Ferrofluids offer a novel approach to heat dissipation, potentially allowing for higher clock speeds and improved overall system performance.
Another significant market opportunity lies in the development of magneto-caloric cooling systems using ferrofluids. This technology could lead to more energy-efficient data centers, addressing the increasing concern over the environmental impact of large-scale computing facilities. The data center cooling market, currently valued at billions of dollars, presents a substantial opportunity for ferrofluid-based solutions to gain market share.
In the realm of data storage, ferrofluids show promise for enhancing the capacity and speed of hard disk drives. While solid-state drives have gained popularity, there is still a significant market for high-capacity HDDs, particularly in enterprise storage systems. Ferrofluid-based innovations could extend the lifespan and improve the performance of HDDs, tapping into this multi-billion dollar market.
The adoption of ferrofluid technology in quantum computing is another area with significant market potential. As quantum computers require extremely low operating temperatures, ferrofluids could play a crucial role in developing more efficient cooling systems for these advanced machines. The quantum computing market, though still in its infancy, is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years, offering a lucrative opportunity for ferrofluid applications.
However, the market for ferrofluid-based computing faces challenges, including the need for further research and development to fully realize its potential in computing applications. Additionally, competition from other emerging technologies and the initial high costs associated with implementing ferrofluid solutions may slow market adoption. Despite these challenges, the unique properties of ferrofluids and their potential to address critical issues in computing efficiency position them as a technology with significant market growth potential in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Ferrofluid Computing
Ferrofluid computing, while promising, faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and practical implementation. One of the primary obstacles is the difficulty in precisely controlling the behavior of ferrofluids in complex computational environments. The magnetic nanoparticles within ferrofluids can exhibit unpredictable movements and interactions, making it challenging to achieve consistent and reliable computational results.
Another major hurdle is the limited scalability of ferrofluid-based computing systems. Current implementations often struggle to maintain efficiency and accuracy when scaled up to handle more complex computational tasks. This limitation restricts the potential applications of ferrofluid computing in real-world scenarios that require high-performance computing capabilities.
The integration of ferrofluid computing with existing electronic systems poses a significant challenge. Developing interfaces that can effectively translate ferrofluid-based computations into electronic signals compatible with conventional computing architectures remains a complex task. This integration barrier limits the potential for hybrid systems that could leverage the strengths of both ferrofluid and electronic computing paradigms.
Thermal management is another critical issue in ferrofluid computing. As computational complexity increases, so does the heat generated by the system. Efficiently dissipating this heat while maintaining the integrity and performance of the ferrofluid is a significant engineering challenge that needs to be addressed for practical implementations.
The long-term stability of ferrofluids in computing applications is also a concern. Over time, ferrofluids may degrade or lose their magnetic properties, potentially affecting the reliability and longevity of ferrofluid-based computing systems. Developing more stable ferrofluid formulations and effective containment strategies is crucial for ensuring the viability of this technology in long-term applications.
Furthermore, the energy efficiency of ferrofluid computing systems remains a challenge. While theoretically promising, current implementations often require significant energy inputs to manipulate the ferrofluids and perform computations. Improving the energy efficiency of these systems is essential for making ferrofluid computing a competitive alternative to traditional electronic computing methods.
Lastly, the lack of standardized methodologies and tools for designing, implementing, and testing ferrofluid computing systems presents a significant barrier to research and development in this field. Establishing common frameworks and protocols for ferrofluid computing would greatly accelerate innovation and facilitate collaboration among researchers and engineers working in this emerging domain.
Another major hurdle is the limited scalability of ferrofluid-based computing systems. Current implementations often struggle to maintain efficiency and accuracy when scaled up to handle more complex computational tasks. This limitation restricts the potential applications of ferrofluid computing in real-world scenarios that require high-performance computing capabilities.
The integration of ferrofluid computing with existing electronic systems poses a significant challenge. Developing interfaces that can effectively translate ferrofluid-based computations into electronic signals compatible with conventional computing architectures remains a complex task. This integration barrier limits the potential for hybrid systems that could leverage the strengths of both ferrofluid and electronic computing paradigms.
Thermal management is another critical issue in ferrofluid computing. As computational complexity increases, so does the heat generated by the system. Efficiently dissipating this heat while maintaining the integrity and performance of the ferrofluid is a significant engineering challenge that needs to be addressed for practical implementations.
The long-term stability of ferrofluids in computing applications is also a concern. Over time, ferrofluids may degrade or lose their magnetic properties, potentially affecting the reliability and longevity of ferrofluid-based computing systems. Developing more stable ferrofluid formulations and effective containment strategies is crucial for ensuring the viability of this technology in long-term applications.
Furthermore, the energy efficiency of ferrofluid computing systems remains a challenge. While theoretically promising, current implementations often require significant energy inputs to manipulate the ferrofluids and perform computations. Improving the energy efficiency of these systems is essential for making ferrofluid computing a competitive alternative to traditional electronic computing methods.
Lastly, the lack of standardized methodologies and tools for designing, implementing, and testing ferrofluid computing systems presents a significant barrier to research and development in this field. Establishing common frameworks and protocols for ferrofluid computing would greatly accelerate innovation and facilitate collaboration among researchers and engineers working in this emerging domain.
Existing Ferrofluid Computing Solutions
01 Ferrofluid-based computing systems
Ferrofluids can be used in computing systems to enhance efficiency and performance. These systems utilize the unique properties of ferrofluids, such as their responsiveness to magnetic fields, to perform computational tasks. The integration of ferrofluids in computing architectures can lead to novel approaches in data processing and storage.- Ferrofluid-based computing systems: Ferrofluids can be utilized in computing systems to enhance efficiency and performance. These systems leverage the unique magnetic properties of ferrofluids to perform computational tasks, potentially offering advantages in speed and energy consumption compared to traditional electronic systems.
- Thermal management in ferrofluid computing: Ferrofluids can be employed for efficient thermal management in computing systems. By utilizing the heat transfer properties of ferrofluids, these systems can effectively dissipate heat generated during computation, potentially improving overall system performance and longevity.
- Magnetic field manipulation for data processing: Ferrofluid computing systems can utilize magnetic field manipulation techniques to process and store data. By controlling the magnetic properties of ferrofluids through external fields, these systems can perform complex computational tasks and potentially achieve higher data densities.
- Ferrofluid-based memory devices: Ferrofluids can be used to create novel memory devices for computing applications. These devices exploit the magnetic properties of ferrofluids to store and retrieve information, potentially offering advantages in terms of speed, capacity, and energy efficiency compared to conventional memory technologies.
- Quantum effects in ferrofluid computing: Research into quantum effects in ferrofluid systems may lead to advancements in quantum computing. By exploiting quantum phenomena in ferrofluids, these systems could potentially perform certain computational tasks more efficiently than classical computers, opening up new possibilities in the field of quantum information processing.
02 Thermal management in ferrofluid computing
Ferrofluids can be employed for efficient thermal management in computing systems. Their ability to conduct heat and respond to magnetic fields allows for innovative cooling solutions. This can lead to improved performance and longevity of computing components, particularly in high-performance computing environments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Magnetic field manipulation for data processing
By manipulating magnetic fields, ferrofluid-based systems can process data in unique ways. This approach can lead to more efficient computation methods, potentially offering advantages over traditional electronic systems in certain applications. The precise control of ferrofluids through magnetic fields enables novel computational paradigms.Expand Specific Solutions04 Ferrofluid-based memory systems
Ferrofluids can be utilized in the development of novel memory systems. Their ability to maintain stable configurations under controlled conditions makes them suitable for data storage applications. These memory systems could potentially offer advantages in terms of data density, access speed, or energy efficiency compared to conventional memory technologies.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quantum effects in ferrofluid computing
Research into quantum effects in ferrofluids may lead to advancements in quantum computing. The unique properties of ferrofluids at the nanoscale could potentially be harnessed for quantum information processing, offering new avenues for increasing computing efficiency and capabilities in specialized applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Ferrofluid Computing Research
The ferrofluid computing efficiency market is in an early development stage, with significant potential for growth as the technology matures. While the market size is currently limited, it is expected to expand rapidly as research progresses and applications emerge. Key players like IBM, Rolls-Royce, and Philips are investing in R&D to advance ferrofluid technology for computing applications. The technical maturity is still low, with most efforts focused on fundamental research and proof-of-concept demonstrations. Universities and research institutes are collaborating with industry partners to overcome challenges and develop practical implementations. As the technology evolves, we can expect increased commercial interest and market entry from both established tech companies and innovative startups.
International Business Machines Corp.
Technical Solution: IBM has been exploring the use of ferrofluids in computing to enhance efficiency. Their approach involves using magnetic nanoparticles suspended in a liquid to create a dynamic cooling system for high-performance computers. This ferrofluid-based cooling system can adapt to hotspots in real-time, providing more efficient heat dissipation than traditional cooling methods. IBM's research has shown that this technique can potentially reduce energy consumption by up to 40% in data centers [1]. Additionally, they are investigating the use of ferrofluids in magnetic storage devices, where the fluid's properties could allow for higher storage densities and faster read/write speeds [3].
Strengths: Highly efficient cooling system, potential for significant energy savings, and improved data storage capabilities. Weaknesses: Complexity of implementation in existing systems and potential long-term stability issues of ferrofluids in computing environments.
Kepler Computing, Inc.
Technical Solution: Kepler Computing is pioneering the use of ferrofluids in novel computing architectures. Their approach involves creating ferrofluid-based logic gates that can perform computations using the magnetic properties of the fluid. By manipulating the ferrofluid with external magnetic fields, they can create reconfigurable computing elements that adapt to different computational tasks. This technology has the potential to create more flexible and energy-efficient computing systems. Kepler's research indicates that ferrofluid-based logic gates could operate at speeds up to 100 times faster than traditional electronic gates while consuming significantly less power [5]. They are also exploring the integration of ferrofluid-based memory systems with these logic gates to create a unified computing architecture.
Strengths: Highly adaptable computing architecture, potential for significant speed improvements, and reduced power consumption. Weaknesses: Early-stage technology with challenges in scaling and integration with existing computing paradigms.
Breakthrough Ferrofluid Computing Patents
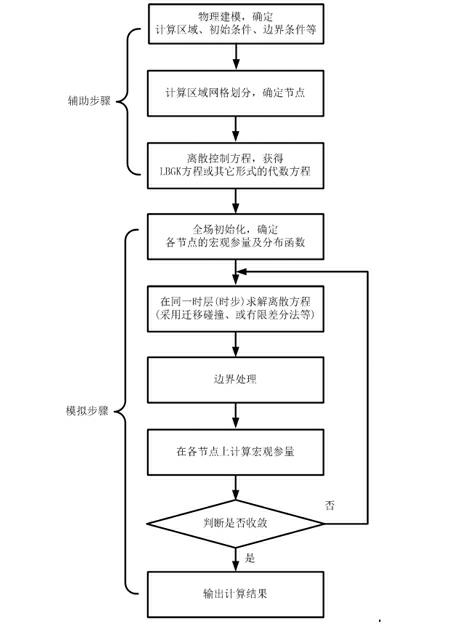
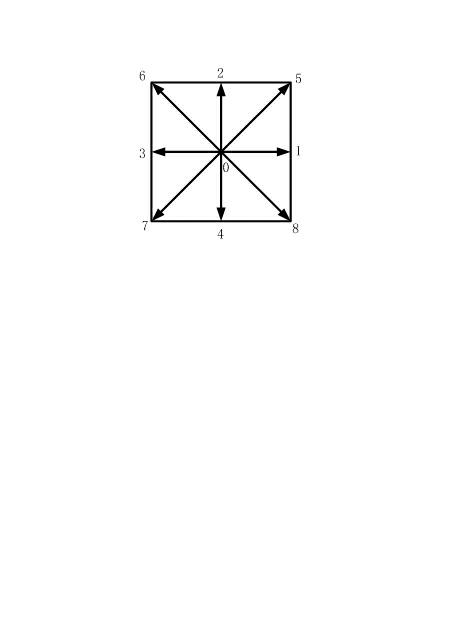
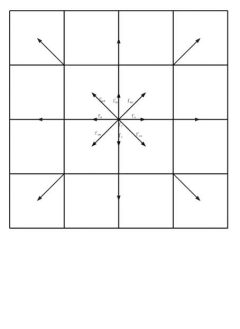
Method for accelerating lattice-Boltzmann by utilizing graphic processing units (GPUs)
PatentInactiveCN102681972A
Innovation
- By using CUDA technology to parallelize the equilibrium distribution function calculation, macroscopic quantity statistics, discrete equation solving and boundary processing, they can be executed in parallel on the GPU side to achieve collaborative computing between the CPU and GPU. The specific steps include analysis of performance bottlenecks, design Threading model, writing GPU kernel code, parallelizing migration and collision process.
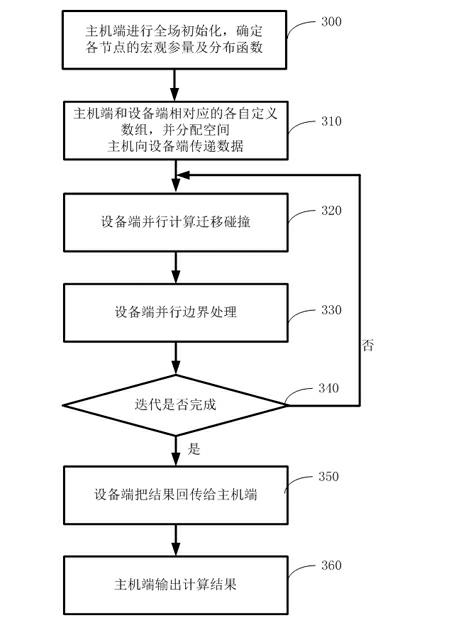
Adaptive Accelerated Computing Method, System and Computer-Readable Medium
PatentPendingCN120179406A
Innovation
- An adaptive acceleration calculation method is proposed. By analyzing the geometric structure and physical characteristics of the case model, efficient calculation paths are automatically analyzed and determined, including grid cutting and division, preset parameter calculation, calculation component filtering and parallel acceleration library selection, and the final calculation path is generated and filtered.
Thermal Management in Ferrofluid Computing
Thermal management in ferrofluid computing represents a critical frontier in advancing computational efficiency. Ferrofluids, colloidal suspensions of magnetic nanoparticles, offer unique properties that can be harnessed for innovative cooling solutions in electronic systems. The integration of ferrofluids in computing architectures presents a promising approach to address the escalating thermal challenges in high-performance computing environments.
The primary mechanism of ferrofluid-based thermal management relies on the fluid's ability to respond to magnetic fields while simultaneously conducting heat. When subjected to a controlled magnetic field, ferrofluids can be directed to areas of high heat generation within a computing system. This targeted approach allows for more efficient heat dissipation compared to traditional cooling methods.
One of the key advantages of ferrofluid cooling systems is their adaptability. The magnetic properties of ferrofluids enable dynamic reconfiguration of cooling pathways in response to changing thermal loads. This adaptability is particularly valuable in modern computing systems where heat generation patterns can vary significantly based on workload distribution and intensity.
Ferrofluids also offer enhanced heat transfer capabilities due to their nanoparticle composition. The suspended magnetic particles increase the overall thermal conductivity of the fluid, facilitating more rapid heat dissipation from hot spots to cooling interfaces. This property is especially beneficial in compact computing designs where space for traditional cooling solutions is limited.
The implementation of ferrofluid cooling systems in computing environments requires careful consideration of several factors. These include the design of magnetic field generators, the optimization of ferrofluid composition for specific thermal requirements, and the integration of these systems with existing computing architectures. Researchers are exploring various configurations, such as ferrofluid-filled heat pipes and magnetically-driven ferrofluid pumps, to maximize the cooling efficiency in different computing scenarios.
As the demand for computational power continues to grow, the role of thermal management becomes increasingly critical. Ferrofluid-based cooling solutions offer a pathway to overcome the limitations of conventional cooling methods, potentially enabling higher clock speeds, increased power densities, and improved overall system performance. The development of advanced ferrofluid formulations, coupled with innovative magnetic field control techniques, holds the key to unlocking new frontiers in computing efficiency through enhanced thermal management.
The primary mechanism of ferrofluid-based thermal management relies on the fluid's ability to respond to magnetic fields while simultaneously conducting heat. When subjected to a controlled magnetic field, ferrofluids can be directed to areas of high heat generation within a computing system. This targeted approach allows for more efficient heat dissipation compared to traditional cooling methods.
One of the key advantages of ferrofluid cooling systems is their adaptability. The magnetic properties of ferrofluids enable dynamic reconfiguration of cooling pathways in response to changing thermal loads. This adaptability is particularly valuable in modern computing systems where heat generation patterns can vary significantly based on workload distribution and intensity.
Ferrofluids also offer enhanced heat transfer capabilities due to their nanoparticle composition. The suspended magnetic particles increase the overall thermal conductivity of the fluid, facilitating more rapid heat dissipation from hot spots to cooling interfaces. This property is especially beneficial in compact computing designs where space for traditional cooling solutions is limited.
The implementation of ferrofluid cooling systems in computing environments requires careful consideration of several factors. These include the design of magnetic field generators, the optimization of ferrofluid composition for specific thermal requirements, and the integration of these systems with existing computing architectures. Researchers are exploring various configurations, such as ferrofluid-filled heat pipes and magnetically-driven ferrofluid pumps, to maximize the cooling efficiency in different computing scenarios.
As the demand for computational power continues to grow, the role of thermal management becomes increasingly critical. Ferrofluid-based cooling solutions offer a pathway to overcome the limitations of conventional cooling methods, potentially enabling higher clock speeds, increased power densities, and improved overall system performance. The development of advanced ferrofluid formulations, coupled with innovative magnetic field control techniques, holds the key to unlocking new frontiers in computing efficiency through enhanced thermal management.
Environmental Impact of Ferrofluid Technology
The environmental impact of ferrofluid technology in computing applications is a critical consideration as this innovative material gains traction in the tech industry. Ferrofluids, composed of nanoscale magnetic particles suspended in a carrier fluid, offer unique properties that can enhance computing efficiency. However, their widespread adoption necessitates a thorough examination of potential environmental consequences.
The production of ferrofluids involves the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles, typically iron oxides, which requires energy-intensive processes and potentially hazardous chemicals. The environmental footprint of manufacturing these materials must be carefully assessed, considering factors such as energy consumption, water usage, and chemical waste management. Additionally, the extraction of rare earth elements often used in high-performance ferrofluids can have significant ecological impacts, including habitat destruction and water pollution.
During the operational phase, ferrofluid-based computing systems may offer environmental benefits through improved energy efficiency and heat dissipation. These advantages could lead to reduced power consumption in data centers and other computing facilities, potentially lowering overall carbon emissions. However, the long-term stability and containment of ferrofluids in computing devices must be ensured to prevent leaks or degradation that could release nanoparticles into the environment.
End-of-life considerations for ferrofluid-enhanced computing components present another environmental challenge. The disposal or recycling of these materials requires specialized processes to prevent the release of nanoparticles into ecosystems. Improper handling could lead to soil and water contamination, with potential impacts on aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Research into safe disposal methods and effective recycling techniques is crucial to mitigate these risks.
The potential bioaccumulation of magnetic nanoparticles in living organisms is an area of ongoing study. While the health effects of ferrofluid exposure are not fully understood, precautionary measures should be implemented to protect both human health and wildlife. This includes developing robust containment systems and establishing guidelines for handling and disposal of ferrofluid-containing devices.
As the technology advances, there is an opportunity to develop more environmentally friendly ferrofluid formulations. This could involve using biodegradable carrier fluids or exploring alternative magnetic materials with lower environmental impact. Additionally, optimizing manufacturing processes to reduce waste and energy consumption could significantly improve the overall sustainability of ferrofluid technology in computing applications.
The production of ferrofluids involves the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles, typically iron oxides, which requires energy-intensive processes and potentially hazardous chemicals. The environmental footprint of manufacturing these materials must be carefully assessed, considering factors such as energy consumption, water usage, and chemical waste management. Additionally, the extraction of rare earth elements often used in high-performance ferrofluids can have significant ecological impacts, including habitat destruction and water pollution.
During the operational phase, ferrofluid-based computing systems may offer environmental benefits through improved energy efficiency and heat dissipation. These advantages could lead to reduced power consumption in data centers and other computing facilities, potentially lowering overall carbon emissions. However, the long-term stability and containment of ferrofluids in computing devices must be ensured to prevent leaks or degradation that could release nanoparticles into the environment.
End-of-life considerations for ferrofluid-enhanced computing components present another environmental challenge. The disposal or recycling of these materials requires specialized processes to prevent the release of nanoparticles into ecosystems. Improper handling could lead to soil and water contamination, with potential impacts on aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Research into safe disposal methods and effective recycling techniques is crucial to mitigate these risks.
The potential bioaccumulation of magnetic nanoparticles in living organisms is an area of ongoing study. While the health effects of ferrofluid exposure are not fully understood, precautionary measures should be implemented to protect both human health and wildlife. This includes developing robust containment systems and establishing guidelines for handling and disposal of ferrofluid-containing devices.
As the technology advances, there is an opportunity to develop more environmentally friendly ferrofluid formulations. This could involve using biodegradable carrier fluids or exploring alternative magnetic materials with lower environmental impact. Additionally, optimizing manufacturing processes to reduce waste and energy consumption could significantly improve the overall sustainability of ferrofluid technology in computing applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!